Abstract
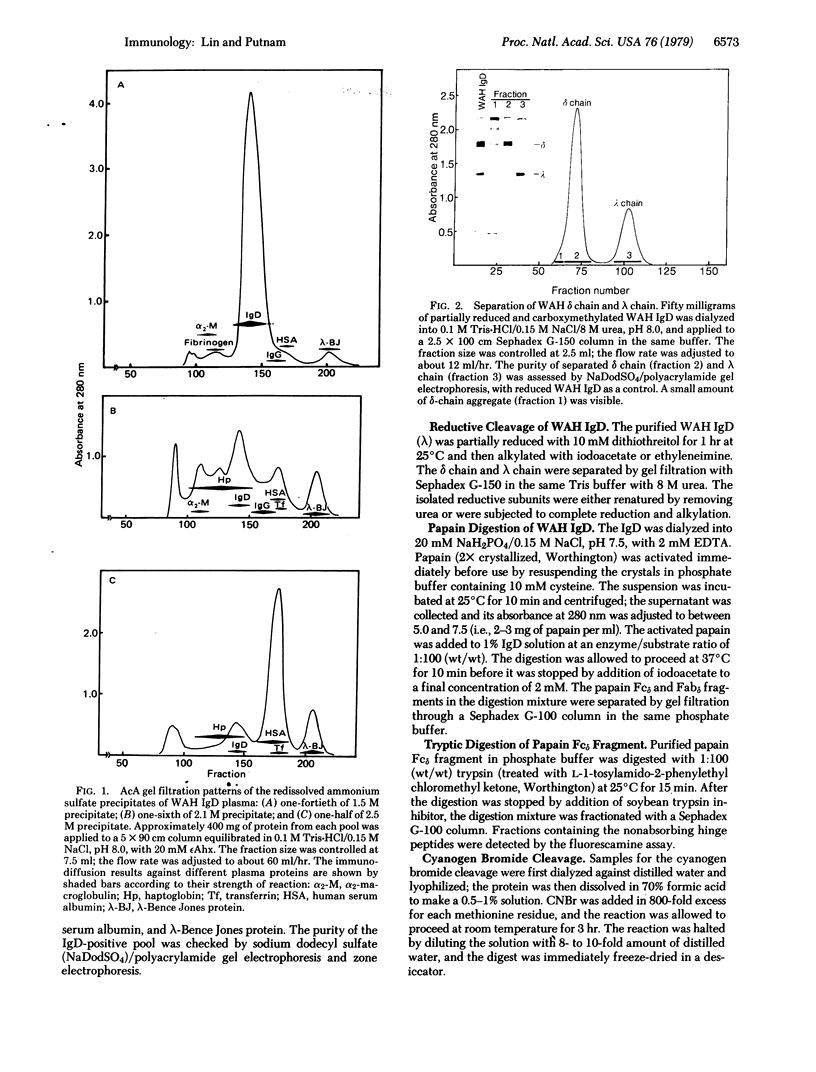
A myeloma IgD immunoglobulin (designated WAH) that was present in high concentration in plasma (≈3.5 g/dl) was purified in >90% yield by a two-step procedure of ammonium sulfate precipitation plus AcA 34 gel filtration. Although the plasma had been stored for 2 years without the addition of a proteolytic inhibitor, no “spontaneous” degradation was apparent and the isolated IgD remained structurally intact. However, the purified IgD showed extreme susceptibility in vitro to various proteolytic enzymes; e.g., Fabδ (Mr ≈ 47,000) and Fcδ (Mr ≈ 80,000) fragments were generated quantitatively after only 10 min of incubation with papain in the absence of cysteine. By combining limited enzymatic digestion, reductive cleavage, and cyanogen bromide fragmentation, several series of well defined fragments corresponding to the different regions and domains of the IgD molecule were generated. These fragments are useful for physical, chemical, and immunological studies, as well as for the sequence determination of the IgD δ chain. A model of the IgD molecule was derived from such studies and from overlapping of the series of fragments. The possible existence of an extra constant domain in the δ chain appears unlikely in view of our finding of an extended hinge region of about 50 residues which can be cleaved off the amino terminus of the papain Fcδ by brief treatment with trypsin. In addition to a distinct stretch of carbohydrate attachment sites, the δ-chain hinge region contains a segment unusually rich in electrical charge. This charged segment is responsible for the lability of IgD to spontaneous degradation and may be related to its biological role as a B lymphocyte receptor.
Keywords: Fabδ and Fcδ fragments, hinge region, lymphocyte receptor
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Collen D., Wiman B. Fast-acting plasmin inhibitor in human plasma. Blood. 1978 Apr;51(4):563–569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths R. W., Gleich G. J. Proteolytic degradation of IgD and its relation to molecular conformation. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jul 25;247(14):4543–4548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jancelewicz Z., Takatsuki K., Sugai S., Pruzanski W. IgD multiple myeloma. Review of 133 cases. Arch Intern Med. 1975 Jan;135(1):87–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferis R., Matthews J. B. Structural studies of human IgD paraproteins. Immunol Rev. 1977;37:25–49. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1977.tb00244.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leslie G. A., Clem L. W., Rowe D. The molecular weight of human IgD heavy chains. Immunochemistry. 1971 Jun;8(6):565–568. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90409-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leslie G. A., Martin L. N. Structure and function of serum and membrane immunoglobulin D (IgD). Contemp Top Mol Immunol. 1978;7:1–49. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-0779-3_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry M. B., Milstein C. Interchain bridges of human IgD. Nature. 1970 Dec 5;228(5275):934–935. doi: 10.1038/228934a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROWE D. S., FAHEY J. L. A NEW CLASS OF HUMAN IMMUNOGLOBULINS. I. A UNIQUE MYELOMA PROTEIN. J Exp Med. 1965 Jan 1;121:171–184. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.1.171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROWE D. S., FAHEY J. L. A NEW CLASS OF HUMAN IMMUNOGLOBULINS. II. NORMAL SERUM IGD. J Exp Med. 1965 Jan 1;121:185–199. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.1.185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe D. S., Hug K., Forni L., Pernis B. Immunoglobulin D as a lymphocyte receptor. J Exp Med. 1973 Oct 1;138(4):965–972. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.4.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelberg H. L., Prahl J. W., Grey H. M. Structural studies of human gamma D myeloma protein. Biochemistry. 1970 May 12;9(10):2115–2122. doi: 10.1021/bi00812a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitetta E. S., Uhr J. W. IgD and B cell differentiation. Immunol Rev. 1977;37:50–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1977.tb00245.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitetta E. S., Uhr J. W. Immunoglobulin-receptors revisited. Science. 1975 Sep 19;189(4207):964–969. doi: 10.1126/science.1083069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




