Abstract
Rationale
Smooth muscle cell (myocyte) large-conductance calcium (Ca2+)-activated potassium (BK) channels are functionally significant modulators of arterial contractility. Arterial myocytes express both pore-forming BKα and auxiliary β1 subunits, which increase channel Ca2+-sensitivity. Recently, several leucine-rich repeat containing (LRRC) proteins have been identified as auxiliary γ subunits that elevate the voltage-sensitivity of recombinant and prostate adenocarcinoma BK channels. LRRC expression and physiological functions in native cell types are unclear.
Objective
Investigate the expression and physiological functions of LRRC26 in arterial myocytes.
Methods and Results
RT-PCR and Western blotting detected LRRC26 mRNA and protein in cerebral artery myocytes. Biotinylation, immunofluorescence resonance energy transfer microscopy and co-immunoprecipitation indicated that LRRC26 was located in close spatial proximity to, and associated with, plasma membrane BKα subunits. LRRC26 knockdown (RNAi) reduced total and surface LRRC26, but did not alter BKα or β1, proteins in arteries. LRRC26 knockdown did not alter Ca2+ sparks, but reduced BK channel voltage-sensitivity, which reduced channel apparent Ca2+-sensitivity and transient BK current frequency and amplitude in myocytes. LRRC26 knockdown also increased myogenic tone over a range (40 – 100 mmHg) of intravascular pressures, and reduced vasoconstriction to iberiotoxin and vasodilation to NS1619, BK channel inhibitors and activators, respectively. In contrast, LRRC26 knockdown did not alter depolarization (60 mmol/L K+)-induced vasoconstriction.
Conclusions
LRRC26 is expressed, associates with BKα subunits, and elevates channel voltage- and apparent Ca2+-sensitivity in arterial myocytes to induce vasodilation. This study indicates that arterial myocytes express a functional BK channel γ subunit.
Keywords: BK, potassium channel, LRRC26, auxiliary subunit, myocyte, vascular smooth muscle, vasodilation
INTRODUCTION
Large-conductance calcium (Ca2+)-activated potassium (BK) channels are expressed in a wide variety of cell types, where these proteins control multiple physiological functions.1-5 Arterial smooth muscle cell (myocyte) BK channels regulate membrane potential, which modulates the activity of voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels and intracellular Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i).6 BK channel inhibition leads to an increase in [Ca2+]i and vasoconstriction, whereas channel activation reduces [Ca2+]i, leading to vasodilation.6-8 Genetic ablation of the BK channel pore-forming α subunit leads to vasoconstriction and hypertension, demonstrating the essential nature of these proteins to physiological control of regional organ blood flow and systemic blood pressure.9
Pore-forming BK channel α (Slo) subunits (Slo) can form heteromultimers with auxiliary β subunits, of which four isoforms (β1-4) have been identified.10-13 In arterial myocytes, Slo1 is the principal BKα subunit, with β1 the molecular and functional β subunit isoform.13 β1 subunits elevate BK channel apparent Ca2+-sensitivity and enhance coupling to Ca2+ sparks, which are local micromolar intracellular Ca2+ transients that occur due to ryanodine receptor (RyR)-mediated sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) Ca2+ release.7, 8, 14-18 A single Ca2+ spark can activate multiple nearby BK channels, leading to a transient BK current. Similarly to BKα subunit knockout, β1 subunit ablation reduces BK channel activity in arterial myocytes, elevates arterial contractility and increases systemic blood pressure.14, 15, 19
Recent studies have identified leucine-rich repeat containing proteins (LRRC) as a novel family of BK channel auxiliary “γ” subunits.20, 21 LRRC proteins are structurally-distinct from β subunits and are characterized by the consensus sequence: LXXLXLXXN/CXL, where X is any amino acid residue and L can be leucine, phenylalanine, isoleucine, or valine.22 Four LRRC proteins (LRRC26, 38, 52, and 55) have been described that each elevate BK channel voltage-sensitivity, although to differing degrees.21 Of these four LRRC proteins, LRRC26 produced the largest negative shift ( ~ −153 mV) in the voltage-dependence of recombinant BKα channels expressed in HEK293 cells.20, 21 LRRC26 also left-shifted the voltage-dependence of BK channels in LNCaP cells, an immortalized human prostate adenocarcinoma cell line.20 LRRC52, which is enriched in testis, shifted recombinant Slo3 activation to lower pH and voltages.23 Real-time PCR of whole organ lysates suggested that LRRC proteins exhibit tissue-specific expression, although which individual cell types express LRRC proteins is unclear.21 Similarly, the physiological function of LRRC proteins in native cell types, including arterial myocytes is uncertain. Such an investigation is appropriate given the functional significance of BK channels in a wide variety of cells and their physiological and pathological involvement in the cardiovascular system.
Here, we explored LRRC26 expression and function in cerebral artery myocytes. LRRC26 transcript and protein were detected in arterial myocytes with the majority of protein located at the plasma membrane. LRRC26 was located in close spatial proximity to BK channel α subunits. In the presence of physiological [Ca2+]i, selective LRRC26 knockdown reduced BK channel voltage- and apparent Ca2+-sensitivity, which inhibited transient BK currents. LRRC26 knockdown also increased pressure-induced vasoconstriction (myogenic tone) and reduced functional BK channel activity. These data indicate that LRRC26 elevates voltage- and apparent Ca2+-sensitivity in arterial myocytes to induce vasodilation. Importantly, this study indicates for the first time that arterial myocytes express a functional BK channel γ subunit.
METHODS
Expanded Methods are available as Supplemental Documentation.
All animal protocols were reviewed and approved by the University of Tennessee Health Science Center Animal Care and Use Committee. Male Sprague-Dawley rats (8 weeks) were euthanized with an intraperitoneal injection of sodium pentobarbital (150 mg/kg). The brain was removed and placed in an ice-cold (4°C) physiological saline solution (PSS) consisting of (in mmol/L): 6 KCl, 112 NaCl, 24 NaHCO3, 1.2 MgSO4, 1.2 KH2PO4, 1.8 CaCl2, and 10 glucose, which was gassed with 21% O2-5% CO2-74% N2 to pH 7.4. Resistance-size arteries were carefully dissected away from the brain and the connective tissue removed. Where appropriate, cerebral artery myocytes were enzymatically dissociated, as previously described.24
PCR
Total RNA was extracted from either whole arteries or ~ 200-300 isolated selected arterial myocytes using TRIzol (Life Technologies) or the Absolutely RNA Nanoprep kit (Stratagene), respectively. First-strand cDNA was generated from 1-5 ng of total RNA using Protoscript M-MULV (New England Biolabs). PCR was performed on first-strand cDNA using primers sequences shown in Online Table I. PCR products were separated on 1.5% agarose gels.
Protein analysis
Samples were separated on SDS-polyacrylamide gels and transferred onto nitrocellulose membranes that were then incubated with either goat polyclonal anti-LRRC26 (Santa Cruz Biotechnology), rabbit polyclonal anti-BK β1 (Abcam), mouse monoclonal anti-BKα (Neuromab, UC Davis), or mouse monoclonal anti-actin (Millipore). Following incubation with their respective secondary antibodies, membranes were developed using a chemiluminescent detection kit (Pierce) and imaged with a Kodak In Vivo F Pro Imaging System (Carestream Molecular Imaging). Band densitometry was analyzed using Quantity One software (Bio-Rad). LRRC26, β1, and BKα band densities were normalized to actin.
Surface biotinylation
Arteries were incubated with EZ-Link Sulfo-NHS-LC-LC-Biotin and EZ-Link Maleimide-PEG2-Biotin (Pierce). Free biotin was quenched by washing the arteries in PBS with glycine. Biotinylated arteries were homogenized, centrifuged and the supernatant collected. Following protein estimation, the sample was incubated with avidin beads (Monomeric Avidin Agarose, Pierce) and the supernatant (nonbiotin-bound proteins) set aside. Biotinylated proteins were eluted from the avidin beads. Western blotting was used to determine the relative distribution of surface (biotinylated) and intracellular (nonbiotinylated) fractions.
Immunofluorescence and immunoFRET microscopy
Isolated myocytes were plated, fixed and permeabilized. For co-localization experiments, cells were blocked (BSA) and incubated with goat polyclonal anti-LRRC26 antibody (Santa Cruz Biotechnology). Cells were then incubated with anti-goat Alexa 488 secondary antibody. Myocytes were incubated with Alexa 546-tagged wheat germ agglutinin (Life Technologies). Images were acquired using a laser scanning confocal microscope (LSM Pascal, Carl Zeiss). Alexa 488 and 546 secondary antibodies were excited at 488 and 543 nm with emission detected at 505-530 and ≥ 560 nm, respectively. Weighted co-localization was determined with the LSM FRET Macro tool (v2.5, Carl Zeiss).
For immunoFRET, myocytes were fixed and incubated with one of the following primary antibodies: goat polyclonal anti-LRRC26 (Santa Cruz Biotechnology), mouse monoclonal anti-BKα (Neuromab, UC Davis) or rabbit polyclonal anti-TRPM4 (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Cells were then incubated with the following secondary antibodies: anti-goat Alexa 488 or anti-goat Alexa 546 (LRRC26), anti-mouse Alexa 546 (BKα), or anti-rabbit Alexa 488 (TRPM4). Fluorescence images were acquired using a laser-scanning confocal microscope. Alexa 488 and 546 secondary antibodies were excited at 488 and 543 nm with emission detected at 505-530 and ≥ 560 nm, respectively. Images were background-subtracted and N-FRET calculated using the Xia method 25 and LSM FRET Macro tool (v2.5, Carl Zeiss).
Co-immunoprecipitation
For each experiment, lysate was harvested from arteries pooled from 6 rats using ice-cold Radio-Immunoprecipitation (RIPA) buffer. Co-immunoprecipitation was performed using the Catch and Release V2.0 Co-immunoprecipitation kit (Millipore) as per the manufacturer’s protocol. Briefly, arterial lysate was incubated with control mouse IgG or BKα mouse monoclonal antibody, antibody affinity ligand and the capture resin in the column provided. Bound proteins were released and run on a SDS-polyacrylamide gel. Protein samples were analyzed by Western blotting using mouse monoclonal anti-BKα (NeuroMab) or goat polyclonal anti-LRRC26 (Santa Cruz) and horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibodies, as previously described.26
LRRC26 knockdown
Cerebral arteries were placed in an electroporation chamber (Bex) with either control or LRRC26-specific siRNAs (Life Technologies). Arteries were transfected using an electroporator (CUY21Vivo-SQ electroporator, Bex Co. Ltd.) and stored at 37°C in DMEM-F12 50/50 (HEPES-free) culture medium supplemented with 1% penicillin-streptomycin for 48-72 hours prior to use.
Electrophysiology
Single BK channel or transient BK currents were recorded at room temperature in isolated myocytes using the inside-out or whole cell patch-clamp configurations, respectively. An Axopatch 200B amplifier and Clampex 8.2 (Molecular Devices) were used to record currents. For inside-out patch-clamp, the pipette and bath solutions both contained (in mmol/L): 130 KCl, 10 HEPES, 5 EGTA, 1.6 HEDTA, 1 MgCl2, and 10 μmol/L free Ca2+ (pH 7.2). Free Ca2+ was adjusted to between 1 and 300 μmol/L and free Mg2+ concentration maintained at 1 mmol/L with CaCl2 and MgCl2, respectively. Free Ca2+ concentration was calculated using WEBMAXC Standard and measured using Ca2+-sensitive (no. 476041; Corning) and reference (no. 476370; Corning) electrodes. To measure channel voltage-sensitivity, 300 ms voltage pulses between −100 and +100 mV were applied in 20 mV increments using a holding potential of −40 mV. BK channel apparent Ca2+-sensitivity was measured at a steady voltage of −40 mV. For whole cell patch-clamp, the bath solution contained (in mmol/L): 134 NaCl, 6 KCl, 2 CaCl2, 1 MgCl2,10 HEPES and 10 glucose (pH 7.4). The pipette solution contained (in mmol/L): 140 KCl, 1.9 MgCl2, 0.037 CaCl2, 10 HEPES, 0.1 EGTA, and 2 Na2ATP (pH 7.2). For all patch-clamp experiments, data were digitized at 5 kHz and filtered at 1 kHz. Analyses for voltage- and apparent Ca2+-sensitivity experiments were performed offline using Clampfit 9.2 (MDS Analytical Technologies). BK channel activity (NPo) was calculated using the following equation: NPo = Σ (t1 + t2…ti), where ti is the relative open time (time open / total time) for each channel level. Open probability (Po) was calculated by dividing NPo by the total number of channels. Voltage- and apparent Ca2+-sensitivity data were fit with the Boltzmann function: Y = Pomin + [(Pomax-Pomin)/(1+exp[(Kd-X)/slope])], where Y is the open probability, Pomin and Pomax represent the minimum and maximum open probability, respectively, Kd is the half-maximal voltage of activation or the dissociation constant for Ca2+, X represents voltage or Ca2+, and slope represents the steepness of the curve. Transient BK currents were analyzed offline.
Confocal Ca2+ imaging
Intracellular Ca2+ signals were imaged in myocytes of cerebral arteries using fluo-4 AM and a Noran Oz laser-scanning confocal microscope, as previously described.27
Pressurized artery myography
Middle cerebral artery segments were cannulated in a perfusion chamber (Living Systems Instrumentation) and continuously perfused with PSS. Intravascular pressure was controlled through a reservoir system and monitored with a pressure transducer. Wall diameter was measured using a charge-coupled device camera and the edge detection function of IonWizard (Ionoptix). Myogenic tone (%) was calculated as: 100 × (1 – Dactive / Dpassive), where Dactive is active arterial diameter and Dpassive is the passive arterial diameter determined by the application of Ca2+-free PSS supplemented with 5 mmol/L EGTA.
Statistical analysis
Data are expressed as mean ± SE. An independent samples t-test was used to determine if a significant difference existed between group means. The criterion for statistical significance was the same for all tests (α = 0.05).
RESULTS
LRRC26 mRNA and protein are present in arterial myocytes
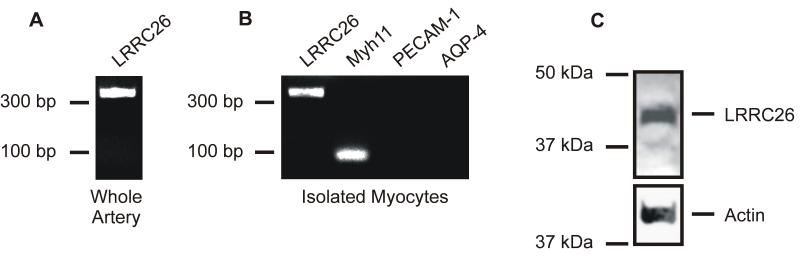
RT-PCR was performed to examine LRRC26 message in cerebral arteries and pure, acutely isolated cerebral artery myocytes. Primers amplified LRRC26 transcript from both whole cerebral artery cDNA and isolated arterial myocyte cDNA (Figure 1, A and B). To examine the specificity of the myocyte cDNA, primers to myosin heavy chain 11 (Myh11), a smooth muscle marker, platelet-endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 [PECAM-1], an endothelial cell marker and aquaporin-4 [AQP4], an astrocyte marker, were used. Only primers to Myh11 amplified transcripts from arterial myocyte cDNA (Figure 1B). Thus, the arterial myocyte cDNA was pure and not contaminated with cDNA from other vascular wall cell types.
Figure 1. LRRC26 is expressed in arterial myocytes.
A: Original gel image indicating that RT-PCR amplified transcripts for LRRC26 in intact cerebral arteries. B: RT-PCR amplified transcripts for LRRC26 and myosin heavy polypeptide 11 (Myh11), a myocyte marker, in isolated cerebral artery myocytes. Endothelial cell (platelet-endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 [PECAM-1]) and astrocyte (aquaporin-4 [AQP4]) markers were not amplified in the same cDNA. C: Western blot indicating that a LRRC26 antibody detected a ~ 42 kDa protein in cerebral artery lysate.
Western blotting using an LRRC26 antibody detected an ~ 42 kDa band in cerebral artery lysate, a molecular weight consistent with that of glycosylated LRRC26 (Figure 1C).21 The antigenic peptide for the LRRC26 antibody abolished the ~ 42 kDa protein band (Online Figure I, A). These data indicate that LRRC26 mRNA and protein are expressed in arterial myocytes.
LRRC26 is plasma membrane-localized and located in close spatial proximity to BKα subunits in arterial myocytes
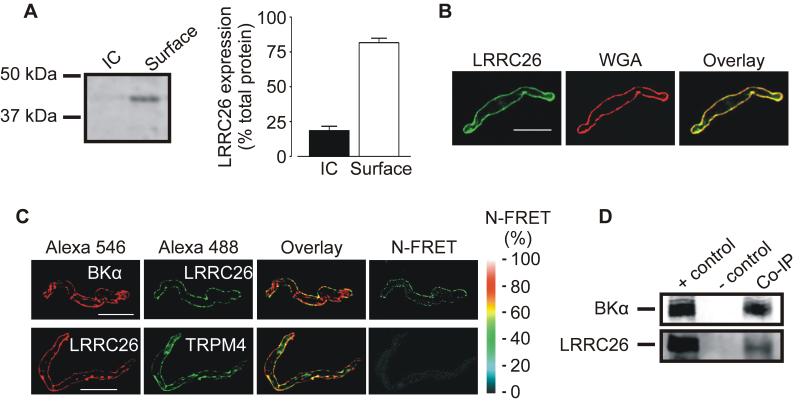
Cellular distribution of LRRC26 was studied using surface biotinylation and immunofluorescence microscopy. Arterial surface biotinylation revealed that ~ 82 % of total LRRC26 was plasma membrane-localized (Figure 2A). Similarly, confocal imaging followed by weighted co-localization analysis indicated that 84±4 % of LRRC26 co-localized with wheat germ agglutinin, a plasma membrane marker, in arterial myocytes (Figure 2B, n=6). These data indicate that the vast majority of LRRC26 is plasma-membrane-localized in arterial myocytes.
Figure 2. LRRC26 is primarily located in the plasma membrane and in close spatial proximity to BKα subunits in arterial myocytes.
A: representative Western blot and mean data of surface biotinylation experiments indicating that the majority of LRRC26 protein is located in the plasma membrane in cerebral arteries (n=6). IC, intracellular fraction. B: representative confocal images illustrating that LRRC26 co-localizes with WGA, a plasma membrane marker (n=6). Scale Bar=10 μm. C: Confocal images illustrating pixel overlay and N-FRET for indicated primary antibodies. D: Western blot illustrating that BKα antibodies co-immunoprecipitate BKα and LRRC26 proteins in arterial lysate.
To investigate the hypothesis that LRRC26 is a BK channel auxiliary subunit, immunofluorescence resonance energy transfer (immunoFRET) microscopy and co-immunoprecipitation were performed. Alexa Fluor488 and 546-tagged secondary antibodies bound to LRRC26 and BKα primary antibodies, respectively, generated N-FRET of 20±2 % in isolated arterial myocytes (Figure 2C, n=8). In contrast, the same fluorescent secondary antibodies to LRRC26 and TRPM4 primary antibodies generated N-FRET of only 5±1 %, which is consistent with background (Figure 2C, n=5).28 The antigenic peptide abolished immunofluorescence produced by the LRRC26 antibody (Online Figure I, B). The selectivity of the BKα and TRPM4 antibodies used has been previously established.28 Given that the Förster co-efficient of the Alexa Fluor pair used for these experiments is ~ 6.3 nm, data indicate that LRRC26 is located in close spatial proximity to BKα subunits.
Co-immunoprecipitation was used to test the hypothesis that LRRC26 and BKα subunits are located in the same macromolecular complex in arterial myocytes. Due to the small size of the resistance-size arteries used in this study, arteries collected from ~ 6 rats were required for each experiment. The BKα antibody co-immunoprecipitated both BKα and LRRC26 protein from arterial lysate (Figure 2D). These data indicate that LRRC26 is primarily plasma membrane-localized, located in very close spatial proximity to BKα, and co-immunoprecipitates with BKα in arterial myocytes.
LRRC26 knockdown reduces BK channel voltage- and apparent Ca2+-sensitivity in arterial myocytes
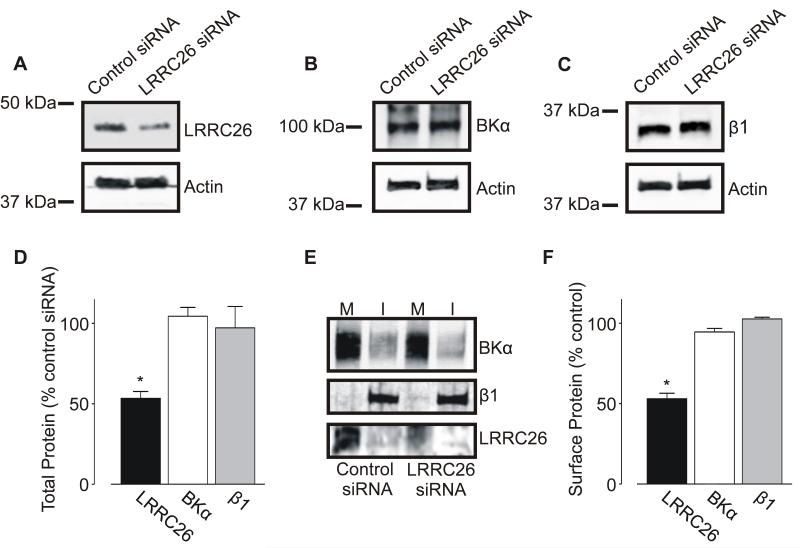
To study physiological functions of LRRC26 in arterial myocytes, expression was inhibited using RNA interference (RNAi). LRRC26-specific siRNA reduced both total and surface arterial LRRC26 protein by ~ 47 and 48 %, respectively, but did not alter total or surface BKα or β1 subunit expression (Figure 3A-F).
Figure 3. LRRC26 knockdown reduces total and surface LRRC26, but not BKα or β1, protein.
A-C: exemplary Western blots illustrating effect of LRRC26 siRNA on LRRC26 (A), BKα (B), and β1 (C) total protein. D: mean data (n=5). E: representative Western blot illustrating regulation of BKα, β1 and LRRC26 surface expression after LRRC26 knockdown. M: Membrane, I: Intracellular. F: mean data (n=6 for each). * P<0.05.
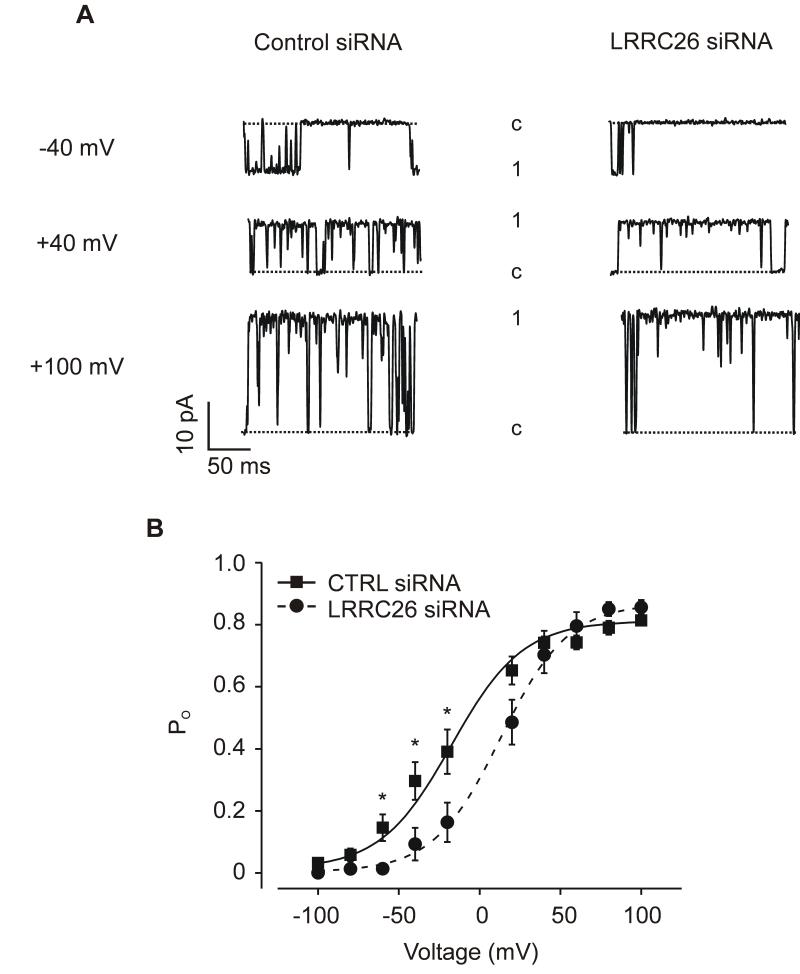
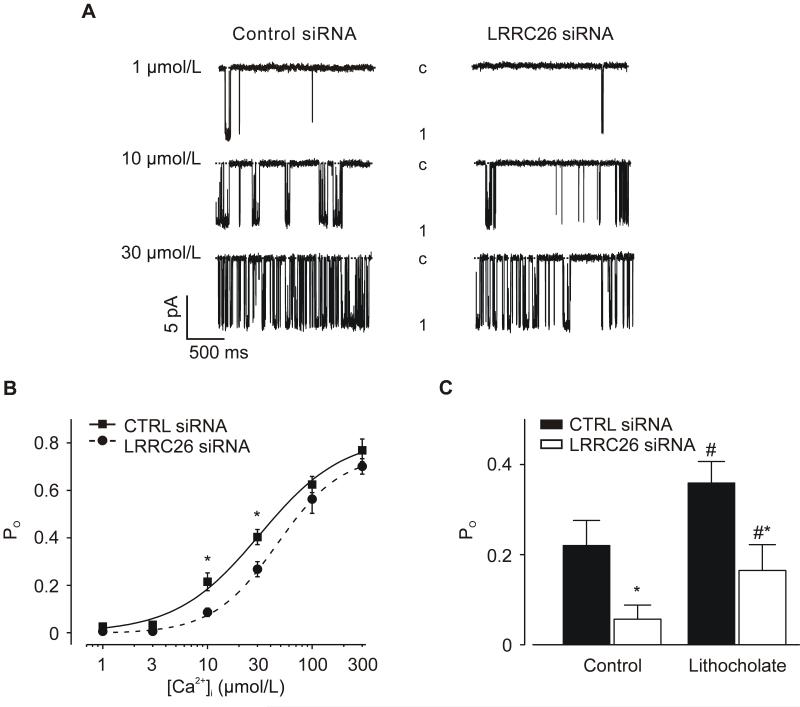
BK channel properties were examined using patch-clamp electrophysiology. Channels were measured in inside-out patches pulled from myocytes isolated from arteries treated with either control siRNA or LRRC26 siRNA. BK channel activity was measured with physiological free [Ca2+]i of 10 μmol/L. In control myocyte patches, the mean half-maximal voltage of activation (V1/2) for BK channels was ~ −20 mV with a maximum open probability (Po) of ~ 0.81 (Figure 4B). LRRC26 knockdown increased mean V1/2 to ~ +13 mV, or by +33 mV, but did not alter maximum Po (Figure 4B). In contrast, LRRC26 knockdown did not alter single BK channel conductance (Online Figure II). These data indicate that native LRRC26 elevates BK channel voltage-sensitivity in arterial myocytes.
Figure 4. LRRC26 knockdown reduces BK channel voltage-sensitivity in arterial myocytes.
A: exemplary BK channel recordings from the same inside-out patches pulled from control siRNA- or LRRC26 siRNA-treated arterial myocytes at −40, +40 or +100 mV. B: mean data illustrating BK channel Po versus voltage (control siRNA: n=10 myocytes, LRRC26 siRNA: n=7 myocytes). Data are fit with a Boltzmann function. * P<0.05.
RNAi was also used to measure the regulation of BK channel apparent Ca2+-sensitivity by LRRC26 at −40 mV, a physiological arterial myocyte membrane potential.6 In inside-out patches pulled from control myocytes, the mean Kd for Ca2+ was ~ 32 μmol/L with a maximum Po of ~ 0.77 (Figure 5B). LRRC26 knockdown induced a rightward shift in the Ca2+-response curve increasing the mean Kd for Ca2+ to ~ 46 μmol/L. In contrast, LRRC26 knockdown did not alter maximum Po (control, 0.77; LRRC26 siRNA, 0.70, Figure 5B). β1 subunits elevate BK channel apparent Ca2+-sensitivity in arterial myocytes.14 To examine the possibility that LRRC26 knockdown reduced BK channel activation by β1, we measured responses to lithocholate, a β1 subunit-specific BK channel activator.29 Lithocholate increased BK channel Po from ~0.22 to 0.36, or 1.64-fold in control siRNA-treated myocytes and from ~0.06 to 0.17, or 2.83-fold in LRRC26 siRNA-treated myocytes (Figure 5C). These results indicate that LRRC26 knockdown does not inhibit β1 subunit-mediated BK channel activation. Collectively, these data indicate that LRRC26 elevates BK channel voltage- and apparent Ca2+-sensitivity in arterial myocytes.
Figure 5. LRRC26 knockdown decreases BK channel apparent Ca2+-sensitivity in arterial myocytes.
A: representative BK channel recordings from inside-out patches pulled from control siRNA- or LRRC26 siRNA-treated arterial myocytes with 1, 10 or 30 μmol/L free Ca2+ at −40 mV. B: mean data. Experimental numbers are (from left to right), control siRNA: 8, 9, 11, 15, 7, 5; LRRC26 siRNA: 5, 4, 12, 7, 10, 11. Data are fit with a Boltzmann function. C: Lithocholate (150 μmol/L) activates BK channels in patches from control siRNA or LRRC26 siRNA-treated myocytes (-40 mV, 10 μmol/L [Ca2+]i). * P<0.05 vs control siRNA, # P<0.05 vs same condition prior to lithocholate.
LRRC26 knockdown inhibits transient BK currents, but does not alter Ca2+ sparks, in cerebral artery myocytes
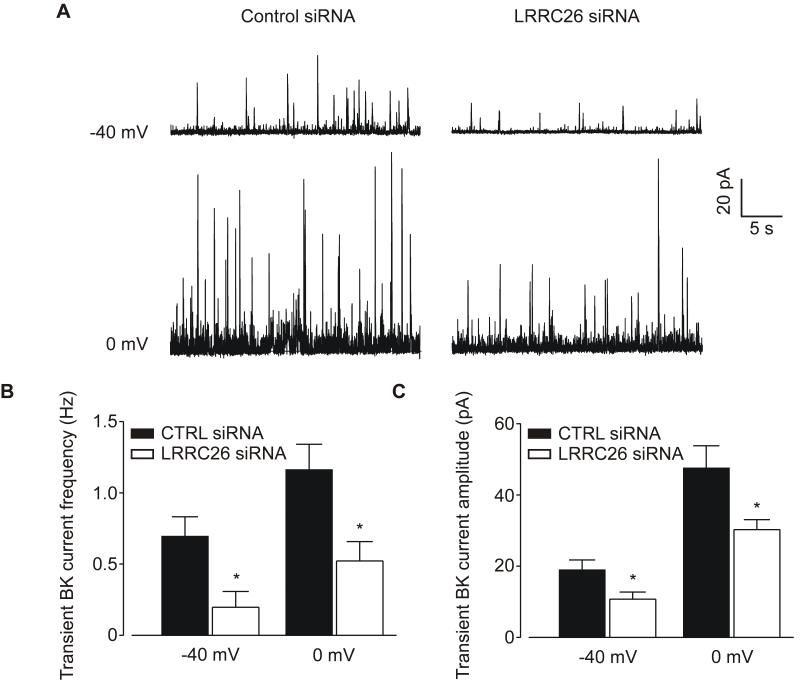
To determine LRRC26 involvement on a functional mechanism of BK channel activation, Ca2+ spark-induced transient BK currents were measured in isolated myocytes. At a physiological voltage of – 40 mV, LRRC26 knockdown reduced mean transient BK current frequency from ~0.70 to 0.20 Hz, or by ~ 71% (Figure 6B). At the same voltage, LRRC26 knockdown also decreased mean BK current amplitude from ~19.0 to 10.7 pA, or by ~ 44% (Figure 6C). Similar data were obtained at 0 mV where LRRC26 knockdown reduced transient BK current frequency and amplitude by ~ 55 % and 36 %, respectively (Figure 6, B and C). In contrast to effects on transient BK currents, LRRC26 knockdown did not alter Ca2+ spark frequency or amplitude in myocytes of intact cerebral arteries (Online Figure III). These data suggest that LRRC26 knockdown attenuates BK channel coupling to Ca2+ sparks, which reduces transient BK current frequency and amplitude in arterial myocytes.
Figure 6. LRRC26 knockdown inhibits transient BK currents in arterial myocytes.
A: representative recordings of transient BK currents recorded in control siRNA- and LRRC26 siRNA-treated arterial myocytes at −40 and 0 mV. B-C: mean data of transient BK current frequency (B) and amplitude (C) at −40 mV (control siRNA: n=11, LRRC26 siRNA: n=8) and 0 mV (control siRNA: n=7, LRRC26 siRNA: n=7). * P<0.05.
LRRC26 regulates functional BK channel activity and arterial contractility
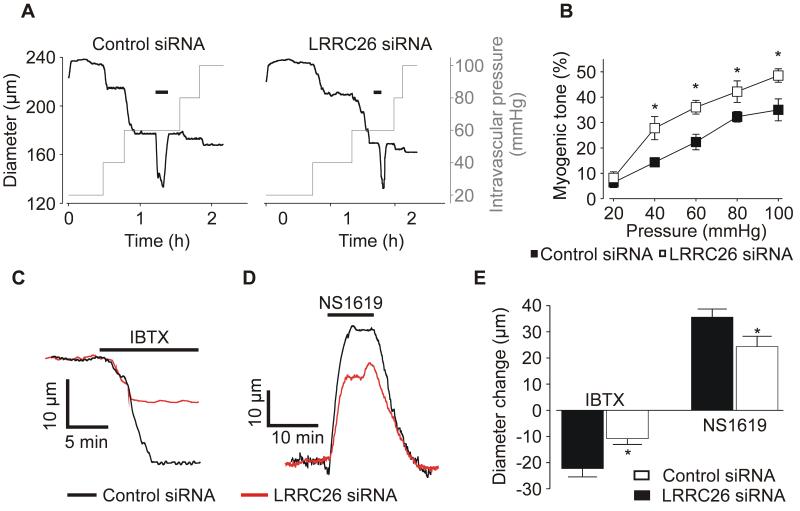
Physiological functions of LRRC26 were measured using cannulated arteries pressurized to between 20 and 100 mmHg. LRRC26 knockdown increased myogenic tone at intravascular pressures between 40 and 100 mmHg (Figure 7B). LRRC26-knockdown reduced vasoconstriction (at 60 mmHg) induced by iberiotoxin, a BK channel inhibitor, from ~22.3 in control to ~10.8 μm, or by ~ 52 % (Figure 7C, E). In contrast, LRRC26 knockdown did not alter membrane depolarization-induced (60 mmol/L K+) vasoconstriction (Online Figure IV), which was larger than that to IBTX (Figure 7, C and E). LRRC26 knockdown also did not alter passive arterial diameter (data at 60 mmHg: control, 284±8 μm, n=13; LRRC26 knockdown, 272±7 μm, n=11). These data support that constriction to IBTX in LRCC26-knockdown arteries are not attenuated due to a reduction in vasocontractile range, but due to reduced BK channel function. In support of this conclusion, LRRC26 knockdown reduced vasodilation to NS1619, a BK channel activator, from ~ 35.6 μm in control to ~24.3 μm, or by ~ 32 % (Figure 7D, E). These data indicate that LRRC26 knockdown reduces BK channel voltage- and apparent Ca2+-sensitivity, leading to a reduction in transient BK currents and an elevation in intravascular pressure-induced vasoconstriction.
Figure 7. LRRC26 knockdown elevates myogenic tone and reduces functional BK channel activity.
A: representative diameter traces at different intravascular pressures illustrating the effect of LRRC26 knockdown on myogenic tone. Horizontal black bars indicate 60 mmol/L K+. B: mean myogenic tone data. Control siRNA (pressure [mmHg], number): 20, 6; 40, 5; 60, 6; 80, 5; 100, 4. LRRC26 siRNA: 20, 7; 40, 7; 60, 7; 80,5; 100, 4. C: representative diameter traces at 60 mmHg demonstrating the effect of LRRC26 knockdown on iberiotoxin (IBTX)-induced constriction. Tone in the traces shown were 21.3% for control siRNA and 27.7 % for LRRC26 knockdown. D: exemplary diameter traces at 60 mmHg illustrating the effect of LRRC26 knockdown on NS1619-induced dilation. Tone in the traces shown were 21.4 % for control siRNA and 28.6% for LRRC26 knockdown. E: mean data of IBTX-induced constriction at 60 mmHg (control siRNA: IBTX n=5, NS1619 n=8; LRRC26 siRNA: IBTX n=6; NS1619 n=6). Mean tone prior to IBTX was: control siRNA, 19.2±2.8 % n=5; LRRC26-knockdown, 30.6±4.6 %, n=6 and before NS1619 was: control siRNA, 22.1±2.0 %, n=8; LRRC26-knockdown, 30.3±2.5 %, n=6. * P<0.05.
DISCUSSION
Here, we investigated for the first time LRRC expression and functionality in arterial myocytes. Our data indicate that LRRC26 is present in arterial myocytes where it is primarily located in the plasma membrane and associated with BK channel α subunits. LRRC26 knockdown decreased native BK channel voltage- and apparent Ca2+-sensitivity and reduced transient BK current frequency and amplitude. LRRC26 knockdown also increased myogenic tone and reduced functional BK channel activity. Taken together, these data indicate that LRRC26 elevates BK channel voltage- and apparent Ca2+-sensitivity, inducing vasodilation. Thus, LRRC26 is a BK channel auxiliary γ subunit in arterial myocytes.
LRRC26 was first identified in immunopurified BK channel complexes from LNCaP cells using liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectroscopy.20 Co-IP experiments using BKα and LRRC26 antibodies for pulldown were performed in LNCaP cells and recombinant expression systems and demonstrated an association between the BK channel and LRRC26. These data in addition to the profound shift in BK channel voltage-sensitivity induced by LRRC26 led to designation of LRRC26 as a BK channel γ auxiliary subunit, terminology now used by others.20, 21, 30 Several members of the LRRC Elron subfamily have since been identified as BK channel γ (γ1-4) subunits that can exhibit tissue-specific expression and function.21, 23
LRRC26 message was detected in whole salivary gland, prostate, trachea, thyroid gland, thymus, colon, fetal brain and aorta.21 Of the four LRRC isoforms studied in aorta, LRRC26 message was highest, with low expression of LRRC38 and little to no expression of LRRC52 and 55. LRRC proteins were not measured. Similarly, which aortic cell type(s) expressed LRRCs was not determined. Aorta is a conduit artery that does not regulate peripheral vascular resistance. It was unclear if resistance-size arteries that control organ blood pressure and flow express LRRC proteins. We detected LRRC26 mRNA in both intact cerebral arteries and isolated pure cerebral artery myocytes. Western blotting using a LRRC26 antibody identified a protein that was abolished by an antigenic peptide at ~ 42 kDa, which is consistent with glycosylated LRRC26.21 Arterial biotinylation, immunofluorescence and immunoFRET indicated that the majority of LRRC26 (> 80%) was located at the myocyte surface and in very close spatial proximity to plasma membrane-resident BKα subunits. Furthermore, the BK channel antibody co-immunoprecipitated BKα and LRRC26 proteins from arterial lysate, suggesting they are located in the same macromolecular complex. These data indicate that native LRRC26 protein is associated with pore-forming BKα subunits in arterial myocytes.
Here, LRRC26 knockdown shifted BK channel V1/2 by ~ +33mV in arterial myocytes. This depolarizing shift occurred within the physiological voltage range of arterial myocytes, which is primarily between −60 and −40 mV.6 Previous studies indicated that LRRC26 overexpression shifted the V1/2 of recombinant BKα subunits expressed in HEK293 cells by ~ −153 mV and BK channels in PC3 prostate cancer cells by ~ −136 mV.20, 21 LRRC26 knockdown in LNCaP cells, which express atypical BK channels with high voltage-sensitivity, right-shifted BK channel V1/2 by +134 mV. There are several explanations for the different degrees of shift in V1/2 measured in these previous studies and in arterial myocytes. First, LRRC26 knockdown reduced total LRRC26 protein by approximately half in cerebral arteries. Conceivably, complete LRRC26 knockout in arterial myocytes may induce a further decrease in BK channel voltage-sensitivity. Second, the HEK293 and PC3 cell experiments previously described compared control BK channel voltage-sensitivity to that after LRRC26 overexpression. LRRC26 expression may be lower in arterial myocytes than in these recombinant systems that typically express large amounts of protein. Furthermore, LNCaP cells may express more LRRC26 than arterial myocytes and knockdown may shift BK channel voltage-sensitivity to a larger degree than we observed in arterial myocytes. Third, arterial myocytes express β1 auxiliary subunits. LRRC26 modulation of BK channel voltage-sensitivity did not require β1, but β1 overexpression blocked the LRRC26-induced voltage-shift in recombinant BK channels expressed in HEK293 cells.20 These data suggested that β1 competes with LRRC26 to modulate BK channel activity.20 In contrast to β1 which induces incremental gating shifts as the number of subunits in the channel complex increases, LRRC26 alters BK channel gating in an all-or-none manner when differing ratios of γ1:BKα RNA are injected in Xenopus oocytes.30, 31 Our data obtained using lithocholate, show that LRRC26 knockdown did not inhibit β1 subunit-mediated BK channel activation. These data were consistent with those demonstrating that LRRC26 knockdown did not alter surface β1 expression. Recent evidence suggests that only a small fraction of total β1 subunits are associated with BK channels in arterial myocytes.32 Intracellular β1 subunits in arterial myocytes are stored within Rab11A-positive recycling endosomes and stimulated to surface-traffic by cGMP- and cAMP-dependent signaling pathways, which elevates BK channel-associated β1 subunits, leading to channel activation.32 Conceivably, endogenous β1 subunits may attenuate the LRRC26-induced elevation in BK channel voltage-sensitivity in arterial myocytes, although this remains to be determined. Future studies should investigate the possibility that LRRC26 and β1 subunits interact to modulate BK channel activity in arterial myocytes.
Our data indicate that LRRC26 knockdown reduced BK channel voltage- and apparent Ca2+-sensitivity, here defined as a shift in the voltage and Ca2+ concentration ranges over which the channel opens, respectively. In contrast, LRRC26 overexpression did not alter the slope of the V1/2 – [Ca2+]i relationship and shifted the V1/2 of recombinant BK channels with mutated Ca2+ activation sites.20 Our data may be explained when taking into account that BK channel apparent Ca2+-sensitivity is voltage-dependent.33 While LRRC26 may not modulate BK channel Ca2+-sensitivity itself, a LRRC26-induced leftward shift in voltage-sensitivity indirectly increases activation by Ca2+, as Ca2+ and voltage-dependence are allosterically coupled. Data also suggest LRRC26 shifts the Ca2+ set point, which is typically defined as the free Ca2+ concentration required for half-maximal activation at 0 mV. Here, single BK channel apparent Ca2+-sensitivity was not determined as a function of voltage, but measured at −40 mV, a voltage similar to that of arteries at a physiological intravascular pressure of ~60 mmHg.34 Ca2+ set points here cannot be calculated according to the standard definition but extrapolation of the current data at −40 mV is possible given that V1/2 was in the linear portion of the Po – V relationship. At 10 μmol/L [Ca2+]i, the V1/2 of control and LRRC26-knockdown BK channels were ~ −20 and +13 mV, respectively, a difference of 33 mV. Therefore, Ca2+ set points are < 10 μmol/L [Ca2+]i for control BK channels and > 10 μmol/L [Ca2+]i for LRRC26-knockdown channels.
Here, LRRC26 knockdown reduced BK channel apparent Ca2+-sensitivity within the micromolar Ca2+ concentration range generated by Ca2+ sparks.17 Ca2+ sparks are local intracellular Ca2+ transients generated by the opening of sarcoplasmic reticulum ryanodine-sensitive Ca2+ release channels.7, 16-18 A single Ca2+ spark activates multiple BK channels producing a transient BK current. Transient BK current frequency is regulated by Ca2+ spark frequency, whereas the effective coupling of BK channels to Ca2+ sparks controls both transient BK current frequency and amplitude. LRRC26 knockdown did not alter Ca2+ sparks, but decreased transient BK current frequency and amplitude at both −40 and 0 mV. Our data suggest that LRRC26 knockdown reduces BK channel apparent Ca2+-sensitivity, thereby attenuating the effective coupling of BK channels to Ca2+ sparks, leading to a decrease in transient BK current frequency and amplitude in arterial myocytes. To summarize, data indicate that LRRC26 elevates the effective coupling of BK channels to Ca2+ sparks, thereby increasing transient BK current frequency and amplitude in arterial myocytes. Previous studies have demonstrated that β1 subunits also increase BK channel sensitivity to Ca2+ sparks in arterial myocytes.14, 15 In contrast to β1 subunits, which elevate BK channel coupling to Ca2+ sparks by directly increasing Ca2+-sensitivity, LRRC26 indirectly elevates Ca2+-sensitivity by increasing voltage-sensitivity. Thus, our data indicate that β1 and γ subunits control BK channel Ca2+-sensitivity and activity via distinct mechanisms in arterial myocytes. Such multi-modal regulation permits fine tuning of BK channel activity.
Intravascular pressure stimulates membrane depolarization, which activates voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels, leading to an [Ca2+]i elevation and vasoconstriction.6 Pressure-induced depolarization also activates Ca2+ sparks, which stimulate BK channels to partially oppose the myogenic response.24, 35 We show that LRRC26 knockdown elevated myogenic tone across a wide range of intravascular pressures. Iberiotoxin was a less effective vasoconstrictor and NS1619 a weaker vasodilator, indicating that LRRC26 knockdown inhibits functional BK channel activity. Thus, data indicate that LRRC26 activates BK channels to oppose the myogenic response.
Findings of this study should stimulate future research into physiological and pathological functions of BK channel γ subunits in arterial myocytes and other cell types. Conceivably, LRRC proteins, including LRRC26, may be expressed in myocytes of vascular beds other than the cerebral circulation, increase BK channel activity and modulate contractility. γ subunit expression and functionality may exhibit regional vascular differences similarly to β1 subunits. For example, cerebral artery myocyte BK channels have a higher β1:α subunit ratio than cremaster artery myocytes, elevating their Ca2+-sensitivity.36 As γ and β1 subunits interact to modulate BK channels, variable expression of each subunit may fine tune and customize BK channel voltage-and Ca2+-sensitivity in myocytes of different vascular beds. Hypertension is associated with a decrease in β1 expression and function in arterial myocytes, leading to a reduction in BK channel activity and vasoconstriction.15, 37, 38 Conceivably, alterations in γ subunits may also contribute to attenuated BK channel activity during vascular disease. Finally, given that BK channels are a potential therapeutic target, γ subunits may be a novel molecular target to treat cardiovascular diseases.
In summary, we show that LRRC26 is expressed in cerebral artery myocytes where it is primarily plasma membrane-localized and associated with BKα subunits. LRRC26 knockdown reduced BK channel voltage- and apparent Ca2+-sensitivity within physiological ranges and inhibited transient BK current frequency and amplitude. LRRC26 knockdown also increased myogenic tone and reduced functional BK channel activity. These data indicate that LRRC26 is an arterial myocyte BK channel auxiliary γ subunit that elevates voltage- and apparent Ca2+-sensitivity to induce vasodilation.
Supplementary Material
Novelty and Significance.
What Is Known?
Large-conductance calcium (Ca2+)-activated potassium (BK) channels modulate arterial contractility, systemic blood pressure and regional organ blood flow.
Leucine-rich repeat containing protein 26 (LRRC26) was recently identified as a novel BK channel auxiliary γ subunit in a prostate adenocarcinoma cell line.
LRRC26 elevated BK channel voltage-sensitivity.
What New Information Does This Article Contribute?
LRRC26 is expressed in cerebral artery myocytes where it is primarily located in the plasma membrane and associated with BK channel α subunits.
LRRC26 elevates BK channel voltage- and apparent Ca2+-sensitivity and Ca2+ spark-induced transient BK currents in arterial myocytes, inducing vasodilation.
LRRC26 is a BK channel auxiliary γ subunit in arterial myocytes.
BK channels regulate arterial myocyte contractility, which controls systemic blood pressure and regional flow. Arterial myocyte BK channels are formed from pore-forming BK α and auxiliary β1 subunits, which elevate channel apparent Ca2+-sensitivity. Recent studies have identified leucine-rich repeat containing proteins (LRRC) as a novel family of BK channel auxiliary γ subunits, although expression and physiological functions in native cell types are unclear. We show that LRRC26 is expressed in arterial myocytes where it is located primarily in the plasma membrane and associated with BK channel α subunits. LRRC26 knockdown decreased native BK channel voltage- and apparent Ca2+-sensitivity and reduced Ca2+ spark-induced transient BK current frequency and amplitude. LRRC26 knockdown increased pressure-induced vasoconstriction (myogenic tone) and reduced functional responses to a BK channel activator and inhibitor. Our data indicate that LRRC26 elevates BK channel voltage- and apparent Ca2+-sensitivity in arterial myocytes, inducing vasodilation. The identification of LRRC26 as a functional BK channel γ subunit should promote the study of novel mechanisms of vascular control by this protein and pathological involvement in cardiovascular diseases.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank Dr. Alejandro Dopico for comments on the manuscript.
SOURCES OF FUNDING
This work was supported by NIH/NHLBI grants to J.H.J (HL67061 and HL110347) and K.W.E (HL116175).
Nonstandard Abbreviations and Acronyms
- LRRC26
leucine-rich repeat containing protein 26
- BK
large-conductance calcium (Ca2+)-activated potassium channel
- [Ca2+]i
intracellular calcium
- RyR
ryanodine receptor
- SR
sarcoplasmic reticulum
- LNCaP
human prostate adenocarcinoma cell
- cDNA
complementary DNA
- immunoFRET
immunofluorescence resonance energy transfer
- TRPM4
transient receptor potential melastatin 4 cation channel
- Myh11
myosin heavy chain 11
- PECAM-1
platelet-endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1
- AQP4
aquaporin-4
- V1/2
half-maximal voltage of activation
- Po
open probability
- PC3
human prostate adenocarcinoma cell
- IC
intracellular
- WGA
wheat germ agglutinin
- Co-IP
co-immunoprecipitation
- IBTX
iberiotoxin
- AP
antigenic peptide
Footnotes
Subject codes:
[138] Cell signalling/signal transduction
[152] Ion channels/membrane transport
[97] Other Vascular biology
DISCLOSURES
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
REFERENCES
- 1.Nelson MT, Quayle JM. Physiological roles and properties of potassium channels in arterial smooth muscle. Am J Physiol. 1995;268:C799–C822. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1995.268.4.C799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Jackson WF. Potassium channels in the peripheral microcirculation. Microcirculation. 2005;12:113–27. doi: 10.1080/10739680590896072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Lee US, Cui J. BK channel activation: structural and functional insights. Trends Neurosci. 2010;33:415–23. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2010.06.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Lu R, Alioua A, Kumar Y, Eghbali M, Stefani E, Toro L. MaxiK channel partners: physiological impact. J Physiol. 2006;570:65–72. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2005.098913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Orio P, Rojas P, Ferreira G, Latorre R. New disguises for an old channel: MaxiK channel β-subunits. News Physiol Sci. 2002;17:156–61. doi: 10.1152/nips.01387.2002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Davis MJ, Hill MA. Signaling mechanisms underlying the vascular myogenic response. Physiol Rev. 1999;79:387–423. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1999.79.2.387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Jaggar JH, Porter VA, Lederer WJ, Nelson MT. Calcium sparks in smooth muscle. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2000;278:C235–C256. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.2000.278.2.C235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Jaggar JH, Wellman GC, Heppner TJ, Porter VA, Perez GJ, Gollasch M, Kleppisch T, Rubart M, Stevenson AS, Lederer WJ, Knot HJ, Bonev AD, Nelson MT. Ca2+ channels, ryanodine receptors and Ca2+-activated K+ channels: a functional unit for regulating arterial tone. Acta Physiol Scand. 1998;164:577–87. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-201X.1998.00462.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Sausbier M, Arntz C, Bucurenciu I, Zhao H, Zhou XB, Sausbier U, Feil S, Kamm S, Essin K, Sailer CA, Abdullah U, Krippeit-Drews P, Feil R, Hofmann F, Knaus HG, Kenyon C, Shipston MJ, Storm JF, Neuhuber W, Korth M, Schubert R, Gollasch M, Ruth P. Elevated blood pressure linked to primary hyperaldosteronism and impaired vasodilation in BK channel-deficient mice. Circulation. 2005;112:60–8. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000156448.74296.FE. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Gutman GA, Chandy KG, Adelman JP, Aiyar J, Bayliss DA, Clapham DE, Covarriubias M, Desir GV, Furuichi K, Ganetzky B, Garcia ML, Grissmer S, Jan LY, Karschin A, Kim D, Kuperschmidt S, Kurachi Y, Lazdunski M, Lesage F, Lester HA, McKinnon D, Nichols CG, O’Kelly I, Robbins J, Robertson GA, Rudy B, Sanguinetti M, Seino S, Stuehmer W, Tamkun MM, Vandenberg CA, Wei A, Wulff H, Wymore RS. International Union of Pharmacology. XLI. Compendium of voltage-gated ion channels: potassium channels. Pharmacol Rev. 2003;55:583–6. doi: 10.1124/pr.55.4.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Sun X, Zaydman MA, Cui J. Regulation of Voltage-Activated K+ Channel Gating by Transmembrane β Subunits. Front Pharmacol. 2012;3:63. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2012.00063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Berkefeld H, Fakler B, Schulte U. Ca2+-activated K+ channels: from protein complexes to function. Physiol Rev. 2010;90:1437–59. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00049.2009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Wu RS, Marx SO. The BK potassium channel in the vascular smooth muscle and kidney: α- and β-subunits. Kidney Int. 2010;78:963–74. doi: 10.1038/ki.2010.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Brenner R, Perez GJ, Bonev AD, Eckman DM, Kosek JC, Wiler SW, Patterson AJ, Nelson MT, Aldrich RW. Vasoregulation by the β1 subunit of the calcium-activated potassium channel. Nature. 2000;407:870–6. doi: 10.1038/35038011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Pluger S, Faulhaber J, Furstenau M, Lohn M, Waldschutz R, Gollasch M, Haller H, Luft FC, Ehmke H, Pongs O. Mice with disrupted BK channel β1 subunit gene feature abnormal Ca2+ spark/STOC coupling and elevated blood pressure. Circ Res. 2000;87:E53–E60. doi: 10.1161/01.res.87.11.e53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Nelson MT, Cheng H, Rubart M, Santana LF, Bonev AD, Knot HJ, Lederer WJ. Relaxation of arterial smooth muscle by calcium sparks. Science. 1995;270:633–7. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5236.633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Perez GJ, Bonev AD, Patlak JB, Nelson MT. Functional coupling of ryanodine receptors to KCa channels in smooth muscle cells from rat cerebral arteries. J Gen Physiol. 1999;113:229–38. doi: 10.1085/jgp.113.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Perez GJ, Bonev AD, Nelson MT. Micromolar Ca2+ from sparks activates Ca2+-sensitive K+ channels in rat cerebral artery smooth muscle. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2001;281:C1769–C1775. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.2001.281.6.C1769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Grimm PR, Irsik DL, Settles DC, Holtzclaw JD, Sansom SC. Hypertension of Kcnmb1-/- is linked to deficient K secretion and aldosteronism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106:11800–5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0904635106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Yan J, Aldrich RW. LRRC26 auxiliary protein allows BK channel activation at resting voltage without calcium. Nature. 2010;466:513–6. doi: 10.1038/nature09162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Yan J, Aldrich RW. BK potassium channel modulation by leucine-rich repeat-containing proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109:7917–22. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1205435109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kobe B, Kajava AV. The leucine-rich repeat as a protein recognition motif. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2001;11:725–32. doi: 10.1016/s0959-440x(01)00266-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Yang C, Zeng XH, Zhou Y, Xia XM, Lingle CJ. LRRC52 (leucine-rich-repeat-containing protein 52), a testis-specific auxiliary subunit of the alkalization-activated Slo3 channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108:19419–24. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1111104108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Jaggar JH. Intravascular pressure regulates local and global Ca2+ signaling in cerebral artery smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2001;281:C439–C448. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.2001.281.2.C439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Xia Z, Liu Y. Reliable and global measurement of fluorescence resonance energy transfer using fluorescence microscopes. Biophys J. 2001;81:2395–402. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(01)75886-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Adebiyi A, Thomas-Gatewood CM, Leo MD, Kidd MW, Neeb ZP, Jaggar JH. An elevation in physical coupling of type 1 inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) receptors to transient receptor potential 3 (TRPC3) channels constricts mesenteric arteries in genetic hypertension. Hypertension. 2012;60:1213–9. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.112.198820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Narayanan D, Xi Q, Pfeffer LM, Jaggar JH. Mitochondria control functional CaV1.2 expression in smooth muscle cells of cerebral arteries. Circ Res. 2010;107:631–41. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.224345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Zhao G, Neeb ZP, Leo MD, Pachuau J, Adebiyi A, Ouyang K, Chen J, Jaggar JH. Type 1 IP3 receptors activate BKCa channels via local molecular coupling in arterial smooth muscle cells. J Gen Physiol. 2010;136:283–91. doi: 10.1085/jgp.201010453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Bukiya AN, Liu J, Toro L, Dopico AM. b1 (KCNMB1) subunits mediate lithocholate activation of large-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels and dilation in small, resistance-size arteries. Mol Pharmacol. 2007;72:359–69. doi: 10.1124/mol.107.034330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Gonzalez-Perez V, Xia XM, Lingle CJ. Functional regulation of BK potassium channels by γ1 auxiliary subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111:4868–73. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1322123111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Wang YW, Ding JP, Xia XM, Lingle CJ. Consequences of the stoichiometry of Slo1 α and auxiliary β subunits on functional properties of large-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels. J Neurosci. 2002;22:1550–61. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-05-01550.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Leo MD, Bannister JP, Narayanan D, Nair A, Grubbs JE, Gabrick KS, Boop FA, Jaggar JH. Dynamic regulation of β1 subunit trafficking controls vascular contractility. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111:2361–6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1317527111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Horrigan FT, Aldrich RW. Coupling between voltage sensor activation, Ca2+ binding and channel opening in large conductance (BK) potassium channels. J Gen Physiol. 2002;120:267–305. doi: 10.1085/jgp.20028605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Knot HJ, Nelson MT. Regulation of arterial diameter and wall [Ca2+] in cerebral arteries of rat by membrane potential and intravascular pressure. J Physiol. 1998;508(Pt 1):199–209. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1998.199br.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Brayden JE, Nelson MT. Regulation of arterial tone by activation of calcium-dependent potassium channels. Science. 1992;256:532–5. doi: 10.1126/science.1373909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Yang Y, Sohma Y, Nourian Z, Ella SR, Li M, Stupica A, Korthuis RJ, Davis MJ, Braun AP, Hill MA. Mechanisms underlying regional differences in the Ca2+ sensitivity of BKCa current in arteriolar smooth muscle. J Physiol. 2013;591:1277–93. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2012.241562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Yang Y, Li PY, Cheng J, Mao L, Wen J, Tan XQ, Liu ZF, Zeng XR. Function of BKCa channels is reduced in human vascular smooth muscle cells from Han Chinese patients with hypertension. Hypertension. 2013;61:519–25. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.111.00211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Amberg GC, Bonev AD, Rossow CF, Nelson MT, Santana LF. Modulation of the molecular composition of large conductance, Ca2+ activated K+ channels in vascular smooth muscle during hypertension. J Clin Invest. 2003;112:717–24. doi: 10.1172/JCI18684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.