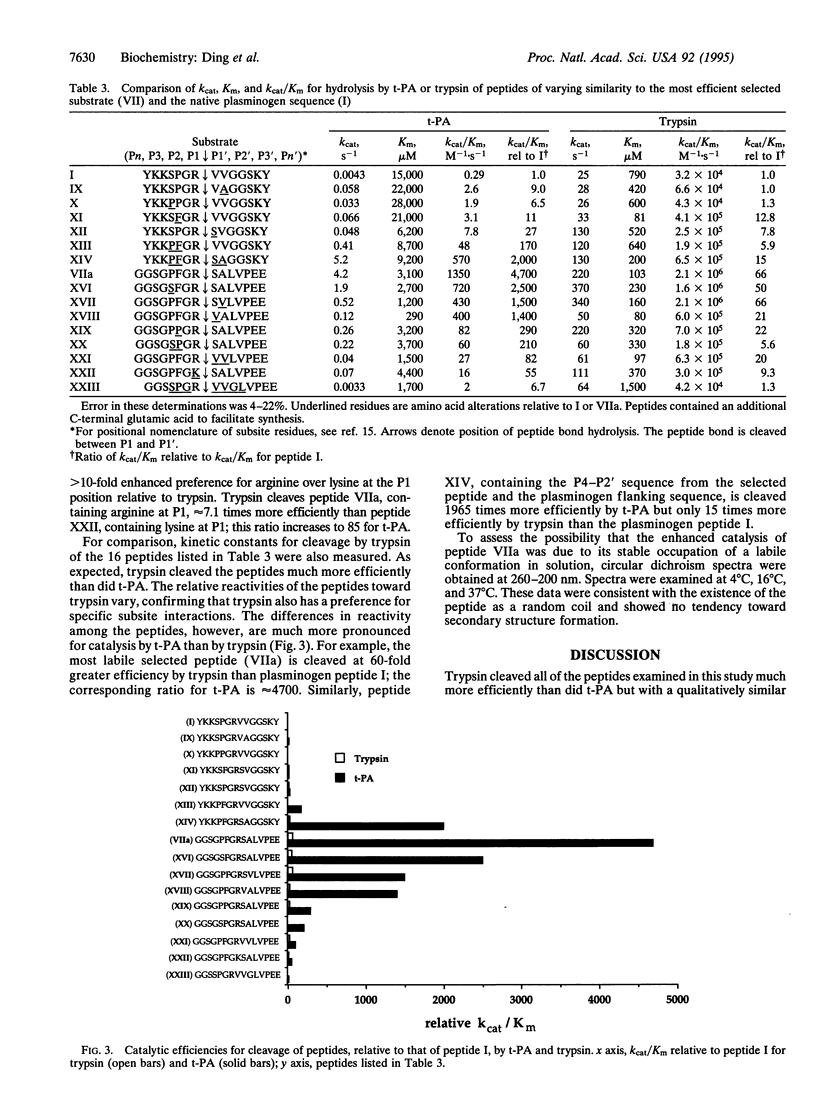
Abstract
The role of subsite interactions in defining the stringent substrate specificity of tissue-type plasminogen activator (t-PA) has been examined by using an fd phage library that displayed random hexapeptide sequences and contained 2 x 10(8) independent recombinants. Forty-four individual hexapeptides were isolated and identified as improved substrates for t-PA. A peptide containing one of the selected amino acid sequences was cleaved by t-PA 5300 times more efficiently than a peptide that contained the primary sequence of the actual cleavage site in plasminogen. These results suggest that small peptides can mimic determinants that mediate specific proteolysis, emphasize the importance of subsite interactions in determining protease specificity, and have important implications for the evolution of protease cascades.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cwirla S. E., Peters E. A., Barrett R. W., Dower W. J. Peptides on phage: a vast library of peptides for identifying ligands. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6378–6382. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoylaerts M., Rijken D. C., Lijnen H. R., Collen D. Kinetics of the activation of plasminogen by human tissue plasminogen activator. Role of fibrin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):2912–2919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jameson G. W., Roberts D. V., Adams R. W., Kyle W. S., Elmore D. T. Determination of the operational molarity of solutions of bovine alpha-chymotrypsin, trypsin, thrombin and factor Xa by spectrofluorimetric titration. Biochem J. 1973 Jan;131(1):107–117. doi: 10.1042/bj1310107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madison E. L., Coombs G. S., Corey D. R. Substrate specificity of tissue type plasminogen activator. Characterization of the fibrin independent specificity of t-PA for plasminogen. J Biol Chem. 1995 Mar 31;270(13):7558–7562. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.13.7558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews D. J., Wells J. A. Substrate phage: selection of protease substrates by monovalent phage display. Science. 1993 May 21;260(5111):1113–1117. doi: 10.1126/science.8493554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neurath H. Evolution of proteolytic enzymes. Science. 1984 Apr 27;224(4647):350–357. doi: 10.1126/science.6369538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neurath H. Proteolytic processing and physiological regulation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Jul;14(7):268–271. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90061-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neurath H. The versatility of proteolytic enzymes. J Cell Biochem. 1986;32(1):35–49. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240320105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennica D., Holmes W. E., Kohr W. J., Harkins R. N., Vehar G. A., Ward C. A., Bennett W. F., Yelverton E., Seeburg P. H., Heyneker H. L. Cloning and expression of human tissue-type plasminogen activator cDNA in E. coli. Nature. 1983 Jan 20;301(5897):214–221. doi: 10.1038/301214a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perona J. J., Craik C. S. Structural basis of substrate specificity in the serine proteases. Protein Sci. 1995 Mar;4(3):337–360. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560040301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. M., Shi L., Navre M. Rapid identification of highly active and selective substrates for stromelysin and matrilysin using bacteriophage peptide display libraries. J Biol Chem. 1995 Mar 24;270(12):6440–6449. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.12.6440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wohl R. C., Summaria L., Robbins K. C. Kinetics of activation of human plasminogen by different activator species at pH 7.4 and 37 degrees C. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 10;255(5):2005–2013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]