Abstract
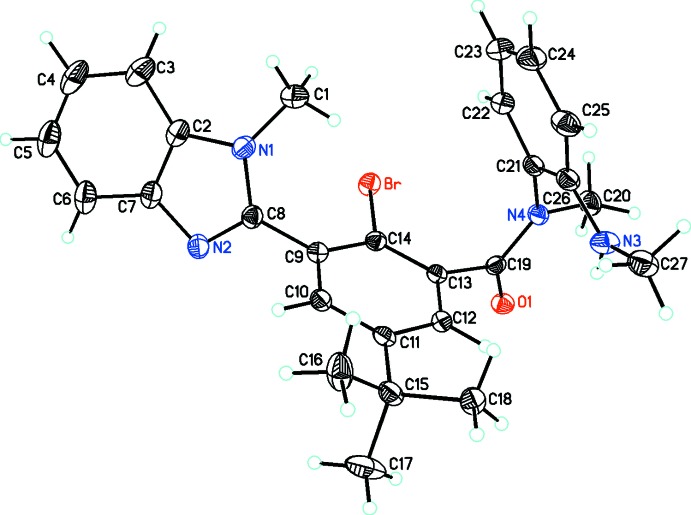
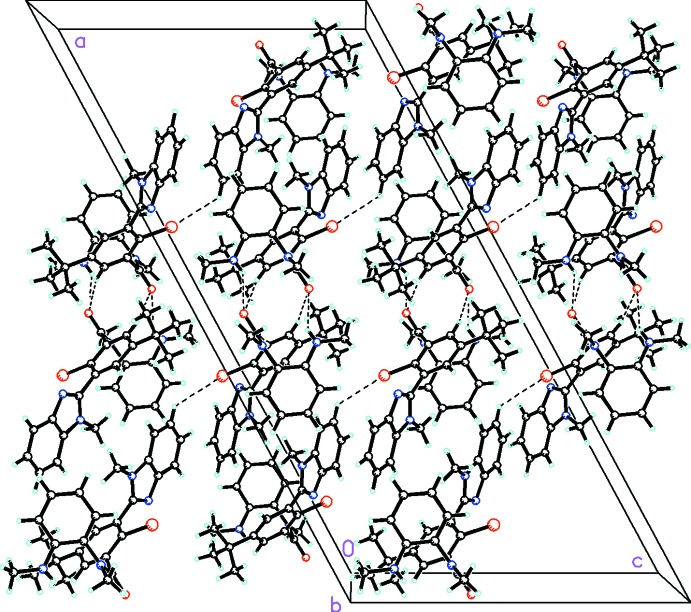
In the title compound, C27H29BrN4O, benzimidazole ring system and the amide moiety are planar [r.m.s. deviations = 0.016 (2) and 0.017 (1) Å, respectively]. The molecule adopts a conformation in which the amide linkage is almost perpendicular to the central ring [dihedral angle = 85.79 (8)°], while the benzimidazole ring system makes a dihedral angle of 70.26 (11)° with the central ring. In the crystal, the molecules form dimers through N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds and C—H⋯O interactions. These dimers are further linked into zigzag ribbons along [201] by weak C—H⋯Br interactions. As a result of the bulky nature of the molecule, as evidenced by the large dihedral angles between rings, there is little evidence for any π–π interactions.
Keywords: crystal structure
Related literature
The metal binding properties of imidazole-containing pincer ligands can be modified by the type of donor atoms and the electron-withdrawing and electron-releasing character of their substituents, see: Selander & Szabó (2011 ▶). For the effect of N-substitution on the catalytic activity of phosphinoimidazolines in palladium-catalysed Heck reactions, see: Busacca et al. (2003 ▶). For the use of bromine-substituted benzimidazole in Heck reactions, see: Reddy & Krishna (2005 ▶). For standard bond lengths, see: Allen et al. (1987 ▶). For the preparation of the precursor, 2-bromo-5-(tert-butyl)isophthalic acid, see: Field et al. (2003 ▶).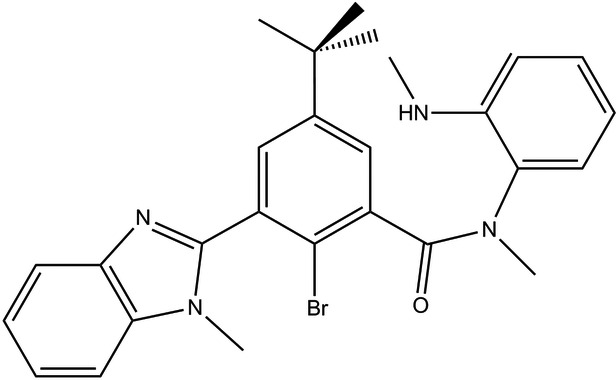
Experimental
Crystal data
C27H29BrN4O
M r = 505.45
Monoclinic,
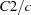
a = 34.4327 (13) Å
b = 9.4152 (2) Å
c = 17.1092 (7) Å
β = 118.312 (5)°
V = 4883.2 (3) Å3
Z = 8
Cu Kα radiation
μ = 2.50 mm−1
T = 123 K
0.38 × 0.32 × 0.23 mm
Data collection
Agilent Xcalibur Ruby Gemini diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2012 ▶) T min = 0.788, T max = 1.000
9307 measured reflections
4929 independent reflections
4100 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.028
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.034
wR(F 2) = 0.093
S = 1.03
4929 reflections
308 parameters
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.43 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.35 e Å−3
Data collection: CrysAlis PRO (Agilent, 2012 ▶); cell refinement: CrysAlis PRO; data reduction: CrysAlis PRO; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814014433/jj2190sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814014433/jj2190Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814014433/jj2190Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1009070
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N3—H3B⋯O1i | 0.81 (3) | 2.35 (3) | 3.038 (3) | 143 (3) |
| C4—H4A⋯Brii | 0.95 | 2.98 | 3.719 (3) | 135 |
| C12—H12A⋯O1i | 0.95 | 2.37 | 3.287 (3) | 163 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 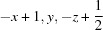 ; (ii)
; (ii) 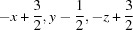 .
.
Acknowledgments
RJB acknowledges the NSF MRI program (grant No. CHE-0619278) for funds to purchase an X-ray diffractometer.
supplementary crystallographic information
S1. Experimental
The methylation reaction of 2 (Fig. 1) was carried out by reacting 1 (0.5 g, 1.12 mmol) with an excess of methyl iodide (1.75 g, 10 eq), followed by the addition of KOH (0.125 g, 2.24 mmol) in dry acetone (20 mL) and some molecular sieves. The reaction mixture was refluxed for 2 h. Then, it was diluted with ethyl acetate and washed with water. The organic layer was dried over Na2SO4 and purified by column chromatography to afford 2 which was crystallized from a mixture of dichloromethane and ether. Anal. Calcd. for C27H29BrON4: C, 64.16; H, 5.78; N, 11.08; found C, 64.30; H, 6.22; N, 9.17.
S1.1. Refinement
H atoms were placed in geometrically idealized positions and constrained to ride on their parent atoms with a C—H distances of 0.95 and 0.98 Å Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C) and 0.96 Å for CH3 [Uiso(H) = 1.5Ueq(C)]. The hydrogen atom attached to N3 was located in a difference Fourier and refined isotropically.
S2. Comment
The presence of imidazole rings in any molecular framework provides excellent modification sites for the fine tuning of properties related to electronic and steric factors. It has been reported in the literature that the strong electronic effect can be modified by the type of donor atoms and the electron-withdrawing and electron-releasing character of their substituents (Selander, & Szabó, 2011). Recently the effect of N-substitution on the catalytic activities of phosphinoimidazolines in palladium catalyzed Heck reactions has been reported (Busacca et al., 2003). Later, Reddy and co-workers (Reddy, & Krishna, 2005) have studied the use of bromine substituted benzimidazole in Heck reactions. Pincer ligands have immense scope in exploring different types of metal coordination chemistry and stabilizing unusual species. They provide the sites which can be easily fine tuned to synthesize a number of metal complexes/species, which can be stabilized by three coordinating/bonding units of the pincer ligands. There are no examples of selenium containing benzimidazoles known in the literature. Therefore, 2, 2'-(2-bromo-5-(tert-butyl)-1,3-diyl)bis(1H-benzimidazole) (1) and its derivatives, having two coordinating imidazole rings were designed to incorporate selenium at 2-position of the phenyl group. An attempted methylation of 1 led to cleavage of the one of the benzimidazole rings and resulted in the formation of unexpected compound 2 (Fig. 1). 2-Bromo-5-(tert-butyl)isophthalic acid, the precursor for synthesizing 1, was prepared according to literature procedure (Field, et al., 2003). Compound 1 was synthesized by the reaction of 2-bromo-5-tert-butyl-isophthalic acid with 1,2-phenylenediamine in polyphosphoric acid at 240°C.
In view of the above, the structure of the title compound, C27H29BrN4O, was determined (Fig. 2). The bond lengths and angles are all in the expected ranges (Allen et al., 1987) for such compounds. All the aromatic groups and the amide moiety are planar (rms deviations of 0.006 (1), 0.008 (2), 0.016 (2), and 0.017 (1) for the central phenyl ring, the substituent phenyl ring, the benzimidazole ring, and the amide moiety, respectively). The molecule adopts a conformation where the amide linkage is almost perpendicular to the central ring with a dihedral angle of 85.79 (8)° between central ring (C9–C14) and amide moiety (C19/C20/C21/N4/O1) while the benzimidazole ring makes a dihedral angle of 70.26° with the central ring. The molecules form dimers through N3—H···O1 intermolecular hydrogen bonds (Fig. 3). These dimers are further linked into zig-zag ribbons in the [2 0 1] direction by weak C—H···Br interactions. Because of the bulky nature of the molecule, as evidenced by the large dihedral angles between rings, there is little evidence for any π–π interactions.
Figures
Fig. 1.
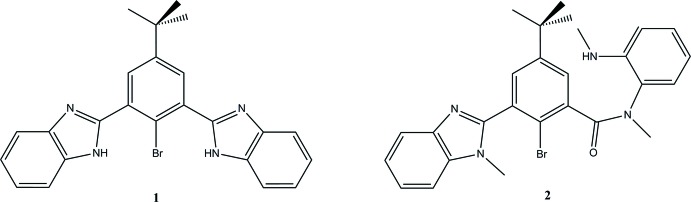
The structures of 1 and 2.
Fig. 2.
The molecular structure of C27H29BrN4O, showing the atom numbering scheme and 30% probability displacement ellipsoids and the linking of the molecules into dimers by N—H···O hydrogen bonds (shown as dashed bonds).
Fig. 3.
The molecular packing for C27H29BrN4O viewed along the b axis showing linking of the hydrogen bonded dimers into zigzag chains in the [2 0 1] direction by C—H···Br interactions (N—H···O and C—H···Br interactions shown as dashed bonds).
Crystal data
| C27H29BrN4O | F(000) = 2096 |
| Mr = 505.45 | Dx = 1.375 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, C2/c | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54184 Å |
| Hall symbol: -C 2yc | Cell parameters from 4036 reflections |
| a = 34.4327 (13) Å | θ = 2.9–75.5° |
| b = 9.4152 (2) Å | µ = 2.50 mm−1 |
| c = 17.1092 (7) Å | T = 123 K |
| β = 118.312 (5)° | Prism, colorless |
| V = 4883.2 (3) Å3 | 0.38 × 0.32 × 0.23 mm |
| Z = 8 |
Data collection
| Agilent Xcalibur Ruby Gemini diffractometer | 4929 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: Enhance (Cu) X-ray Source | 4100 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.028 |
| Detector resolution: 10.5081 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 75.6°, θmin = 2.9° |
| ω scans | h = −42→42 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2012) | k = −8→11 |
| Tmin = 0.788, Tmax = 1.000 | l = −20→21 |
| 9307 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.034 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.093 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.03 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0514P)2 + 0.4711P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 4929 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.004 |
| 308 parameters | Δρmax = 0.43 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.35 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Experimental. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 7.87-7.71 (1H, m), 7.46-7.31 (4H, m), 7.09-7.07 (1H, m), 6.54-6.48 (1H, m), 3.53 (2H, s), 3.45 (2H, s), 2.89 (2H, s), 1.38 (1H, s), 1.13 (6H, s). 13C NMR (CDCl3): δ 29.4, 30.9, 31.1, 31.9, 31.2, 34.7, 35.1, 35.5, 53.9, 109.7, 109.9, 120.2, 122.1, 122.5, 122.7, 123.1, 123.3, 129.4, 129.7, 131.2, 133.0, 135.6, 142.8, 151.7, 152.6, 152.8. |
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Br | 0.630352 (8) | 0.53882 (3) | 0.543344 (15) | 0.03435 (9) | |
| O1 | 0.52147 (5) | 0.66100 (17) | 0.36987 (11) | 0.0338 (3) | |
| N1 | 0.70366 (6) | 0.3018 (2) | 0.53797 (13) | 0.0370 (4) | |
| N2 | 0.65609 (7) | 0.1320 (2) | 0.53017 (14) | 0.0380 (4) | |
| N3 | 0.56938 (7) | 0.7887 (2) | 0.19074 (15) | 0.0406 (5) | |
| H3B | 0.5490 (9) | 0.765 (3) | 0.1989 (18) | 0.033 (7)* | |
| N4 | 0.57538 (6) | 0.78517 (19) | 0.36118 (13) | 0.0315 (4) | |
| C1 | 0.72063 (8) | 0.4328 (3) | 0.52039 (19) | 0.0447 (6) | |
| H1A | 0.6998 | 0.4684 | 0.4614 | 0.067* | |
| H1B | 0.7492 | 0.4142 | 0.5227 | 0.067* | |
| H1C | 0.7244 | 0.5039 | 0.5653 | 0.067* | |
| C2 | 0.72791 (8) | 0.2049 (3) | 0.60366 (16) | 0.0401 (5) | |
| C3 | 0.77297 (9) | 0.1991 (4) | 0.66449 (19) | 0.0541 (7) | |
| H3A | 0.7929 | 0.2717 | 0.6682 | 0.065* | |
| C4 | 0.78664 (11) | 0.0803 (4) | 0.7190 (2) | 0.0620 (9) | |
| H4A | 0.8171 | 0.0697 | 0.7600 | 0.074* | |
| C5 | 0.75708 (12) | −0.0240 (4) | 0.7155 (2) | 0.0615 (8) | |
| H5A | 0.7679 | −0.1020 | 0.7554 | 0.074* | |
| C6 | 0.71279 (11) | −0.0174 (3) | 0.6561 (2) | 0.0542 (7) | |
| H6A | 0.6929 | −0.0892 | 0.6541 | 0.065* | |
| C7 | 0.69805 (8) | 0.1004 (3) | 0.59819 (16) | 0.0402 (5) | |
| C8 | 0.66112 (7) | 0.2518 (2) | 0.49703 (15) | 0.0323 (4) | |
| C9 | 0.62557 (7) | 0.3270 (2) | 0.42009 (14) | 0.0292 (4) | |
| C10 | 0.60873 (7) | 0.2663 (2) | 0.33589 (15) | 0.0300 (4) | |
| H10A | 0.6198 | 0.1769 | 0.3297 | 0.036* | |
| C11 | 0.57614 (7) | 0.3331 (2) | 0.26044 (14) | 0.0292 (4) | |
| C12 | 0.55997 (7) | 0.4627 (2) | 0.27251 (15) | 0.0294 (4) | |
| H12A | 0.5371 | 0.5086 | 0.2224 | 0.035* | |
| C13 | 0.57612 (6) | 0.5266 (2) | 0.35517 (14) | 0.0264 (4) | |
| C14 | 0.60895 (7) | 0.4577 (2) | 0.42851 (14) | 0.0276 (4) | |
| C15 | 0.55815 (8) | 0.2676 (2) | 0.16780 (16) | 0.0358 (5) | |
| C16 | 0.59482 (11) | 0.1859 (3) | 0.15917 (19) | 0.0543 (7) | |
| H16A | 0.6042 | 0.1043 | 0.1996 | 0.081* | |
| H16B | 0.6200 | 0.2490 | 0.1744 | 0.081* | |
| H16C | 0.5835 | 0.1524 | 0.0980 | 0.081* | |
| C17 | 0.52108 (12) | 0.1646 (4) | 0.1534 (2) | 0.0693 (11) | |
| H17A | 0.4978 | 0.2157 | 0.1592 | 0.104* | |
| H17B | 0.5328 | 0.0888 | 0.1979 | 0.104* | |
| H17C | 0.5089 | 0.1232 | 0.0938 | 0.104* | |
| C18 | 0.54015 (8) | 0.3820 (3) | 0.09601 (15) | 0.0363 (5) | |
| H18A | 0.5131 | 0.4223 | 0.0925 | 0.054* | |
| H18B | 0.5336 | 0.3400 | 0.0387 | 0.054* | |
| H18C | 0.5622 | 0.4573 | 0.1108 | 0.054* | |
| C19 | 0.55554 (7) | 0.6638 (2) | 0.36324 (13) | 0.0275 (4) | |
| C20 | 0.55836 (9) | 0.9201 (2) | 0.3754 (2) | 0.0426 (6) | |
| H20A | 0.5362 | 0.9011 | 0.3947 | 0.064* | |
| H20B | 0.5448 | 0.9743 | 0.3199 | 0.064* | |
| H20C | 0.5827 | 0.9751 | 0.4212 | 0.064* | |
| C21 | 0.61458 (7) | 0.7918 (2) | 0.35017 (17) | 0.0326 (5) | |
| C22 | 0.65527 (8) | 0.8083 (3) | 0.42439 (18) | 0.0414 (5) | |
| H22A | 0.6574 | 0.8092 | 0.4818 | 0.050* | |
| C23 | 0.69305 (8) | 0.8234 (3) | 0.4155 (2) | 0.0511 (7) | |
| H23A | 0.7211 | 0.8336 | 0.4664 | 0.061* | |
| C24 | 0.68929 (8) | 0.8235 (3) | 0.3315 (2) | 0.0507 (7) | |
| H24A | 0.7151 | 0.8333 | 0.3251 | 0.061* | |
| C25 | 0.64900 (8) | 0.8098 (3) | 0.2569 (2) | 0.0435 (6) | |
| H25A | 0.6474 | 0.8101 | 0.2000 | 0.052* | |
| C26 | 0.60991 (7) | 0.7951 (2) | 0.26395 (17) | 0.0346 (5) | |
| C27 | 0.56379 (9) | 0.7866 (3) | 0.10141 (18) | 0.0464 (6) | |
| H27A | 0.5323 | 0.7794 | 0.0588 | 0.070* | |
| H27B | 0.5795 | 0.7047 | 0.0945 | 0.070* | |
| H27C | 0.5758 | 0.8743 | 0.0905 | 0.070* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Br | 0.03690 (13) | 0.03680 (13) | 0.02700 (13) | 0.00268 (9) | 0.01323 (10) | −0.00251 (9) |
| O1 | 0.0297 (7) | 0.0358 (8) | 0.0387 (8) | −0.0016 (6) | 0.0186 (7) | −0.0021 (7) |
| N1 | 0.0310 (9) | 0.0397 (10) | 0.0355 (10) | 0.0022 (8) | 0.0118 (8) | 0.0008 (9) |
| N2 | 0.0409 (10) | 0.0310 (9) | 0.0377 (10) | 0.0037 (8) | 0.0151 (9) | 0.0023 (8) |
| N3 | 0.0332 (10) | 0.0481 (12) | 0.0406 (11) | −0.0087 (9) | 0.0175 (9) | −0.0048 (9) |
| N4 | 0.0269 (9) | 0.0257 (8) | 0.0416 (10) | 0.0007 (7) | 0.0159 (8) | −0.0004 (8) |
| C1 | 0.0359 (12) | 0.0481 (14) | 0.0495 (15) | −0.0062 (11) | 0.0196 (12) | −0.0017 (12) |
| C2 | 0.0389 (12) | 0.0445 (13) | 0.0324 (12) | 0.0115 (10) | 0.0132 (10) | 0.0003 (10) |
| C3 | 0.0398 (14) | 0.072 (2) | 0.0381 (14) | 0.0112 (13) | 0.0085 (12) | −0.0019 (14) |
| C4 | 0.0498 (16) | 0.083 (2) | 0.0357 (14) | 0.0283 (16) | 0.0059 (13) | 0.0053 (15) |
| C5 | 0.071 (2) | 0.0625 (19) | 0.0414 (15) | 0.0313 (17) | 0.0189 (15) | 0.0140 (14) |
| C6 | 0.0675 (19) | 0.0453 (15) | 0.0460 (15) | 0.0195 (14) | 0.0237 (15) | 0.0108 (12) |
| C7 | 0.0439 (13) | 0.0377 (12) | 0.0349 (12) | 0.0119 (10) | 0.0153 (11) | 0.0026 (10) |
| C8 | 0.0334 (11) | 0.0304 (10) | 0.0312 (11) | 0.0043 (9) | 0.0138 (9) | −0.0007 (9) |
| C9 | 0.0270 (10) | 0.0282 (10) | 0.0307 (11) | −0.0011 (8) | 0.0124 (9) | 0.0003 (8) |
| C10 | 0.0302 (10) | 0.0243 (9) | 0.0355 (11) | −0.0010 (8) | 0.0155 (9) | −0.0012 (8) |
| C11 | 0.0321 (10) | 0.0241 (9) | 0.0313 (11) | −0.0072 (8) | 0.0150 (9) | −0.0027 (8) |
| C12 | 0.0292 (10) | 0.0267 (10) | 0.0294 (10) | −0.0019 (8) | 0.0115 (9) | 0.0023 (8) |
| C13 | 0.0246 (9) | 0.0239 (9) | 0.0302 (10) | −0.0031 (8) | 0.0125 (8) | −0.0007 (8) |
| C14 | 0.0279 (10) | 0.0289 (10) | 0.0249 (10) | −0.0031 (8) | 0.0117 (8) | −0.0022 (8) |
| C15 | 0.0483 (13) | 0.0268 (10) | 0.0300 (11) | −0.0073 (10) | 0.0167 (10) | −0.0028 (9) |
| C16 | 0.082 (2) | 0.0392 (13) | 0.0388 (14) | 0.0177 (14) | 0.0262 (15) | 0.0001 (11) |
| C17 | 0.089 (2) | 0.071 (2) | 0.0360 (14) | −0.053 (2) | 0.0204 (16) | −0.0103 (14) |
| C18 | 0.0436 (12) | 0.0350 (11) | 0.0307 (11) | 0.0006 (10) | 0.0179 (10) | −0.0003 (9) |
| C19 | 0.0249 (9) | 0.0289 (10) | 0.0242 (10) | 0.0005 (8) | 0.0080 (8) | −0.0015 (8) |
| C20 | 0.0406 (12) | 0.0276 (11) | 0.0617 (16) | 0.0050 (10) | 0.0261 (12) | 0.0003 (11) |
| C21 | 0.0271 (10) | 0.0223 (9) | 0.0484 (13) | −0.0001 (8) | 0.0179 (10) | 0.0013 (9) |
| C22 | 0.0332 (12) | 0.0383 (12) | 0.0450 (14) | −0.0049 (10) | 0.0123 (11) | 0.0063 (11) |
| C23 | 0.0282 (12) | 0.0508 (15) | 0.0623 (18) | −0.0053 (11) | 0.0116 (12) | 0.0077 (13) |
| C24 | 0.0316 (12) | 0.0470 (14) | 0.077 (2) | −0.0034 (11) | 0.0282 (13) | 0.0031 (14) |
| C25 | 0.0407 (13) | 0.0375 (12) | 0.0617 (16) | −0.0055 (10) | 0.0320 (13) | −0.0044 (12) |
| C26 | 0.0310 (11) | 0.0244 (9) | 0.0477 (13) | −0.0018 (8) | 0.0182 (10) | −0.0021 (9) |
| C27 | 0.0515 (15) | 0.0427 (13) | 0.0443 (14) | −0.0125 (12) | 0.0221 (12) | −0.0076 (11) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Br—C14 | 1.901 (2) | C12—C13 | 1.388 (3) |
| O1—C19 | 1.232 (3) | C12—H12A | 0.9500 |
| N1—C8 | 1.373 (3) | C13—C14 | 1.389 (3) |
| N1—C2 | 1.379 (3) | C13—C19 | 1.510 (3) |
| N1—C1 | 1.456 (3) | C15—C18 | 1.526 (3) |
| N2—C8 | 1.310 (3) | C15—C17 | 1.527 (3) |
| N2—C7 | 1.391 (3) | C15—C16 | 1.545 (4) |
| N3—C26 | 1.365 (3) | C16—H16A | 0.9800 |
| N3—C27 | 1.447 (3) | C16—H16B | 0.9800 |
| N3—H3B | 0.81 (3) | C16—H16C | 0.9800 |
| N4—C19 | 1.340 (3) | C17—H17A | 0.9800 |
| N4—C21 | 1.450 (3) | C17—H17B | 0.9800 |
| N4—C20 | 1.467 (3) | C17—H17C | 0.9800 |
| C1—H1A | 0.9800 | C18—H18A | 0.9800 |
| C1—H1B | 0.9800 | C18—H18B | 0.9800 |
| C1—H1C | 0.9800 | C18—H18C | 0.9800 |
| C2—C7 | 1.394 (4) | C20—H20A | 0.9800 |
| C2—C3 | 1.401 (4) | C20—H20B | 0.9800 |
| C3—C4 | 1.388 (5) | C20—H20C | 0.9800 |
| C3—H3A | 0.9500 | C21—C22 | 1.383 (3) |
| C4—C5 | 1.395 (5) | C21—C26 | 1.406 (3) |
| C4—H4A | 0.9500 | C22—C23 | 1.387 (3) |
| C5—C6 | 1.376 (5) | C22—H22A | 0.9500 |
| C5—H5A | 0.9500 | C23—C24 | 1.379 (4) |
| C6—C7 | 1.412 (4) | C23—H23A | 0.9500 |
| C6—H6A | 0.9500 | C24—C25 | 1.375 (4) |
| C8—C9 | 1.484 (3) | C24—H24A | 0.9500 |
| C9—C14 | 1.393 (3) | C25—C26 | 1.414 (3) |
| C9—C10 | 1.395 (3) | C25—H25A | 0.9500 |
| C10—C11 | 1.395 (3) | C27—H27A | 0.9800 |
| C10—H10A | 0.9500 | C27—H27B | 0.9800 |
| C11—C12 | 1.396 (3) | C27—H27C | 0.9800 |
| C11—C15 | 1.531 (3) | ||
| C8—N1—C2 | 106.0 (2) | C18—C15—C11 | 111.07 (18) |
| C8—N1—C1 | 128.4 (2) | C17—C15—C11 | 108.6 (2) |
| C2—N1—C1 | 125.5 (2) | C18—C15—C16 | 108.3 (2) |
| C8—N2—C7 | 104.4 (2) | C17—C15—C16 | 109.0 (3) |
| C26—N3—C27 | 122.4 (2) | C11—C15—C16 | 110.6 (2) |
| C26—N3—H3B | 117 (2) | C15—C16—H16A | 109.5 |
| C27—N3—H3B | 119 (2) | C15—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| C19—N4—C21 | 123.86 (18) | H16A—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| C19—N4—C20 | 119.04 (18) | C15—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C21—N4—C20 | 117.02 (18) | H16A—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| N1—C1—H1A | 109.5 | H16B—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| N1—C1—H1B | 109.5 | C15—C17—H17A | 109.5 |
| H1A—C1—H1B | 109.5 | C15—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| N1—C1—H1C | 109.5 | H17A—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| H1A—C1—H1C | 109.5 | C15—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| H1B—C1—H1C | 109.5 | H17A—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| N1—C2—C7 | 105.7 (2) | H17B—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| N1—C2—C3 | 131.4 (3) | C15—C18—H18A | 109.5 |
| C7—C2—C3 | 123.0 (3) | C15—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 115.7 (3) | H18A—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—H3A | 122.1 | C15—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—H3A | 122.1 | H18A—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 122.0 (3) | H18B—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—H4A | 119.0 | O1—C19—N4 | 122.7 (2) |
| C5—C4—H4A | 119.0 | O1—C19—C13 | 119.92 (19) |
| C6—C5—C4 | 122.0 (3) | N4—C19—C13 | 117.37 (17) |
| C6—C5—H5A | 119.0 | N4—C20—H20A | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—H5A | 119.0 | N4—C20—H20B | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 117.2 (3) | H20A—C20—H20B | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—H6A | 121.4 | N4—C20—H20C | 109.5 |
| C7—C6—H6A | 121.4 | H20A—C20—H20C | 109.5 |
| N2—C7—C2 | 110.2 (2) | H20B—C20—H20C | 109.5 |
| N2—C7—C6 | 129.8 (3) | C22—C21—C26 | 121.5 (2) |
| C2—C7—C6 | 120.0 (3) | C22—C21—N4 | 119.1 (2) |
| N2—C8—N1 | 113.7 (2) | C26—C21—N4 | 119.1 (2) |
| N2—C8—C9 | 124.9 (2) | C21—C22—C23 | 120.3 (3) |
| N1—C8—C9 | 121.4 (2) | C21—C22—H22A | 119.8 |
| C14—C9—C10 | 118.6 (2) | C23—C22—H22A | 119.8 |
| C14—C9—C8 | 122.40 (19) | C24—C23—C22 | 119.0 (3) |
| C10—C9—C8 | 119.00 (19) | C24—C23—H23A | 120.5 |
| C9—C10—C11 | 121.9 (2) | C22—C23—H23A | 120.5 |
| C9—C10—H10A | 119.0 | C25—C24—C23 | 121.4 (2) |
| C11—C10—H10A | 119.0 | C25—C24—H24A | 119.3 |
| C10—C11—C12 | 117.3 (2) | C23—C24—H24A | 119.3 |
| C10—C11—C15 | 121.96 (19) | C24—C25—C26 | 120.8 (3) |
| C12—C11—C15 | 120.7 (2) | C24—C25—H25A | 119.6 |
| C13—C12—C11 | 122.3 (2) | C26—C25—H25A | 119.6 |
| C13—C12—H12A | 118.8 | N3—C26—C21 | 121.4 (2) |
| C11—C12—H12A | 118.8 | N3—C26—C25 | 121.8 (2) |
| C12—C13—C14 | 118.62 (19) | C21—C26—C25 | 116.8 (2) |
| C12—C13—C19 | 119.05 (19) | N3—C27—H27A | 109.5 |
| C14—C13—C19 | 122.21 (19) | N3—C27—H27B | 109.5 |
| C13—C14—C9 | 121.17 (19) | H27A—C27—H27B | 109.5 |
| C13—C14—Br | 119.78 (16) | N3—C27—H27C | 109.5 |
| C9—C14—Br | 119.01 (16) | H27A—C27—H27C | 109.5 |
| C18—C15—C17 | 109.2 (2) | H27B—C27—H27C | 109.5 |
| C8—N1—C2—C7 | 0.1 (2) | C12—C13—C14—Br | −177.74 (14) |
| C1—N1—C2—C7 | 177.6 (2) | C19—C13—C14—Br | −1.6 (3) |
| C8—N1—C2—C3 | 178.1 (3) | C10—C9—C14—C13 | 0.4 (3) |
| C1—N1—C2—C3 | −4.3 (4) | C8—C9—C14—C13 | 179.08 (19) |
| N1—C2—C3—C4 | −176.7 (3) | C10—C9—C14—Br | 178.12 (15) |
| C7—C2—C3—C4 | 1.0 (4) | C8—C9—C14—Br | −3.2 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −2.2 (4) | C10—C11—C15—C18 | −154.3 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 1.9 (5) | C12—C11—C15—C18 | 26.3 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | −0.2 (5) | C10—C11—C15—C17 | 85.6 (3) |
| C8—N2—C7—C2 | −0.3 (3) | C12—C11—C15—C17 | −93.8 (3) |
| C8—N2—C7—C6 | −178.8 (3) | C10—C11—C15—C16 | −34.1 (3) |
| N1—C2—C7—N2 | 0.1 (3) | C12—C11—C15—C16 | 146.5 (2) |
| C3—C2—C7—N2 | −178.1 (2) | C21—N4—C19—O1 | −177.7 (2) |
| N1—C2—C7—C6 | 178.7 (2) | C20—N4—C19—O1 | 5.7 (3) |
| C3—C2—C7—C6 | 0.5 (4) | C21—N4—C19—C13 | 1.1 (3) |
| C5—C6—C7—N2 | 177.4 (3) | C20—N4—C19—C13 | −175.5 (2) |
| C5—C6—C7—C2 | −0.9 (4) | C12—C13—C19—O1 | 82.7 (3) |
| C7—N2—C8—N1 | 0.4 (3) | C14—C13—C19—O1 | −93.4 (2) |
| C7—N2—C8—C9 | 177.9 (2) | C12—C13—C19—N4 | −96.1 (2) |
| C2—N1—C8—N2 | −0.3 (3) | C14—C13—C19—N4 | 87.7 (2) |
| C1—N1—C8—N2 | −177.8 (2) | C19—N4—C21—C22 | −98.6 (3) |
| C2—N1—C8—C9 | −177.9 (2) | C20—N4—C21—C22 | 78.2 (3) |
| C1—N1—C8—C9 | 4.6 (4) | C19—N4—C21—C26 | 87.6 (3) |
| N2—C8—C9—C14 | 112.4 (3) | C20—N4—C21—C26 | −95.7 (3) |
| N1—C8—C9—C14 | −70.3 (3) | C26—C21—C22—C23 | −2.4 (4) |
| N2—C8—C9—C10 | −68.9 (3) | N4—C21—C22—C23 | −176.1 (2) |
| N1—C8—C9—C10 | 108.4 (2) | C21—C22—C23—C24 | 0.8 (4) |
| C14—C9—C10—C11 | 0.4 (3) | C22—C23—C24—C25 | 0.4 (4) |
| C8—C9—C10—C11 | −178.28 (19) | C23—C24—C25—C26 | 0.1 (4) |
| C9—C10—C11—C12 | −1.6 (3) | C27—N3—C26—C21 | −177.6 (2) |
| C9—C10—C11—C15 | 179.03 (19) | C27—N3—C26—C25 | 4.3 (4) |
| C10—C11—C12—C13 | 2.0 (3) | C22—C21—C26—N3 | −175.4 (2) |
| C15—C11—C12—C13 | −178.63 (19) | N4—C21—C26—N3 | −1.7 (3) |
| C11—C12—C13—C14 | −1.2 (3) | C22—C21—C26—C25 | 2.8 (3) |
| C11—C12—C13—C19 | −177.46 (18) | N4—C21—C26—C25 | 176.5 (2) |
| C12—C13—C14—C9 | 0.0 (3) | C24—C25—C26—N3 | 176.5 (2) |
| C19—C13—C14—C9 | 176.10 (18) | C24—C25—C26—C21 | −1.6 (4) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N3—H3B···O1i | 0.81 (3) | 2.35 (3) | 3.038 (3) | 143 (3) |
| C4—H4A···Brii | 0.95 | 2.98 | 3.719 (3) | 135 |
| C12—H12A···O1i | 0.95 | 2.37 | 3.287 (3) | 163 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, y, −z+1/2; (ii) −x+3/2, y−1/2, −z+3/2.
Footnotes
Supporting information for this paper is available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: JJ2190).
References
- Agilent (2012). CrysalisAlis PRO and CrysAlis RED Agilent Technologies, Yarnton, England.
- Allen, F. H., Kennard, O., Watson, D. G., Brammer, L., Orpen, A. G. & Taylor, R. (1987). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. S1–19.
- Busacca, C. A., Grossbach, D., So, R. C., O’Brien, E. M. & Spinelli, E. M. (2003). Org. Lett. 5, 595–598. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Field, J. E., Hill, T. J. & Venkataraman, D. J. (2003). J. Org. Chem. 68, 6071–6078. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Reddy, K. R. & Krishna, G. G. (2005). Tetrahedron Lett. 46, 661–663.
- Selander, N. J. & Szabó, K. (2011). Chem. Rev. 111, 2048–2076. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814014433/jj2190sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814014433/jj2190Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814014433/jj2190Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1009070
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report