Abstract
The title compound, C13H16N4O3S2·H2O, crystallizes in a ‘folded’ conformation with the ester group lying over the carbamoyl moiety, with one solvent water molecule. The molecular conformation is stabilized by an intramolecular C—H⋯O hydrogen bond, and an N—H⋯O hydrogen-bonding interaction involving the lattice water molecule. The packing involves N—H⋯N, N—H⋯O, O—H⋯N and O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds and consists of tilted layers running approximately parallel to the c axis, with the ester groups on the outer sides of the layers and with channels running parallel to (101).
Related literature
For the synthesis of amino-cyano pyridines, see: Shi et al. (2005 ▶). For pyridines as intermediates in the synthesis of different heterocyclic compounds, see: Konda et al. (2010 ▶). For the pharmaceutical activity of functionalized pyridine derivatives, see: Dorigo et al. (1993 ▶); Dolle et al. (1995 ▶); Murata et al. (2003 ▶). For industrial applications of pyridine compounds, see: Lohray et al. (2004 ▶); Merja et al. (2004 ▶); Chaki et al. (1995 ▶); Thomae et al. (2007 ▶). For hydrogen-bond motifs, see: Bernstein et al. (1995 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C13H16N4O3S2·H2O
M r = 358.45
Triclinic,

a = 9.0806 (12) Å
b = 9.2444 (12) Å
c = 10.7856 (14) Å
α = 101.843 (2)°
β = 100.1750 (19)°
γ = 105.9480 (19)°
V = 825.48 (19) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.35 mm−1
T = 150 K
0.26 × 0.26 × 0.12 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART APEX CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2013 ▶) T min = 0.83, T max = 0.96
15313 measured reflections
4292 independent reflections
3773 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.034
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.037
wR(F 2) = 0.099
S = 1.05
4292 reflections
210 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.44 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.37 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2013 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2013 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXT (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL2014 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: DIAMOND (Brandenburg & Putz, 2012 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814012495/sj5406sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814012495/sj5406Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814012495/sj5406Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1005734
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N3—H3A⋯N2i | 0.91 | 2.43 | 3.3291 (18) | 168 |
| N3—H3B⋯O1ii | 0.91 | 2.03 | 2.9345 (18) | 177 |
| N4—H4A⋯O4 | 0.91 | 2.01 | 2.9212 (16) | 174 |
| O4—H4B⋯N2iii | 0.84 | 2.17 | 3.0032 (19) | 172 |
| O4—H4C⋯O2iv | 0.84 | 2.09 | 2.9122 (18) | 168 |
| C4—H4⋯O1 | 0.95 | 2.25 | 2.8484 (17) | 121 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 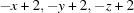 ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  ; (iv)
; (iv)  .
.
Acknowledgments
JTM thanks Tulane University for support of the Tulane Crystallography Laboratory.
supplementary crystallographic information
S1. Comment
A great deal of interest has been focused on the synthesis of functionalized pyridine derivatives due to their biological activities (Shi et al., 2005). For example, some 2-pyridine radicals are incorporated into the structures of cardiotonic agents such as milrinone (Dorigo et al., 1993) and HIV-1 specific transcriptase inhibitors (Dolle et al., 1995). Amino-cyanopyridines have been identified as IKK-β inhibitors (Murata et al., 2003). Many pyridine derivatives are of commercial interest being used as herbicides, fungicides, pesticides, and dyes (Lohray et al., 2004; Merja et al., 2004; Chaki et al., 1995; Thomae et al., 2007). Besides, pyridine derivatives are important and useful intermediates in the preparation of a variety of heterocyclic compounds (Konda et al., 2010). In view of these observations and in continuation of our work on the synthesis of heterocyclic systems for biological evaluations, we report here the synthesis and crystal structure of the title compound.
The title compound (Fig. 1) crystallizes in a "folded" conformation with the ester group lying over the carbamoyl moiety such that the dihedral angle between the best planes through the pyridyl ring and the C11–C13/O3 unit is 22.4 (1)°.
Molecular conformation is stabilized by an intramolecular C—H···O hydrogen bond, forming a S(6) motif, Fig. 1, (Bernstein et al., 1995) and an N—H···O hydrogen bonding interaction involving the lattice water molecule.
This conformation appears to result from the several hydrogen bonding interactions involving the lattice water molecule, Fig. 2 and Table 1. The packing consists of tilted layers running approximately parallel to the c axis, Fig. 3, with the ester groups on the outsides of the layers and having channels running parallel to (101), Fig. 4.
S2. Experimental
To a solution of N-[4-amino-5-cyano-6-(methylthio)pyridin-2-yl]-2-chloroacetamide (0.5 g, 1.95 mmol) in 30 ml ethanol and a few drops of triethylamine as a catalyst, ethyl mercaptoacetate (0.23 g, 1.95 mmol) was added. The reaction mixture was refluxed for 3 h at 350 K. The reaction mixture was allowed to cool down and the excess solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure. The precipitate which formed was filtered off, dried under vacuum and recrystallized from ethanol to furnish colourless crystals (yield 0.62 g; 95%). Mp. 423 – 425 K.
IR (νmax, cm-1): 3431, 3335, 3227, (NH2+NH), 2915 (CH aliph.), 2203 (C≡N), 1728 (C=O ester), 1641 (C=O amidic); 1HNMR (DMSO-d6), δ, p.p.m.: 10.34 (s, 1H, NH exchanged by D2O), 7.28 (s, 1H, CH pyridyl), 7.00 (s, 2H, NH2 exchanged by D2O), 4.11- 4.06(q, J = 8 Hz, 2H, CH2), 3.50 (s, 2H, CH2), 3.49 (s, 2H, CH2), 2.53 (s, 3H, CH3), 1.2–1.17 (t, J = 8 Hz, 3H, CH3).
S3. Refinement
H-atoms attached to carbon were placed in calculated positions (C—H = 0.95 - 0.98 Å) while those attached to nitrogen were placed in locations derived from a difference map and their coordinates adjusted to give N—H = 0.91 Å. All were included as riding contributions with isotropic displacement parameters 1.2 - 1.5 times those of the attached atoms.
Figures
Fig. 1.
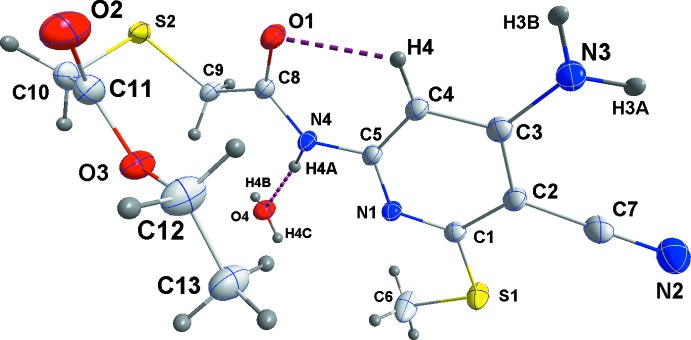
Perspective view of the asymmetric unit with 50% probability ellipsoids and hydrogen bonds depicted by dashed lines.
Fig. 2.
Packing projected down the b axis showing the inter- and intramolecular hydrogen bonds as dashed lines.
Fig. 3.
Packing projected along the c axis showing the tilted layers.
Fig. 4.
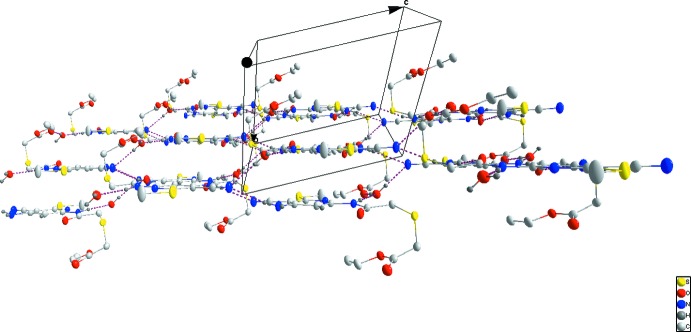
Packing viewed along the axis of the channels. Displacement ellipsoids for non-H atoms are drawn at the 50% probability level.
Crystal data
| C13H16N4O3S2·H2O | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 358.45 | F(000) = 376 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.442 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 9.0806 (12) Å | Cell parameters from 9913 reflections |
| b = 9.2444 (12) Å | θ = 2.4–29.2° |
| c = 10.7856 (14) Å | µ = 0.35 mm−1 |
| α = 101.843 (2)° | T = 150 K |
| β = 100.1750 (19)° | Plate, colourless |
| γ = 105.9480 (19)° | 0.26 × 0.26 × 0.12 mm |
| V = 825.48 (19) Å3 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEX CCD diffractometer | 4292 independent reflections |
| Graphite monochromator | 3773 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Detector resolution: 8.3660 pixels mm-1 | Rint = 0.034 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 29.2°, θmin = 2.0° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2013) | h = −12→12 |
| Tmin = 0.83, Tmax = 0.96 | k = −12→12 |
| 15313 measured reflections | l = −14→14 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | 0 restraints |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: mixed |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.037 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.099 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0515P)2 + 0.3031P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.05 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 4292 reflections | Δρmax = 0.44 e Å−3 |
| 210 parameters | Δρmin = −0.37 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. Bond distances, angles etc. have been calculated using the rounded fractional coordinates. All su's are estimated from the variances of the (full) variance-covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account in the estimation of distances, angles and torsion angles |
| Refinement. Refinement on F2 for ALL reflections except those flagged by the user for potential systematic errors. Weighted R-factors wR and all goodnesses of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The observed criterion of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating -R-factor-obs etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R-factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| S1 | 1.14877 (5) | 0.74276 (5) | 0.62470 (3) | 0.0316 (1) | |
| S2 | 0.40426 (4) | 0.82259 (4) | 0.00905 (3) | 0.0218 (1) | |
| O1 | 0.50975 (12) | 0.88281 (13) | 0.30154 (9) | 0.0263 (3) | |
| O2 | 0.16728 (13) | 0.58384 (14) | 0.15365 (11) | 0.0325 (3) | |
| O3 | 0.38626 (12) | 0.51837 (12) | 0.14447 (9) | 0.0244 (3) | |
| N1 | 0.91851 (13) | 0.79013 (14) | 0.46377 (11) | 0.0200 (3) | |
| N2 | 1.05234 (16) | 0.87115 (18) | 0.92745 (12) | 0.0330 (4) | |
| N3 | 0.73517 (14) | 0.97498 (15) | 0.76432 (11) | 0.0257 (3) | |
| N4 | 0.73715 (13) | 0.82181 (14) | 0.30697 (10) | 0.0204 (3) | |
| C1 | 0.98222 (15) | 0.80180 (16) | 0.58659 (13) | 0.0193 (3) | |
| C2 | 0.92486 (15) | 0.86183 (16) | 0.69216 (12) | 0.0192 (3) | |
| C3 | 0.79351 (15) | 0.91523 (16) | 0.66734 (12) | 0.0194 (3) | |
| C4 | 0.72390 (15) | 0.89929 (16) | 0.53540 (12) | 0.0207 (4) | |
| C5 | 0.79125 (15) | 0.83911 (15) | 0.44086 (12) | 0.0185 (3) | |
| C6 | 1.1786 (2) | 0.6781 (3) | 0.46517 (17) | 0.0480 (7) | |
| C7 | 0.99695 (16) | 0.86718 (17) | 0.82188 (13) | 0.0225 (4) | |
| C8 | 0.60550 (15) | 0.84739 (16) | 0.24588 (12) | 0.0194 (3) | |
| C9 | 0.59280 (16) | 0.82956 (17) | 0.10018 (13) | 0.0215 (4) | |
| C10 | 0.28999 (17) | 0.61849 (17) | −0.02404 (13) | 0.0247 (4) | |
| C11 | 0.27024 (16) | 0.57242 (17) | 0.09924 (13) | 0.0237 (4) | |
| C12 | 0.3870 (2) | 0.4842 (2) | 0.27094 (15) | 0.0315 (5) | |
| C13 | 0.5180 (2) | 0.4186 (2) | 0.30413 (16) | 0.0335 (5) | |
| O4 | 0.91965 (12) | 0.72768 (13) | 0.12641 (10) | 0.0287 (3) | |
| H3A | 0.79320 | 1.00160 | 0.84830 | 0.0310* | |
| H3B | 0.65660 | 1.01610 | 0.74450 | 0.0310* | |
| H4 | 0.63290 | 0.92930 | 0.51240 | 0.0250* | |
| H4A | 0.79970 | 0.79450 | 0.25550 | 0.0240* | |
| H6A | 1.08460 | 0.59240 | 0.41090 | 0.0720* | |
| H6B | 1.27060 | 0.64170 | 0.47300 | 0.0720* | |
| H6C | 1.19680 | 0.76500 | 0.42460 | 0.0720* | |
| H9A | 0.61410 | 0.73250 | 0.06270 | 0.0260* | |
| H9B | 0.67560 | 0.91820 | 0.08960 | 0.0260* | |
| H10A | 0.18450 | 0.59830 | −0.08140 | 0.0300* | |
| H10B | 0.34350 | 0.55330 | −0.07120 | 0.0300* | |
| H12A | 0.28430 | 0.40770 | 0.26670 | 0.0380* | |
| H12B | 0.40330 | 0.58080 | 0.33910 | 0.0380* | |
| H13A | 0.50470 | 0.32690 | 0.23340 | 0.0500* | |
| H13B | 0.51520 | 0.38810 | 0.38570 | 0.0500* | |
| H13C | 0.61990 | 0.49790 | 0.31490 | 0.0500* | |
| H4B | 0.94980 | 0.77280 | 0.07090 | 0.0340* | |
| H4C | 0.99220 | 0.69030 | 0.14630 | 0.0340* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S1 | 0.0310 (2) | 0.0527 (3) | 0.0213 (2) | 0.0314 (2) | 0.0049 (1) | 0.0089 (2) |
| S2 | 0.0225 (2) | 0.0265 (2) | 0.0184 (2) | 0.0128 (1) | 0.0009 (1) | 0.0072 (1) |
| O1 | 0.0212 (5) | 0.0418 (6) | 0.0196 (5) | 0.0182 (4) | 0.0036 (4) | 0.0063 (4) |
| O2 | 0.0282 (5) | 0.0444 (7) | 0.0334 (6) | 0.0193 (5) | 0.0132 (5) | 0.0134 (5) |
| O3 | 0.0255 (5) | 0.0313 (5) | 0.0225 (5) | 0.0142 (4) | 0.0094 (4) | 0.0108 (4) |
| N1 | 0.0184 (5) | 0.0261 (6) | 0.0182 (5) | 0.0121 (4) | 0.0041 (4) | 0.0054 (4) |
| N2 | 0.0328 (7) | 0.0520 (9) | 0.0211 (6) | 0.0253 (6) | 0.0055 (5) | 0.0097 (6) |
| N3 | 0.0227 (6) | 0.0408 (7) | 0.0167 (5) | 0.0186 (5) | 0.0037 (4) | 0.0041 (5) |
| N4 | 0.0185 (5) | 0.0299 (6) | 0.0156 (5) | 0.0132 (5) | 0.0038 (4) | 0.0053 (4) |
| C1 | 0.0171 (6) | 0.0242 (6) | 0.0188 (6) | 0.0111 (5) | 0.0032 (5) | 0.0055 (5) |
| C2 | 0.0168 (6) | 0.0253 (6) | 0.0167 (6) | 0.0098 (5) | 0.0024 (4) | 0.0054 (5) |
| C3 | 0.0159 (6) | 0.0238 (6) | 0.0180 (6) | 0.0075 (5) | 0.0030 (4) | 0.0039 (5) |
| C4 | 0.0175 (6) | 0.0281 (7) | 0.0179 (6) | 0.0119 (5) | 0.0022 (5) | 0.0047 (5) |
| C5 | 0.0158 (5) | 0.0225 (6) | 0.0168 (6) | 0.0078 (5) | 0.0010 (4) | 0.0046 (5) |
| C6 | 0.0526 (11) | 0.0851 (15) | 0.0276 (8) | 0.0544 (11) | 0.0149 (7) | 0.0128 (9) |
| C7 | 0.0190 (6) | 0.0314 (7) | 0.0202 (6) | 0.0135 (5) | 0.0053 (5) | 0.0056 (5) |
| C8 | 0.0180 (6) | 0.0226 (6) | 0.0178 (6) | 0.0088 (5) | 0.0022 (4) | 0.0050 (5) |
| C9 | 0.0190 (6) | 0.0309 (7) | 0.0190 (6) | 0.0128 (5) | 0.0047 (5) | 0.0097 (5) |
| C10 | 0.0264 (7) | 0.0266 (7) | 0.0197 (6) | 0.0094 (6) | 0.0026 (5) | 0.0045 (5) |
| C11 | 0.0223 (6) | 0.0249 (7) | 0.0235 (6) | 0.0087 (5) | 0.0043 (5) | 0.0053 (5) |
| C12 | 0.0360 (8) | 0.0431 (9) | 0.0269 (7) | 0.0198 (7) | 0.0151 (6) | 0.0184 (7) |
| C13 | 0.0391 (9) | 0.0396 (9) | 0.0301 (8) | 0.0198 (7) | 0.0100 (6) | 0.0161 (7) |
| O4 | 0.0258 (5) | 0.0376 (6) | 0.0301 (5) | 0.0171 (5) | 0.0113 (4) | 0.0116 (5) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| S1—C1 | 1.7550 (15) | C2—C3 | 1.415 (2) |
| S1—C6 | 1.7952 (18) | C2—C7 | 1.4208 (19) |
| S2—C9 | 1.7945 (15) | C3—C4 | 1.4111 (18) |
| S2—C10 | 1.8113 (16) | C4—C5 | 1.3776 (19) |
| O1—C8 | 1.2181 (18) | C8—C9 | 1.5262 (18) |
| O2—C11 | 1.2051 (19) | C10—C11 | 1.502 (2) |
| O3—C11 | 1.3436 (19) | C12—C13 | 1.499 (3) |
| O3—C12 | 1.4613 (19) | C4—H4 | 0.9500 |
| O4—H4C | 0.8400 | C6—H6B | 0.9800 |
| O4—H4B | 0.8400 | C6—H6A | 0.9800 |
| N1—C1 | 1.3181 (18) | C6—H6C | 0.9800 |
| N1—C5 | 1.3543 (19) | C9—H9B | 0.9900 |
| N2—C7 | 1.1494 (19) | C9—H9A | 0.9900 |
| N3—C3 | 1.3414 (18) | C10—H10B | 0.9900 |
| N4—C5 | 1.4013 (16) | C10—H10A | 0.9900 |
| N4—C8 | 1.3639 (19) | C12—H12B | 0.9900 |
| N3—H3A | 0.9100 | C12—H12A | 0.9900 |
| N3—H3B | 0.9100 | C13—H13C | 0.9800 |
| N4—H4A | 0.9100 | C13—H13A | 0.9800 |
| C1—C2 | 1.4088 (19) | C13—H13B | 0.9800 |
| C1—S1—C6 | 101.26 (8) | O2—C11—C10 | 125.82 (14) |
| C9—S2—C10 | 101.89 (7) | O3—C12—C13 | 108.59 (14) |
| C11—O3—C12 | 115.32 (12) | C5—C4—H4 | 121.00 |
| H4B—O4—H4C | 102.00 | C3—C4—H4 | 121.00 |
| C1—N1—C5 | 116.87 (12) | S1—C6—H6A | 109.00 |
| C5—N4—C8 | 127.62 (12) | S1—C6—H6B | 109.00 |
| H3A—N3—H3B | 120.00 | H6A—C6—H6B | 110.00 |
| C3—N3—H3B | 119.00 | H6A—C6—H6C | 109.00 |
| C3—N3—H3A | 119.00 | S1—C6—H6C | 109.00 |
| C5—N4—H4A | 116.00 | H6B—C6—H6C | 109.00 |
| C8—N4—H4A | 116.00 | S2—C9—H9B | 109.00 |
| S1—C1—N1 | 119.69 (11) | C8—C9—H9A | 109.00 |
| S1—C1—C2 | 116.86 (10) | S2—C9—H9A | 109.00 |
| N1—C1—C2 | 123.45 (13) | H9A—C9—H9B | 108.00 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 119.22 (12) | C8—C9—H9B | 109.00 |
| C1—C2—C7 | 120.40 (13) | S2—C10—H10A | 109.00 |
| C3—C2—C7 | 120.38 (12) | C11—C10—H10A | 109.00 |
| N3—C3—C4 | 121.32 (13) | C11—C10—H10B | 109.00 |
| N3—C3—C2 | 121.69 (12) | H10A—C10—H10B | 108.00 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 116.98 (12) | S2—C10—H10B | 109.00 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 118.29 (13) | O3—C12—H12A | 110.00 |
| N1—C5—N4 | 110.75 (11) | C13—C12—H12A | 110.00 |
| N4—C5—C4 | 124.09 (13) | C13—C12—H12B | 110.00 |
| N1—C5—C4 | 125.16 (12) | O3—C12—H12B | 110.00 |
| N2—C7—C2 | 178.60 (17) | H12A—C12—H12B | 108.00 |
| O1—C8—C9 | 123.62 (13) | C12—C13—H13B | 110.00 |
| O1—C8—N4 | 123.88 (12) | C12—C13—H13C | 109.00 |
| N4—C8—C9 | 112.49 (12) | C12—C13—H13A | 109.00 |
| S2—C9—C8 | 114.23 (10) | H13A—C13—H13C | 109.00 |
| S2—C10—C11 | 111.95 (10) | H13B—C13—H13C | 109.00 |
| O3—C11—C10 | 110.84 (12) | H13A—C13—H13B | 109.00 |
| O2—C11—O3 | 123.32 (13) | ||
| C6—S1—C1—N1 | −0.35 (15) | S1—C1—C2—C7 | −2.41 (19) |
| C6—S1—C1—C2 | −179.63 (14) | N1—C1—C2—C3 | −1.0 (2) |
| C10—S2—C9—C8 | −83.84 (12) | N1—C1—C2—C7 | 178.34 (14) |
| C9—S2—C10—C11 | 63.79 (12) | C1—C2—C3—N3 | −179.28 (14) |
| C12—O3—C11—O2 | −4.3 (2) | C1—C2—C3—C4 | 2.2 (2) |
| C12—O3—C11—C10 | 174.39 (12) | C7—C2—C3—N3 | 1.4 (2) |
| C11—O3—C12—C13 | 177.43 (13) | C7—C2—C3—C4 | −177.10 (14) |
| C5—N1—C1—S1 | −179.33 (11) | N3—C3—C4—C5 | 179.07 (14) |
| C5—N1—C1—C2 | −0.1 (2) | C2—C3—C4—C5 | −2.4 (2) |
| C1—N1—C5—N4 | 179.28 (13) | C3—C4—C5—N1 | 1.5 (2) |
| C1—N1—C5—C4 | −0.2 (2) | C3—C4—C5—N4 | −177.88 (13) |
| C8—N4—C5—N1 | 174.69 (14) | O1—C8—C9—S2 | −13.0 (2) |
| C8—N4—C5—C4 | −5.9 (2) | N4—C8—C9—S2 | 168.00 (10) |
| C5—N4—C8—O1 | −3.9 (2) | S2—C10—C11—O2 | 86.96 (18) |
| C5—N4—C8—C9 | 175.09 (13) | S2—C10—C11—O3 | −91.73 (13) |
| S1—C1—C2—C3 | 178.25 (11) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N3—H3A···N2i | 0.91 | 2.43 | 3.3291 (18) | 168 |
| N3—H3B···O1ii | 0.91 | 2.03 | 2.9345 (18) | 177 |
| N4—H4A···O4 | 0.91 | 2.01 | 2.9212 (16) | 174 |
| O4—H4B···N2iii | 0.84 | 2.17 | 3.0032 (19) | 172 |
| O4—H4C···O2iv | 0.84 | 2.09 | 2.9122 (18) | 168 |
| C4—H4···O1 | 0.95 | 2.25 | 2.8484 (17) | 121 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+2, −y+2, −z+2; (ii) −x+1, −y+2, −z+1; (iii) x, y, z−1; (iv) x+1, y, z.
Footnotes
Supporting information for this paper is available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: SJ5406).
References
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 34, 1555–1573.
- Brandenburg, K. & Putz, H. (2012). DIAMOND Crystal Impact GbR, Bonn, Germany.
- Bruker (2013). APEX2, SADABS and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Chaki, H., Yamabe, H., Sugano, M., Morita, S., Bessho, T., Tabata, R., Saito, K. I., Egawa, M., Tobe, A. & Morinaka, Y. (1995). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett 5, 1495–1500.
- Dolle, V., Nguyen, E. C. H., Aubertin, A. M., Kirm, A. M., Andreola, L., Jamieson, G., Tarrago-Litvak, L. & Bisagni, E. (1995). J. Med. Chem. 38, 4679–4686. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Dorigo, P., Gaion, R. M., Belluco, P., Fraccarollo, D., Maragano, I., Bombien, G., Benelollo, F., Mostil, L. & Orsini, F. (1993). J. Med. Chem. 36, 2475–2484. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Konda, S. G., Khedkar, V. T. & Dawane, B. S. (2010). J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2, 1–6.
- Lohray, B. B., Lohray, V. B. & Srivastava, B. K. (2004). Bioorg. Med. Chem. 17, 4557–4564. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Merja, B. C., Joshi, A. M. & Parikh, K. A. (2004). Indian J. Chem. Sect. B, 4, 909–912.
- Murata, T., Shimada, M., Sakakibara, S., Yoshino, T. & Kadono, H. (2003). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 13, 913–918. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Shi, F., Shujiang Tu, S., Fang, F. & Li, T. (2005). Arkivoc, i, 137–142.
- Thomae, D., Kirsch, G. & Seck, P. (2007). Synthesis, 7, 1027–1032.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814012495/sj5406sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814012495/sj5406Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814012495/sj5406Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1005734
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




