The platinum(II) complex with notable antitumor activity shows a slightly distorted square-planar coordination and intramolecular C—H⋯Cl and intermolecular N—H⋯Cl and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds.
Keywords: crystal structure, cis-platinum(II) complexes, hydrogen bonding, anticancer activity
Abstract
The title compound, [Pt(C10H6NO2)Cl(C5H11N)], crystallizes with one molecule in the asymmetric unit. The PtII cation has a slightly distorted square-planar coordination environment defined by a chloride anion, the quinoline N atom and a carboxylate O atom of the bidentate quinaldate ligand and a piperidine N atom. An intramolecular C—H⋯Cl hydrogen bond occurs. In the crystal, molecules are stacked into columns along the c axis by the formation of N—H⋯Cl and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds.
Chemical context
The title compound belongs to a series of platinum(II) complexes bearing piperidine (pip) as a ligand, which exhibit notable antitumour activity (Da et al., 2001 ▶; Rounaq Ali Khan et al., 2000 ▶; Solin et al., 1982 ▶). In comparison with the earlier reported complex [PtCl2(pip)(quinoline)] (Nguyen Thi Thanh et al., 2014 ▶), the quinoline ligand is replaced by an N,O-bidentate quinaldate ligand. It is interesting to note that in the [PtCl2(pip)(quinoline)] complex, the quinoline and piperidine ligands are arranged in cis positions (Nguyen Thi Thanh et al., 2014 ▶). In the title compound, the quinoline ring of the quinaldate ligand occupies a trans position with respect to the piperidine ring. We suggest that in the reaction solution there exists a chemical equilibrium between the neutral and bipolar forms of quinaldic acid. Thus, the quinaldic acid in its ionic form coordinates with PtII
via the O atom of the carboxylate group first and in a cis position with respect to piperidine based on the trans effect. In a second step, the quinaldic acid coordinates with PtII also via its N atom, resulting in the cyclic complex.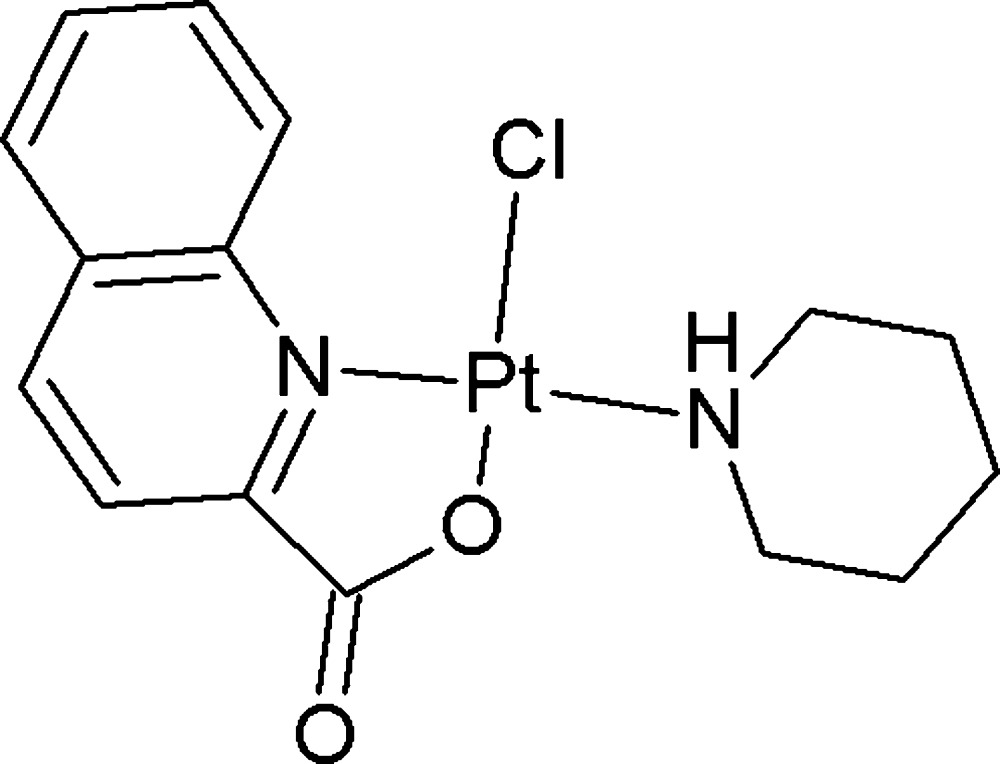
The anticancer activity of the title compound was tested according to the method described in Skehan et al. (1990 ▶) on four human cancer cells of HepG2, RD, MCF7 and Fl. The IC50 values calculated based on OD values taken on an Elisa instrument at 515–540 nm are 4.46, 2.59, >10 and 5.60 µg ml−1, respectively.
Structural commentary
The title complex crystallizes with one molecule per asymmetric unit (Fig. 1 ▶). The PtII cation is surrounded by two N atoms, one O atom and one Cl atom, resulting in a slightly distorted square-planar coordination environment [angles around platinum: O1—Pt1—N1 81.38 (9), O1—Pt1—N2 88.26 (9), Cl1—Pt1—N2 84.26 (7) and Cl1—Pt1—N1 106.11 (7)°]. The Cl− and the PtII atoms are displaced from the least-squares plane of the quinoline ring and all other coordinating atoms by 0.2936 (7) and 0.0052 (1) Å, respectively. The piperidine ring adopts a chair conformation and is almost perpendicular to the coordination plane of the PtII cation [dihedral angle between the best plane through the piperidine ring and the four atoms coordinating to the PtII cation = 79.66 (13)°]. Bond lengths are normal and agree well with related platinum compounds (Cambridge Structural Database, version 5.34; Allen, 2002 ▶). There is an intramolecular hydrogen bond between atom Cl1 and atom H8 (Fig. 1 ▶ and Table 1 ▶).
Figure 1.

View of the molecular structure of the title compound, showing the atom-labelling scheme, with ellipsoids drawn at the 50% probability level. The intramolecular C—H⋯Cl hydrogen bond is shown as a green dashed line.
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2—H2A⋯Cl1i | 0.93 | 2.74 | 3.624 (2) | 160 |
| C3—H3⋯O2ii | 0.96 | 2.53 | 3.360 (4) | 145 |
| C8—H8⋯Cl1 | 0.95 | 2.40 | 3.268 (3) | 152 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  .
.
Supramolecular features
The crystal packing is characterized by N—H⋯Cl and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds (Table 1 ▶). Molecules are arranged into columns along the c axis (Fig. 2 ▶) with the piperidine rings all directed towards the center of the column, favouring hydrophobic interactions.
Figure 2.
View of the crystal packing for the title compound, with (N/C)—H⋯Cl and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds drawn as green and red dashed lines, respectively. [Symmetry codes: (i) x, −y + 1, z −  ; (ii) −x + 1, y, −z +
; (ii) −x + 1, y, −z +  .]
.]
Synthesis and crystallization
The starting complex K[PtCl3(piperidine)] (0.425 g, 1 mmol), prepared according to the synthetic protocol of Da et al. (2001 ▶), was dissolved in water (10 ml) and filtered to afford a clear solution. To this solution, quinaldic acid (1.2 mmol) in an aqueous ethanol solution (5 ml, 1:1 v/v) was added gradually while stirring at room temperature for 1 h. The reaction mixture was stirred further for 4 h. The precipitated yellow substance was filtered off and washed consecutively with a 0.1 M HCl solution (2 × 2 ml), warm water (3 × 2 ml) and cold ethanol (2 ml). The product was then dried in a vacuum at 323 K for 4 h. The yield was 80%. Single crystals suitable for X-ray diffraction analysis were obtained by slow evaporation from an ethanol–water (1:1 v/v) solution at room temperature. Positive ESI–MS: m/z 1973 [4M + Na]+, 1483 [3M + Na]+, 998 [2M + Na]+, 510 [M + Na]+, 977 [2M + H]+, 489 [M + H]+; IR (KBr) cm−1: 3192 (νNH); 3080, 2930, 2866 (νCH); 1678 (νC=O); 1592, 1459 (νC=C arom); 1334 (νC—O); 1H NMR (δ p.p.m; CDCl3, 500Hz): 9.50 (1H, d, 3 J = 9.0 Hz, Ar-H), 8.51 (1H, d, 3 J = 8.0 Hz, Ar-H), 8.06 (1H, d, 3 J = 8.0 Hz, Ar-H), 7.91–7.88 (2H, ov, Ar-H), 7.71 (1H, t, 3 J = 8.0 Hz, Ar-H), 3.52 (2Hα e, d, 2 J ae = 12.5 Hz, C5 H10NH), 3.27 (2Hα a, q, 2 J ae, 3 J aa, 3 J aa(NH) = 12.5 Hz, C5 H10NH), 1.76–1.61 (4Hβ, 2Hγ, ov, C5 H10NH), 4.00 (1H, br, C5H10NH).
Refinement
All H atoms were refined using a riding model, with C—H = 0.95 Å for aromatic, C—H = 0.99 Å for CH2 and N—H = 0.93 Å for amino H atoms, with U iso = 1.2U eq(C,N).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681401191X/wm0005sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681401191X/wm0005Isup2.hkl
CCDC reference: 1004305
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 2. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | [Pt(C10H6NO2)Cl(C5H11N)] |
| M r | 487.85 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, C2/c |
| Temperature (K) | 200 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 22.7542 (8), 9.7540 (3), 14.0139 (5) |
| β (°) | 95.542 (3) |
| V (Å3) | 3095.78 (19) |
| Z | 8 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 9.24 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.3 × 0.3 × 0.2 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Agilent SuperNova (single source at offset, Eos detector) |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2012 ▶) |
| T min, T max | 0.473, 1.000 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 31419, 3166, 2951 |
| R int | 0.026 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.625 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.015, 0.035, 1.12 |
| No. of reflections | 3166 |
| No. of parameters | 190 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.80, −0.53 |
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Vietnamese Ministry of Education (project No. B2013-17-39) for financial support and the Hercules Foundation for supporting the purchase of the diffractometer through project AKUL/09/0035.
supplementary crystallographic information
Crystal data
| [Pt(C10H6NO2)Cl(C5H11N)] | F(000) = 1856 |
| Mr = 487.85 | Dx = 2.093 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, C2/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.7107 Å |
| a = 22.7542 (8) Å | Cell parameters from 16449 reflections |
| b = 9.7540 (3) Å | θ = 3.4–29.8° |
| c = 14.0139 (5) Å | µ = 9.24 mm−1 |
| β = 95.542 (3)° | T = 200 K |
| V = 3095.78 (19) Å3 | Block, yellow |
| Z = 8 | 0.3 × 0.3 × 0.2 mm |
Data collection
| Agilent SuperNova (single source at offset, Eos detector) diffractometer | 3166 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: SuperNova (Mo) X-ray Source | 2951 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Mirror monochromator | Rint = 0.026 |
| Detector resolution: 15.9631 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 26.4°, θmin = 2.8° |
| ω scans | h = −28→28 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2012) | k = −12→12 |
| Tmin = 0.473, Tmax = 1.000 | l = −17→17 |
| 31419 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.015 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.035 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.12 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0118P)2 + 9.138P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3166 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.002 |
| 190 parameters | Δρmax = 0.80 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.53 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.29348 (12) | 0.6098 (3) | 0.5028 (2) | 0.0268 (6) | |
| C2 | 0.25609 (13) | 0.5746 (3) | 0.4211 (2) | 0.0327 (7) | |
| H2 | 0.2227 | 0.5176 | 0.4264 | 0.039* | |
| C3 | 0.26831 (14) | 0.6232 (3) | 0.3338 (2) | 0.0354 (7) | |
| H3 | 0.2432 | 0.6014 | 0.2777 | 0.042* | |
| C4 | 0.31811 (14) | 0.7052 (3) | 0.3278 (2) | 0.0324 (7) | |
| C5 | 0.33360 (18) | 0.7554 (4) | 0.2386 (2) | 0.0432 (8) | |
| H5 | 0.3085 | 0.7372 | 0.1818 | 0.052* | |
| C6 | 0.38367 (19) | 0.8290 (4) | 0.2332 (2) | 0.0516 (10) | |
| H6 | 0.3934 | 0.8625 | 0.1730 | 0.062* | |
| C7 | 0.42105 (18) | 0.8556 (4) | 0.3167 (2) | 0.0503 (9) | |
| H7 | 0.4565 | 0.9057 | 0.3121 | 0.060* | |
| C8 | 0.40769 (16) | 0.8111 (3) | 0.4047 (2) | 0.0400 (8) | |
| H8 | 0.4336 | 0.8309 | 0.4603 | 0.048* | |
| C9 | 0.35561 (14) | 0.7362 (3) | 0.4130 (2) | 0.0285 (6) | |
| C10 | 0.28109 (13) | 0.5514 (3) | 0.5984 (2) | 0.0318 (7) | |
| C11 | 0.42217 (15) | 0.5840 (3) | 0.8206 (2) | 0.0402 (8) | |
| H11A | 0.4518 | 0.5401 | 0.7832 | 0.048* | |
| H11B | 0.3857 | 0.5281 | 0.8125 | 0.048* | |
| C12 | 0.44551 (16) | 0.5867 (4) | 0.9262 (3) | 0.0479 (9) | |
| H12A | 0.4509 | 0.4914 | 0.9499 | 0.058* | |
| H12B | 0.4845 | 0.6323 | 0.9333 | 0.058* | |
| C13 | 0.40413 (18) | 0.6613 (5) | 0.9861 (2) | 0.0550 (10) | |
| H13A | 0.4225 | 0.6690 | 1.0528 | 0.066* | |
| H13B | 0.3671 | 0.6083 | 0.9869 | 0.066* | |
| C14 | 0.39015 (16) | 0.8039 (4) | 0.9459 (2) | 0.0443 (9) | |
| H14A | 0.4263 | 0.8607 | 0.9527 | 0.053* | |
| H14B | 0.3604 | 0.8481 | 0.9828 | 0.053* | |
| C15 | 0.36650 (13) | 0.7956 (3) | 0.8404 (2) | 0.0337 (7) | |
| H15A | 0.3285 | 0.7455 | 0.8344 | 0.040* | |
| H15B | 0.3591 | 0.8893 | 0.8150 | 0.040* | |
| Cl1 | 0.45271 (3) | 0.88368 (8) | 0.62745 (5) | 0.03279 (16) | |
| N1 | 0.34113 (10) | 0.6894 (2) | 0.50082 (16) | 0.0255 (5) | |
| N2 | 0.40915 (10) | 0.7240 (2) | 0.78242 (16) | 0.0264 (5) | |
| H2A | 0.4443 | 0.7733 | 0.7893 | 0.032* | |
| O1 | 0.31888 (9) | 0.5856 (2) | 0.66939 (14) | 0.0369 (5) | |
| O2 | 0.23904 (10) | 0.4760 (3) | 0.60452 (16) | 0.0433 (6) | |
| Pt1 | 0.380802 (4) | 0.720087 (11) | 0.639573 (7) | 0.02386 (4) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0264 (14) | 0.0266 (14) | 0.0271 (14) | 0.0071 (12) | 0.0005 (11) | −0.0021 (12) |
| C2 | 0.0288 (15) | 0.0374 (17) | 0.0308 (15) | 0.0016 (13) | −0.0034 (12) | −0.0040 (13) |
| C3 | 0.0374 (16) | 0.0387 (18) | 0.0281 (15) | 0.0067 (14) | −0.0071 (12) | −0.0063 (13) |
| C4 | 0.0425 (17) | 0.0282 (16) | 0.0256 (15) | 0.0079 (13) | −0.0006 (12) | −0.0035 (12) |
| C5 | 0.067 (2) | 0.0370 (18) | 0.0247 (16) | −0.0022 (17) | −0.0017 (15) | −0.0011 (13) |
| C6 | 0.086 (3) | 0.042 (2) | 0.0269 (16) | −0.014 (2) | 0.0094 (17) | 0.0007 (15) |
| C7 | 0.071 (3) | 0.046 (2) | 0.0345 (18) | −0.0231 (19) | 0.0125 (17) | −0.0054 (16) |
| C8 | 0.052 (2) | 0.0383 (18) | 0.0298 (16) | −0.0106 (15) | 0.0033 (14) | −0.0039 (13) |
| C9 | 0.0397 (16) | 0.0213 (14) | 0.0242 (14) | 0.0045 (12) | 0.0010 (12) | −0.0031 (11) |
| C10 | 0.0282 (15) | 0.0393 (17) | 0.0268 (14) | 0.0012 (13) | −0.0028 (12) | −0.0017 (13) |
| C11 | 0.0421 (18) | 0.0303 (17) | 0.0443 (19) | 0.0005 (14) | −0.0153 (15) | 0.0051 (14) |
| C12 | 0.051 (2) | 0.040 (2) | 0.048 (2) | −0.0110 (16) | −0.0235 (17) | 0.0172 (16) |
| C13 | 0.060 (2) | 0.072 (3) | 0.0299 (17) | −0.024 (2) | −0.0086 (16) | 0.0155 (18) |
| C14 | 0.0404 (18) | 0.065 (3) | 0.0262 (16) | −0.0016 (17) | −0.0010 (13) | −0.0030 (15) |
| C15 | 0.0296 (15) | 0.0433 (19) | 0.0275 (15) | 0.0027 (13) | −0.0014 (12) | 0.0001 (13) |
| Cl1 | 0.0348 (4) | 0.0335 (4) | 0.0292 (3) | −0.0071 (3) | −0.0013 (3) | −0.0006 (3) |
| N1 | 0.0274 (12) | 0.0244 (12) | 0.0241 (11) | 0.0033 (9) | −0.0002 (9) | −0.0026 (9) |
| N2 | 0.0240 (11) | 0.0299 (13) | 0.0242 (12) | −0.0014 (10) | −0.0028 (9) | 0.0022 (10) |
| O1 | 0.0349 (11) | 0.0493 (14) | 0.0251 (10) | −0.0115 (10) | −0.0044 (9) | 0.0061 (10) |
| O2 | 0.0350 (12) | 0.0585 (16) | 0.0350 (12) | −0.0179 (11) | −0.0031 (9) | 0.0032 (11) |
| Pt1 | 0.02348 (6) | 0.02556 (6) | 0.02184 (6) | 0.00129 (4) | −0.00148 (4) | −0.00049 (4) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| C1—C2 | 1.402 (4) | C11—H11B | 0.9900 |
| C1—C10 | 1.507 (4) | C11—C12 | 1.524 (4) |
| C1—N1 | 1.336 (4) | C11—N2 | 1.486 (4) |
| C2—H2 | 0.9500 | C12—H12A | 0.9900 |
| C2—C3 | 1.365 (4) | C12—H12B | 0.9900 |
| C3—H3 | 0.9500 | C12—C13 | 1.507 (6) |
| C3—C4 | 1.396 (5) | C13—H13A | 0.9900 |
| C4—C5 | 1.419 (4) | C13—H13B | 0.9900 |
| C4—C9 | 1.432 (4) | C13—C14 | 1.522 (5) |
| C5—H5 | 0.9500 | C14—H14A | 0.9900 |
| C5—C6 | 1.355 (5) | C14—H14B | 0.9900 |
| C6—H6 | 0.9500 | C14—C15 | 1.526 (4) |
| C6—C7 | 1.403 (5) | C15—H15A | 0.9900 |
| C7—H7 | 0.9500 | C15—H15B | 0.9900 |
| C7—C8 | 1.369 (5) | C15—N2 | 1.497 (4) |
| C8—H8 | 0.9500 | Cl1—Pt1 | 2.3035 (7) |
| C8—C9 | 1.407 (5) | N1—Pt1 | 2.085 (2) |
| C9—N1 | 1.382 (4) | N2—H2A | 0.9300 |
| C10—O1 | 1.295 (3) | N2—Pt1 | 2.043 (2) |
| C10—O2 | 1.217 (4) | O1—Pt1 | 1.999 (2) |
| C11—H11A | 0.9900 | ||
| C2—C1—C10 | 118.8 (3) | H12A—C12—H12B | 107.9 |
| N1—C1—C2 | 123.8 (3) | C13—C12—C11 | 111.8 (3) |
| N1—C1—C10 | 117.4 (2) | C13—C12—H12A | 109.3 |
| C1—C2—H2 | 120.4 | C13—C12—H12B | 109.3 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 119.1 (3) | C12—C13—H13A | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 120.4 | C12—C13—H13B | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 120.3 | C12—C13—C14 | 110.8 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 119.3 (3) | H13A—C13—H13B | 108.1 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 120.3 | C14—C13—H13A | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 121.6 (3) | C14—C13—H13B | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—C9 | 119.5 (3) | C13—C14—H14A | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—C9 | 118.9 (3) | C13—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.5 | C13—C14—C15 | 110.6 (3) |
| C6—C5—C4 | 120.9 (3) | H14A—C14—H14B | 108.1 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.5 | C15—C14—H14A | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—H6 | 120.1 | C15—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 119.8 (3) | C14—C15—H15A | 109.4 |
| C7—C6—H6 | 120.1 | C14—C15—H15B | 109.4 |
| C6—C7—H7 | 119.2 | H15A—C15—H15B | 108.0 |
| C8—C7—C6 | 121.6 (3) | N2—C15—C14 | 111.4 (3) |
| C8—C7—H7 | 119.2 | N2—C15—H15A | 109.4 |
| C7—C8—H8 | 120.0 | N2—C15—H15B | 109.4 |
| C7—C8—C9 | 120.1 (3) | C1—N1—C9 | 118.3 (2) |
| C9—C8—H8 | 120.0 | C1—N1—Pt1 | 110.10 (18) |
| C8—C9—C4 | 118.7 (3) | C9—N1—Pt1 | 131.61 (19) |
| N1—C9—C4 | 119.9 (3) | C11—N2—C15 | 110.5 (2) |
| N1—C9—C8 | 121.4 (3) | C11—N2—H2A | 107.4 |
| O1—C10—C1 | 114.8 (3) | C11—N2—Pt1 | 111.61 (18) |
| O2—C10—C1 | 120.5 (3) | C15—N2—H2A | 107.4 |
| O2—C10—O1 | 124.7 (3) | C15—N2—Pt1 | 112.37 (17) |
| H11A—C11—H11B | 107.9 | Pt1—N2—H2A | 107.4 |
| C12—C11—H11A | 109.2 | C10—O1—Pt1 | 115.95 (19) |
| C12—C11—H11B | 109.2 | N1—Pt1—Cl1 | 106.11 (7) |
| N2—C11—H11A | 109.2 | N2—Pt1—Cl1 | 84.26 (7) |
| N2—C11—H11B | 109.2 | N2—Pt1—N1 | 169.63 (9) |
| N2—C11—C12 | 111.9 (3) | O1—Pt1—Cl1 | 171.99 (6) |
| C11—C12—H12A | 109.3 | O1—Pt1—N1 | 81.38 (9) |
| C11—C12—H12B | 109.3 | O1—Pt1—N2 | 88.26 (9) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.8 (5) | C9—N1—Pt1—Cl1 | 8.2 (3) |
| C1—C10—O1—Pt1 | 5.1 (3) | C9—N1—Pt1—N2 | −171.6 (4) |
| C1—N1—Pt1—Cl1 | −171.51 (17) | C9—N1—Pt1—O1 | −174.7 (3) |
| C1—N1—Pt1—N2 | 8.6 (6) | C10—C1—C2—C3 | −177.6 (3) |
| C1—N1—Pt1—O1 | 5.58 (18) | C10—C1—N1—C9 | 175.6 (2) |
| C2—C1—C10—O1 | 177.8 (3) | C10—C1—N1—Pt1 | −4.7 (3) |
| C2—C1—C10—O2 | −0.7 (4) | C10—O1—Pt1—N1 | −6.0 (2) |
| C2—C1—N1—C9 | −2.1 (4) | C10—O1—Pt1—N2 | 174.6 (2) |
| C2—C1—N1—Pt1 | 177.6 (2) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | −53.6 (4) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 178.4 (3) | C11—N2—Pt1—Cl1 | −129.0 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—C9 | 0.4 (4) | C11—N2—Pt1—N1 | 50.9 (6) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −176.6 (3) | C11—N2—Pt1—O1 | 53.9 (2) |
| C3—C4—C9—C8 | 175.7 (3) | C12—C11—N2—C15 | −56.3 (3) |
| C3—C4—C9—N1 | −2.5 (4) | C12—C11—N2—Pt1 | 177.9 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | 0.3 (6) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | 54.5 (4) |
| C4—C9—N1—C1 | 3.3 (4) | C13—C14—C15—N2 | −56.9 (4) |
| C4—C9—N1—Pt1 | −176.4 (2) | C14—C15—N2—C11 | 57.6 (3) |
| C5—C4—C9—C8 | −2.3 (4) | C14—C15—N2—Pt1 | −177.0 (2) |
| C5—C4—C9—N1 | 179.4 (3) | C15—N2—Pt1—Cl1 | 106.25 (19) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | −1.3 (6) | C15—N2—Pt1—N1 | −73.9 (6) |
| C6—C7—C8—C9 | 0.3 (6) | C15—N2—Pt1—O1 | −70.9 (2) |
| C7—C8—C9—C4 | 1.5 (5) | N1—C1—C2—C3 | 0.0 (5) |
| C7—C8—C9—N1 | 179.7 (3) | N1—C1—C10—O1 | 0.0 (4) |
| C8—C9—N1—C1 | −174.9 (3) | N1—C1—C10—O2 | −178.5 (3) |
| C8—C9—N1—Pt1 | 5.4 (4) | N2—C11—C12—C13 | 54.9 (4) |
| C9—C4—C5—C6 | 1.4 (5) | O2—C10—O1—Pt1 | −176.5 (3) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N2—H2A···Cl1i | 0.93 | 2.74 | 3.624 (2) | 160 |
| C3—H3···O2ii | 0.96 | 2.53 | 3.360 (4) | 145 |
| C8—H8···Cl1 | 0.95 | 2.40 | 3.268 (3) | 152 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, y, −z+3/2; (ii) x, −y+1, z−1/2.
References
- Agilent (2012). CrysAlis PRO Agilent Technologies, Yarnton, England.
- Allen, F. H. (2002). Acta Cryst. B58, 380–388. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Da, T. T., Vu, D. B. & Dinh, N. H. (2001). J. Pharm. Sci. (Vietnam), 6, 6–8.
- Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K. & Puschmann, H. (2009). J. Appl. Cryst. 42, 339–341.
- Nguyen Thi Thanh, C., Nguyen Bich, N. & Van Meervelt, L. (2014). Acta Cryst. C70, 297–301. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Rounaq Ali Khan, S., Guzman-Jimenez, I., Whitmire, K. H. & Khokhar, A. R. (2000). Polyhedron, 19, 975–981.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Skehan, P., Storeng, R., Scudiero, D., Monks, A., McMahon, J., Vistica, D., Warren, J. T., Bokesch, H., Kenney, S. & Boyd, M. R. (1990). J. Natl Cancer Inst. 82, 1107–1112. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Solin, T., Matsumoto, K. & Fuwa, K. (1982). Inorg. Chim. Acta, 65, L172–L172.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681401191X/wm0005sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681401191X/wm0005Isup2.hkl
CCDC reference: 1004305
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report



