Abstract
In the title molecule, C22H18O, the o-tolyl ring is connected through a conjugated double bond. The molecule adopts an E conformation and the C—C=C—C torsion angle is 178.77 (13)°. The overall conformation may be described by the values of dihedral angles between the different planes. The terminal rings are twisted by an angle of 54.75 (8)°, while the biphenyl part is not planar, the dihedral angle between the planes of the rings being 40.65 (8)°. The dihedral angle between the benzene rings is 14.10 (7)°. There are three weak C—H⋯π interactions found in the crystal structure. No classic hydrogen bonds are observed.
Keywords: crystal structure
Related literature
For the bioactivity of chalcones, see: Dimmock et al. (1999 ▶). For biological applications of chalcones, see: Opletalova (2000 ▶); Opletalova & Sedivy (1999 ▶). For chalcones as non-linear optical materials, see: Fichou et al. (1988 ▶); Goto et al. (1991 ▶). For further applications of chalcones, see: Sarojini et al. (2006 ▶). For the crystal structures of related compounds, see: Betz et al. (2011a
▶,b
▶). For bond-length data, see: Allen et al. (1987 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C22H18O
M r = 298.36
Triclinic,

a = 7.6396 (3) Å
b = 9.9106 (4) Å
c = 11.9263 (4) Å
α = 103.166 (2)°
β = 104.713 (2)°
γ = 103.308 (2)°
V = 809.66 (6) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.07 mm−1
T = 273 K
0.40 × 0.35 × 0.30 mm
Data collection
Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2004 ▶) T min = 0.908, T max = 1.000
18636 measured reflections
4534 independent reflections
3291 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.024
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.048
wR(F 2) = 0.151
S = 1.06
4534 reflections
209 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.23 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.17 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2004 ▶); cell refinement: APEX2 and SAINT (Bruker, 2004 ▶); data reduction: SAINT and XPREP (Bruker, 2004 ▶); program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS2013 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL2014 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 2012 ▶) and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL2014 and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814014317/jj2188sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814014317/jj2188Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814014317/jj2188Isup3.cdx
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814014317/jj2188Isup4.cml
CCDC reference: 977614
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
Cg1, Cg2 and Cg3 are the centroids of the C2–C7 methylbenzene, C11–C16 benzene and C17–C22 phenyl rings, respectively.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1—H1C⋯Cg2i | 0.96 | 2.97 | 3.6689 (17) | 131 |
| C5—H5⋯Cg3ii | 0.93 | 2.84 | 3.5126 (18) | 130 |
| C21—H21⋯Cg1iii | 0.93 | 2.99 | 3.632 (2) | 127 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 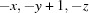 ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the Sophisticated Analytical Instrument Facility (SAIF), IITM, Chennai 600 036, Tamilnadu, India, for the single-crystal X-ray data.
supplementary crystallographic information
S1. Comment
Bioactivities of chalcones were reported by Dimmock et al., (1999). The antibacterial, fungistatic and fungicidal properties of these compounds have also been reviewed (Opletalova et al. 2000, 1999). In addition with appropriate substituents, chalcones are a class of non-linear optical materials (Fichou et al. 1988, Goto et al. 1991). Recently, it has been noted that among many organic second harmonic generation, chalcone derivatives have excellent blue light transmittance and good cyrstallizability (Sarojini et al. 2006). The related compounds whose structures have been solved by X-ray are (2E)-1-(4,4''-Difluoro-5'-methoxy-1,1':3',1''-terphenyl-4'-yl)- 3-(4-fluorophenyl)prop-2-en-1-one (Betz et al. 2011a) and (E)-1-(4,4''-Difluoro-5'-methoxy-1,1':3',1''-terphenyl-4' -yl)-3-(4-nitrophenyl)prop-2-en-1-one (Betz et al. 2011b).
In the title molecule (Fig. 1), C22H18O, the o-tolyl ring is connected through a conjugated double bond. The molecule adopts an E configuration and the C7—C8—C9—C10 torsion angle is 178.77 (13)°. Further, the torsion angle [C8—C9—C10—C11 = -164.91 (13)°] shows that the prop-2-en-1-one unit is not planar. The overall conformation of the compound may be described by the values of dihedral angles between the different planes. The terminal rings (C2—C7) and (C17—C22) are twisted by an angle of 54.75 (8)°, while the biphenyl part is not planar, the dihedral angle between the planes of the rings (C11—C16) and (C17—C22) being 40.65 (8)°. The dihedral angle between the benzene rings (C2—C7) and (C11—C16) is 14.10 (7)°.
There are three weak C1—H1C···π, C5—H5···π and C21—H21···π interactions involving the central benzene ring (C11—C16), the terminal phenyl ring (C17—C22) and the terminal benzene ring (C2—C7), respectively, are found in the crystal structure. The Car—Csp3, Car—Car and C═O bond lengths in (I) are within their normal ranges (Allen et al., 1987). No classic hydrogen bonds are observed.
S2. Experimental
Biphenyl acetone (1.06 g, 10 mmol) and 2-methylbenzaldehyde (1.06 g, 10 mmol) in ethanol (25 ml) is mixed in the presence of NaOH (10 ml 30%). The reaction mixture was stirred for 6 h. Then the contents of the flask were poured into ice cold water (250 ml) and left for 12 h. The solid obtained was filtered and recrystallized for three to four times with ethanol. The colourless single crystals of the title compound used for X-ray diffraction studies were grown by slow evaporation of acetone. Yield: 1.48 g (70%).
S3. Refinement
All H-atoms were positioned geometrically and allowed to ride on their parent atoms, with C—H = 0.93 Å (aromatic), 0.96 Å (methyl group), with Uiso(H) = 1.2 or 1.5Ueq(C); for aromatic and methyl group.
Figures
Fig. 1.

The molecular structure of the title compound, with displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 30% probability level. H atoms are shown as small spheres of arbitrary radius.
Fig. 2.

The partial packing of the title compound, showing the three weak C—H···π interactions.
Crystal data
| C22H18O | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 298.36 | F(000) = 316 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.224 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Melting point: 393 K |
| a = 7.6396 (3) Å | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| b = 9.9106 (4) Å | Cell parameters from 7102 reflections |
| c = 11.9263 (4) Å | θ = 2.8–26.3° |
| α = 103.166 (2)° | µ = 0.07 mm−1 |
| β = 104.713 (2)° | T = 273 K |
| γ = 103.308 (2)° | Block, colourless |
| V = 809.66 (6) Å3 | 0.40 × 0.35 × 0.30 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer | 4534 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 3291 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.024 |
| ω and φ scan | θmax = 29.6°, θmin = 2.2° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2004) | h = −10→10 |
| Tmin = 0.908, Tmax = 1.000 | k = −13→13 |
| 18636 measured reflections | l = −16→16 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.048 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.151 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.06 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.073P)2 + 0.1155P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 4534 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 209 parameters | Δρmax = 0.23 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.17 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. Bond distances, angles etc. have been calculated using the rounded fractional coordinates. All su's are estimated from the variances of the (full) variance-covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account in the estimation of distances, angles and torsion angles |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.37261 (17) | 0.60727 (11) | 0.09681 (9) | 0.0666 (4) | |
| C1 | 0.1424 (2) | 0.25545 (16) | −0.31150 (12) | 0.0598 (5) | |
| C2 | 0.02836 (17) | 0.14897 (13) | −0.26587 (10) | 0.0413 (3) | |
| C3 | −0.08815 (19) | 0.01392 (14) | −0.34508 (11) | 0.0489 (4) | |
| C4 | −0.1977 (2) | −0.08585 (15) | −0.30810 (13) | 0.0555 (4) | |
| C5 | −0.1963 (2) | −0.05199 (16) | −0.18929 (14) | 0.0594 (5) | |
| C6 | −0.0836 (2) | 0.08192 (15) | −0.10901 (12) | 0.0513 (4) | |
| C7 | 0.02996 (17) | 0.18386 (13) | −0.14437 (10) | 0.0396 (3) | |
| C8 | 0.14997 (19) | 0.32479 (13) | −0.05697 (10) | 0.0447 (3) | |
| C9 | 0.13129 (18) | 0.38670 (14) | 0.04796 (11) | 0.0477 (4) | |
| C10 | 0.26312 (18) | 0.52846 (14) | 0.13063 (10) | 0.0448 (4) | |
| C11 | 0.26370 (17) | 0.57385 (13) | 0.25891 (10) | 0.0404 (3) | |
| C12 | 0.1919 (2) | 0.47482 (14) | 0.31431 (11) | 0.0478 (4) | |
| C13 | 0.20814 (19) | 0.51956 (14) | 0.43612 (11) | 0.0476 (4) | |
| C14 | 0.29252 (17) | 0.66487 (13) | 0.50571 (10) | 0.0397 (3) | |
| C15 | 0.35955 (18) | 0.76420 (13) | 0.44861 (10) | 0.0429 (3) | |
| C16 | 0.34808 (18) | 0.71934 (13) | 0.32782 (10) | 0.0427 (3) | |
| C17 | 0.30998 (17) | 0.71263 (14) | 0.63651 (10) | 0.0422 (3) | |
| C18 | 0.35892 (19) | 0.62864 (15) | 0.71095 (11) | 0.0481 (4) | |
| C19 | 0.3769 (2) | 0.67267 (17) | 0.83319 (12) | 0.0560 (5) | |
| C20 | 0.3468 (2) | 0.80073 (19) | 0.88272 (12) | 0.0636 (5) | |
| C21 | 0.2975 (3) | 0.8849 (2) | 0.81035 (13) | 0.0695 (6) | |
| C22 | 0.2805 (2) | 0.84196 (17) | 0.68813 (12) | 0.0574 (5) | |
| H1A | 0.12155 | 0.21253 | −0.39637 | 0.0897* | |
| H1B | 0.27494 | 0.28020 | −0.26678 | 0.0897* | |
| H1C | 0.10373 | 0.34179 | −0.30056 | 0.0897* | |
| H3 | −0.09204 | −0.00968 | −0.42594 | 0.0587* | |
| H4 | −0.27269 | −0.17613 | −0.36309 | 0.0666* | |
| H5 | −0.27074 | −0.11885 | −0.16353 | 0.0712* | |
| H6 | −0.08350 | 0.10469 | −0.02891 | 0.0615* | |
| H8 | 0.24937 | 0.37590 | −0.07733 | 0.0536* | |
| H9 | 0.03187 | 0.33939 | 0.07040 | 0.0573* | |
| H12 | 0.13232 | 0.37751 | 0.26899 | 0.0574* | |
| H13 | 0.16190 | 0.45138 | 0.47211 | 0.0572* | |
| H15 | 0.41293 | 0.86238 | 0.49267 | 0.0514* | |
| H16 | 0.39719 | 0.78701 | 0.29226 | 0.0512* | |
| H18 | 0.37988 | 0.54158 | 0.67813 | 0.0576* | |
| H19 | 0.40953 | 0.61518 | 0.88177 | 0.0672* | |
| H20 | 0.35956 | 0.83064 | 0.96495 | 0.0763* | |
| H21 | 0.27551 | 0.97129 | 0.84371 | 0.0834* | |
| H22 | 0.24891 | 0.90049 | 0.64033 | 0.0688* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0822 (8) | 0.0610 (6) | 0.0424 (5) | −0.0025 (5) | 0.0263 (5) | 0.0071 (4) |
| C1 | 0.0701 (10) | 0.0586 (8) | 0.0426 (7) | 0.0047 (7) | 0.0249 (6) | 0.0080 (6) |
| C2 | 0.0422 (6) | 0.0426 (6) | 0.0362 (5) | 0.0136 (5) | 0.0117 (4) | 0.0071 (4) |
| C3 | 0.0517 (8) | 0.0478 (7) | 0.0379 (6) | 0.0152 (6) | 0.0086 (5) | 0.0020 (5) |
| C4 | 0.0492 (8) | 0.0431 (7) | 0.0561 (8) | 0.0065 (6) | 0.0045 (6) | 0.0030 (6) |
| C5 | 0.0536 (8) | 0.0522 (8) | 0.0661 (9) | 0.0044 (6) | 0.0186 (7) | 0.0191 (7) |
| C6 | 0.0555 (8) | 0.0524 (8) | 0.0445 (6) | 0.0119 (6) | 0.0196 (6) | 0.0130 (5) |
| C7 | 0.0407 (6) | 0.0410 (6) | 0.0352 (5) | 0.0135 (5) | 0.0112 (4) | 0.0082 (4) |
| C8 | 0.0502 (7) | 0.0439 (6) | 0.0354 (5) | 0.0097 (5) | 0.0137 (5) | 0.0084 (5) |
| C9 | 0.0459 (7) | 0.0517 (7) | 0.0371 (6) | 0.0085 (6) | 0.0139 (5) | 0.0038 (5) |
| C10 | 0.0481 (7) | 0.0484 (7) | 0.0341 (5) | 0.0138 (5) | 0.0123 (5) | 0.0075 (5) |
| C11 | 0.0410 (6) | 0.0434 (6) | 0.0329 (5) | 0.0127 (5) | 0.0100 (4) | 0.0066 (4) |
| C12 | 0.0564 (8) | 0.0383 (6) | 0.0404 (6) | 0.0067 (5) | 0.0159 (5) | 0.0040 (5) |
| C13 | 0.0565 (8) | 0.0421 (7) | 0.0408 (6) | 0.0070 (6) | 0.0183 (5) | 0.0114 (5) |
| C14 | 0.0398 (6) | 0.0430 (6) | 0.0340 (5) | 0.0128 (5) | 0.0108 (4) | 0.0083 (4) |
| C15 | 0.0497 (7) | 0.0358 (6) | 0.0359 (5) | 0.0099 (5) | 0.0094 (5) | 0.0057 (4) |
| C16 | 0.0482 (7) | 0.0406 (6) | 0.0362 (5) | 0.0100 (5) | 0.0116 (5) | 0.0120 (4) |
| C17 | 0.0395 (6) | 0.0481 (7) | 0.0347 (5) | 0.0104 (5) | 0.0121 (4) | 0.0077 (5) |
| C18 | 0.0505 (7) | 0.0489 (7) | 0.0420 (6) | 0.0085 (6) | 0.0166 (5) | 0.0136 (5) |
| C19 | 0.0536 (8) | 0.0686 (9) | 0.0429 (7) | 0.0081 (7) | 0.0165 (6) | 0.0212 (6) |
| C20 | 0.0582 (9) | 0.0913 (12) | 0.0376 (6) | 0.0204 (8) | 0.0194 (6) | 0.0108 (7) |
| C21 | 0.0794 (11) | 0.0832 (11) | 0.0489 (8) | 0.0428 (9) | 0.0238 (7) | 0.0041 (7) |
| C22 | 0.0673 (9) | 0.0667 (9) | 0.0428 (7) | 0.0353 (8) | 0.0169 (6) | 0.0116 (6) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1—C10 | 1.2192 (18) | C19—C20 | 1.369 (2) |
| C1—C2 | 1.499 (2) | C20—C21 | 1.375 (3) |
| C2—C3 | 1.3873 (18) | C21—C22 | 1.385 (2) |
| C2—C7 | 1.4072 (16) | C1—H1A | 0.9600 |
| C3—C4 | 1.370 (2) | C1—H1B | 0.9600 |
| C4—C5 | 1.376 (2) | C1—H1C | 0.9600 |
| C5—C6 | 1.377 (2) | C3—H3 | 0.9300 |
| C6—C7 | 1.388 (2) | C4—H4 | 0.9300 |
| C7—C8 | 1.4628 (17) | C5—H5 | 0.9300 |
| C8—C9 | 1.3207 (17) | C6—H6 | 0.9300 |
| C9—C10 | 1.4743 (19) | C8—H8 | 0.9300 |
| C10—C11 | 1.4917 (16) | C9—H9 | 0.9300 |
| C11—C12 | 1.3901 (19) | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| C11—C16 | 1.3904 (18) | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| C12—C13 | 1.3828 (17) | C15—H15 | 0.9300 |
| C13—C14 | 1.3909 (18) | C16—H16 | 0.9300 |
| C14—C15 | 1.3948 (18) | C18—H18 | 0.9300 |
| C14—C17 | 1.4847 (16) | C19—H19 | 0.9300 |
| C15—C16 | 1.3809 (16) | C20—H20 | 0.9300 |
| C17—C18 | 1.3900 (19) | C21—H21 | 0.9300 |
| C17—C22 | 1.384 (2) | C22—H22 | 0.9300 |
| C18—C19 | 1.3840 (18) | ||
| C1—C2—C3 | 120.06 (11) | C2—C1—H1C | 109.00 |
| C1—C2—C7 | 121.73 (11) | H1A—C1—H1B | 109.00 |
| C3—C2—C7 | 118.16 (12) | H1A—C1—H1C | 109.00 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 122.16 (12) | H1B—C1—H1C | 109.00 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 119.78 (14) | C2—C3—H3 | 119.00 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 119.30 (15) | C4—C3—H3 | 119.00 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 121.79 (13) | C3—C4—H4 | 120.00 |
| C2—C7—C6 | 118.80 (12) | C5—C4—H4 | 120.00 |
| C2—C7—C8 | 120.48 (12) | C4—C5—H5 | 120.00 |
| C6—C7—C8 | 120.72 (11) | C6—C5—H5 | 120.00 |
| C7—C8—C9 | 126.52 (13) | C5—C6—H6 | 119.00 |
| C8—C9—C10 | 122.06 (13) | C7—C6—H6 | 119.00 |
| O1—C10—C9 | 121.45 (11) | C7—C8—H8 | 117.00 |
| O1—C10—C11 | 119.84 (12) | C9—C8—H8 | 117.00 |
| C9—C10—C11 | 118.70 (12) | C8—C9—H9 | 119.00 |
| C10—C11—C12 | 122.41 (11) | C10—C9—H9 | 119.00 |
| C10—C11—C16 | 118.91 (11) | C11—C12—H12 | 120.00 |
| C12—C11—C16 | 118.59 (11) | C13—C12—H12 | 120.00 |
| C11—C12—C13 | 120.66 (12) | C12—C13—H13 | 119.00 |
| C12—C13—C14 | 121.08 (13) | C14—C13—H13 | 119.00 |
| C13—C14—C15 | 117.89 (11) | C14—C15—H15 | 119.00 |
| C13—C14—C17 | 120.99 (12) | C16—C15—H15 | 119.00 |
| C15—C14—C17 | 121.12 (11) | C11—C16—H16 | 120.00 |
| C14—C15—C16 | 121.17 (12) | C15—C16—H16 | 120.00 |
| C11—C16—C15 | 120.55 (12) | C17—C18—H18 | 120.00 |
| C14—C17—C18 | 120.50 (12) | C19—C18—H18 | 120.00 |
| C14—C17—C22 | 121.33 (12) | C18—C19—H19 | 120.00 |
| C18—C17—C22 | 118.16 (11) | C20—C19—H19 | 120.00 |
| C17—C18—C19 | 120.97 (14) | C19—C20—H20 | 120.00 |
| C18—C19—C20 | 120.12 (14) | C21—C20—H20 | 120.00 |
| C19—C20—C21 | 119.72 (13) | C20—C21—H21 | 120.00 |
| C20—C21—C22 | 120.46 (17) | C22—C21—H21 | 120.00 |
| C17—C22—C21 | 120.57 (15) | C17—C22—H22 | 120.00 |
| C2—C1—H1A | 109.00 | C21—C22—H22 | 120.00 |
| C2—C1—H1B | 109.00 | ||
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −178.74 (14) | C16—C11—C12—C13 | −1.5 (2) |
| C7—C2—C3—C4 | −1.1 (2) | C10—C11—C16—C15 | −176.84 (13) |
| C1—C2—C7—C6 | 177.97 (13) | C12—C11—C16—C15 | −0.2 (2) |
| C1—C2—C7—C8 | −2.3 (2) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | 1.5 (2) |
| C3—C2—C7—C6 | 0.4 (2) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | 0.3 (2) |
| C3—C2—C7—C8 | −179.93 (14) | C12—C13—C14—C17 | −179.94 (14) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 1.1 (2) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | −2.0 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −0.3 (2) | C17—C14—C15—C16 | 178.22 (13) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | −0.4 (2) | C13—C14—C17—C18 | 40.6 (2) |
| C5—C6—C7—C2 | 0.4 (2) | C13—C14—C17—C22 | −140.18 (15) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | −179.34 (14) | C15—C14—C17—C18 | −139.63 (15) |
| C2—C7—C8—C9 | 161.41 (14) | C15—C14—C17—C22 | 39.6 (2) |
| C6—C7—C8—C9 | −18.9 (2) | C14—C15—C16—C11 | 2.0 (2) |
| C7—C8—C9—C10 | 178.77 (13) | C14—C17—C18—C19 | 179.54 (14) |
| C8—C9—C10—O1 | 13.9 (2) | C22—C17—C18—C19 | 0.3 (2) |
| C8—C9—C10—C11 | −164.91 (13) | C14—C17—C22—C21 | −179.96 (16) |
| O1—C10—C11—C12 | −158.73 (15) | C18—C17—C22—C21 | −0.7 (2) |
| O1—C10—C11—C16 | 17.8 (2) | C17—C18—C19—C20 | −0.1 (2) |
| C9—C10—C11—C12 | 20.1 (2) | C18—C19—C20—C21 | 0.4 (3) |
| C9—C10—C11—C16 | −163.39 (13) | C19—C20—C21—C22 | −0.8 (3) |
| C10—C11—C12—C13 | 175.01 (14) | C20—C21—C22—C17 | 1.0 (3) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
Cg1, Cg2 and Cg3 are the centroids of the C2–C7 methylbenzene, C11–C16 benzene and C17–C22 phenyl rings, respectively.
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C1—H1C···Cg2i | 0.96 | 2.97 | 3.6689 (17) | 131 |
| C5—H5···Cg3ii | 0.93 | 2.84 | 3.5126 (18) | 130 |
| C21—H21···Cg1iii | 0.93 | 2.99 | 3.632 (2) | 127 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, −y+1, −z; (ii) x−1, y−1, z−1; (iii) x, y+1, z+1.
Footnotes
Supporting information for this paper is available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: JJ2188).
References
- Allen, F. H., Kennard, O., Watson, D. G., Brammer, L., Orpen, A. G. & Taylor, R. (1987). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. S1–19.
- Betz, R., Gerber, T., Hosten, E., Samshuddin, S., Narayana, B. & Sarojini, B. K. (2011a). Acta Cryst. E67, o2996–o2997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Betz, R., Gerber, T., Hosten, E., Samshuddin, S., Narayana, B. & Yathirajan, H. S. (2011b). Acta Cryst. E67, o3179–o3180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Bruker (2004). APEX2, SAINT, XPREP and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Dimmock, J. R., Elias, D. W., Beazely, M. A. & Kandepu, N. M. (1999). Curr. Med. Chem. 6, 1125–1150. [PubMed]
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
- Fichou, D., Watanabe, T., Takeda, T., Miyata, S., Goto, Y. & Nakayama, M. (1988). Jpn J. Appl. Phys. 27, L429–L430.
- Goto, Y., Hayashi, A., Kimura, Y. & Nakayam, M. (1991). J. Cryst. Growth, 108, 688–698.
- Opletalova, V. (2000). Ceska Slov. Farm. 49, 278–284. [PubMed]
- Opletalova, V. & Sedivy, D. (1999). Ceska Slov. Farm. 48, 252–255. [PubMed]
- Sarojini, B. K., Narayana, B., Ashalatha, B. V., Indira, J. & Lobo, K. G. (2006). J. Cryst. Growth, 295, 54–59.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814014317/jj2188sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814014317/jj2188Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814014317/jj2188Isup3.cdx
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814014317/jj2188Isup4.cml
CCDC reference: 977614
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report


