Abstract
In the title hydrated compound, C15H15N3O3·H2O, the nicotinohydrazide molecule adopts a trans conformation with respect to the C=N double bond. The dihedral angle between the benzene and pyridine rings is 5.10 (14)°. In the crystal, the solvent water molecule acts as an acceptor, forming an N—H⋯O hydrogen bond supported by two C—H⋯O contacts. It also acts as a donor, forming bifurcated O—H⋯(O,O) and O—H⋯N hydrogen bonds that combine with the former contacts to form zigzag chains of molecules along the c-axis direction. An additional O—H⋯O donor contact completes a set of six hydrogen bonds to and from the water molecule and connects it to a third nicotinohydrazide molecule. This latter contact combines with weaker C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds supported by a C—H⋯π contact to stack molecules along b in a three-dimensional network.
Related literature
For the biological activity of hydrazone compounds, see: Singh & Raghav (2011 ▶); Patil et al. (2011 ▶). For background to the use of nicotinohydrazides as catalysts and of their transition metal complexes in the treatment of tuberculosis, see: Torje et al. (2012 ▶). For closely related structures, see: Novina et al. (2013 ▶); Wang et al. (2010 ▶).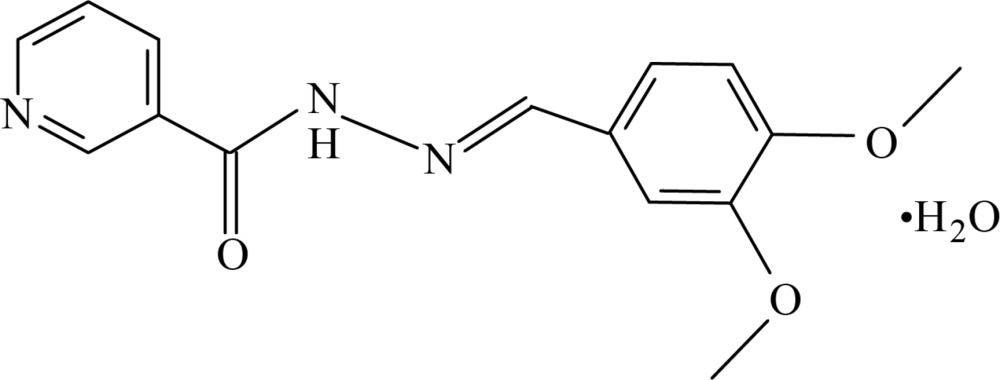
Experimental
Crystal data
C15H15N3O3·H2O
M r = 303.32
Monoclinic,

a = 4.9128 (6) Å
b = 25.137 (4) Å
c = 12.2950 (16) Å
β = 96.513 (4)°
V = 1508.6 (4) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.10 mm−1
T = 296 K
0.50 × 0.35 × 0.30 mm
Data collection
Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2004 ▶) T min = 0.952, T max = 0.971
11633 measured reflections
3704 independent reflections
2250 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.036
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.048
wR(F 2) = 0.141
S = 1.02
3704 reflections
209 parameters
3 restraints
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.21 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.23 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2004 ▶); cell refinement: APEX2 and SAINT (Bruker, 2004 ▶); data reduction: SAINT and XPREP (Bruker, 2004 ▶); program(s) used to solve structure: SIR92 (Altomare et al., 1993 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 2012 ▶) and Mercury (Macrae et al., 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814013798/sj5412sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814013798/sj5412Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814013798/sj5412Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1008073
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
Cg2 is the centroid of the C2–C7 benzene ring.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2—H2N2⋯O1W i | 0.86 | 2.06 | 2.8942 (19) | 165 |
| O1W—H2O1⋯O3 | 0.85 (2) | 2.15 (2) | 2.955 (2) | 157 (3) |
| O1W—H2O1⋯N1 | 0.85 (2) | 2.49 (2) | 3.1087 (19) | 130 (2) |
| C11—H11⋯O1W i | 0.93 | 2.30 | 3.199 (3) | 162 |
| C8—H8⋯O1W i | 0.93 | 2.67 | 3.425 (2) | 139 |
| O1W—H1O1⋯O3ii | 0.86 (2) | 2.09 (2) | 2.901 (2) | 159 (3) |
| C1—H1C⋯Cg2ii | 0.96 | 2.88 | 3.729 (3) | 148 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Sophisticated Analytical Instrument Facility, STIC, Cochin University of Science & Technology, Cochin, for the data collection.
supplementary crystallographic information
S1. Comment
Hydrazones constitute an important class of biologically active drug molecules that have attracted the attention of medicinal chemists due to their wide range of pharmacological properties (Singh & Raghav, 2011). Hydrazone derivatives containing an azomethine (–CONHN═CH–) group have been shown to exhibit antiproliferative activities and act as cytotoxic agents with the ability to prevent cell progression in cancerous cells through different mechanisms (Patil et al., 2011). Moreover, hydrazone derivatives may act as multidentate ligands and their transition metal complexes have been used in the treatment of tuberculosis, in colorimetric or fluorimetric analytic determinations, as well as in applications involving catalytic processes (Torje et al., 2012). As part of our studies of substituent effects on the structure and other aspects of hydrazone derivatives, such as (E)—N'-(4-Methoxybenzylidene)pyridine-3-carbohydrazide dihydrate (Novina et al., 2013), in the present work we report the synthesis and crystal structure of the title compound.
The molecule of the title hydrazide derivative (Fig. 1), C15H15N3O3·H2O, exists in a trans conformation with respect to the C8═N1 double bond [1.277 (2) Å] with the torsion angle N2—N1—-C8—C5 = -177.58 (14)°. It also adopts the amido form with the C9═O3 bond length of 1.2322 (19) Å which is very close to the reported C═O bond length of a similar structure (Wang et al., 2010). The benzene and pyridine rings (C2—C7 and N3/C10—C14, respectively) are each planar with a dihedral angle of 5.10 (14)° between their mean-planes. This is comparable to the corresponding angle found in a related structure (Novina et al., 2013). One of the methoxy group is almost coplanar with the C2—C7 benzene ring whereas the other one deviates somewhat from the benzene ring plane [torsion angles: C1—O1—C2—C7 = -3.9 (3), C15—O2—C3—C4 = 16.5 (3)°].
The water molecule forms six H–bonds with three different nicotinohydrazone molecules. N—H···O, O—H···O, O—H···N and C—H···O hydrogen bonds are present in the crystal system (Table 1). One of the H atoms of the water molecule forms bifurcated hydrogen bonds to the azomethine nitrogen and the carbonyl oxygen atoms of one neighboring molecule (Fig. 2). The water molecule acts as a hydrogen bond acceptor towards another nicotinohydrazone molecule through N–H···O and C—H···O hydrogen bonds. Through these interactions the molecules are interconnected through the water molecule to form infinite chains parallel to the b axis of the unit cell (Fig. 2). Furthermore, a C1—H1C···π interaction involving the phenyl (C2—C7) ring together with O–H···O and C–H···O contacts to generate a three dimensional network of molecules stacked along the a axis direction (Fig. 3).
S2. Experimental
3,4-dimethoxybenzaldehyde (4.1 ml, 0.025 mol) was added to an ethanolic solution of nicotinicacid hydrazide (3.4 g, 0.025 mol). After the addition was complete the reaction mixture was stirred well in an ice cold condition for 3 hrs. The colourless solid that formed was filtered and washed several times with petroleum ether (40–60%). The crude solid obtained was dried and recrystallized from absolute alcohol. The recrystallized product was dried over vacuum.
S3. Refinement
The H atoms of the solvent water were located in a difference map and refined freely with isotropic displacement parameters with their bond distances restrained to 0.86 (2) Å. Other H atoms were placed in geometrically idealized positions and constrained to ride on their parent atoms with C—H = 0.93 Å, CH3 = 0.96 Å, N—H = 0.86 Å and with Uiso(H) = 1.5Ueq(CH3) and 1.2Ueq(CH, NH).
Figures
Fig. 1.

The molecular structure of the title compound, with the atom labelling. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
Fig. 2.
Crystal packing of the title compound viewed along the b axis. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines.
Fig. 3.

The crystal packing of the title compound viewed along the a axis. Hydrogen bonds are drawn as dashed lines and a representative C–H···π contact is shown as a dotted line.
Crystal data
| C15H15N3O3·H2O | F(000) = 640 |
| Mr = 303.32 | Dx = 1.335 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2yn | Cell parameters from 2357 reflections |
| a = 4.9128 (6) Å | θ = 4.7–51.8° |
| b = 25.137 (4) Å | µ = 0.10 mm−1 |
| c = 12.2950 (16) Å | T = 296 K |
| β = 96.513 (4)° | Block, colorless |
| V = 1508.6 (4) Å3 | 0.50 × 0.35 × 0.30 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer | 3704 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2250 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.036 |
| ω and φ scan | θmax = 28.3°, θmin = 3.0° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2004) | h = −6→6 |
| Tmin = 0.952, Tmax = 0.971 | k = −33→33 |
| 11633 measured reflections | l = −16→16 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.048 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.141 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.02 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0655P)2 + 0.1374P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3704 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 209 parameters | Δρmax = 0.21 e Å−3 |
| 3 restraints | Δρmin = −0.23 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 1.8728 (4) | 0.00081 (9) | 0.12935 (17) | 0.0591 (6) | |
| H1A | 1.7449 | −0.0075 | 0.0667 | 0.089* | |
| H1B | 1.9736 | −0.0306 | 0.1531 | 0.089* | |
| H1C | 1.9975 | 0.0277 | 0.1101 | 0.089* | |
| C2 | 1.5690 (3) | 0.06393 (7) | 0.19504 (13) | 0.0345 (4) | |
| C3 | 1.4107 (3) | 0.07841 (7) | 0.27937 (13) | 0.0349 (4) | |
| C4 | 1.2439 (3) | 0.12194 (7) | 0.26645 (13) | 0.0360 (4) | |
| H4 | 1.1402 | 0.1315 | 0.3221 | 0.043* | |
| C5 | 1.2269 (3) | 0.15227 (7) | 0.17060 (13) | 0.0343 (4) | |
| C8 | 1.0486 (3) | 0.19839 (7) | 0.15615 (13) | 0.0376 (4) | |
| H8 | 1.0267 | 0.2158 | 0.0889 | 0.045* | |
| C9 | 0.6145 (3) | 0.27874 (7) | 0.28846 (13) | 0.0356 (4) | |
| C10 | 0.4296 (3) | 0.32458 (7) | 0.25774 (13) | 0.0358 (4) | |
| C14 | 0.2785 (4) | 0.34525 (9) | 0.33488 (15) | 0.0512 (5) | |
| H14 | 0.2956 | 0.3293 | 0.4035 | 0.061* | |
| C13 | 0.0882 (4) | 0.40894 (9) | 0.22029 (18) | 0.0574 (6) | |
| H13 | −0.0306 | 0.4376 | 0.2065 | 0.069* | |
| C12 | 0.2313 (5) | 0.39213 (11) | 0.13952 (19) | 0.0764 (8) | |
| H12 | 0.2132 | 0.4093 | 0.0721 | 0.092* | |
| C11 | 0.4038 (5) | 0.34939 (10) | 0.15793 (17) | 0.0704 (7) | |
| H11 | 0.5030 | 0.3373 | 0.1028 | 0.084* | |
| C6 | 1.3787 (3) | 0.13702 (7) | 0.08749 (13) | 0.0396 (4) | |
| H6 | 1.3658 | 0.1564 | 0.0227 | 0.047* | |
| C7 | 1.5492 (3) | 0.09318 (7) | 0.10011 (13) | 0.0388 (4) | |
| H7 | 1.6511 | 0.0834 | 0.0440 | 0.047* | |
| C15 | 1.2265 (4) | 0.05011 (9) | 0.43970 (15) | 0.0578 (6) | |
| H15A | 1.2328 | 0.0847 | 0.4730 | 0.087* | |
| H15C | 1.2545 | 0.0234 | 0.4956 | 0.087* | |
| H15B | 1.0510 | 0.0449 | 0.3982 | 0.087* | |
| N1 | 0.9212 (3) | 0.21555 (6) | 0.23409 (11) | 0.0364 (3) | |
| N2 | 0.7497 (3) | 0.25839 (6) | 0.20898 (10) | 0.0370 (3) | |
| H2N2 | 0.7300 | 0.2717 | 0.1441 | 0.044* | |
| N3 | 0.1091 (4) | 0.38654 (8) | 0.31852 (15) | 0.0637 (5) | |
| O1 | 1.7281 (2) | 0.01981 (5) | 0.21562 (10) | 0.0467 (3) | |
| O1W | 1.1763 (3) | 0.21759 (7) | 0.47728 (11) | 0.0606 (4) | |
| O2 | 1.4351 (3) | 0.04615 (5) | 0.36928 (10) | 0.0496 (4) | |
| O3 | 0.6430 (3) | 0.26124 (6) | 0.38267 (9) | 0.0505 (4) | |
| H1O1 | 1.310 (4) | 0.2231 (12) | 0.440 (2) | 0.101 (10)* | |
| H2O1 | 1.028 (4) | 0.2235 (11) | 0.4360 (19) | 0.102 (10)* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0537 (11) | 0.0579 (14) | 0.0675 (14) | 0.0190 (10) | 0.0148 (10) | −0.0139 (11) |
| C2 | 0.0304 (8) | 0.0321 (9) | 0.0414 (9) | −0.0008 (7) | 0.0062 (6) | −0.0027 (7) |
| C3 | 0.0366 (8) | 0.0365 (10) | 0.0318 (8) | −0.0006 (7) | 0.0052 (6) | 0.0023 (7) |
| C4 | 0.0401 (9) | 0.0401 (10) | 0.0291 (8) | 0.0058 (8) | 0.0094 (6) | −0.0026 (7) |
| C5 | 0.0368 (8) | 0.0356 (10) | 0.0307 (8) | 0.0022 (7) | 0.0038 (6) | −0.0009 (7) |
| C8 | 0.0437 (9) | 0.0406 (10) | 0.0287 (8) | 0.0060 (8) | 0.0049 (7) | 0.0027 (7) |
| C9 | 0.0381 (9) | 0.0392 (10) | 0.0297 (8) | 0.0015 (7) | 0.0052 (6) | 0.0002 (7) |
| C10 | 0.0360 (8) | 0.0383 (10) | 0.0335 (8) | 0.0035 (7) | 0.0060 (6) | −0.0004 (7) |
| C14 | 0.0625 (12) | 0.0551 (13) | 0.0375 (10) | 0.0177 (10) | 0.0117 (8) | 0.0020 (9) |
| C13 | 0.0603 (12) | 0.0493 (13) | 0.0627 (13) | 0.0206 (10) | 0.0075 (10) | 0.0025 (10) |
| C12 | 0.0972 (17) | 0.0813 (18) | 0.0549 (13) | 0.0482 (15) | 0.0267 (12) | 0.0252 (12) |
| C11 | 0.0879 (16) | 0.0809 (18) | 0.0476 (12) | 0.0467 (14) | 0.0305 (11) | 0.0188 (11) |
| C6 | 0.0448 (9) | 0.0441 (11) | 0.0310 (8) | 0.0003 (8) | 0.0094 (7) | 0.0046 (8) |
| C7 | 0.0391 (9) | 0.0432 (11) | 0.0368 (9) | 0.0017 (8) | 0.0152 (7) | −0.0038 (8) |
| C15 | 0.0555 (12) | 0.0773 (16) | 0.0427 (10) | 0.0078 (11) | 0.0142 (9) | 0.0198 (10) |
| N1 | 0.0409 (8) | 0.0367 (9) | 0.0313 (7) | 0.0080 (6) | 0.0023 (6) | 0.0011 (6) |
| N2 | 0.0447 (8) | 0.0388 (9) | 0.0274 (7) | 0.0107 (7) | 0.0038 (6) | 0.0049 (6) |
| N3 | 0.0736 (12) | 0.0635 (13) | 0.0565 (11) | 0.0278 (10) | 0.0180 (9) | −0.0034 (9) |
| O1 | 0.0467 (7) | 0.0415 (8) | 0.0543 (8) | 0.0114 (6) | 0.0159 (6) | 0.0009 (6) |
| O1W | 0.0661 (10) | 0.0840 (12) | 0.0303 (7) | −0.0146 (9) | −0.0007 (7) | 0.0055 (7) |
| O2 | 0.0559 (8) | 0.0533 (9) | 0.0418 (7) | 0.0151 (7) | 0.0153 (6) | 0.0152 (6) |
| O3 | 0.0611 (8) | 0.0611 (9) | 0.0305 (6) | 0.0175 (7) | 0.0106 (5) | 0.0088 (6) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| C1—O1 | 1.424 (2) | C14—N3 | 1.331 (2) |
| C1—H1A | 0.9600 | C14—H14 | 0.9300 |
| C1—H1B | 0.9600 | C13—N3 | 1.326 (3) |
| C1—H1C | 0.9600 | C13—C12 | 1.348 (3) |
| C2—O1 | 1.364 (2) | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| C2—C7 | 1.373 (2) | C12—C11 | 1.371 (3) |
| C2—C3 | 1.412 (2) | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| C3—O2 | 1.3652 (19) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| C3—C4 | 1.366 (2) | C6—C7 | 1.382 (2) |
| C4—C5 | 1.398 (2) | C6—H6 | 0.9300 |
| C4—H4 | 0.9300 | C7—H7 | 0.9300 |
| C5—C6 | 1.386 (2) | C15—O2 | 1.418 (2) |
| C5—C8 | 1.452 (2) | C15—H15A | 0.9600 |
| C8—N1 | 1.277 (2) | C15—H15C | 0.9600 |
| C8—H8 | 0.9300 | C15—H15B | 0.9600 |
| C9—O3 | 1.2322 (19) | N1—N2 | 1.3806 (19) |
| C9—N2 | 1.344 (2) | N2—H2N2 | 0.8600 |
| C9—C10 | 1.489 (2) | O1W—H1O1 | 0.856 (17) |
| C10—C11 | 1.370 (3) | O1W—H2O1 | 0.854 (17) |
| C10—C14 | 1.371 (2) | ||
| O1—C1—H1A | 109.5 | N3—C13—C12 | 123.02 (19) |
| O1—C1—H1B | 109.5 | N3—C13—H13 | 118.5 |
| H1A—C1—H1B | 109.5 | C12—C13—H13 | 118.5 |
| O1—C1—H1C | 109.5 | C13—C12—C11 | 119.2 (2) |
| H1A—C1—H1C | 109.5 | C13—C12—H12 | 120.4 |
| H1B—C1—H1C | 109.5 | C11—C12—H12 | 120.4 |
| O1—C2—C7 | 125.21 (15) | C10—C11—C12 | 119.83 (18) |
| O1—C2—C3 | 115.16 (15) | C10—C11—H11 | 120.1 |
| C7—C2—C3 | 119.62 (15) | C12—C11—H11 | 120.1 |
| O2—C3—C4 | 124.52 (14) | C7—C6—C5 | 120.51 (16) |
| O2—C3—C2 | 115.86 (15) | C7—C6—H6 | 119.7 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 119.61 (15) | C5—C6—H6 | 119.7 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 120.85 (15) | C2—C7—C6 | 120.38 (15) |
| C3—C4—H4 | 119.6 | C2—C7—H7 | 119.8 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 119.6 | C6—C7—H7 | 119.8 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 119.01 (16) | O2—C15—H15A | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—C8 | 119.90 (15) | O2—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—C8 | 121.07 (14) | H15A—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| N1—C8—C5 | 121.19 (15) | O2—C15—H15B | 109.5 |
| N1—C8—H8 | 119.4 | H15A—C15—H15B | 109.5 |
| C5—C8—H8 | 119.4 | H15C—C15—H15B | 109.5 |
| O3—C9—N2 | 122.34 (16) | C8—N1—N2 | 115.72 (14) |
| O3—C9—C10 | 121.05 (15) | C9—N2—N1 | 118.29 (13) |
| N2—C9—C10 | 116.61 (14) | C9—N2—H2N2 | 120.9 |
| C11—C10—C14 | 116.41 (17) | N1—N2—H2N2 | 120.9 |
| C11—C10—C9 | 124.86 (16) | C13—N3—C14 | 116.83 (17) |
| C14—C10—C9 | 118.70 (15) | C2—O1—C1 | 117.29 (15) |
| N3—C14—C10 | 124.68 (18) | H1O1—O1W—H2O1 | 108 (2) |
| N3—C14—H14 | 117.7 | C3—O2—C15 | 116.70 (13) |
| C10—C14—H14 | 117.7 | ||
| O1—C2—C3—O2 | −0.8 (2) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | −178.5 (2) |
| C7—C2—C3—O2 | 177.74 (15) | C13—C12—C11—C10 | −0.3 (4) |
| O1—C2—C3—C4 | −179.80 (15) | C4—C5—C6—C7 | −1.4 (3) |
| C7—C2—C3—C4 | −1.3 (2) | C8—C5—C6—C7 | −179.96 (16) |
| O2—C3—C4—C5 | −178.69 (15) | O1—C2—C7—C6 | 179.32 (15) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.2 (3) | C3—C2—C7—C6 | 1.0 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 1.1 (3) | C5—C6—C7—C2 | 0.4 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—C8 | 179.61 (15) | C5—C8—N1—N2 | −177.58 (14) |
| C6—C5—C8—N1 | −175.03 (16) | O3—C9—N2—N1 | 1.6 (3) |
| C4—C5—C8—N1 | 6.5 (3) | C10—C9—N2—N1 | −179.42 (14) |
| O3—C9—C10—C11 | 174.1 (2) | C8—N1—N2—C9 | −178.76 (15) |
| N2—C9—C10—C11 | −4.9 (3) | C12—C13—N3—C14 | −0.8 (4) |
| O3—C9—C10—C14 | −3.7 (3) | C10—C14—N3—C13 | −0.3 (3) |
| N2—C9—C10—C14 | 177.30 (17) | C7—C2—O1—C1 | −3.9 (3) |
| C11—C10—C14—N3 | 1.0 (3) | C3—C2—O1—C1 | 174.54 (15) |
| C9—C10—C14—N3 | 178.98 (18) | C4—C3—O2—C15 | 16.5 (3) |
| N3—C13—C12—C11 | 1.1 (4) | C2—C3—O2—C15 | −162.44 (16) |
| C14—C10—C11—C12 | −0.7 (4) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
Cg2 is the centroid of the C2–C7 benzene ring.
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N2—H2N2···O1Wi | 0.86 | 2.06 | 2.8942 (19) | 165 |
| O1W—H2O1···O3 | 0.85 (2) | 2.15 (2) | 2.955 (2) | 157 (3) |
| O1W—H2O1···N1 | 0.85 (2) | 2.49 (2) | 3.1087 (19) | 130 (2) |
| C11—H11···O1Wi | 0.93 | 2.30 | 3.199 (3) | 162 |
| C8—H8···O1Wi | 0.93 | 2.67 | 3.425 (2) | 139 |
| O1W—H1O1···O3ii | 0.86 (2) | 2.09 (2) | 2.901 (2) | 159 (3) |
| C1—H1C···Cg2ii | 0.96 | 2.88 | 3.729 (3) | 148 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x−1/2, −y+1/2, z−1/2; (ii) x+1, y, z.
Footnotes
Supporting information for this paper is available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: SJ5412).
References
- Altomare, A., Cascarano, G., Giacovazzo, C. & Guagliardi, A. (1993). J. Appl. Cryst. 26, 343–350.
- Bruker (2004). APEX2, SAINT and XPREP Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
- Macrae, C. F., Bruno, I. J., Chisholm, J. A., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Rodriguez-Monge, L., Taylor, R., van de Streek, J. & Wood, P. A. (2008). J. Appl. Cryst. 41, 466–470.
- Novina, J. J., Vasuki, G., Suresh, M. & Padusha, M. S. A. (2013). Acta Cryst. E69, o1177–o1178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Patil, B. R., Machakanur, S. S., Hunoor, R. S., Badiger, D. S., Gudasi, K. B. & Bligh, S. W. A. (2011). Pharma Chem. 3, 377–388.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Singh, M. & Raghav, N. (2011). Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 3, 26–32.
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Torje, I. A., Vălean, A.-M. & Cristea, C. (2012). Rev. Roum. Chim. 57, 337–344.
- Wang, P., Li, C. & Su, Y.-Q. (2010). Acta Cryst. E66, o542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814013798/sj5412sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814013798/sj5412Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814013798/sj5412Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1008073
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report



