Abstract
In the title compound, C11H10BrNO3, two independent molecules (A and B) crystallize in the asymmetric unit. The dihedral angles between the mean planes of the 4-bromophenyl ring and amide group are 24.8 (7) in molecule A and 77.1 (6)° in molecule B. The mean plane of the methylidene group is further inclined by 75.6 (4) in molecule A and 72.5 (6)° in molecule B from that of the amide group. In the crystal, N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds formed by amide groups and O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds formed by carboxylic acid groups are observed and supported additionally by weak C—H⋯O interactions between the methylidene and amide groups. Together, these link the molecules into chains of dimers along [110] and form R 2 2(8) graph-set motifs.
Related literature
For the pharmacological activity of amide derivatives, see: Galanakis et al. (2004 ▶); Kumar & Knaus (1993 ▶); Ban et al. (1998 ▶); Ukrainets et al. (2006 ▶), Lesyk & Zimenkovsky (2004 ▶); Gududuru et al. (2004 ▶). For related structures, see: Nayak et al. (2013a
▶,b
▶). For standard bond lengths, see: Allen et al. (1987 ▶).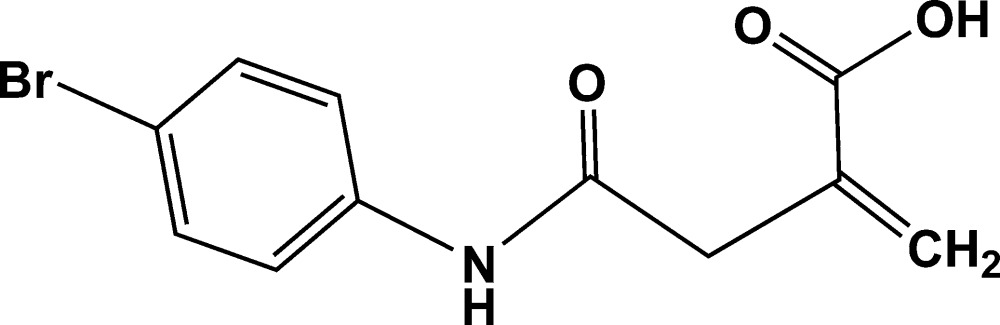
Experimental
Crystal data
C11H10BrNO3
M r = 284.11
Triclinic,

a = 6.2782 (4) Å
b = 8.3251 (5) Å
c = 21.3244 (12) Å
α = 96.462 (5)°
β = 92.026 (5)°
γ = 95.390 (5)°
V = 1101.38 (11) Å3
Z = 4
Cu Kα radiation
μ = 5.04 mm−1
T = 173 K
0.44 × 0.28 × 0.14 mm
Data collection
Agilent Eos Gemini diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO and CrysAlis RED; Agilent, 2012 ▶) T min = 0.162, T max = 1.000
7163 measured reflections
4131 independent reflections
3490 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.033
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.076
wR(F 2) = 0.227
S = 1.03
4131 reflections
291 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 2.73 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.79 e Å−3
Data collection: CrysAlis PRO (Agilent, 2012 ▶); cell refinement: CrysAlis PRO; data reduction: CrysAlis RED (Agilent, 2012 ▶); program(s) used to solve structure: SUPERFLIP (Palatinus et al., 2012 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL2012 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: OLEX2 (Dolomanov et al., 2009 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: OLEX2.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814012872/bt6983sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814012872/bt6983Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814012872/bt6983Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1006395
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O3A—H3A⋯O2B i | 0.84 | 1.85 | 2.685 (5) | 174 |
| N1A—H1A⋯O1B ii | 0.88 | 2.06 | 2.933 (5) | 170 |
| O3B—H3B⋯O2A iii | 0.84 | 1.82 | 2.654 (5) | 170 |
| N1B—H1B⋯O1A iv | 0.88 | 2.04 | 2.848 (6) | 152 |
| C5B—H5BB⋯O1A v | 0.95 | 2.54 | 3.464 (7) | 164 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  ; (iv)
; (iv)  ; (v)
; (v)  .
.
Acknowledgments
BN thanks the UGC for financial assistance through a BSR one-time grant for the purchase of chemicals. PSN thanks Mangalore University for research facilities and DST–PURSE financial assistance. JPJ acknowledges the NSF–MRI program (grant No. CHE-1039027) for funds to purchase the X-ray diffractometer.
supplementary crystallographic information
S1. Comment
Amide bonds play a major role in the elaboration and composition of biological systems, which are the main chemical bonds that link amino acid building blocks together to give proteins. Amide bonds are not limited to biological systems and are indeed present in a huge array of molecules, including major marketed drugs. Amide derivatives possessing anti-inflammatory (Galanakis et al., 2004; Kumar et al., 1993; Ban et al., 1998), antimicrobial (Ukrainets et al., 2006), anti-tubercular (Lesyk et al., 2004) and antiproliferative (Gududuru et al., 2004) activities are reported in the literature. Crystal structures of some related amide derivatives include, viz., 4-(4-iodoanilino)-2-methylene-4-oxobutanoic acid and 4-(3-fluoro-4-methylanilino)-2-methylidene-4-oxobutanoic acid (Nayak et al., 2013a,b). Hence in view of its pharmacological importance, the title compound 4-[(4-bromophenyl)amino]-2-methylidene-4-oxobutanoic acid (I), C11H10BrNO3, was synthesized from 3-methylidenedihydrofuran-2,5-dione with good yields and its crystal structure is reported here.
In the title compound, two independent molecules (A & B) crystallize in the asymmetric unit (Fig. 1). The N–C(=O) bond lengths of 1.359 (6)A (A) and 1.346 (6)Å (B) are indicative of amide-type resonance. The bond lengths of the remaining atoms are in normal ranges (Allen et al., 1987). In the crystal, classical N—H···O and O—H···O hydrogen bonds are observed supported additionally by weak C—H···O intermolecular interactions between the 2-methylidene and amide groups (Table 1, Fig. 2) linking the molecules into chains of dimers along [1 1 0]. The N—H···O hydrogen bonds are supported by the carbonyl oxygen atom of the amide functionality as the acceptor. The carboxylic acid groups form a dimeric hydrogen bonding pattern commonly seen for many carbolylic acids into R22(8) graph-set motifs (Fig. 3). The dihedral angles between the mean planes of the 4-bromophenyl ring (C6A–C11A or C6B–C11B) and oxoamine group (N1A/C1A/O1A/C2A or N1B/C1B/O1B/C2B) are 24.8 (7)° (A) and 77.1 (6)° (B), respectively. The mean plane of the 2-methylidene group (C2A–C5A or C2B–C5B) is further inclined by 75.6 (4)° (A) and 72.5 (6)° (B) from that of the oxoamine group (N1A/C1A/O1A/C2A or N1B/C1B/O1B/C2B).
S2. Experimental
3-Methylidenedihydrofuran-2,5-dione (0.112 g, 1 mmol) was dissolved in 30 ml acetone and stirred at ambient temperature. 4-Bromoaniline (0.172 g, 1 mmol) in 20 mL acetone was added over 30 mins (Fig. 4). After sirring for 1.5 h the slurry was filtered. The solid was washed with acetone and dried to give title compound, C11H10BrNO3. Single crystals were grown from methanol by the slow evaporation method (yield 0.248 g, 87.32%; m.p.: 441–443 K).
S3. Refinement
All of the H atoms were placed in their calculated positions and then refined using the riding model with Atom—H lengths of 0.95Å (CH), 0.99Å (CH2), 0.88Å (NH) or 0.84Å (OH). Isotropic displacement parameters for these atoms were set to 1.2 (CH, CH2, NH) or 1.5 (OH) times Ueq of the parent atom. The idealised tetrahedral OH was refined as a rotating group: O3A(H3A), O3B(H3B). The highest four peaks in the residual density map are at approximately 1Å from the bromine atoms and have a height of about 2 e-/Å3.
Figures
Fig. 1.

ORTEP drawing of the title compound, C11H10BrNO3, showing the labeling scheme with 30% probability displacement ellipsoids.
Fig. 2.
Molecular packing for the title compound viewed along the a axis. Dashed lines indicate N—H···O, O—H···O hydrogen bonds and weak C—H···O intermolecular interactions linking the molecules into chains of dimers along [1 1 0]. H atoms not involved in hydrogen bonding or weak intermolecular interactions have been removed for clarity.
Fig. 3.
Molecular packing for the title compound viewed along the b axis. Dashed lines indicate O—H···O hydrogen bonds between the carboxylic groups forming R22(8) graph-set motifs linking the molecules into chains of dimers along [1 1 0]. H atoms not involved in hydrogen bonding have been removed for clarity.
Fig. 4.

Synthesis of C11H10BrNO3.
Crystal data
| C11H10BrNO3 | V = 1101.38 (11) Å3 |
| Mr = 284.11 | Z = 4 |
| Triclinic, P1 | F(000) = 568 |
| a = 6.2782 (4) Å | Dx = 1.713 Mg m−3 |
| b = 8.3251 (5) Å | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54184 Å |
| c = 21.3244 (12) Å | µ = 5.04 mm−1 |
| α = 96.462 (5)° | T = 173 K |
| β = 92.026 (5)° | Prism, colourless |
| γ = 95.390 (5)° | 0.44 × 0.28 × 0.14 mm |
Data collection
| Agilent Eos Gemini diffractometer | 3490 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Detector resolution: 16.0416 pixels mm-1 | Rint = 0.033 |
| ω scans | θmax = 71.3°, θmin = 4.2° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO and CrysAlis RED; Agilent, 2012) | h = −7→6 |
| Tmin = 0.162, Tmax = 1.000 | k = −8→10 |
| 7163 measured reflections | l = −26→25 |
| 4131 independent reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.076 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.227 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.1446P)2 + 3.2341P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.03 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 4131 reflections | Δρmax = 2.73 e Å−3 |
| 291 parameters | Δρmin = −0.79 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Br1A | 0.19572 (14) | 0.90862 (10) | 0.46174 (4) | 0.0619 (3) | |
| O1A | 0.8488 (6) | 0.7490 (4) | 0.20741 (18) | 0.0363 (9) | |
| O2A | 0.6832 (6) | 0.6335 (5) | 0.05368 (18) | 0.0338 (8) | |
| O3A | 1.0137 (6) | 0.7205 (5) | 0.02870 (19) | 0.0370 (9) | |
| H3A | 0.9464 | 0.7607 | 0.0005 | 0.056* | |
| N1A | 0.5872 (7) | 0.5635 (5) | 0.2341 (2) | 0.0275 (9) | |
| H1A | 0.5246 | 0.4649 | 0.2229 | 0.033* | |
| C1A | 0.7571 (7) | 0.6114 (6) | 0.2006 (2) | 0.0240 (9) | |
| C2A | 0.8300 (8) | 0.4766 (6) | 0.1541 (2) | 0.0266 (10) | |
| H2AA | 0.9036 | 0.4004 | 0.1777 | 0.032* | |
| H2AB | 0.7033 | 0.4152 | 0.1307 | 0.032* | |
| C3A | 0.9795 (8) | 0.5448 (6) | 0.1078 (2) | 0.0274 (10) | |
| C4A | 0.8780 (8) | 0.6358 (6) | 0.0606 (2) | 0.0269 (10) | |
| C5A | 1.1839 (9) | 0.5217 (7) | 0.1064 (3) | 0.0354 (11) | |
| H5AA | 1.2692 | 0.5636 | 0.0749 | 0.042* | |
| H5AB | 1.2461 | 0.4633 | 0.1370 | 0.042* | |
| C6A | 0.5009 (8) | 0.6552 (6) | 0.2849 (2) | 0.0279 (10) | |
| C7A | 0.6134 (10) | 0.7860 (7) | 0.3221 (3) | 0.0375 (12) | |
| H7A | 0.7542 | 0.8230 | 0.3118 | 0.045* | |
| C8A | 0.5228 (11) | 0.8617 (8) | 0.3733 (3) | 0.0448 (14) | |
| H8A | 0.6006 | 0.9516 | 0.3981 | 0.054* | |
| C9A | 0.3196 (10) | 0.8086 (7) | 0.3892 (3) | 0.0400 (13) | |
| C10A | 0.2019 (9) | 0.6772 (8) | 0.3529 (3) | 0.0426 (13) | |
| H10A | 0.0608 | 0.6415 | 0.3634 | 0.051* | |
| C11A | 0.2942 (9) | 0.6008 (7) | 0.3017 (3) | 0.0392 (12) | |
| H11A | 0.2172 | 0.5099 | 0.2774 | 0.047* | |
| Br1B | 1.30729 (11) | 0.53869 (9) | 0.55597 (3) | 0.0518 (3) | |
| O1B | 0.6584 (6) | 0.7564 (4) | 0.79041 (17) | 0.0313 (8) | |
| O2B | 0.8098 (5) | 0.8720 (5) | 0.94320 (18) | 0.0333 (8) | |
| O3B | 0.4808 (6) | 0.7820 (5) | 0.96889 (19) | 0.0365 (8) | |
| H3B | 0.5499 | 0.7275 | 0.9919 | 0.055* | |
| N1B | 0.8836 (7) | 0.9562 (5) | 0.7586 (2) | 0.0310 (9) | |
| H1B | 0.9272 | 1.0606 | 0.7645 | 0.037* | |
| C1B | 0.7305 (7) | 0.8992 (6) | 0.7954 (2) | 0.0237 (9) | |
| C2B | 0.6529 (8) | 1.0295 (6) | 0.8428 (2) | 0.0276 (10) | |
| H2BA | 0.7784 | 1.0939 | 0.8657 | 0.033* | |
| H2BB | 0.5740 | 1.1040 | 0.8198 | 0.033* | |
| C3B | 0.5089 (8) | 0.9580 (5) | 0.8900 (2) | 0.0252 (9) | |
| C4B | 0.6144 (8) | 0.8670 (6) | 0.9365 (2) | 0.0258 (9) | |
| C5B | 0.3032 (8) | 0.9786 (7) | 0.8930 (2) | 0.0331 (11) | |
| H5BA | 0.2219 | 0.9351 | 0.9250 | 0.040* | |
| H5BB | 0.2367 | 1.0368 | 0.8632 | 0.040* | |
| C6B | 0.9792 (8) | 0.8566 (6) | 0.7107 (2) | 0.0297 (10) | |
| C7B | 1.1837 (9) | 0.8118 (7) | 0.7222 (3) | 0.0334 (11) | |
| H7B | 1.2567 | 0.8449 | 0.7620 | 0.040* | |
| C8B | 1.2805 (8) | 0.7188 (7) | 0.6754 (3) | 0.0343 (11) | |
| H8B | 1.4207 | 0.6889 | 0.6830 | 0.041* | |
| C9B | 1.1733 (9) | 0.6699 (7) | 0.6181 (2) | 0.0336 (11) | |
| C10B | 0.9703 (9) | 0.7144 (8) | 0.6061 (3) | 0.0424 (13) | |
| H10B | 0.8977 | 0.6808 | 0.5663 | 0.051* | |
| C11B | 0.8740 (8) | 0.8084 (7) | 0.6526 (3) | 0.0359 (12) | |
| H11B | 0.7350 | 0.8398 | 0.6445 | 0.043* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Br1A | 0.0789 (6) | 0.0637 (5) | 0.0493 (5) | 0.0310 (4) | 0.0312 (4) | 0.0047 (3) |
| O1A | 0.041 (2) | 0.0251 (18) | 0.040 (2) | −0.0048 (16) | 0.0117 (16) | −0.0027 (14) |
| O2A | 0.0245 (18) | 0.039 (2) | 0.040 (2) | 0.0063 (15) | 0.0030 (14) | 0.0113 (15) |
| O3A | 0.0278 (18) | 0.047 (2) | 0.039 (2) | 0.0037 (16) | 0.0037 (15) | 0.0125 (16) |
| N1A | 0.027 (2) | 0.0222 (19) | 0.032 (2) | −0.0017 (16) | 0.0045 (16) | −0.0020 (15) |
| C1A | 0.026 (2) | 0.020 (2) | 0.026 (2) | 0.0045 (18) | 0.0000 (17) | 0.0010 (17) |
| C2A | 0.029 (2) | 0.021 (2) | 0.030 (2) | 0.0065 (18) | 0.0011 (18) | 0.0014 (17) |
| C3A | 0.028 (2) | 0.021 (2) | 0.031 (2) | 0.0035 (18) | 0.0017 (19) | −0.0039 (18) |
| C4A | 0.026 (2) | 0.026 (2) | 0.027 (2) | 0.0023 (18) | 0.0053 (18) | −0.0024 (18) |
| C5A | 0.033 (3) | 0.040 (3) | 0.034 (3) | 0.011 (2) | 0.001 (2) | 0.003 (2) |
| C6A | 0.030 (2) | 0.024 (2) | 0.032 (2) | 0.0059 (19) | 0.0064 (19) | 0.0058 (18) |
| C7A | 0.044 (3) | 0.030 (3) | 0.038 (3) | 0.000 (2) | 0.007 (2) | 0.001 (2) |
| C8A | 0.055 (4) | 0.040 (3) | 0.038 (3) | 0.004 (3) | 0.007 (3) | −0.001 (2) |
| C9A | 0.047 (3) | 0.039 (3) | 0.039 (3) | 0.019 (3) | 0.021 (2) | 0.008 (2) |
| C10A | 0.030 (3) | 0.046 (3) | 0.054 (4) | 0.009 (2) | 0.016 (2) | 0.008 (3) |
| C11A | 0.030 (3) | 0.034 (3) | 0.054 (3) | 0.003 (2) | 0.011 (2) | 0.002 (2) |
| Br1B | 0.0503 (5) | 0.0635 (5) | 0.0428 (4) | 0.0220 (3) | 0.0143 (3) | −0.0059 (3) |
| O1B | 0.0333 (19) | 0.0234 (17) | 0.0361 (19) | −0.0004 (14) | 0.0089 (14) | −0.0006 (14) |
| O2B | 0.0243 (18) | 0.038 (2) | 0.039 (2) | 0.0041 (15) | 0.0041 (14) | 0.0113 (15) |
| O3B | 0.0252 (17) | 0.047 (2) | 0.040 (2) | 0.0045 (16) | 0.0022 (14) | 0.0143 (16) |
| N1B | 0.030 (2) | 0.024 (2) | 0.037 (2) | 0.0008 (17) | 0.0092 (17) | −0.0013 (16) |
| C1B | 0.020 (2) | 0.024 (2) | 0.027 (2) | 0.0057 (18) | −0.0015 (17) | 0.0004 (17) |
| C2B | 0.030 (2) | 0.022 (2) | 0.032 (2) | 0.0050 (19) | 0.0047 (19) | 0.0008 (18) |
| C3B | 0.026 (2) | 0.020 (2) | 0.029 (2) | 0.0034 (18) | 0.0031 (18) | −0.0034 (17) |
| C4B | 0.024 (2) | 0.025 (2) | 0.028 (2) | 0.0052 (18) | 0.0026 (17) | −0.0013 (17) |
| C5B | 0.031 (3) | 0.037 (3) | 0.031 (3) | 0.008 (2) | 0.002 (2) | −0.001 (2) |
| C6B | 0.028 (2) | 0.026 (2) | 0.036 (3) | 0.0035 (19) | 0.0087 (19) | 0.0030 (19) |
| C7B | 0.032 (3) | 0.035 (3) | 0.033 (3) | 0.004 (2) | 0.002 (2) | 0.002 (2) |
| C8B | 0.030 (3) | 0.041 (3) | 0.034 (3) | 0.013 (2) | 0.005 (2) | 0.004 (2) |
| C9B | 0.033 (3) | 0.036 (3) | 0.033 (3) | 0.008 (2) | 0.009 (2) | 0.000 (2) |
| C10B | 0.032 (3) | 0.060 (4) | 0.034 (3) | 0.009 (3) | −0.002 (2) | −0.001 (2) |
| C11B | 0.026 (2) | 0.046 (3) | 0.038 (3) | 0.011 (2) | 0.002 (2) | 0.006 (2) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Br1A—C9A | 1.899 (5) | Br1B—C9B | 1.893 (5) |
| O1A—C1A | 1.223 (6) | O1B—C1B | 1.224 (6) |
| O2A—C4A | 1.225 (6) | O2B—C4B | 1.226 (6) |
| O3A—H3A | 0.8400 | O3B—H3B | 0.8400 |
| O3A—C4A | 1.312 (6) | O3B—C4B | 1.311 (6) |
| N1A—H1A | 0.8800 | N1B—H1B | 0.8800 |
| N1A—C1A | 1.359 (6) | N1B—C1B | 1.346 (6) |
| N1A—C6A | 1.408 (6) | N1B—C6B | 1.428 (6) |
| C1A—C2A | 1.527 (6) | C1B—C2B | 1.525 (6) |
| C2A—H2AA | 0.9900 | C2B—H2BA | 0.9900 |
| C2A—H2AB | 0.9900 | C2B—H2BB | 0.9900 |
| C2A—C3A | 1.506 (7) | C2B—C3B | 1.511 (7) |
| C3A—C4A | 1.487 (7) | C3B—C4B | 1.488 (7) |
| C3A—C5A | 1.316 (7) | C3B—C5B | 1.321 (7) |
| C5A—H5AA | 0.9500 | C5B—H5BA | 0.9500 |
| C5A—H5AB | 0.9500 | C5B—H5BB | 0.9500 |
| C6A—C7A | 1.391 (7) | C6B—C7B | 1.392 (7) |
| C6A—C11A | 1.406 (7) | C6B—C11B | 1.382 (8) |
| C7A—H7A | 0.9500 | C7B—H7B | 0.9500 |
| C7A—C8A | 1.367 (8) | C7B—C8B | 1.385 (8) |
| C8A—H8A | 0.9500 | C8B—H8B | 0.9500 |
| C8A—C9A | 1.377 (9) | C8B—C9B | 1.375 (8) |
| C9A—C10A | 1.400 (9) | C9B—C10B | 1.383 (8) |
| C10A—H10A | 0.9500 | C10B—H10B | 0.9500 |
| C10A—C11A | 1.374 (8) | C10B—C11B | 1.384 (8) |
| C11A—H11A | 0.9500 | C11B—H11B | 0.9500 |
| C4A—O3A—H3A | 109.5 | C4B—O3B—H3B | 109.5 |
| C1A—N1A—H1A | 116.6 | C1B—N1B—H1B | 118.2 |
| C1A—N1A—C6A | 126.8 (4) | C1B—N1B—C6B | 123.7 (4) |
| C6A—N1A—H1A | 116.6 | C6B—N1B—H1B | 118.2 |
| O1A—C1A—N1A | 123.8 (4) | O1B—C1B—N1B | 123.0 (4) |
| O1A—C1A—C2A | 122.0 (4) | O1B—C1B—C2B | 123.2 (4) |
| N1A—C1A—C2A | 114.1 (4) | N1B—C1B—C2B | 113.8 (4) |
| C1A—C2A—H2AA | 109.4 | C1B—C2B—H2BA | 109.2 |
| C1A—C2A—H2AB | 109.4 | C1B—C2B—H2BB | 109.2 |
| H2AA—C2A—H2AB | 108.0 | H2BA—C2B—H2BB | 107.9 |
| C3A—C2A—C1A | 111.3 (4) | C3B—C2B—C1B | 112.3 (4) |
| C3A—C2A—H2AA | 109.4 | C3B—C2B—H2BA | 109.2 |
| C3A—C2A—H2AB | 109.4 | C3B—C2B—H2BB | 109.2 |
| C4A—C3A—C2A | 115.1 (4) | C4B—C3B—C2B | 116.0 (4) |
| C5A—C3A—C2A | 123.7 (5) | C5B—C3B—C2B | 123.6 (5) |
| C5A—C3A—C4A | 121.1 (5) | C5B—C3B—C4B | 120.3 (5) |
| O2A—C4A—O3A | 123.5 (5) | O2B—C4B—O3B | 123.7 (4) |
| O2A—C4A—C3A | 121.9 (5) | O2B—C4B—C3B | 122.0 (5) |
| O3A—C4A—C3A | 114.5 (4) | O3B—C4B—C3B | 114.2 (4) |
| C3A—C5A—H5AA | 120.0 | C3B—C5B—H5BA | 120.0 |
| C3A—C5A—H5AB | 120.0 | C3B—C5B—H5BB | 120.0 |
| H5AA—C5A—H5AB | 120.0 | H5BA—C5B—H5BB | 120.0 |
| C7A—C6A—N1A | 124.1 (5) | C7B—C6B—N1B | 119.2 (5) |
| C7A—C6A—C11A | 118.7 (5) | C11B—C6B—N1B | 121.0 (5) |
| C11A—C6A—N1A | 117.0 (5) | C11B—C6B—C7B | 119.8 (5) |
| C6A—C7A—H7A | 119.7 | C6B—C7B—H7B | 120.1 |
| C8A—C7A—C6A | 120.5 (6) | C8B—C7B—C6B | 119.8 (5) |
| C8A—C7A—H7A | 119.7 | C8B—C7B—H7B | 120.1 |
| C7A—C8A—H8A | 119.7 | C7B—C8B—H8B | 120.1 |
| C7A—C8A—C9A | 120.5 (6) | C9B—C8B—C7B | 119.8 (5) |
| C9A—C8A—H8A | 119.7 | C9B—C8B—H8B | 120.1 |
| C8A—C9A—Br1A | 120.8 (5) | C8B—C9B—Br1B | 118.8 (4) |
| C8A—C9A—C10A | 120.5 (5) | C8B—C9B—C10B | 120.8 (5) |
| C10A—C9A—Br1A | 118.6 (4) | C10B—C9B—Br1B | 120.4 (4) |
| C9A—C10A—H10A | 120.6 | C9B—C10B—H10B | 120.3 |
| C11A—C10A—C9A | 118.7 (5) | C9B—C10B—C11B | 119.4 (5) |
| C11A—C10A—H10A | 120.6 | C11B—C10B—H10B | 120.3 |
| C6A—C11A—H11A | 119.5 | C6B—C11B—C10B | 120.3 (5) |
| C10A—C11A—C6A | 121.1 (5) | C6B—C11B—H11B | 119.8 |
| C10A—C11A—H11A | 119.5 | C10B—C11B—H11B | 119.8 |
| Br1A—C9A—C10A—C11A | −177.6 (5) | Br1B—C9B—C10B—C11B | 179.0 (5) |
| O1A—C1A—C2A—C3A | −15.6 (6) | O1B—C1B—C2B—C3B | 10.3 (6) |
| N1A—C1A—C2A—C3A | 166.0 (4) | N1B—C1B—C2B—C3B | −170.7 (4) |
| N1A—C6A—C7A—C8A | −175.5 (5) | N1B—C6B—C7B—C8B | −178.3 (5) |
| N1A—C6A—C11A—C10A | 176.3 (5) | N1B—C6B—C11B—C10B | 178.8 (5) |
| C1A—N1A—C6A—C7A | −22.1 (8) | C1B—N1B—C6B—C7B | −103.4 (6) |
| C1A—N1A—C6A—C11A | 163.5 (5) | C1B—N1B—C6B—C11B | 78.4 (7) |
| C1A—C2A—C3A—C4A | −70.4 (5) | C1B—C2B—C3B—C4B | 69.5 (5) |
| C1A—C2A—C3A—C5A | 112.3 (5) | C1B—C2B—C3B—C5B | −113.4 (5) |
| C2A—C3A—C4A—O2A | −10.9 (7) | C2B—C3B—C4B—O2B | 11.7 (7) |
| C2A—C3A—C4A—O3A | 167.5 (4) | C2B—C3B—C4B—O3B | −168.0 (4) |
| C5A—C3A—C4A—O2A | 166.4 (5) | C5B—C3B—C4B—O2B | −165.5 (5) |
| C5A—C3A—C4A—O3A | −15.1 (7) | C5B—C3B—C4B—O3B | 14.8 (7) |
| C6A—N1A—C1A—O1A | −6.1 (8) | C6B—N1B—C1B—O1B | −0.6 (8) |
| C6A—N1A—C1A—C2A | 172.3 (4) | C6B—N1B—C1B—C2B | −179.6 (4) |
| C6A—C7A—C8A—C9A | 0.7 (9) | C6B—C7B—C8B—C9B | −0.6 (8) |
| C7A—C6A—C11A—C10A | 1.6 (9) | C7B—C6B—C11B—C10B | 0.6 (9) |
| C7A—C8A—C9A—Br1A | 178.0 (5) | C7B—C8B—C9B—Br1B | −178.5 (4) |
| C7A—C8A—C9A—C10A | −0.6 (10) | C7B—C8B—C9B—C10B | 0.9 (9) |
| C8A—C9A—C10A—C11A | 1.0 (9) | C8B—C9B—C10B—C11B | −0.4 (10) |
| C9A—C10A—C11A—C6A | −1.5 (9) | C9B—C10B—C11B—C6B | −0.3 (9) |
| C11A—C6A—C7A—C8A | −1.1 (8) | C11B—C6B—C7B—C8B | −0.1 (8) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O3A—H3A···O2Bi | 0.84 | 1.85 | 2.685 (5) | 174 |
| N1A—H1A···O1Bii | 0.88 | 2.06 | 2.933 (5) | 170 |
| O3B—H3B···O2Aiii | 0.84 | 1.82 | 2.654 (5) | 170 |
| N1B—H1B···O1Aiv | 0.88 | 2.04 | 2.848 (6) | 152 |
| C5B—H5BB···O1Av | 0.95 | 2.54 | 3.464 (7) | 164 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, y, z−1; (ii) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1; (iii) x, y, z+1; (iv) −x+2, −y+2, −z+1; (v) −x+1, −y+2, −z+1.
Footnotes
Supporting information for this paper is available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: BT6983).
References
- Agilent (2012). CrysAlis PRO and CrysAlis RED Agilent Technologies, Yarnton, England.
- Allen, F. H., Kennard, O., Watson, D. G., Brammer, L., Orpen, A. G. & Taylor, R. (1987). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. S1–19.
- Ban, M., Taguchi, H., Katushima, T., Takahashi, M., Shinoda, K., Watanabe, A. & Tominaga, T. (1998). Bioorg. Med. Chem. 6, 1069–1076. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K. & Puschmann, H. (2009). J. Appl. Cryst. 42, 339–341.
- Galanakis, D., Kourounakis, A. P., Tsiakitzis, K. C., Doulgkeris, C., Rekka, E. A., Gavalas, A., Kravaritou, C., Christos, C. & Kourounakis, P. N. (2004). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 14, 3639–3643. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Gududuru, V., Hurh, E., Dalton, J. T. & Miller, D. D. (2004). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 14, 5289–5293. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P. & Knaus, E. E. (1993). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 28, 881–885.
- Lesyk, R. & Zimenkovsky, B. (2004). Curr. Org. Chem. 8, 1547–1578.
- Nayak, P. S., Narayana, B., Jasinski, J. P., Yathirajan, H. S. & Kaur, M. (2013b). Acta Cryst. E69, o1752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Nayak, P. S., Narayana, B., Yathirajan, H. S., Gerber, T., Brecht, B. van & Betz, R. (2013a). Acta Cryst. E69, o83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Palatinus, L., Prathapa, S. J. & van Smaalen, S. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 575–580.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Ukrainets, I. V., Sidorenko, L. V., Petrushovo, L. A. & Gorokhova, O. V. (2006). Chem. Heterocycl. Comput. 42, 64–69.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814012872/bt6983sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814012872/bt6983Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814012872/bt6983Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1006395
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




