Abstract
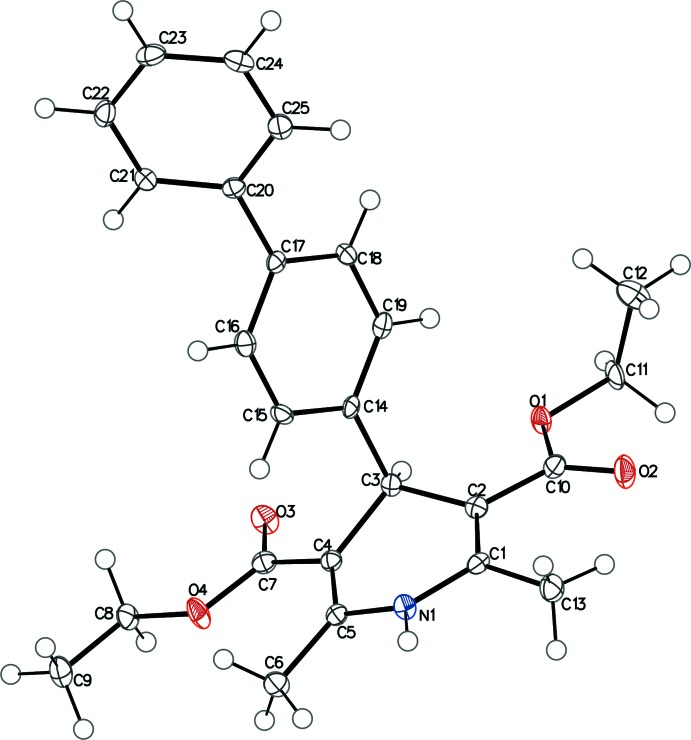
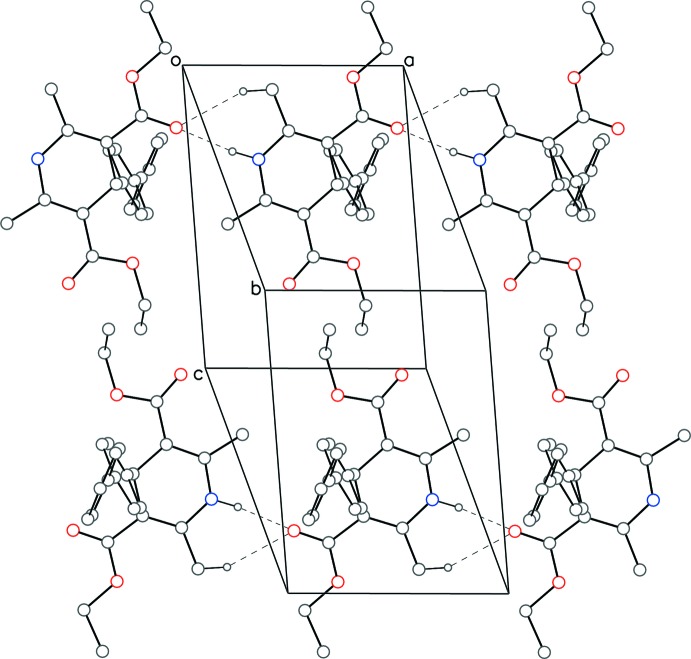
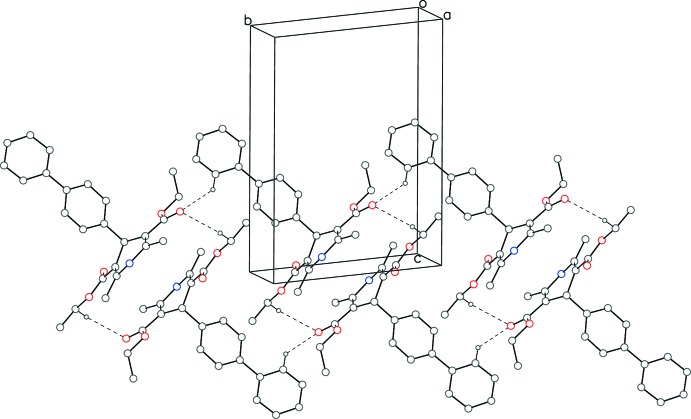
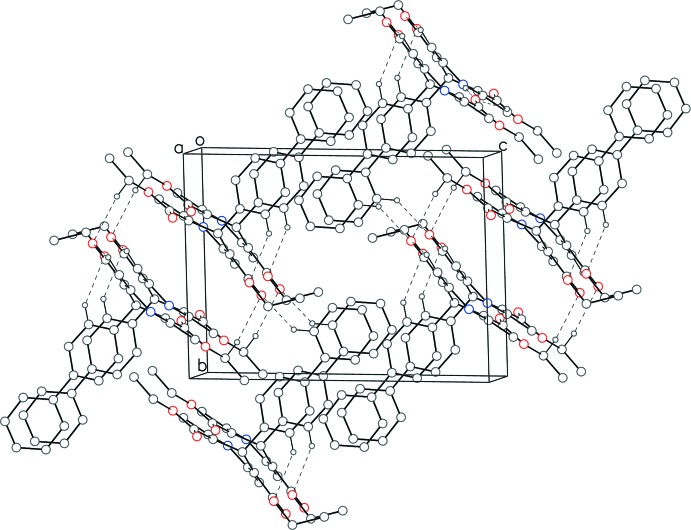
The title compound, C25H27NO4, has a flattened dihydropyridine ring. The benzene and phenyl rings are synclinal to one another, forming a dihedral angle of 49.82 (8)°; the axis of the biphenyl rings makes an 81.05 (9)° angle to the plane of the dihydropyridine ring. In the crystal, N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds link the molecules into chain motifs running along the a-axis direction. The chains are cross-linked by C—H⋯O interactions, forming sheet motifs running slightly off the (110) plane, together with an intermolecular interaction between head-to tail biphenyl groups, thus making the whole crystal packing a three-dimensional network. Intramolecular C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds are also observed.
Related literature
For general structure–activity relationship studies of 1,4-dihydropyridines (DHPs) as calcium channel modulators, see: Bossert et al. (1981 ▶); Triggle (2003 ▶). For binding studies of DHPs to multiple drug resistant protein 1 (MDR1), see: Abe et al. (1995 ▶); Cole et al. (1989 ▶); Tasaki et al. (1995 ▶); Vanhoefer et al. (1999 ▶); Tolomero et al. (1994 ▶); Cindric et al. (2010 ▶).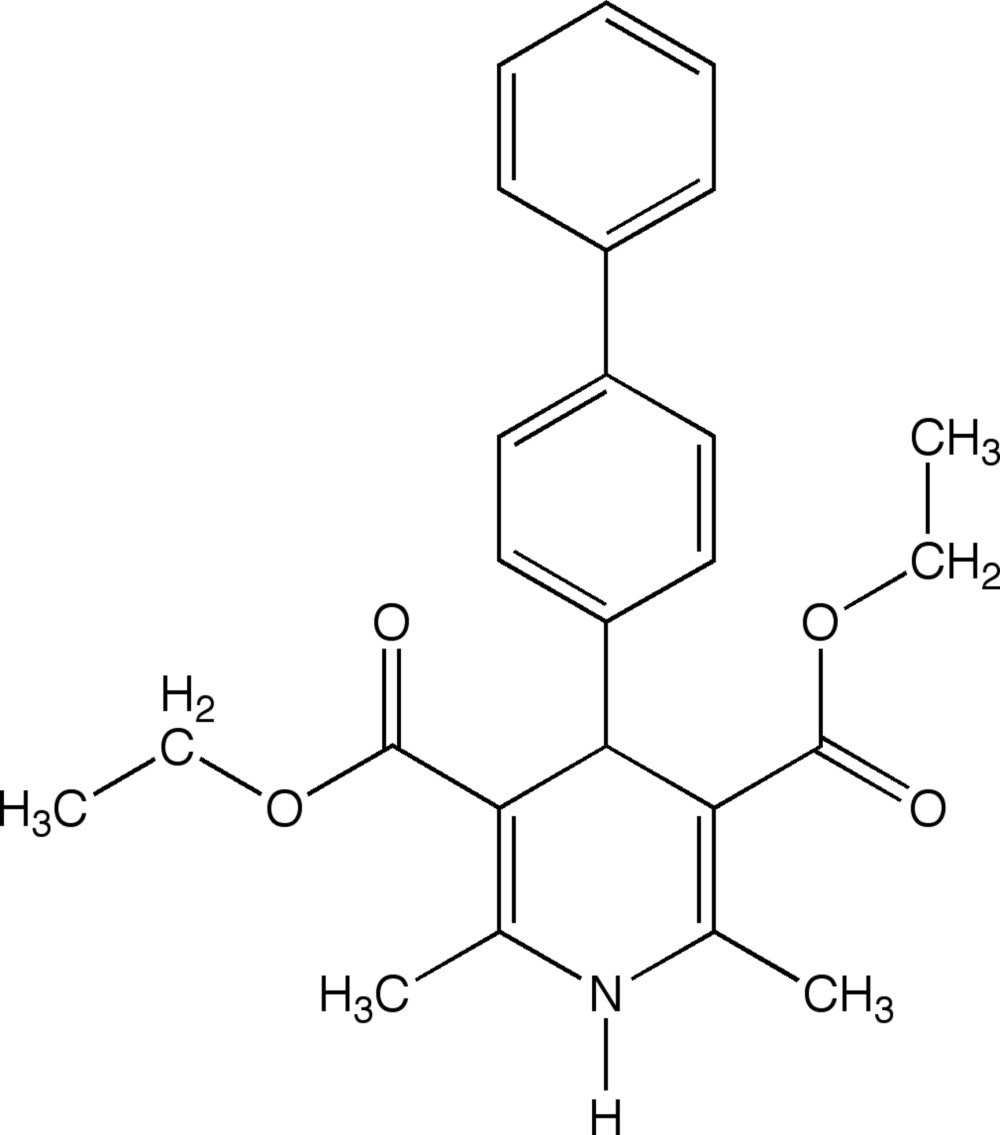
Experimental
Crystal data
C25H27NO4
M r = 405.47
Triclinic,
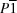
a = 7.3431 (3) Å
b = 10.6075 (4) Å
c = 13.8449 (6) Å
α = 85.762 (3)°
β = 88.124 (3)°
γ = 73.530 (2)°
V = 1031.25 (7) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.09 mm−1
T = 100 K
0.15 × 0.14 × 0.13 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART BREEZE CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2012 ▶) T min = 0.919, T max = 1.000
19956 measured reflections
4752 independent reflections
2983 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.072
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.062
wR(F 2) = 0.149
S = 1.02
4752 reflections
279 parameters
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.43 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.37 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2012 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2012 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: OLEX2 (Dolomanov et al., 2009 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: OLEX2 (Dolomanov et al., 2009 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814013294/zl2590sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814013294/zl2590Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814013294/zl2590Isup3.cml
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C21—H21⋯O2i | 0.95 | 2.50 | 3.256 (3) | 137 |
| C6—H6A⋯O3ii | 0.98 | 2.59 | 3.452 (3) | 147 |
| C19—H19⋯O1 | 0.95 | 2.51 | 3.227 (3) | 132 |
| C13—H13B⋯O2 | 0.98 | 2.11 | 2.857 (3) | 131 |
| C8—H8A⋯O2iii | 0.99 | 2.55 | 3.344 (3) | 137 |
| N1—H1⋯O3ii | 0.91 (3) | 2.03 (3) | 2.938 (3) | 173 (2) |
Symmetry codes: (i) 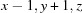 ; (ii)
; (ii) 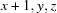 ; (iii)
; (iii) 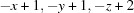 .
.
Acknowledgments
SS and NRN thank the National Institutes of Health for grants NINDS P20RR015583 Center for Structural and Functional Neuroscience (CSFN) and P20 RR017670 Center for Environmental Health Sciences (CEHS).
supplementary crystallographic information
S1. Comment
Hantzsch 1,4-dihydropyridines (DHPs) are an extensively studied class of compounds that are known predominantly for their L-type voltage gated calcium channel modulation. (Bossert et al. 1981, Triggle 2003) There have been extensive structure-activity relationship (SAR) studies done on DHPs that have revealed the basic structural requirements for robust binding affinity to calcium channels. (Triggle 2003) Other studies in the field have shown that DHPs bind to multiple receptors, most notably the multiple drug resistant protein 1 (MDR1) (Abe et al. 1995, Cole et al. 1989, Tasaki et al. 1995, Vanhoefer et al. 1999, Tolomero et al. 1994, Cindric et al. 2010). Using established SAR more selective compounds can be designed for greater selectivity resulting in more clinically relevant compounds.
The title compound, C25H27NO4, has very similar structural features as other DHPs. Such features include a flattened boat conformation of the 1,4-DHP ring and two ester groups coplanar to the double bonds in the 1,4-DHP, with one carbonyl being cis and the other carbonyl being trans to the double bonds (Figure 1). Although the phenyl group attached at C(3) is still orthogonal to the bottom [C(1)—C(2)—C(4)—C(5)] of the 1,4-DHP ring [81.05 (9)°], it twists away from the N(1)—C(3) at an angle of 47.77 (8)°. The next phenyl ring twists again, with 49.82 (8)° from the center phenyl group, and becomes almost orthogonal to the N(1)—C(3) axis [12.97 (9)°]. Intermolecular hydrogen bonds between N(1) – H(1) and O(3), together with the intermolecular C(6) – H(6) ··· O(3) interactions, link the molecules into chain motifs running along the a axis (Figure 2). Two intermolecular C – H ··· O interactions both from O(2) cross link the molecules into sheet motifs running slightly off the 110 plane (Figure 3). These interations form a three-dimensional network in the cyrstal packing (Figure 4). There are two intramolecular H-bonds observed in the molecule, C(19) – H(19) ··· O(1) and C(13) – H(13B) ··· O(2).
S2. Experimental
S2.1. Synthesis and crystallization
An oven-dried 100 mL round bottom flask was charged with 1.90g of biphenyl-4-carbaldehyde, 2.86 g of ethyl acetoacetate, 2.49 mL of 14.8M ammonium hydroxide, and a magenetic stir bar. The mixture was taken up in 50 mL of absolute ethanol, and the round bottom flask was fitted with a dean stark trap and heated to reflux while stirring. Reaction progress was monitored via TLC. Once the reaction was complete, excess solvent was removed via rotary evaporation. The solution was then purified via a silica column chromatography. The product was re-crystallized into white to yellow crystalline clumps with hexane and dichloromethane (yield = 1.24g , 3.06 mmol, 29.31%).
S2.2. Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 1. The methyl H atoms were constrained to an ideal geometry, with C – H = 0.98 Å and Uiso(H) = 1.5Ueq(C), and were allowed to rotate freely about the C – C bonds. The rest of the H atoms were placed in calculated positions with C – H = 0.95 ~ 1.00 Å and refined as riding on their carrier atoms with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C). The positions of amine H atoms were determined from difference Fourier maps and refined freely along with their isotropic displacement parameters. One low-angle reflection was omitted from the refinement because its observed intensity was much lower than the calculated value as a result of being partially obscured by the beam stop.
Figures
Fig. 1.
Crystal structure of the title compound with labeling and displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 50% probability level.
Fig. 2.
Packing diagram of the title compound, showing the intermolecular hydrogen bonds which form chain motifs running along the a axis. For the sake of clarity, H atoms not involved in H-bonds are removed.
Fig. 3.
Packing diagram of the title compound, showing intermolecular C – H ··· O interactions in dashed lines which cross link the molecules into a sheet motif running slightly off the 110 plane. For the sake of clarity, H atoms not involved in the interactions are removed.
Fig. 4.
Packing diagram of the title compound. The intermolecular interactions form a three-dimensional network in the crystal packing. For the sake of clarity, H atoms not involved in the interactions are removed.
Crystal data
| C25H27NO4 | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 405.47 | F(000) = 432 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.306 Mg m−3 |
| a = 7.3431 (3) Å | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| b = 10.6075 (4) Å | Cell parameters from 5122 reflections |
| c = 13.8449 (6) Å | θ = 2.4–27.4° |
| α = 85.762 (3)° | µ = 0.09 mm−1 |
| β = 88.124 (3)° | T = 100 K |
| γ = 73.530 (2)° | Prism, pale white |
| V = 1031.25 (7) Å3 | 0.15 × 0.14 × 0.13 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART BREEZE CCD diffractometer | 2983 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Radiation source: 2 kW sealed X-ray tube | Rint = 0.072 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 27.6°, θmin = 2.0° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2012) | h = −9→9 |
| Tmin = 0.919, Tmax = 1.000 | k = −13→13 |
| 19956 measured reflections | l = −17→18 |
| 4752 independent reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: mixed |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.062 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F2) = 0.149 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0537P)2 + 0.8331P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.02 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 4752 reflections | Δρmax = 0.43 e Å−3 |
| 279 parameters | Δρmin = −0.37 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O3 | 0.1263 (2) | 0.73985 (17) | 0.98682 (13) | 0.0183 (4) | |
| O1 | 0.4574 (2) | 0.44644 (15) | 0.75695 (12) | 0.0149 (4) | |
| O4 | 0.2751 (2) | 0.84869 (17) | 1.07429 (13) | 0.0191 (4) | |
| N1 | 0.7805 (3) | 0.68215 (19) | 0.92579 (15) | 0.0127 (5) | |
| O2 | 0.7739 (2) | 0.38137 (18) | 0.73785 (14) | 0.0248 (5) | |
| C3 | 0.4394 (3) | 0.6641 (2) | 0.85636 (17) | 0.0111 (5) | |
| H3 | 0.3408 | 0.6153 | 0.8619 | 0.013* | |
| C4 | 0.4521 (3) | 0.7191 (2) | 0.95378 (17) | 0.0115 (5) | |
| C20 | 0.1965 (3) | 1.0952 (2) | 0.55708 (17) | 0.0118 (5) | |
| C14 | 0.3787 (3) | 0.7763 (2) | 0.77713 (17) | 0.0107 (5) | |
| C25 | 0.2602 (3) | 1.0854 (2) | 0.46091 (18) | 0.0156 (5) | |
| H25 | 0.3384 | 1.0037 | 0.4406 | 0.019* | |
| C1 | 0.7918 (3) | 0.5861 (2) | 0.86166 (17) | 0.0122 (5) | |
| C18 | 0.2529 (3) | 0.8563 (2) | 0.61659 (18) | 0.0141 (5) | |
| H18 | 0.2085 | 0.8383 | 0.5569 | 0.017* | |
| C5 | 0.6197 (3) | 0.7352 (2) | 0.98050 (17) | 0.0112 (5) | |
| C2 | 0.6293 (3) | 0.5673 (2) | 0.83079 (17) | 0.0118 (5) | |
| C7 | 0.2713 (3) | 0.7670 (2) | 1.00548 (18) | 0.0136 (5) | |
| C21 | 0.0758 (3) | 1.2152 (2) | 0.58379 (18) | 0.0138 (5) | |
| H21 | 0.0290 | 1.2231 | 0.6485 | 0.017* | |
| C22 | 0.0236 (3) | 1.3226 (2) | 0.51739 (19) | 0.0167 (6) | |
| H22 | −0.0601 | 1.4031 | 0.5365 | 0.020* | |
| C17 | 0.2607 (3) | 0.9835 (2) | 0.63075 (17) | 0.0107 (5) | |
| C16 | 0.3313 (3) | 1.0043 (2) | 0.71876 (18) | 0.0144 (5) | |
| H16 | 0.3398 | 1.0897 | 0.7301 | 0.017* | |
| C6 | 0.6587 (3) | 0.8067 (2) | 1.06364 (18) | 0.0163 (6) | |
| H6A | 0.7962 | 0.7883 | 1.0711 | 0.025* | |
| H6B | 0.6033 | 0.7768 | 1.1233 | 0.025* | |
| H6C | 0.6021 | 0.9017 | 1.0508 | 0.025* | |
| C19 | 0.3093 (3) | 0.7555 (2) | 0.68872 (18) | 0.0139 (5) | |
| H19 | 0.3004 | 0.6701 | 0.6776 | 0.017* | |
| C15 | 0.3893 (3) | 0.9031 (2) | 0.78989 (18) | 0.0125 (5) | |
| H15 | 0.4374 | 0.9204 | 0.8488 | 0.015* | |
| C13 | 0.9930 (3) | 0.5135 (3) | 0.8374 (2) | 0.0204 (6) | |
| H13A | 1.0506 | 0.5717 | 0.7965 | 0.031* | |
| H13B | 0.9946 | 0.4360 | 0.8025 | 0.031* | |
| H13C | 1.0654 | 0.4853 | 0.8972 | 0.031* | |
| C8 | 0.0994 (3) | 0.9041 (2) | 1.12773 (18) | 0.0152 (5) | |
| H8A | 0.0608 | 0.8337 | 1.1667 | 0.018* | |
| H8B | −0.0041 | 0.9496 | 1.0825 | 0.018* | |
| C10 | 0.6336 (3) | 0.4574 (2) | 0.77147 (18) | 0.0146 (5) | |
| C9 | 0.1404 (4) | 1.0005 (2) | 1.19262 (19) | 0.0195 (6) | |
| H9A | 0.1838 | 1.0672 | 1.1532 | 0.029* | |
| H9B | 0.2395 | 0.9535 | 1.2386 | 0.029* | |
| H9C | 0.0246 | 1.0433 | 1.2283 | 0.029* | |
| C23 | 0.0929 (4) | 1.3132 (2) | 0.42313 (19) | 0.0177 (6) | |
| H23 | 0.0603 | 1.3878 | 0.3781 | 0.021* | |
| C24 | 0.2102 (3) | 1.1940 (2) | 0.39484 (19) | 0.0168 (6) | |
| H24 | 0.2564 | 1.1868 | 0.3300 | 0.020* | |
| C11 | 0.4471 (4) | 0.3420 (2) | 0.69640 (18) | 0.0176 (6) | |
| H11A | 0.3249 | 0.3213 | 0.7091 | 0.021* | |
| H11B | 0.5507 | 0.2616 | 0.7141 | 0.021* | |
| C12 | 0.4631 (4) | 0.3793 (3) | 0.59046 (19) | 0.0245 (6) | |
| H12A | 0.4454 | 0.3093 | 0.5526 | 0.037* | |
| H12B | 0.5891 | 0.3912 | 0.5763 | 0.037* | |
| H12C | 0.3654 | 0.4618 | 0.5733 | 0.037* | |
| H1 | 0.893 (4) | 0.696 (3) | 0.9411 (19) | 0.023 (8)* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O3 | 0.0103 (9) | 0.0255 (10) | 0.0221 (11) | −0.0085 (8) | 0.0015 (7) | −0.0084 (8) |
| O1 | 0.0152 (9) | 0.0113 (9) | 0.0194 (10) | −0.0046 (7) | 0.0007 (7) | −0.0057 (7) |
| O4 | 0.0115 (9) | 0.0269 (10) | 0.0210 (10) | −0.0064 (8) | 0.0055 (7) | −0.0145 (8) |
| N1 | 0.0078 (10) | 0.0152 (11) | 0.0168 (12) | −0.0054 (9) | 0.0013 (8) | −0.0049 (9) |
| O2 | 0.0154 (9) | 0.0238 (10) | 0.0328 (12) | 0.0018 (8) | −0.0007 (8) | −0.0158 (9) |
| C3 | 0.0091 (11) | 0.0108 (12) | 0.0145 (13) | −0.0040 (9) | −0.0004 (10) | −0.0026 (10) |
| C4 | 0.0122 (12) | 0.0108 (12) | 0.0110 (13) | −0.0026 (9) | 0.0003 (9) | 0.0000 (9) |
| C20 | 0.0106 (12) | 0.0127 (12) | 0.0127 (13) | −0.0044 (10) | −0.0018 (10) | −0.0002 (10) |
| C14 | 0.0068 (11) | 0.0106 (12) | 0.0130 (13) | 0.0005 (9) | 0.0019 (9) | −0.0018 (10) |
| C25 | 0.0126 (12) | 0.0170 (13) | 0.0181 (14) | −0.0047 (10) | −0.0010 (10) | −0.0039 (11) |
| C1 | 0.0108 (12) | 0.0119 (12) | 0.0126 (13) | −0.0016 (10) | −0.0005 (10) | 0.0021 (10) |
| C18 | 0.0143 (12) | 0.0145 (13) | 0.0128 (14) | −0.0018 (10) | −0.0022 (10) | −0.0052 (10) |
| C5 | 0.0126 (12) | 0.0093 (11) | 0.0118 (13) | −0.0038 (9) | −0.0001 (10) | 0.0011 (10) |
| C2 | 0.0131 (12) | 0.0111 (12) | 0.0120 (13) | −0.0050 (10) | 0.0003 (10) | 0.0006 (10) |
| C7 | 0.0142 (12) | 0.0131 (12) | 0.0136 (14) | −0.0044 (10) | −0.0007 (10) | 0.0012 (10) |
| C21 | 0.0149 (12) | 0.0138 (12) | 0.0126 (13) | −0.0033 (10) | −0.0010 (10) | −0.0028 (10) |
| C22 | 0.0154 (13) | 0.0113 (12) | 0.0229 (15) | −0.0020 (10) | −0.0035 (11) | −0.0040 (11) |
| C17 | 0.0076 (11) | 0.0116 (12) | 0.0119 (13) | −0.0013 (9) | 0.0018 (9) | −0.0011 (10) |
| C16 | 0.0161 (13) | 0.0114 (12) | 0.0168 (14) | −0.0051 (10) | 0.0004 (10) | −0.0032 (10) |
| C6 | 0.0125 (12) | 0.0205 (13) | 0.0167 (14) | −0.0050 (10) | −0.0001 (10) | −0.0040 (11) |
| C19 | 0.0129 (12) | 0.0091 (12) | 0.0191 (14) | −0.0017 (10) | 0.0003 (10) | −0.0020 (10) |
| C15 | 0.0131 (12) | 0.0147 (12) | 0.0109 (13) | −0.0050 (10) | −0.0022 (10) | −0.0033 (10) |
| C13 | 0.0133 (13) | 0.0238 (14) | 0.0220 (15) | −0.0003 (11) | 0.0000 (11) | −0.0078 (12) |
| C8 | 0.0102 (12) | 0.0200 (13) | 0.0145 (14) | −0.0024 (10) | 0.0040 (10) | −0.0048 (11) |
| C10 | 0.0147 (13) | 0.0121 (12) | 0.0156 (14) | −0.0016 (10) | −0.0009 (10) | 0.0002 (10) |
| C9 | 0.0163 (13) | 0.0194 (14) | 0.0230 (16) | −0.0041 (11) | 0.0036 (11) | −0.0089 (11) |
| C23 | 0.0221 (14) | 0.0155 (13) | 0.0163 (14) | −0.0075 (11) | −0.0065 (11) | 0.0048 (11) |
| C24 | 0.0172 (13) | 0.0244 (14) | 0.0108 (13) | −0.0091 (11) | −0.0004 (10) | −0.0011 (11) |
| C11 | 0.0228 (14) | 0.0110 (12) | 0.0203 (15) | −0.0052 (11) | 0.0002 (11) | −0.0081 (11) |
| C12 | 0.0253 (15) | 0.0329 (16) | 0.0195 (15) | −0.0135 (13) | −0.0007 (12) | −0.0067 (12) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O3—C7 | 1.219 (3) | C21—C22 | 1.382 (3) |
| O1—C10 | 1.354 (3) | C22—H22 | 0.9500 |
| O1—C11 | 1.458 (3) | C22—C23 | 1.385 (4) |
| O4—C7 | 1.340 (3) | C17—C16 | 1.396 (3) |
| O4—C8 | 1.459 (3) | C16—H16 | 0.9500 |
| N1—C1 | 1.383 (3) | C16—C15 | 1.385 (3) |
| N1—C5 | 1.383 (3) | C6—H6A | 0.9800 |
| N1—H1 | 0.91 (3) | C6—H6B | 0.9800 |
| O2—C10 | 1.217 (3) | C6—H6C | 0.9800 |
| C3—H3 | 1.0000 | C19—H19 | 0.9500 |
| C3—C4 | 1.525 (3) | C15—H15 | 0.9500 |
| C3—C14 | 1.536 (3) | C13—H13A | 0.9800 |
| C3—C2 | 1.527 (3) | C13—H13B | 0.9800 |
| C4—C5 | 1.356 (3) | C13—H13C | 0.9800 |
| C4—C7 | 1.464 (3) | C8—H8A | 0.9900 |
| C20—C25 | 1.398 (3) | C8—H8B | 0.9900 |
| C20—C21 | 1.396 (3) | C8—C9 | 1.506 (3) |
| C20—C17 | 1.484 (3) | C9—H9A | 0.9800 |
| C14—C19 | 1.397 (3) | C9—H9B | 0.9800 |
| C14—C15 | 1.392 (3) | C9—H9C | 0.9800 |
| C25—H25 | 0.9500 | C23—H23 | 0.9500 |
| C25—C24 | 1.388 (4) | C23—C24 | 1.388 (3) |
| C1—C2 | 1.352 (3) | C24—H24 | 0.9500 |
| C1—C13 | 1.500 (3) | C11—H11A | 0.9900 |
| C18—H18 | 0.9500 | C11—H11B | 0.9900 |
| C18—C17 | 1.395 (3) | C11—C12 | 1.500 (4) |
| C18—C19 | 1.389 (3) | C12—H12A | 0.9800 |
| C5—C6 | 1.502 (3) | C12—H12B | 0.9800 |
| C2—C10 | 1.468 (3) | C12—H12C | 0.9800 |
| C21—H21 | 0.9500 | ||
| C10—O1—C11 | 115.95 (18) | C5—C6—H6B | 109.5 |
| C7—O4—C8 | 117.92 (18) | C5—C6—H6C | 109.5 |
| C1—N1—H1 | 115.9 (17) | H6A—C6—H6B | 109.5 |
| C5—N1—C1 | 123.2 (2) | H6A—C6—H6C | 109.5 |
| C5—N1—H1 | 119.4 (17) | H6B—C6—H6C | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 108.3 | C14—C19—H19 | 119.1 |
| C4—C3—C14 | 110.48 (18) | C18—C19—C14 | 121.8 (2) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 110.09 (19) | C18—C19—H19 | 119.1 |
| C14—C3—H3 | 108.3 | C14—C15—H15 | 119.2 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 108.3 | C16—C15—C14 | 121.6 (2) |
| C2—C3—C14 | 111.20 (19) | C16—C15—H15 | 119.2 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 119.3 (2) | C1—C13—H13A | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—C7 | 124.8 (2) | C1—C13—H13B | 109.5 |
| C7—C4—C3 | 115.4 (2) | C1—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| C25—C20—C17 | 121.4 (2) | H13A—C13—H13B | 109.5 |
| C21—C20—C25 | 118.4 (2) | H13A—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| C21—C20—C17 | 120.2 (2) | H13B—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| C19—C14—C3 | 121.1 (2) | O4—C8—H8A | 110.5 |
| C15—C14—C3 | 121.9 (2) | O4—C8—H8B | 110.5 |
| C15—C14—C19 | 117.0 (2) | O4—C8—C9 | 106.34 (19) |
| C20—C25—H25 | 119.7 | H8A—C8—H8B | 108.7 |
| C24—C25—C20 | 120.5 (2) | C9—C8—H8A | 110.5 |
| C24—C25—H25 | 119.7 | C9—C8—H8B | 110.5 |
| N1—C1—C13 | 112.5 (2) | O1—C10—C2 | 112.0 (2) |
| C2—C1—N1 | 118.8 (2) | O2—C10—O1 | 121.3 (2) |
| C2—C1—C13 | 128.7 (2) | O2—C10—C2 | 126.7 (2) |
| C17—C18—H18 | 119.6 | C8—C9—H9A | 109.5 |
| C19—C18—H18 | 119.6 | C8—C9—H9B | 109.5 |
| C19—C18—C17 | 120.8 (2) | C8—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| N1—C5—C6 | 112.8 (2) | H9A—C9—H9B | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—N1 | 118.6 (2) | H9A—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 128.6 (2) | H9B—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 119.2 (2) | C22—C23—H23 | 120.2 |
| C1—C2—C10 | 120.9 (2) | C22—C23—C24 | 119.6 (2) |
| C10—C2—C3 | 119.9 (2) | C24—C23—H23 | 120.2 |
| O3—C7—O4 | 121.7 (2) | C25—C24—C23 | 120.3 (2) |
| O3—C7—C4 | 124.1 (2) | C25—C24—H24 | 119.9 |
| O4—C7—C4 | 114.2 (2) | C23—C24—H24 | 119.9 |
| C20—C21—H21 | 119.5 | O1—C11—H11A | 109.1 |
| C22—C21—C20 | 120.9 (2) | O1—C11—H11B | 109.1 |
| C22—C21—H21 | 119.5 | O1—C11—C12 | 112.4 (2) |
| C21—C22—H22 | 119.9 | H11A—C11—H11B | 107.9 |
| C21—C22—C23 | 120.2 (2) | C12—C11—H11A | 109.1 |
| C23—C22—H22 | 119.9 | C12—C11—H11B | 109.1 |
| C18—C17—C20 | 122.8 (2) | C11—C12—H12A | 109.5 |
| C18—C17—C16 | 117.5 (2) | C11—C12—H12B | 109.5 |
| C16—C17—C20 | 119.7 (2) | C11—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| C17—C16—H16 | 119.3 | H12A—C12—H12B | 109.5 |
| C15—C16—C17 | 121.3 (2) | H12A—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| C15—C16—H16 | 119.3 | H12B—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—H6A | 109.5 | ||
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | 8.3 (3) | C14—C3—C2—C10 | −87.0 (3) |
| N1—C1—C2—C10 | −173.2 (2) | C25—C20—C21—C22 | −1.3 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—N1 | −10.0 (3) | C25—C20—C17—C18 | −50.9 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 169.1 (2) | C25—C20—C17—C16 | 129.5 (2) |
| C3—C4—C7—O3 | 16.6 (3) | C1—N1—C5—C4 | −17.3 (3) |
| C3—C4—C7—O4 | −161.2 (2) | C1—N1—C5—C6 | 163.4 (2) |
| C3—C14—C19—C18 | 179.7 (2) | C1—C2—C10—O1 | 173.1 (2) |
| C3—C14—C15—C16 | −178.9 (2) | C1—C2—C10—O2 | −6.4 (4) |
| C3—C2—C10—O1 | −8.3 (3) | C18—C17—C16—C15 | −0.8 (3) |
| C3—C2—C10—O2 | 172.2 (2) | C5—N1—C1—C2 | 18.3 (4) |
| C4—C3—C14—C19 | −163.0 (2) | C5—N1—C1—C13 | −160.6 (2) |
| C4—C3—C14—C15 | 16.7 (3) | C5—C4—C7—O3 | −171.8 (2) |
| C4—C3—C2—C1 | −31.2 (3) | C5—C4—C7—O4 | 10.5 (3) |
| C4—C3—C2—C10 | 150.2 (2) | C2—C3—C4—C5 | 32.1 (3) |
| C20—C25—C24—C23 | −1.3 (4) | C2—C3—C4—C7 | −155.7 (2) |
| C20—C21—C22—C23 | −0.9 (4) | C2—C3—C14—C19 | 74.4 (3) |
| C20—C17—C16—C15 | 178.8 (2) | C2—C3—C14—C15 | −105.9 (2) |
| C14—C3—C4—C5 | −91.1 (3) | C7—O4—C8—C9 | −174.9 (2) |
| C14—C3—C4—C7 | 81.1 (2) | C7—C4—C5—N1 | 178.6 (2) |
| C14—C3—C2—C1 | 91.6 (3) | C7—C4—C5—C6 | −2.3 (4) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C21—H21···O2i | 0.95 | 2.50 | 3.256 (3) | 137 |
| C6—H6A···O3ii | 0.98 | 2.59 | 3.452 (3) | 147 |
| C19—H19···O1 | 0.95 | 2.51 | 3.227 (3) | 132 |
| C13—H13B···O2 | 0.98 | 2.11 | 2.857 (3) | 131 |
| C8—H8A···O2iii | 0.99 | 2.55 | 3.344 (3) | 137 |
| N1—H1···O3ii | 0.91 (3) | 2.03 (3) | 2.938 (3) | 173 (2) |
Symmetry codes: (i) x−1, y+1, z; (ii) x+1, y, z; (iii) −x+1, −y+1, −z+2.
Footnotes
Supporting information for this paper is available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: ZL2590).
References
- Abe, T., Koike, K., Ohga, T., Kubo, T., Wada, M., Kohno, K., Mori, T., Hidaka, K. & Kuwano, M. (1995). Br. J. Cancer, 72, 418–423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Bossert, F., Meyer, H. & Wehinger, E. (1981). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 20, 762–769.
- Bruker (2012). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Ins., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Cindric, M., Cipak, A., Serly, J., Plotniece, A., Jaganjac, M., Mrakovcic, L., Lovakovic, T., Dedic, A., Soldo, I., Duburs, G., Zarkovic, N. & Molnar, J. (2010). Anticancer Res. 30, 4063–4070. [PubMed]
- Cole, S., Downes, H. & Slovak, M. (1989). Br. J. Cancer, 59, 42–46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K. & Puschmann, H. (2009). J. Appl. Cryst. 42, 339–341.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Tasaki, Y., Nakagawa, M., Ogata, J., Kiue, A., Tanimura, H., Kuwano, M. & Nomura, Y. (1995). J. Urol. 154, 1210–1216. [PubMed]
- Tolomero, M., Gancitano, R., Musso, M., Porretto, F., Perricone, R., Abbadessa, V. & Cajozzo, A. (1994). Haematologica, 79, 328–333. [PubMed]
- Triggle, D. (2003). Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 23, 293–303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Vanhoefer, U., Muller, M., Hilger, R., Lindtner, B., Klaassen, U., Schleucher, N., Rustum, Y., Seeber, S. & Harstrick, A. (1999). Br. J. Cancer, 81, 1304–1310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814013294/zl2590sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814013294/zl2590Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814013294/zl2590Isup3.cml
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report