Abstract
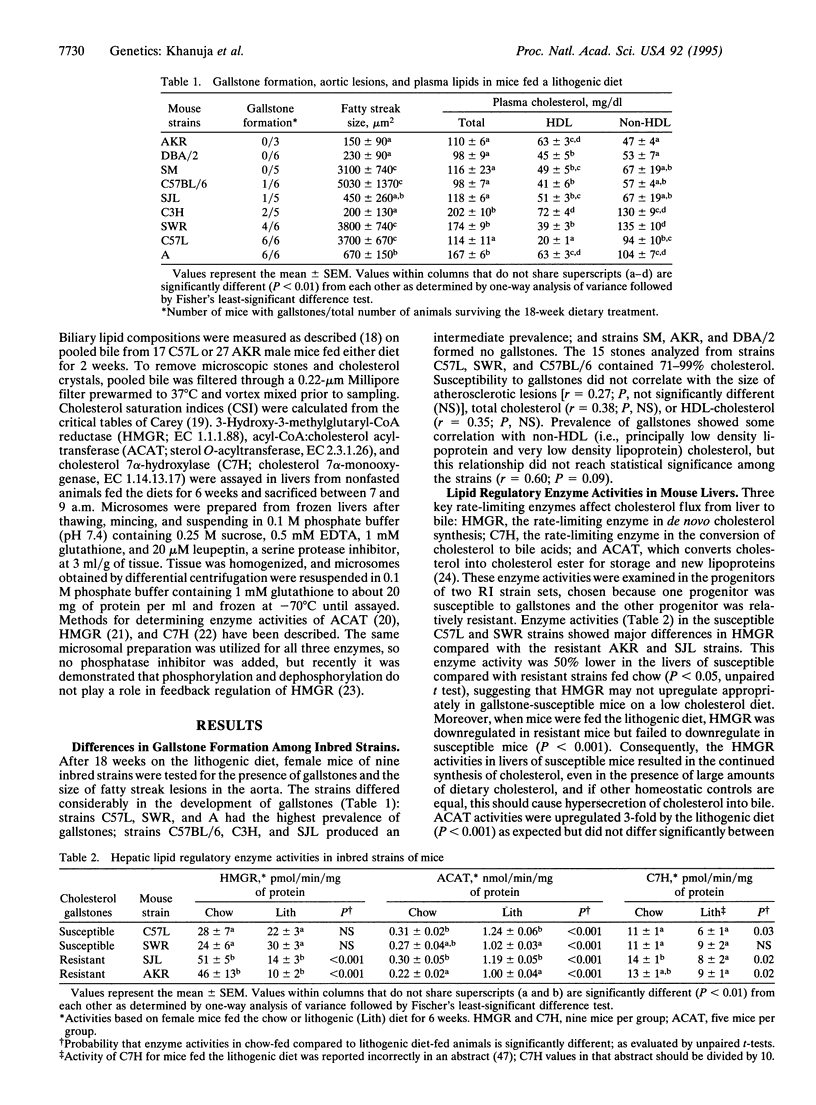
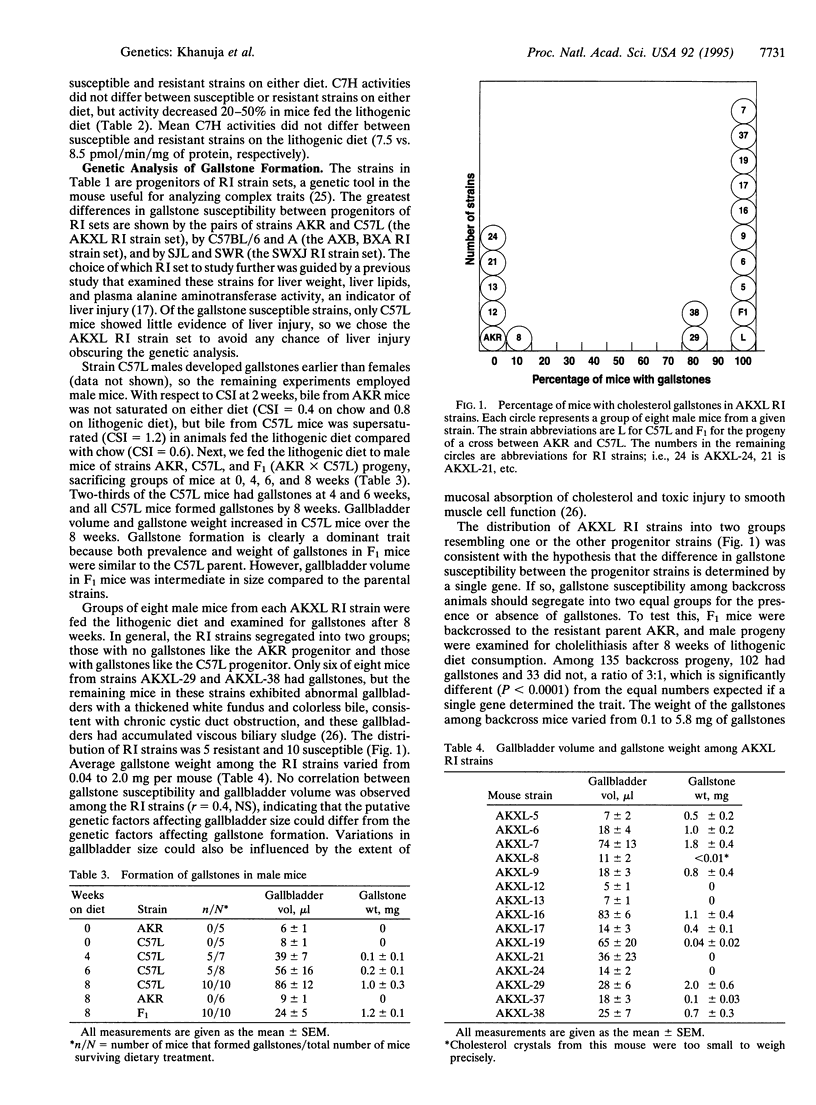
The prevalence of cholesterol gallstones differs among inbred strains of mice fed a diet containing 15% (wt/wt) dairy fat, 1% (wt/wt) cholesterol, and 0.5% (wt/wt) cholic acid. Strains C57L, SWR, and A were notable for a high prevalence of cholelithiasis; strains C57BL/6, C3H, and SJL had an intermediate prevalence; and strains SM, AKR, and DBA/2 exhibited no cholelithiasis after consuming the diet for 18 weeks. Genetic analysis of the difference in gallstone prevalence rates between strains AKR and C57L was carried out by using the AKXL recombinant inbred strain set and (AKR x C57L)F1 x AKR backcross mice. Susceptibility to gallstone formation was found to be a dominant trait determined by at least two genes. A major gene, named Lith1, mapped to mouse chromosome 2. When examined after 6 weeks on the lithogenic diet, the activity of hepatic 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase (EC 1.1.1.88) was downregulated as expected in the gallstone-resistant strains, AKR and SJL, but this enzyme failed to downregulate in C57L and SWR, the gallstone-susceptible strains. This suggests that regulation of the rate-limiting enzyme in cholesterol biosynthesis may be pivotal in determining the occurrence and severity of cholesterol hypersecretion and hence lithogenicity of gallbladder bile. These studies indicate that genetic factors are critical in determining gallstone formation and that the genetic resources of the mouse model may permit these factors to be identified.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander M., Portman O. W. Different susceptibilities to the formation of cholesterol gallstones in mice. Hepatology. 1987 Mar-Apr;7(2):257–265. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840070209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antero Kesäniemi Y., Koskenvuo M., Vuoristo M., Miettinen T. A. Biliary lipid composition in monozygotic and dizygotic pairs of twins. Gut. 1989 Dec;30(12):1750–1756. doi: 10.1136/gut.30.12.1750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billheimer J. T., Tavani D., Nes W. R. Effect of a dispersion of cholesterol in Triton WR-1339 on acyl CoA: cholesterol acyltransferase in rat liver microsomes. Anal Biochem. 1981 Mar 1;111(2):331–335. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90570-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey M. C. Critical tables for calculating the cholesterol saturation of native bile. J Lipid Res. 1978 Nov;19(8):945–955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey M. C., Lamont J. T. Cholesterol gallstone formation. 1. Physical-chemistry of bile and biliary lipid secretion. Prog Liver Dis. 1992;10:139–163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey M. C. Pathogenesis of gallstones. Recenti Prog Med. 1992 Jul-Aug;83(7-8):379–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen D. E., Leighton L. S., Carey M. C. Bile salt hydrophobicity controls vesicle secretion rates and transformations in native bile. Am J Physiol. 1992 Sep;263(3 Pt 1):G386–G395. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1992.263.3.G386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coyne M. J., Bonorris G. G., Goldstein L. I., Schoenfield L. J. Effect of chenodeoxycholic acid and phenobarbital on the rate-limiting enzymes of hepatic cholesterol and bile acid synthesis in patients with gallstones. J Lab Clin Med. 1976 Feb;87(2):281–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danzinger R. G., Gordon H., Schoenfield L. J., Thistle J. L. Lithogenic bile in siblings of young women with cholelithiasis. Mayo Clin Proc. 1972 Oct;47(10):762–766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duane W. C. Effects of lovastatin and dietary cholesterol on bile acid kinetics and bile lipid composition in healthy male subjects. J Lipid Res. 1994 Mar;35(3):501–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dueland S., Drisko J., Graf L., Machleder D., Lusis A. J., Davis R. A. Effect of dietary cholesterol and taurocholate on cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase and hepatic LDL receptors in inbred mice. J Lipid Res. 1993 Jun;34(6):923–931. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einarsson K., Angelin B., Ewerth S., Nilsell K., Björkhem I. Bile acid synthesis in man: assay of hepatic microsomal cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase activity by isotope dilution-mass spectrometry. J Lipid Res. 1986 Jan;27(1):82–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favata M. F., Trzaskos J. M., Chen H. W., Fischer R. T., Greenberg R. S. Modulation of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase by azole antimycotics requires lanosterol demethylation, but not 24,25-epoxylanosterol formation. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 5;262(25):12254–12260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujihira E., Kaneta S., Ohshima T. Strain difference in mouse cholelithiasis and the effect of taurine on the gallstone formation in C57BL/C mice. Biochem Med. 1978 Apr;19(2):211–217. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(78)90022-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilat T., Feldman C., Halpern Z., Dan M., Bar-Meir S. An increased familial frequency of gallstones. Gastroenterology. 1983 Feb;84(2):242–246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goh E. H., Colles S. M., Otte K. D. HPLC analysis of desmosterol, 7-dehydrocholesterol, and cholesterol. Lipids. 1989 Jul;24(7):652–655. doi: 10.1007/BF02535083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Regulation of the mevalonate pathway. Nature. 1990 Feb 1;343(6257):425–430. doi: 10.1038/343425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwa J. J., Zollman S., Warden C. H., Taylor B. A., Edwards P. A., Fogelman A. M., Lusis A. J. Genetic and dietary interactions in the regulation of HMG-CoA reductase gene expression. J Lipid Res. 1992 May;33(5):711–725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACKSON C. E., GAY B. C. Inheritance of gall-bladder disease. Surgery. 1959 Nov;46:853–857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston D. E., Kaplan M. M. Pathogenesis and treatment of gallstones. N Engl J Med. 1993 Feb 11;328(6):412–421. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199302113280608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern F., Jr Effects of dietary cholesterol on cholesterol and bile acid homeostasis in patients with cholesterol gallstones. J Clin Invest. 1994 Mar;93(3):1186–1194. doi: 10.1172/JCI117072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Key P. H., Bonorris G. G., Marks J. W., Chung A., Schoenfield L. J. Biliary lipid synthesis and secretion in gallstone patients before and during treatment with chenodeoxycholic acid. J Lab Clin Med. 1980 Jun;95(6):816–826. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamont J. T., Carey M. C. Cholesterol gallstone formation. 2. Pathobiology and pathomechanics. Prog Liver Dis. 1992;10:165–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander E. S., Botstein D. Mapping mendelian factors underlying quantitative traits using RFLP linkage maps. Genetics. 1989 Jan;121(1):185–199. doi: 10.1093/genetics/121.1.185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander E. S., Green P., Abrahamson J., Barlow A., Daly M. J., Lincoln S. E., Newberg L. A., Newburg L. MAPMAKER: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics. 1987 Oct;1(2):174–181. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(87)90010-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard S., Sinensky M. Somatic cell genetics and the study of cholesterol metabolism. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Feb 24;947(1):101–112. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(88)90021-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maton P. N., Ellis H. J., Higgins M. J., Dowling R. H. Hepatic HMGCoA reductase in human cholelithiasis: effects of chenodeoxycholic and ursodeoxycholic acids. Eur J Clin Invest. 1980 Aug;10(4):325–332. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1980.tb00040.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishina P. M., Verstuyft J., Paigen B. Synthetic low and high fat diets for the study of atherosclerosis in the mouse. J Lipid Res. 1990 May;31(5):859–869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishina P. M., Wang J., Toyofuku W., Kuypers F. A., Ishida B. Y., Paigen B. Atherosclerosis and plasma and liver lipids in nine inbred strains of mice. Lipids. 1993 Jul;28(7):599–605. doi: 10.1007/BF02536053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEDREIRA F., TEPPERMAN J. BILE FLOW RATE AND CHOLESTEROL CONTENT IN MICE FED A GALLSTONE-INDUCING DIET. Am J Physiol. 1964 Mar;206:635–640. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.206.3.635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paigen B., Ishida B. Y., Verstuyft J., Winters R. B., Albee D. Atherosclerosis susceptibility differences among progenitors of recombinant inbred strains of mice. Arteriosclerosis. 1990 Mar-Apr;10(2):316–323. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.10.2.316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramirez M. I., Karaoglu D., Haro D., Barillas C., Bashirzadeh R., Gil G. Cholesterol and bile acids regulate cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase expression at the transcriptional level in culture and in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;14(4):2809–2821. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.4.2809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudling M. Hepatic mRNA levels for the LDL receptor and HMG-CoA reductase show coordinate regulation in vivo. J Lipid Res. 1992 Apr;33(4):493–501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salen G., Nicolau G., Shefer S., Mosbach E. H. Hepatic cholesterol metabolism in patients with gallstones. Gastroenterology. 1975 Sep;69(3):676–684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampliner R. E., Bennett P. H., Comess L. J., Rose F. A., Burch T. A. Gallbladder disease in pima indians. Demonstration of high prevalence and early onset by cholecystography. N Engl J Med. 1970 Dec 17;283(25):1358–1364. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197012172832502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato R., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Replacement of serine-871 of hamster 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase prevents phosphorylation by AMP-activated kinase and blocks inhibition of sterol synthesis induced by ATP depletion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 15;90(20):9261–9265. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.20.9261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TEPPERMAN J., CALDWELL F. T., TEPPERMAN H. M. INDUCTION OF GALLSTONES IN MICE BY FEEDING A CHOLESTEROL-CHOLIC ACID CONTAINING DIET. Am J Physiol. 1964 Mar;206:628–634. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.206.3.628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thijs C., Knipschild P., Brombacher P. Serum lipids and gallstones: a case-control study. Gastroenterology. 1990 Sep;99(3):843–849. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)90978-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VANDERLINDEN W., LINDELOEF G. THE FAMILIAL OCCURRENCE OF GALLSTONE DISEASE. Acta Genet Stat Med. 1965;15:159–164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlahcevic Z. R., Pandak W. M., Heuman D. M., Hylemon P. B. Function and regulation of hydroxylases involved in the bile acid biosynthesis pathways. Semin Liver Dis. 1992 Nov;12(4):403–419. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1040410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss K. M., Ferrell R. E., Hanis C. L., Styne P. N. Genetics and epidemiology of gallbladder disease in New World native peoples. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Nov;36(6):1259–1278. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



