Extended Data Figure 7. SMYD3 and MAP3K2 knockdown both impair MAP Kinase signaling.
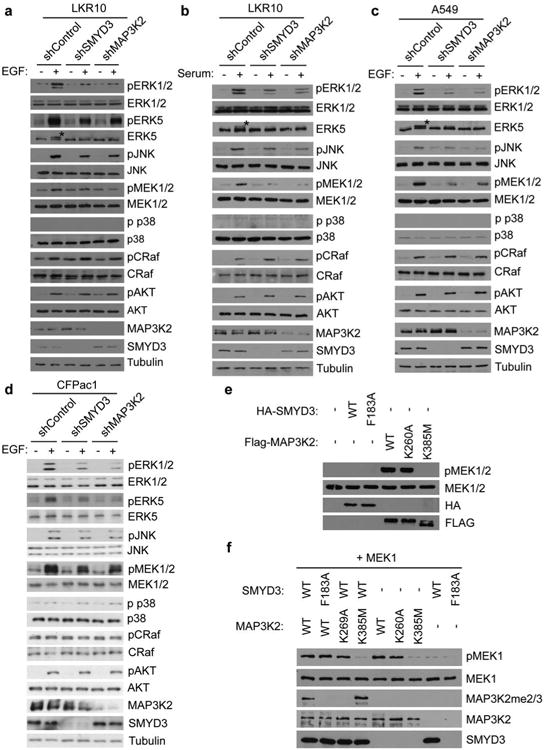
a-d, Immunoblot analysis with the indicated antibodies of LKR10 (a-b), A549 (c), and CFPac1 (d) lysates. Asterisk indicates slower migrating ERK5 species that is phosphorylated. Stimulation: 10% serum-complemented media for 15min (b) or EGF for 15min at 25ng/μl (a, c, d). Immunoblots are representative of 3 independant biological replicates. e-f, SMYD3 methylation of MAP3K2 does not alter the intrinsic kinase activity of MAP3K2. e, Immunoblot analysis with the indicated antibodies from lysates of 293T cells transfected with control vector, wild-type SMYD3, catalytically dead SMYD3F183A, wild-type MAP3K2, MAP3K2K260A, or kinase dead MAP3K2K385M. f, Methylation of MAP3K2 does not alter its in vitro kinase activity. In vitro kinase assays were performed with the indicated recombinant versions of MAP3K2 (wild-type, SMYD3-resistant K260A mutant, or kinase dead K385 mutant) pre-methylated with wild-type SMYD3 or as a control, inactive SMYD3, using MEK1 as a substrate. MEK1 phosphorylation was detected by immunoblot analysis with the indicated antibody.
