Abstract
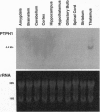
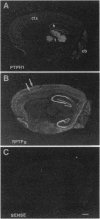
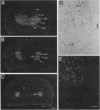
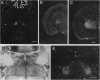
Studies to date have identified only a few proteins that are expressed in a segment-specific manner within the mammalian brain. Here we report that a nonreceptor protein tyrosine phosphatase, PTPH1, is selectively expressed in the adult thalamus. Expression of PTPH1 mRNA is detected in most, but not all, thalamic nuclei. Nuclei that are derived embryonically from the dorsal thalamus and project to the neocortex express this gene, whereas those derived from the ventral thalamus do not. PTPH1 mRNA expression is also restricted to the dorsal thalamus during development and, thus, can serve as a specific marker for the dorsal thalamic nuclei. Since the subcellular localization of PTPH1 protein is not known, its functional role is not clear. However, the restriction of its expression to the thalamic nuclei that have thalamocortical connections suggests that PTPH1 may play a role in the maintenance of these connections or in determining the physiological properties of thalamic relay nuclei.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adachi M., Sekiya M., Miyachi T., Matsuno K., Hinoda Y., Imai K., Yachi A. Molecular cloning of a novel protein-tyrosine phosphatase SH-PTP3 with sequence similarity to the src-homology region 2. FEBS Lett. 1992 Dec 21;314(3):335–339. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81500-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad S., Banville D., Zhao Z., Fischer E. H., Shen S. H. A widely expressed human protein-tyrosine phosphatase containing src homology 2 domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2197–2201. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arpin M., Algrain M., Louvard D. Membrane-actin microfilament connections: an increasing diversity of players related to band 4.1. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;6(1):136–141. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(94)90127-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnea G., Silvennoinen O., Shaanan B., Honegger A. M., Canoll P. D., D'Eustachio P., Morse B., Levy J. B., Laforgia S., Huebner K. Identification of a carbonic anhydrase-like domain in the extracellular region of RPTP gamma defines a new subfamily of receptor tyrosine phosphatases. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1497–1506. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulfone A., Puelles L., Porteus M. H., Frohman M. A., Martin G. R., Rubenstein J. L. Spatially restricted expression of Dlx-1, Dlx-2 (Tes-1), Gbx-2, and Wnt-3 in the embryonic day 12.5 mouse forebrain defines potential transverse and longitudinal segmental boundaries. J Neurosci. 1993 Jul;13(7):3155–3172. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-07-03155.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COGGESHALL R. E. A STUDY OF DIENCEPHALIC DEVELOPMENT IN THE ALBINO RAT. J Comp Neurol. 1964 Apr;122:241–269. doi: 10.1002/cne.901220208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charbonneau H., Tonks N. K. 1002 protein phosphatases? Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:463–493. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.08.110192.002335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church D. M., Banks L. T., Rogers A. C., Graw S. L., Housman D. E., Gusella J. F., Buckler A. J. Identification of human chromosome 9 specific genes using exon amplification. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Nov;2(11):1915–1920. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.11.1915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng G. S., Hui C. C., Pawson T. SH2-containing phosphotyrosine phosphatase as a target of protein-tyrosine kinases. Science. 1993 Mar 12;259(5101):1607–1611. doi: 10.1126/science.8096088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan K. L., Haun R. S., Watson S. J., Geahlen R. L., Dixon J. E. Cloning and expression of a protein-tyrosine-phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1501–1505. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hariharan I. K., Chuang P. T., Rubin G. M. Cloning and characterization of a receptor-class phosphotyrosine phosphatase gene expressed on central nervous system axons in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11266–11270. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmings H. C., Jr, Greengard P., Tung H. Y., Cohen P. DARPP-32, a dopamine-regulated neuronal phosphoprotein, is a potent inhibitor of protein phosphatase-1. Nature. 1984 Aug 9;310(5977):503–505. doi: 10.1038/310503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinck L., Näthke I. S., Papkoff J., Nelson W. J. Beta-catenin: a common target for the regulation of cell adhesion by Wnt-1 and Src signaling pathways. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Dec;19(12):538–542. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90057-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller F., Rimvall K., Barbe M. F., Levitt P. A membrane glycoprotein associated with the limbic system mediates the formation of the septo-hippocampal pathway in vitro. Neuron. 1989 Nov;3(5):551–561. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90265-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt P. A monoclonal antibody to limbic system neurons. Science. 1984 Jan 20;223(4633):299–301. doi: 10.1126/science.6199842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombroso P. J., Murdoch G., Lerner M. Molecular characterization of a protein-tyrosine-phosphatase enriched in striatum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7242–7246. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombroso P. J., Naegele J. R., Sharma E., Lerner M. A protein tyrosine phosphatase expressed within dopaminoceptive neurons of the basal ganglia and related structures. J Neurosci. 1993 Jul;13(7):3064–3074. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-07-03064.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick D. A., Bal T. Sensory gating mechanisms of the thalamus. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1994 Aug;4(4):550–556. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(94)90056-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon A. P., Bradley A. The Wnt-1 (int-1) proto-oncogene is required for development of a large region of the mouse brain. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1073–1085. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90385-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murtha M. T., Leckman J. F., Ruddle F. H. Detection of homeobox genes in development and evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10711–10715. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberdick J., Levinthal F., Levinthal C. A Purkinje cell differentiation marker shows a partial DNA sequence homology to the cellular sis/PDGF2 gene. Neuron. 1988 Jul;1(5):367–376. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90186-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubenstein J. L., Martinez S., Shimamura K., Puelles L. The embryonic vertebrate forebrain: the prosomeric model. Science. 1994 Oct 28;266(5185):578–580. doi: 10.1126/science.7939711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahin M., Dowling J. J., Hockfield S. Seven protein tyrosine phosphatases are differentially expressed in the developing rat brain. J Comp Neurol. 1995 Jan 23;351(4):617–631. doi: 10.1002/cne.903510410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahin M., Hockfield S. Protein tyrosine phosphatases expressed in the developing rat brain. J Neurosci. 1993 Nov;13(11):4968–4978. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-11-04968.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salinas P. C., Nusse R. Regional expression of the Wnt-3 gene in the developing mouse forebrain in relationship to diencephalic neuromeres. Mech Dev. 1992 Dec;39(3):151–160. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(92)90042-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegelbaum S. A. Channel regulation. Ion channel control by tyrosine phosphorylation. Curr Biol. 1994 Mar 1;4(3):242–245. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(00)00054-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takekawa M., Itoh F., Hinoda Y., Arimura Y., Toyota M., Sekiya M., Adachi M., Imai K., Yachi A. Cloning and characterization of a human cDNA encoding a novel putative cytoplasmic protein-tyrosine-phosphatase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Dec 15;189(2):1223–1230. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)92335-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tian S. S., Tsoulfas P., Zinn K. Three receptor-linked protein-tyrosine phosphatases are selectively expressed on central nervous system axons in the Drosophila embryo. Cell. 1991 Nov 15;67(4):675–685. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90063-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel W., Lammers R., Huang J., Ullrich A. Activation of a phosphotyrosine phosphatase by tyrosine phosphorylation. Science. 1993 Mar 12;259(5101):1611–1614. doi: 10.1126/science.7681217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton K. M., Dixon J. E. Protein tyrosine phosphatases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:101–120. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.000533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton K. M., Martell K. J., Kwak S. P., Dixon J. E., Largent B. L. A novel receptor-type protein tyrosine phosphatase is expressed during neurogenesis in the olfactory neuroepithelium. Neuron. 1993 Aug;11(2):387–400. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90193-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Q., Co D., Sommercorn J., Tonks N. K. Cloning and expression of PTP-PEST. A novel, human, nontransmembrane protein tyrosine phosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 25;268(9):6622–6628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Q., Tonks N. K. Isolation of a cDNA clone encoding a human protein-tyrosine phosphatase with homology to the cytoskeletal-associated proteins band 4.1, ezrin, and talin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):5949–5953. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.5949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang X. H., Seow K. T., Bahri S. M., Oon S. H., Chia W. Two Drosophila receptor-like tyrosine phosphatase genes are expressed in a subset of developing axons and pioneer neurons in the embryonic CNS. Cell. 1991 Nov 15;67(4):661–673. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90062-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- den Hertog J., Pals C. E., Jonk L. J., Kruijer W. Differential expression of a novel murine non-receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase during differentiation of P19 embryonal carcinoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 May 15;184(3):1241–1249. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]