Abstract
The resistance among various microbial species (infectious agents) to different antimicrobial drugs has emerged as a cause of public health threat all over the world at a terrifying rate. Due to the pacing advent of new resistance mechanisms and decrease in efficiency of treating common infectious diseases, it results in failure of microbial response to standard treatment, leading to prolonged illness, higher expenditures for health care, and an immense risk of death. Almost all the capable infecting agents (e.g., bacteria, fungi, virus, and parasite) have employed high levels of multidrug resistance (MDR) with enhanced morbidity and mortality; thus, they are referred to as “super bugs.” Although the development of MDR is a natural phenomenon, the inappropriate use of antimicrobial drugs, inadequate sanitary conditions, inappropriate food-handling, and poor infection prevention and control practices contribute to emergence of and encourage the further spread of MDR. Considering the significance of MDR, this paper, emphasizes the problems associated with MDR and the need to understand its significance and mechanisms to combat microbial infections.
1. Introduction
During the last few decades, the incidence of microbial infections has increased dramatically. Continuous deployment of antimicrobial drugs in treating infections has led to the emergence of resistance among the various strains of microorganisms. Multidrug resistance (MDR) is defined as insensitivity or resistance of a microorganism to the administered antimicrobial medicines (which are structurally unrelated and have different molecular targets) despite earlier sensitivity to it [1, 2]. According to WHO, these resistant microorganisms (like bacteria, fungi, viruses, and parasites) are able to combat attack by antimicrobial drugs, which leads to ineffective treatment resulting in persistence and spreading of infections. Although the development of MDR is a natural phenomenon, extensive rise in the number of immunocompromised conditions, like HIV-infection, diabetic patients, individuals who have undergone organ transplantation, and severe burn patients, makes the body an easy target for hospital acquired infectious diseases, thereby contributing to further spread of MDR. Studies from WHO report have shown very high rates of resistance (Table 1) in bacteria such as Escherichia coli against antibiotics as cephalosporin and fluoroquinolones, Klebsiella pneumoniae against cephalosporin and carbapenems, Staphylococcus aureus against methicillin, Streptococcus pneumoniae against penicillin, Nontyphoidal Salmonella against fluoroquinolones, Shigella species against fluoroquinolones, Neisseria gonorrhoeae against cephalosporin, and Mycobacterium tuberculosis against rifampicin, isoniazid, and fluoroquinolone causing common infections [3, 4] (like urinary tract infections, pneumonia, and bloodstream infections) and high percentage of hospital-acquired infections. A limited number of antifungal drugs are available for the treatment of chronic fungal infections. Resistance to drugs such as polyene macrolides (amphotericin B), azole derivatives (ketoconazole, fluconazole, itraconazole, and voriconazole), DNA and RNA synthesis inhibitors (flucytosine), and 1,3-β-glucan synthase inhibitors (echinocandins) exists in isolates of Candida spp., Aspergillus spp., Cryptococcus neoformans, Trichosporon beigelii, Scopulariopsis spp., and Pseudallescheria boydii [5]. Prolonged drug exposure and nonstop viral replication result in the advent of various resistant strains and persistence of infections despite therapy. This has made antiviral resistance a matter of concern in immunocompromised patients. Consequences of antiviral drug resistance were observed in immunosuppressed transplant recipients and oncology patients infected by either cytomegalovirus (CMV), herpes simplex virus (HSV), Varicella-zoster virus (VZV) [6], human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), influenza A virus, hepatitis C (HCV), or hepatitis B virus (HBV) [7]. Parasitic multidrug resistance has been analyzed in isolates of Plasmodia, Leishmania, Entamoeba, Trichomonas vaginalis, schistosomes [8, 9], and Toxoplasma gondii [10–12] against drugs such as, chloroquine, pyrimethamine, artemisinin, pentavalent antimonials, miltefosine, paromomycin, and amphotericin B [13, 14] as well as atovaquone and sulfadiazine. One of the most prime examples of disease prone to MDR is malaria, caused by Plasmodium falciparum [15]. Another protozoan parasite, Entamoeba spp., causes amoebiasis which is also a major public health threat in many tropical and subtropical countries [16]. A global health threat of schistosomiasis is also considered similar to that of malaria and other chronic diseases [9]. This review article emphasizes the significance of MDR, various mechanisms contributing to its development, and problems associated with MDR and its possible remedies.
Table 1.
Common drug resistant microbes and diseases caused by them.
| Drug(s) resistant to | Typical diseases | |
|---|---|---|
| Name of Bacterium | ||
| Escherichia coli | Cephalosporins and fluoroquinolones | Urinary tract infections and blood stream infections |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae | Cephalosporins and carbapenems | Pneumonia, blood stream, and urinary tract infections |
| Staphylococcus aureus | Methicillin | Wound and blood stream infections |
| Streptococcus pneumoniae | Penicillin | Pneumonia, meningitis, and otitis |
| Nontyphoidal Salmonella | Fluoroquinolones | Foodborne diarrhoea, blood stream infections |
| Shigella species | Fluoroquinolones | Diarrhoea (bacillary dysentery) |
| Neisseria gonorrhoeae | Cephalosporins | Gonorrhoea |
| Mycobacterium tuberculosis | Rifampicin, isoniazid, and fluoroquinolone [4] | Tuberculosis |
| Name of Fungi | ||
| Candida spp. | Fluconazole and echinocandins [5] | Candidiasis |
| Cryptococcus neoformans | Fluconazole [17] | Cryptococcosis |
| Aspergillus spp. | Azoles [18] | Aspergillosis |
| Scopulariopsis spp. | Amphotericin B, flucytosine, and azoles [19] | Onychomycosis |
| Name of Virus | ||
| Cytomegalovirus (CMV) | Ganciclovir and foscarnet [20] | In AIDS and oncology patients |
| Herpes simplex virus (HSV) | Acyclovir, famciclovir, and valacyclovir [21] | Herpes simplex |
| Human immunodeficiency | ||
| virus (HIV) | Antiretroviral drugs [22] | AIDS |
| Influenza virus | Adamantane derivatives (Amantadine and rimantadine) and neuraminidase inhibitors [23] | Influenza |
| Varicella zoster virus | Acyclovir and valacyclovir [21] | Chicken pox |
| Hepatitis B virus (HBV) | Lamivudine [24] | Hepatitis B |
| Name of Parasite | ||
| Plasmodia spp. | Chloroquine, artemisinin, and atovaquone [25] | Malaria |
| Leishmania spp. | Pentavalent antimonials, miltefosine, paromomycin, and amphotericin B [13, 14] | Leishmaniasis |
| Schistosomes | Praziquantel and oxamniquine [26, 27] | Schistosomiasis |
| Entamoeba | Metronidazole [28] | Amoebiasis |
| Trichomonas vaginalis | Nitroimidazoles [29] | Trichomoniasis |
| Toxoplasma gondii | Artemisinin, atovaquone, and sulfadiazine [10–12] | Toxoplasmosis |
2. Significance of MDR
Antimicrobial drugs have been used for several decades across the world. Surveillance in different regions of the world such as Africa, some parts of America, Eastern Mediterranean Region, Europe, South-East Asia, and Western Pacific Region has shown that many infectious microorganisms have evolved over the years and there is an alarming high number of antibiotic-resistant species enabling themselves to resist the inhibitory effects of these drugs. Not only a single but almost all the capable infecting agents (e.g., bacteria, fungi, virus, and parasite) have employed high levels of MDR with enhanced morbidity and mortality and, thus, are referred to as “super bugs.” Tuberculosis, pneumonia, HIV, influenza, malaria, yeast infections, and many other deadly diseases are major causes of deaths in modern era, therefore, indicating MDR as a serious worldwide threat to public health. The chances of controlling tuberculosis have decreased due to resistance of MTB to respective antibiotics, thus, making it a global concern. A 2012 survey suggests that an overall 6% of recent TB cases and 20% of formerly treated TB cases are likely to possess MDR, while 92 countries were found to have extensively drug resistant TB (XDR-TB). Another bacterial infection, pneumonia, has become untreatable because its causative agent has been found to be resistant to cephalosporin as well as carbapenems due to extended spectrum β-lactamases (ESBL) mediated mechanism [30], thereby rendering all available treatment using β-lactam antibiotics. In recent years, HIV drug resistance has driven the antiretroviral therapy failure to such an extent that it is charging exorbitant rates along with a number of side effects. The protozoan parasite responsible for malaria had embarked on showing resistance to some of its most effective drugs, chloroquine, artemisinin, and pyrimethamine [31]. This has resulted in replacement of these old ineffective drugs by novel drugs, which has increased the health care expenses. The emergence of resistance to antifungal drugs in invasive yeast infections, for example, Candidiasis, has led to worldwide morbidity and mortality, contributing to global economic burden. Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) or MDR is the reason why microbes fail to respond to standard drugs, thus, extending the duration of course of treatment further increasing the health care costs which tend to worsen the situation of people who are not capable of such expenses.
3. Problems Associated with MDR
Antimicrobial resistance is associated with high mortality rates and high medical costs and has a significant impact on the effectiveness of antimicrobial agents (Figure 1). MDR provokes obstruction in disease control by intensifying the possibility of spreading of resistant pathogens, thus, declining efficacy of treatment and, hence, resulting in prolonged time of infection in patient. The cost of treatment is also increased due to MDR as the pathogens have become resistant to commercially available drugs, which has triggered the use of more expensive therapies. The rate of success of present-day medical applications like organ transplantation and cancer chemotherapy has contributed immensely towards development of MDR. Differences in the resistance profiles of bacterial and fungal pathogens as well as the quality of public hygiene also have a considerable impact on the effectiveness of antimicrobial agents. Expansion of global trade and tourism lead to increased potential of MDR to spread all over the world and decrease in export and import of various products affecting the economy of developing countries [4, 32, 33].
Figure 1.
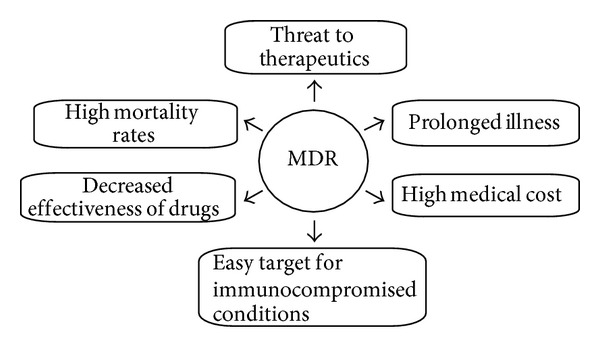
Problems associated with MDR.
4. Classification of MDR
Despite of administration of appropriate doses of drugs for a specific duration of time, survival of various microbial strains recommends the high levels of resistance developed in them. This clinical failure is due to not only the antimicrobial resistance but also the suppressed immune function, poor/deprived drug bioavailability, or increased rate of drug metabolism. Persistence of microbes after conventional/standard treatments points out different types of antimicrobial drug resistance which is an expanding problem in medical world. MDR can be classified (Figure 2) as primary or secondary resistance.
Figure 2.
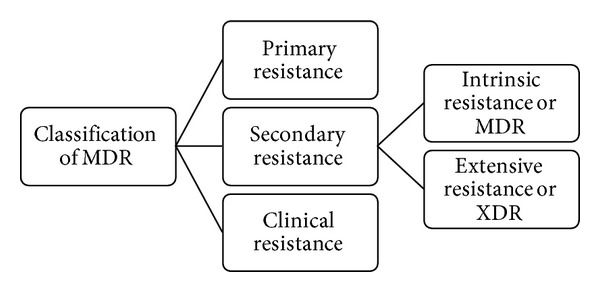
Classification of MDR.
4.1. Primary Resistance
It occurs when the organism has never encountered the drug of interest in a particular host.
4.2. Secondary Resistance
Also known as “acquired resistance,” this term is used to describe the resistance that only arises in an organism after an exposure to the drug [5, 34]. It may further be classified as follows.
Intrinsic resistance: it refers to the insensitivity of all microorganisms of a single species to certain common first-line drugs, which are used to treat diseases based on the clinical evidence of the patient. It is also known as multidrug resistance (MDR), for example, Mycobacterium tuberculosis to rifampicin and isoniazid or Candida spp. to fluconazole [5].
Extensive resistance: it defines the ability of organisms to withstand the inhibitory effects of at least one or two most effective antimicrobial drugs. Also termed as XDR, this seemed to arise in patients after they have undergone a treatment with first line drugs, for example, XDR-TB resistance against fluoroquinolone [35, 36].
4.3. Clinical Resistance
In addition to the above-mentioned types, clinical resistance is defined by the situation in which the infecting organism is inhibited by a concentration of an antimicrobial agent that is associated with a high likelihood of therapeutic failure or reappearance of infections within an organism due to impaired host immune function. In other words, the pathogen is inhibited by an antimicrobial concentration that is higher than could be safely achieved with normal dosing [5].
5. Mechanisms of MDR
Resistance is the term referred to as the insensitivity of a microbe to an antimicrobial drug when compared with other isolates of the same species. Although several new drugs have been introduced commercially, this development of resistance among infectious microorganisms is increasing especially in patients under prolonged drug exposure [5]. Antimicrobial drugs generally act on the microbes either by inhibiting a metabolic pathway like nucleotide synthesis which in turn leads to the inhibition of DNA/RNA synthesis and further protein synthesis and disruption of the cell membrane or by competing with the substrate of any enzyme involved in cell wall synthesis (e.g., chitin synthase) [37]. Microorganisms have evolved a multitude of mechanisms to overcome the effectiveness of drugs, thereby surviving exposure to the drugs. This section will mainly describe the resistance mechanisms that the microbes develop to avoid getting killed by the drugs (Figure 3).
Figure 3.
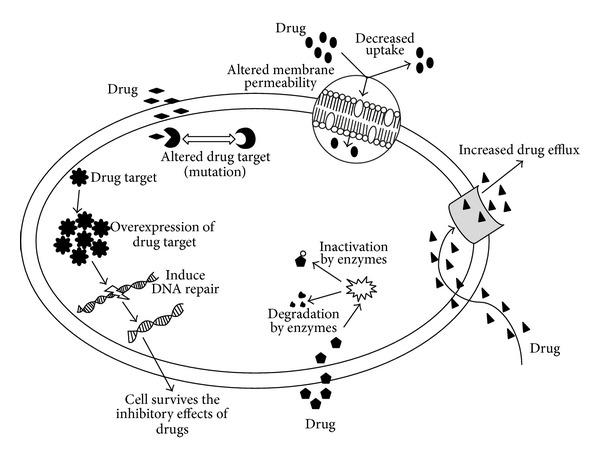
Mechanisms of MDR.
Cell wall, in both bacteria and fungi, plays a crucial role in their survival. As discussed above, drugs inhibit the cell wall synthesis by binding with the peptidoglycan layer in bacteria or affecting ergosterol synthesis (e.g., polyenes [38]) in fungi, thus, blocking the cell growth and division. These organisms undergo certain chromosomal mutations [39] or exchange of extrachromosomal DNA elements through conjugation or transformation (horizontal gene transfer) such as in K. pneumoniae [4], which can cause alteration in the cell membrane composition (e.g., a reduction in the ergosterol content in fungal plasma membrane) resulting in decreased permeability and uptake of drugs into the cell [1, 5, 37, 40]. Altered membrane composition (such as β-1,3-glucan and lipid content in fungal cell membrane) also leads to lack of active target sites for the drugs (e.g., echinocandins in fungi [38]) to bind. Mutations in the genes encoding for the target cause modifications at the molecular level and retain cellular function by reducing susceptibility to inhibition [1, 5, 37, 41].
Another mechanism of MDR was found to be an overexpression of drug target enzymes leading to target bypass due to modification in certain metabolic pathways (e.g., azoles and allylamines in fungi [38]), which causes production of alternate target molecules and interference in some protein synthesis. This can influence the access of drugs to the target sites.
Inactivation or enzymatic degradation of antimicrobials by hydrolysis of ester or amide bonds (such as resistance to β-lactams due to β-lactamases, etc.) and chemical transformation of these compounds by acetylation, phosphorylation, adenylation, glycosylation, and hydroxylation have also become increasingly apparent as causes of MDR [1, 37, 39]. The resistant strains of clinical isolates of different microorganisms have developed the ability to oxidize or reduce the antimicrobial compounds to prevent their interaction with the respective targets [37]. Antiviral drugs usually target viral DNA polymerase having the reverse transcriptase activity to inhibit the viral replication. Drug resistant mutant strains undergo mutations in the reverse transcriptase domains of the polymerase gene which affects the interaction between the drug and the enzyme. Resistance to the inhibitory effects of drug on the enzyme can also emerge due to any conformational changes or altered binding of substrate to the viral polymerase [6]. With the lack of effective antiparasitic vaccines yet in sight and new drugs developing slowly, MDR in parasites is emerging as a global public health threat. These parasites such as Plasmodia spp. and Toxoplasma gondii, like bacteria or fungi, also undergo certain point mutations/substitutions resulting in altered drug targets, alter calcium homeostasis in endoplasmic reticulum [11], and expel drugs (e.g., chloroquine, atovaquone, antifolate combination drugs, and artemisinin) out of the cells [10, 25].
MDR mediated by drug efflux pumps remains the predominant mechanism of MDR. The overexpression of genes encoding for ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter membrane proteins (e.g., P-glycoprotein (Pgp)), also known as the multidrug efflux pumps which are responsible for the export or expulsion of drugs out of the cell [3, 39, 42], usually generates MDR and continues cellular functions without any interference. Overexpression of P-glycoprotein, in Entamoeba spp. and Leishmania spp. membrane or multidrug resistant proteins (MRP), affects the fluidity and permeability, leading to an ATP-dependent efflux of the antimicrobials and decreasing their intracellular concentration [16, 43, 44]. MDR is also employed by cancer cells, which limits the long-term use of chemotherapy. An insight into the mechanisms involved in the chemoresistance, which can occur either at the beginning of the therapy (innate) or during the course of treatment, reveals that the cancer cells exhibit overexpression of certain multidrug resistance proteins (e.g., MRP and Pgp) which induce DNA repair mechanism, inhibit apoptosis, alter drug targets, and modify cell membrane composition as well as promoting an increased efflux of drugs preventing proper diffusion into the cells [45, 46].
6. Remedies for MDR
The development of MDR is a complicated issue which has become an international dreadful concern. To decrease the rise and spread of MDR, cooperative efforts (Figure 4) are requisite because diseases which were curable earlier are becoming major causes of deaths in this era [1, 4, 32]. Moreover, focusing on areas which are susceptible to inappropriate use of antimicrobials by implementation of antibiotic stewardship (defined as coordinated interventions designed to improve and measure the appropriate use of antimicrobials) is the need of the hour [47]. In fact, various antimicrobial stewardship programs (ASPs) are conducted nowadays to optimize antimicrobial therapy, reduce treatment-related cost, improve clinical outcomes and safety, and minimize or stabilize MDR [48]. Interventions through ASPs are either by restricting the availability of selected antimicrobial agents, known as “front-end,” or by examining broad spectrum use of antibiotics and then streamlining or discontinuing it, known as “back-end” [49]. Therefore, there is an urgent need of support and coordination at the global, regional, subregional, and national level to serve in future progress [4].
Figure 4.
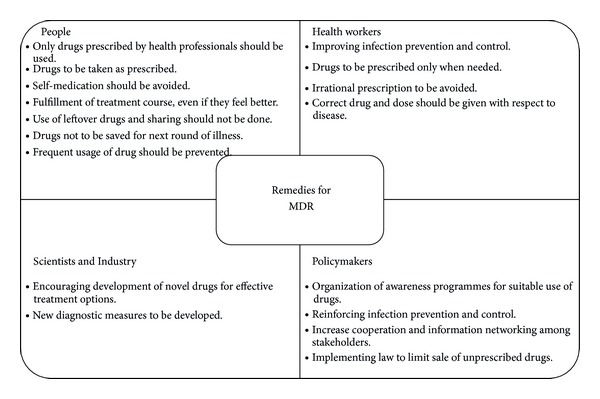
Remedies of MDR.
7. Conclusion
Rapid increase of severe systemic infections and the spread of resistant microorganisms are indisputable facts. Inadequacy of available antimicrobial drugs compels continuous development of newer drugs. Moreover, various awareness programmes which should facilitate their appropriate use to reestablish dominance over diseases must be implemented. MDR is an unavoidable natural phenomenon, posing a serious worldwide menace to public health. A cooperative action at global level is a must to combat the MDR. Pathogens tend to adopt various resistance mechanisms to survive the unfavorable conditions. Improved knowledge of molecular mechanisms controlling MDR should facilitate the development of novel therapies to combat these intransigent infections and will help cultivate a deeper understanding of the pathobiology of microbial organisms.
Acknowledgments
Saif Hameed thanks the financial assistance in the form of Young Scientist award (SR/FT/LS-12/2012) from Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB), New Delhi. The authors thank Professor S. M. Paul Khurana, Dean, Faculty of Science, Engineering & Technology, for encouragement.
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
Authors' Contribution
Jyoti Tanwar and Shrayanee Das equally contributed to this work.
References
- 1.Singh V. Microbial Pathogens and Strategies for Combating Them: Science, Technology and Education. Vol. 1. Formatex Research Center; 2013. Antimicrobial resistance; pp. 291–296. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Popęda M, Płuciennik E, Bednarek AK. Proteins in cancer resistance. Postępy Higieny i Medycyny Doświadczalnej. 2014;68:616–632. doi: 10.5604/17322693.1103268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Nikaido H. Multidrug resistance in bacteria. Annual Review of Biochemistry. 2009;78:119–146. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.78.082907.145923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Antimicrobial Resistance Global Report on Surveillance. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2014. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Loeffler J, Stevens DA. Antifungal drug resistance. Clinical Infectious Diseases. 2003;36(1):S31–S41. doi: 10.1086/344658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Strasfeld L, Chou S. Antiviral drug resistance: mechanisms and clinical implications. Infectious Disease Clinics of North America. 2010;24(2):413–437. doi: 10.1016/j.idc.2010.01.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Margeridon-Thermet S, Shafer RW. Comparison of the mechanisms of drug resistance among HIV, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C. Viruses. 2010;2(12):2696–2739. doi: 10.3390/v2122696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ullman B. Multidrug resistance and P-glycoproteins in parasitic protozoa. Journal of Bioenergetics and Biomembranes. 1995;27(1):77–84. doi: 10.1007/BF02110334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Greenberg RM. New approaches for understanding mechanisms of drug resistance in schistosomes. Parasitology. 2013;140(12):1534–1546. doi: 10.1017/S0031182013000231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.McFadden DC, Tomavo S, Berry EA, Boothroyd JC. Characterization of cytochrome b from Toxoplasma gondii and Q(o) domain mutations as a mechanism of atovaquone-resistance. Molecular and Biochemical Parasitology. 2000;108(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/s0166-6851(00)00184-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Nagamune K, Moreno SNJ, Sibley LD. Artemisinin-resistant mutants of Toxoplasma gondii have altered calcium homeostasis. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 2007;51(11):3816–3823. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00582-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Doliwa C, Escotte-Binet S, Aubert D, et al. Sulfadiazine resistance in Toxoplasma gondii: no involvement of overexpression or polymorphisms in genes of therapeutic targets and ABC transporters. Parasite. 2013;20(19):1–6. doi: 10.1051/parasite/2013020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Vanaerschot M, Dumetz F, Roy S, Ponte-Sucre A, Arevalo J, Dujardin JC. Treatment failure in leishmaniasis: drug-resistance or another (epi-) phenotype? Expert Review of Anti-Infective Therapy. 2014;12(8):937–946. doi: 10.1586/14787210.2014.916614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Mohapatra S. Drug resistance in leishmaniasis: newer developments. Tropical Parasitology. 2014;4(1):4–9. doi: 10.4103/2229-5070.129142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Yang Z, Li C, Miao M, et al. Multidrug- resistant genotypes of plasmodium falciparum, Myanmar. Emerging Infectious Diseases. 2011;17(3):498–501. doi: 10.3201/eid1703.100870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Bansal D, Sehgal R, Chawla Y, Malla N, Mahajan RC. Multidrug resistance in amoebiasis patients. Indian Journal of Medical Research. 2006;124(2):189–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Rodero L, Mellado E, Rodriguez AC, et al. G484S amino acid substitution in lanosterol 14-α demethylase (ERG11) is related to fluconazole resistance in a recurrent Cryptococcus neoformans clinical isolate. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 2003;47(11):3653–3656. doi: 10.1128/AAC.47.11.3653-3656.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Howard SJ, Arendrup MC. Acquired antifungal drug resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus: epidemiology and detection. Medical Mycology. 2011;49(1):S90–S95. doi: 10.3109/13693786.2010.508469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Cuenca-Estrella M, Gomez-Lopez A, Mellado E, Buitrago MJ, Monzón A, Rodriguez-Tudela JL. Scopulariopsis brevicaulis, a fungal pathogen resistant to broad-spectrum antifungal agents. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 2003;47(7):2339–2341. doi: 10.1128/AAC.47.7.2339-2341.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Lurain NS, Chou S. Antiviral drug resistance of human cytomegalovirus. Clinical Microbiology Reviews. 2010;23(4):689–712. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00009-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Wutzler P. Antiviral therapy of herpes simplex and varicella-zoster virus infections. Intervirology. 1997;40(5-6):343–356. doi: 10.1159/000150567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Cortez KJ, Maldarelli F. Clinical management of HIV drug resistance. Viruses. 2011;3(4):347–378. doi: 10.3390/v3040347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Hurt AC. The epidemiology and spread of drug resistant human influenza viruses. Current Opinion in Virology. 2014;8:22–29. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2014.04.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Suppiah J, Zain RM, Nawi SH, Bahari N, Saat Z. Drug-resistance associated mutations in polymerase (p) gene of hepatitis B virus isolated from malaysian HBV carriers. Hepatitis Monthly. 2014;14(1):7 pages. doi: 10.5812/hepatmon.13173.e13173 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Bloland PB. Drug Resistance in Malaria. World Health Organization; 2001. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Fallon PG, Doenhoff MJ. Drug-resistant schistosomiasis: resistance to praziquantel and oxamniquine induced in Schistosoma mansoni in mice is drug specific. The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene. 1994;51(1):83–88. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1994.51.83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Qi L, Cui J. A schistosomiasis model with praziquantel resistance. Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society. 2013;2013:13 pages.945767 [Google Scholar]
- 28.Bansal D, Malla N, Mahajan RC. Drug resistance in amoebiasis. Indian Journal of Medical Research. 2006;123(2):115–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Muzny CA, Schwebke JR. The clinical spectrum of Trichomonas vaginalis infection and challenges to management. Sexually Transmitted Infections. 2013;89(6):423–425. doi: 10.1136/sextrans-2012-050893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Bennett JW, Robertson JL, Hospenthal DR, et al. Impact of extended spectrum beta-lactamase producing Klebsiella pneumoniae infections in severely burned patients. Journal of the American College of Surgeons. 2010;211(3):391–399. doi: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2010.03.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Olasehinde GI, Ojurongbe O, Adeyeba AO, et al. In vitro studies on the sensitivity pattern of Plasmodium falciparum to anti-malarial drugs and local herbal extracts. Malaria Journal. 2014;13(article 63) doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-13-63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.World Health Organization. Antimicrobial resistance. 2014.
- 33.Fishbain J, Peleg AY. Treatment of Acinetobacter infections. Clinical Infectious Diseases. 2010;51(1):79–84. doi: 10.1086/653120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Khalilzadeh S, Boloorsaz MR, Safavi A, Farnia P, Velayati AA. Primary and acquired drug resistance in childhood tuberculosis. Eastern Mediterranean Health Journal. 2006;12(6):909–914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Lee CR, Cho IH, Jeong BC, Lee SH. Strategies to minimize antibiotic resistance. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2013;10(9):4274–4304. doi: 10.3390/ijerph10094274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Marks SM, Flood J, Seaworth B, et al. Treatment practices, outcomes, and costs of multidrug-resistant and extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis, United States, 2005–2007. Emerging Infectious Diseases. 2014;20(5):812–821. doi: 10.3201/eid2005.131037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Chethana GS, Hari venkatesh KR, Mirzaei F, Gopinath SM. Review on multidrug resistant bacteria and its implication in medical sciences. Journal of Biological Scientific Opinion. 2013;1(1):32–37. [Google Scholar]
- 38.He X, Li S, Kaminskyj SG. Using Aspergillus nidulans to identify antifungal drug resistance mutations. Eukaryotic Cell. 2013;13(2):288–294. doi: 10.1128/EC.00334-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Alekshun MN, Levy SB. Molecular mechanisms of antibacterial multidrug resistance. Cell. 2007;128(6):1037–1050. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.03.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Tenover FC. Mechanisms of antimicrobial resistance in bacteria. The American Journal of Medicine. 2006;119(6):S3–S10. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2006.03.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Dzidic S, Suskovic J, Kos B. Antibiotic resistance mechanisms in bacteria: biochemical and genetic aspects. Food Technology and Biotechnology. 2008;46(1):11–21. [Google Scholar]
- 42.Li XZ, Nikaido H. Efflux-mediated drug resistance in bacteria: an update. Drugs. 2009;69(12):1555–1623. doi: 10.2165/11317030-000000000-00000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Orozco E, López C, Gómez C, et al. Multidrug resistance in the protozoan parasite Entamoeba histolytica . Parasitology International. 2002;51(4):353–359. doi: 10.1016/s1383-5769(02)00041-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Ouellette M, Légaré D, Papadopoulou B. Multidrug resistance and ABC transporters in parasitic protozoa. Journal of Molecular Microbiology and Biotechnology. 2001;3(2):201–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Kunjachan S, Rychlik B, Storm G, Kiessling F, Lammers T. Multidrug resistance: physiological principles and nanomedical solutions. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews. 2013;65(13-14):1852–1865. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2013.09.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Wu CP, Ohnuma S, Ambudkar SV. Discovering natural product modulators to overcome multidrug resistance in cancer chemotherapy. Current Pharmaceutical Biotechnology. 2011;12(4):609–620. doi: 10.2174/138920111795163887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Hamilton KW, Fishman NO. Antimicrobial stewardship interventions: thinking inside and outside the box. Infectious Disease Clinics of North America. 2014;28(2):301–313. doi: 10.1016/j.idc.2014.01.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Owens RC., Jr. Antimicrobial stewardship: concepts and strategies in the 21st century. Diagnostic Microbiology and Infectious Disease. 2008;61(1):110–128. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2008.02.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Moehring RW, Anderson DJ. Antimicrobial stewardship as part of the infection prevention effort. Current Infectious Disease Reports. 2012;14(6):592–600. doi: 10.1007/s11908-012-0289-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


