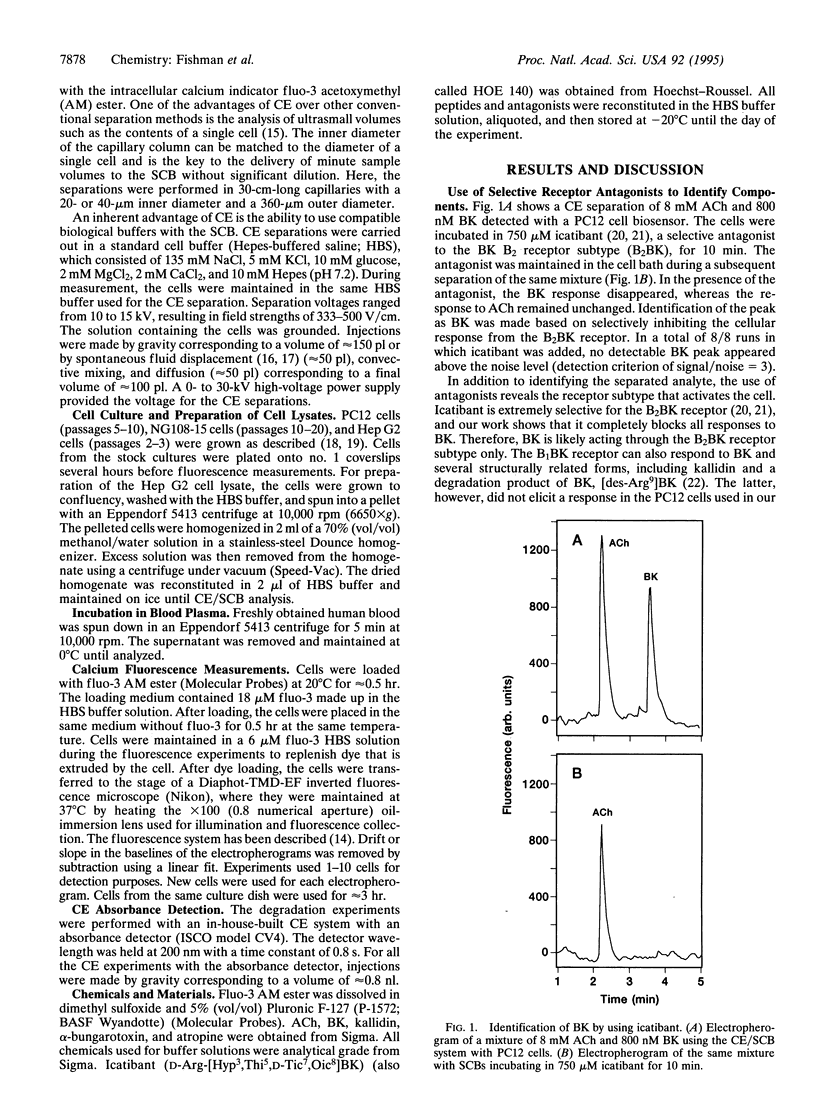
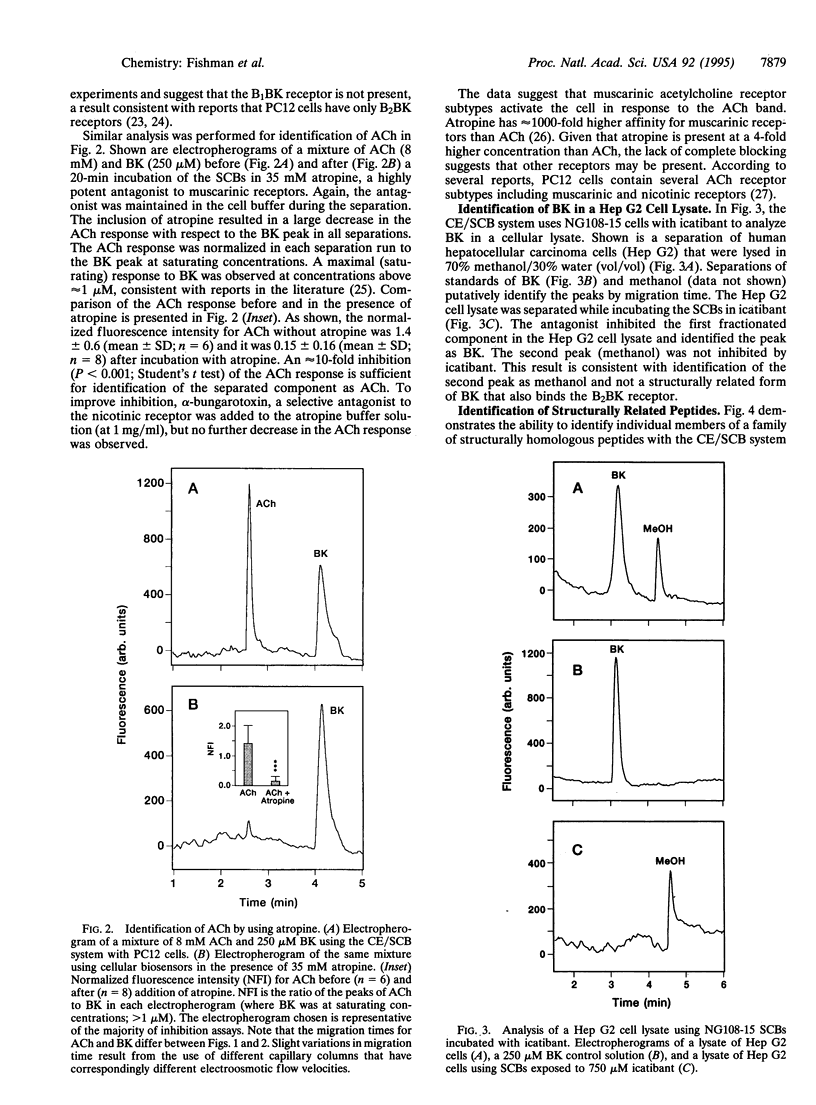
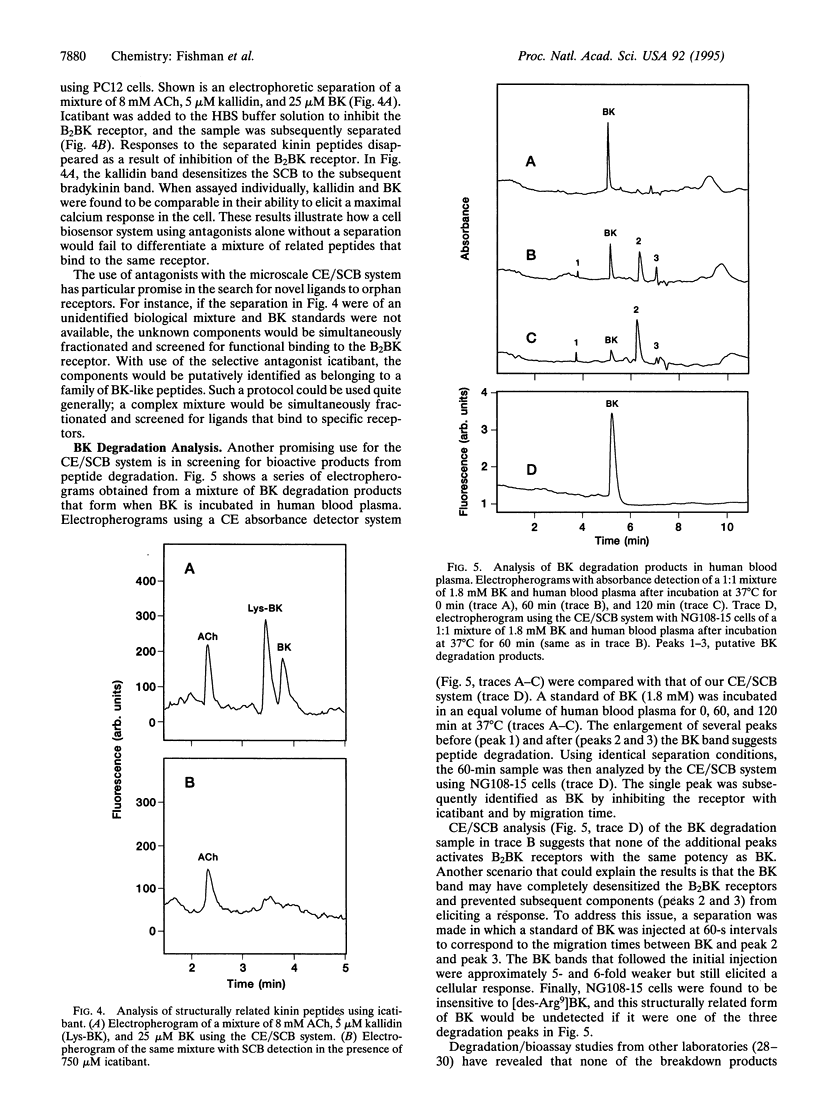
Abstract
A capillary electrophoresis system with single-cell biosensors as a detector has been used to separate and identify ligands in complex biological samples. The power of this procedure was significantly increased by introducing antagonists that inhibited the cellular response from selected ligand-receptor interactions. The single-cell biosensor was based on the ligand-receptor binding and G-protein-mediated signal transduction pathways in PC12 and NG108-15 cell lines. Receptor activation was measured as increases in cytosolic free calcium ion concentration by using fluorescence microscopy with the intracellular calcium ion indicator fluo-3-acetoxymethyl ester. Specifically, a mixture of bradykinin (BK) and acetylcholine (ACh) was fractionated and the components were identified by inhibiting the cellular response with icatibant (HOE 140), a selective antagonist to the BK B2 receptor subtype (B2BK), and atropine, an antagonist to muscarinic ACh receptor subtypes. Structurally related forms of BK were also identified based on inhibiting B2BK receptors. Applications of this technique include identification of endogenous BK in a lysate of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells (Hep G2) and screening for bioactivity of BK degradation products in human blood plasma. The data demonstrate that the use of antagonists with a single-cell biosensor separation system aids identification of separated components and receptor subtypes.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bathon J. M., Proud D. Bradykinin antagonists. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1991;31:129–162. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.31.040191.001021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgermeister W., Klein W. L., Nirenberg M., Witkop B. Comparative binding studies with cholinergic ligands and histrionicotoxin at muscarinic receptors of neural cell lines. Mol Pharmacol. 1978 Sep;14(5):751–767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bush A. B., Borden L. A., Greene L. A., Maxfield F. R. Nerve growth factor potentiates bradykinin-induced calcium influx and release in PC12 cells. J Neurochem. 1991 Aug;57(2):562–574. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb03787.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elferink L. A., Peterson M. R., Scheller R. H. A role for synaptotagmin (p65) in regulated exocytosis. Cell. 1993 Jan 15;72(1):153–159. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90059-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fasolato C., Pandiella A., Meldolesi J., Pozzan T. Generation of inositol phosphates, cytosolic Ca2+, and ionic fluxes in PC12 cells treated with bradykinin. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 25;263(33):17350–17359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman H. A., Amudi N. M., Lee T. T., Scheller R. H., Zare R. N. Spontaneous injection in microcolumn separations. Anal Chem. 1994 Jul 15;66(14):2318–2329. doi: 10.1021/ac00086a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman H. A., Scheller R. H., Zare R. N. Microcolumn sample injection by spontaneous fluid displacement. J Chromatogr A. 1994 Sep 30;680(1):99–107. doi: 10.1016/0021-9673(94)80057-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamprecht B., Glaser T., Reiser G., Bayer E., Propst F. Culture and characteristics of hormone-responsive neuroblastoma X glioma hybrid cells. Methods Enzymol. 1985;109:316–341. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(85)09096-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hock F. J., Wirth K., Albus U., Linz W., Gerhards H. J., Wiemer G., Henke S., Breipohl G., König W., Knolle J. Hoe 140 a new potent and long acting bradykinin-antagonist: in vitro studies. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Mar;102(3):769–773. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12248.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy R. T., Oates M. D., Cooper B. R., Nickerson B., Jorgenson J. W. Microcolumn separations and the analysis of single cells. Science. 1989 Oct 6;246(4926):57–63. doi: 10.1126/science.2675314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leal W. S., Shi X., Liang D., Schal C., Meinwald J. Application of chiral gas chromatography with electroantennographic detection to the determination of the stereochemistry of a cockroach sex pheromone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Feb 14;92(4):1033–1037. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.4.1033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leal W. S., Shi X., Nakamuta K., Ono M., Meinwald J. Structure, stereochemistry, and thermal isomerization of the male sex pheromone of the longhorn beetle Anaglyptus subfasciatus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Feb 14;92(4):1038–1042. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.4.1038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little H. J. Mechanisms that may underlie the behavioural effects of ethanol. Prog Neurobiol. 1991;36(3):171–194. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(91)90029-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConnell H. M., Owicki J. C., Parce J. W., Miller D. L., Baxter G. T., Wada H. G., Pitchford S. The cytosensor microphysiometer: biological applications of silicon technology. Science. 1992 Sep 25;257(5078):1906–1912. doi: 10.1126/science.1329199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLane K. E., Tang F., Conti-Tronconi B. M. Localization of sequence segments forming a kappa-bungarotoxin-binding site on the alpha 3 neuronal nicotinic receptor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 25;265(3):1537–1544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nardone J., Gerald C., Rimawi L., Song L., Hogan P. G. Identification of a B2 bradykinin receptor expressed by PC12 pheochromocytoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 May 10;91(10):4412–4416. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.10.4412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechnitz G. A., Riechel T. L., Kobos R. K., Meyerhoff M. E. Glutamine-selective membrane electrode that uses living bacterial cells. Science. 1978 Jan 27;199(4327):440–441. doi: 10.1126/science.619467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shear J. B., Fishman H. A., Allbritton N. L., Garigan D., Zare R. N., Scheller R. H. Single cells as biosensors for chemical separations. Science. 1995 Jan 6;267(5194):74–77. doi: 10.1126/science.7809609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheikh I. A., Kaplan A. P. Mechanism of digestion of bradykinin and lysylbradykinin (kallidin) in human serum. Role of carboxypeptidase, angiotensin-converting enzyme and determination of final degradation products. Biochem Pharmacol. 1989 Mar 15;38(6):993–1000. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(89)90290-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheikh I. A., Kaplan A. P. Studies of the digestion of bradykinin, Lys-bradykinin, and des-Arg9-bradykinin by angiotensin converting enzyme. Biochem Pharmacol. 1986 Jun 15;35(12):1951–1956. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(86)90726-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shima C., Majima M., Katori M. A stable metabolite, Arg-Pro-Pro-Gly-Phe, of bradykinin in the degradation pathway in human plasma. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1992 Oct;60(2):111–119. doi: 10.1254/jjp.60.111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirth K., Hock F. J., Albus U., Linz W., Alpermann H. G., Anagnostopoulos H., Henk S., Breipohl G., König W., Knolle J. Hoe 140 a new potent and long acting bradykinin-antagonist: in vivo studies. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Mar;102(3):774–777. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12249.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]