Fig. 1.
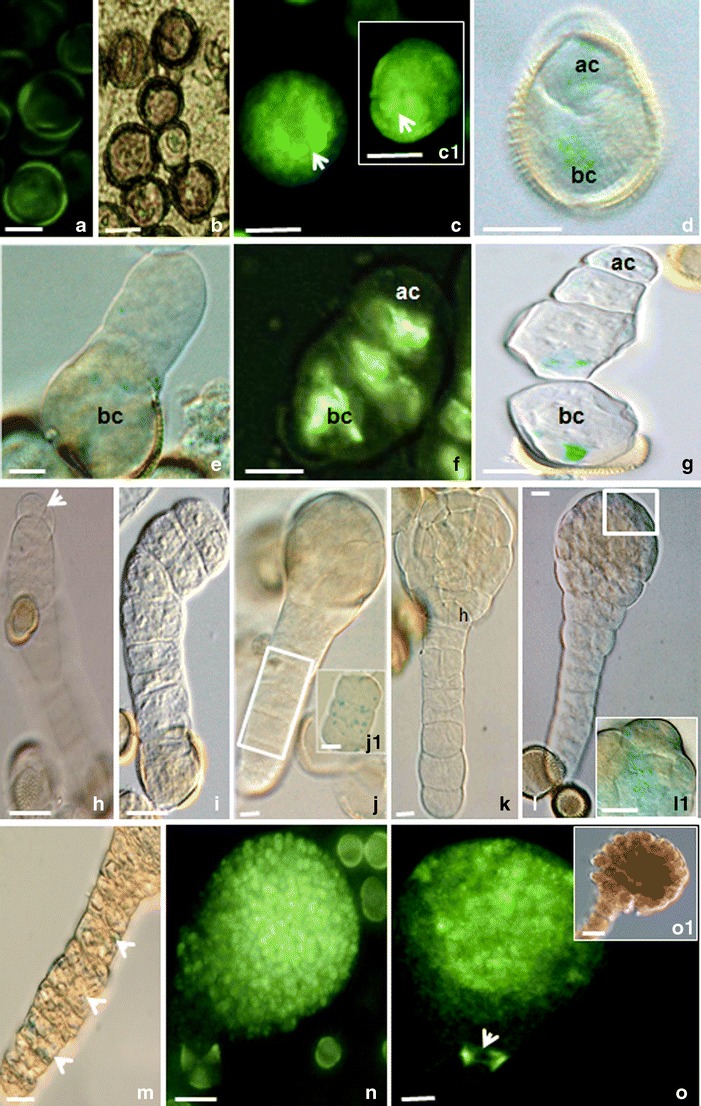
Local auxin distribution in the “mild” heat-treated microspores and MDEs of B. napus. a Uni-nucleated control microspores. Autofluorescence. b Uni-nucleated microspores 2 days co-cultured with A. tumefaciens. c -c1 Microspores with unequal auxin distribution on the one pole (arrows). d Two-celled pro-embryo with the basal (bc) and apical (ac) cells. e, f Linear file of three cells with the DR5 (e) or DR5rev (f) activities in all cells. g Linear file of four cells with higher DR5 activity in the basal cell (bc). h–l The pro-embryo proper with the suspensor-like structure. h Two-celled pro-embryo proper with a long suspensor-like filament. The tip cell of the suspensor-like structure was delineated to become the embryo proper after longitudinal division. i The embryo proper in the octant stage. j The globular embryo stage with the DR5 activity in the cells of the suspensor-like structure (j1). k The embryo proper in the dermatogen stage. Note the hypophysis region (h). l The globular embryo proper with maximum of the DR5 activity in the protoderm of the apical region of the embryo proper (square). The higher magnification of the region of protoderm with the DR5 activity on l (l1). m The DR5 activity in the cells of the suspensor-like structures at the globular stage embryo proper. n DR5rev activity in the apical part of the globular pro-embryo proper with suspensor. o Globular embryo proper with the suspensor. The DR5rev activity concentrated in the apical part of the pro-embryo, in the provasculature, and in the hypophysis (arrow). DIC image of the same representative as on o (o1). Blue and light green colors show the expression of the reporter gus and gfp genes driven by the DR5 or DR5rev promoters (respectively). Bar = 20 μm
