Abstract
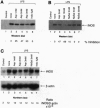
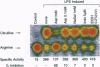
Nitric oxide synthesized by inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) has been implicated as a mediator of inflammation in rheumatic and autoimmune diseases. We report that exposure of lipopolysaccharide-stimulated murine macrophages to therapeutic concentrations of aspirin (IC50 = 3 mM) and hydrocortisone (IC50 = 5 microM) inhibited the expression of iNOS and production of nitrite. In contrast, sodium salicylate (1-3 mM), indomethacin (5-20 microM), and acetaminophen (60-120 microM) had no significant effect on the production of nitrite at pharmacological concentrations. At suprapharmacological concentrations, sodium salicylate (IC50 = 20 mM) significantly inhibited nitrite production. Immunoblot analysis of iNOS expression in the presence of aspirin showed inhibition of iNOS expression (IC50 = 3 mM). Sodium salicylate variably inhibited iNOS expression (0-35%), whereas indomethacin had no effect. Furthermore, there was no significant effect of these nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on iNOS mRNA expression at pharmacological concentrations. The effect of aspirin was not due to inhibition of cyclooxygenase 2 because both aspirin and indomethacin inhibited prostaglandin E2 synthesis by > 75%. Aspirin and N-acetylimidazole (an effective acetylating agent), but not sodium salicylate or indomethacin, also directly interfered with the catalytic activity of iNOS in cell-free extracts. These studies indicate that the inhibition of iNOS expression and function represents another mechanism of action for aspirin, if not for all aspirin-like drugs. The effects are exerted at the level of translational/posttranslational modification and directly on the catalytic activity of iNOS.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abramson S. B., Leszczynska-Piziak J., Clancy R. M., Philips M., Weissmann G. Inhibition of neutrophil function by aspirin-like drugs (NSAIDS): requirement for assembly of heterotrimeric G proteins in bilayer phospholipid. Biochem Pharmacol. 1994 Feb 9;47(3):563–572. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(94)90189-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abramson S. B. Treatment of gout and crystal arthropathies and uses and mechanisms of action of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 1992 Jun;4(3):295–300. doi: 10.1097/00002281-199206000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abramson S., Korchak H., Ludewig R., Edelson H., Haines K., Levin R. I., Herman R., Rider L., Kimmel S., Weissmann G. Modes of action of aspirin-like drugs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7227–7231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clancy R. M., Levartovsky D., Leszczynska-Piziak J., Yegudin J., Abramson S. B. Nitric oxide reacts with intracellular glutathione and activates the hexose monophosphate shunt in human neutrophils: evidence for S-nitrosoglutathione as a bioactive intermediary. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 26;91(9):3680–3684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.9.3680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Rosa M., Radomski M., Carnuccio R., Moncada S. Glucocorticoids inhibit the induction of nitric oxide synthase in macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Nov 15;172(3):1246–1252. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91583-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furst D. E. Are there differences among nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs? Comparing acetylated salicylates, nonacetylated salicylates, and nonacetylated nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs. Arthritis Rheum. 1994 Jan;37(1):1–9. doi: 10.1002/art.1780370102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilliam M. B., Sherman M. P., Griscavage J. M., Ignarro L. J. A spectrophotometric assay for nitrate using NADPH oxidation by Aspergillus nitrate reductase. Anal Biochem. 1993 Aug 1;212(2):359–365. doi: 10.1006/abio.1993.1341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopp E., Ghosh S. Inhibition of NF-kappa B by sodium salicylate and aspirin. Science. 1994 Aug 12;265(5174):956–959. doi: 10.1126/science.8052854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecomte M., Laneuville O., Ji C., DeWitt D. L., Smith W. L. Acetylation of human prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase-2 (cyclooxygenase-2) by aspirin. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 6;269(18):13207–13215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marletta M. A. Nitric oxide synthase: aspects concerning structure and catalysis. Cell. 1994 Sep 23;78(6):927–930. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90268-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misko T. P., Moore W. M., Kasten T. P., Nickols G. A., Corbett J. A., Tilton R. G., McDaniel M. L., Williamson J. R., Currie M. G. Selective inhibition of the inducible nitric oxide synthase by aminoguanidine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Mar 16;233(1):119–125. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)90357-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell J. A., Akarasereenont P., Thiemermann C., Flower R. J., Vane J. R. Selectivity of nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs as inhibitors of constitutive and inducible cyclooxygenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 15;90(24):11693–11697. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.24.11693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C., Xie Q. W. Nitric oxide synthases: roles, tolls, and controls. Cell. 1994 Sep 23;78(6):915–918. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90266-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Ferrige A. G., Moncada S. Nitric oxide release accounts for the biological activity of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Nature. 1987 Jun 11;327(6122):524–526. doi: 10.1038/327524a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvemini D., Misko T. P., Masferrer J. L., Seibert K., Currie M. G., Needleman P. Nitric oxide activates cyclooxygenase enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 1;90(15):7240–7244. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.15.7240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt H. H., Walter U. NO at work. Cell. 1994 Sep 23;78(6):919–925. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90267-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimokawa T., Smith W. L. Prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase. The aspirin acetylation region. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 15;267(17):12387–12392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. K., Krohn R. I., Hermanson G. T., Mallia A. K., Gartner F. H., Provenzano M. D., Fujimoto E. K., Goeke N. M., Olson B. J., Klenk D. C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem. 1985 Oct;150(1):76–85. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefanovic-Racic M., Meyers K., Meschter C., Coffey J. W., Hoffman R. A., Evans C. H. N-monomethyl arginine, an inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase, suppresses the development of adjuvant arthritis in rats. Arthritis Rheum. 1994 Jul;37(7):1062–1069. doi: 10.1002/art.1780370712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuehr D. J., Cho H. J., Kwon N. S., Weise M. F., Nathan C. F. Purification and characterization of the cytokine-induced macrophage nitric oxide synthase: an FAD- and FMN-containing flavoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7773–7777. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tetsuka T., Daphna-Iken D., Srivastava S. K., Baier L. D., DuMaine J., Morrison A. R. Cross-talk between cyclooxygenase and nitric oxide pathways: prostaglandin E2 negatively modulates induction of nitric oxide synthase by interleukin 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Dec 6;91(25):12168–12172. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.25.12168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vane J. R., Mitchell J. A., Appleton I., Tomlinson A., Bishop-Bailey D., Croxtall J., Willoughby D. A. Inducible isoforms of cyclooxygenase and nitric-oxide synthase in inflammation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 15;91(6):2046–2050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.6.2046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vane J. Towards a better aspirin. Nature. 1994 Jan 20;367(6460):215–216. doi: 10.1038/367215a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vodovotz Y., Bogdan C., Paik J., Xie Q. W., Nathan C. Mechanisms of suppression of macrophage nitric oxide release by transforming growth factor beta. J Exp Med. 1993 Aug 1;178(2):605–613. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.2.605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells I., Marnett L. J. Acetylation of prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase by N-acetylimidazole: comparison to acetylation by aspirin. Biochemistry. 1992 Oct 13;31(40):9520–9525. doi: 10.1021/bi00155a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie Q. W., Kashiwabara Y., Nathan C. Role of transcription factor NF-kappa B/Rel in induction of nitric oxide synthase. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 18;269(7):4705–4708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]