Abstract
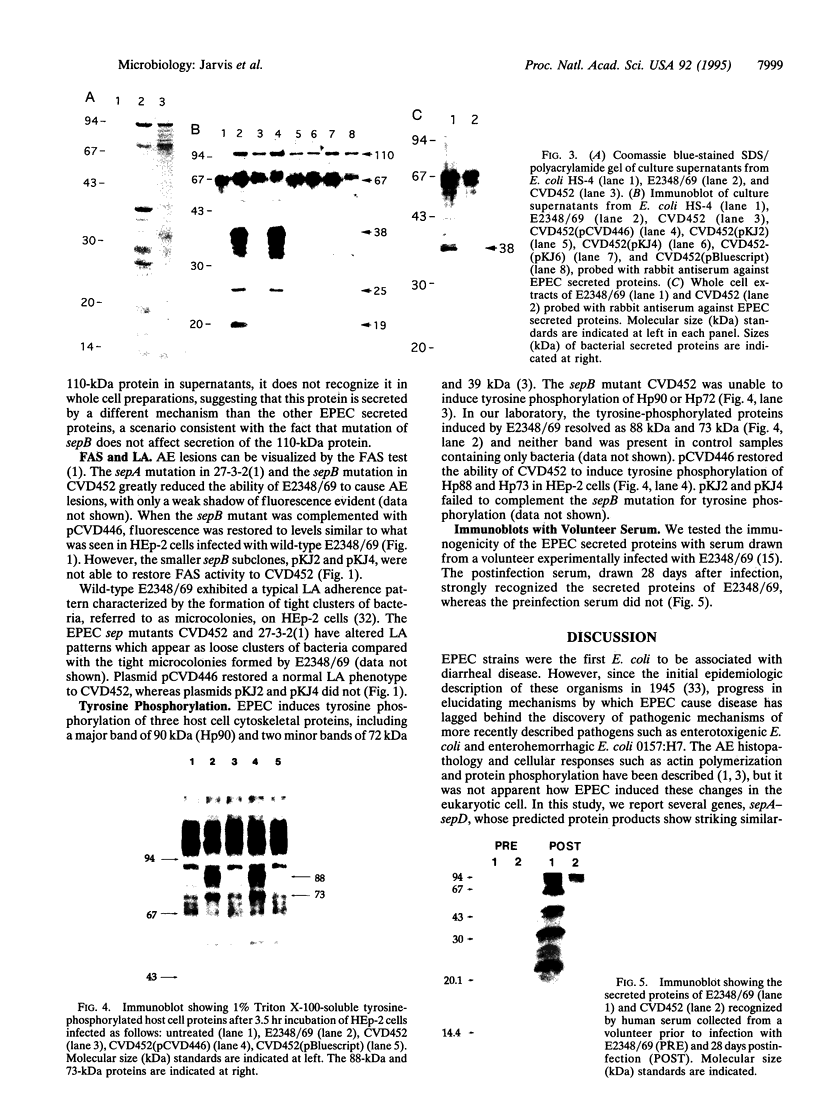
Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) causes a characteristic histopathology in intestinal epithelial cells called the attaching and effacing lesion. Although the histopathological lesion is well described the bacterial factors responsible for it are poorly characterized. We have identified four EPEC chromosomal genes whose predicted protein sequences are similar to components of a recently described secretory pathway (type III) responsible for exporting proteins lacking a typical signal sequence. We have designated the genes sepA, sepB, sepC, and sepD (sep, for secretion of E. coli proteins). The predicted Sep polypeptides are similar to the Lcr (low calcium response) and Ysc (yersinia secretion) proteins of Yersinia species and the Mxi (membrane expression of invasion plasmid antigens) and Spa (surface presentation of antigens) regions of Shigella flexneri. Culture supernatants of EPEC strain E2348/69 contain several polypeptides ranging in size from 110 kDa to 19 kDa. Proteins of comparable size were recognized by human convalescent serum from a volunteer experimentally infected with strain E2348/69. A sepB mutant of EPEC secreted only the 110-kDa polypeptide and was defective in the formation of attaching and effacing lesions and protein-tyrosine phosphorylation in tissue culture cells. These phenotypes were restored upon complementation with a plasmid carrying an intact sepB gene. These data suggest that the EPEC Sep proteins are components of a type III secretory apparatus necessary for the export of virulence determinants.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allaoui A., Sansonetti P. J., Parsot C. MxiD, an outer membrane protein necessary for the secretion of the Shigella flexneri lpa invasins. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Jan;7(1):59–68. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01097.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allaoui A., Sansonetti P. J., Parsot C. MxiJ, a lipoprotein involved in secretion of Shigella Ipa invasins, is homologous to YscJ, a secretion factor of the Yersinia Yop proteins. J Bacteriol. 1992 Dec;174(23):7661–7669. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.23.7661-7669.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews G. P., Maurelli A. T. mxiA of Shigella flexneri 2a, which facilitates export of invasion plasmid antigens, encodes a homolog of the low-calcium-response protein, LcrD, of Yersinia pestis. Infect Immun. 1992 Aug;60(8):3287–3295. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.8.3287-3295.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin T. J., Ward W., Aitken A., Knutton S., Williams P. H. Elevation of intracellular free calcium levels in HEp-2 cells infected with enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1991 May;59(5):1599–1604. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.5.1599-1604.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnenberg M. S., Calderwood S. B., Donohue-Rolfe A., Keusch G. T., Kaper J. B. Construction and analysis of TnphoA mutants of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli unable to invade HEp-2 cells. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1565–1571. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1565-1571.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnenberg M. S., Kaper J. B. Construction of an eae deletion mutant of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli by using a positive-selection suicide vector. Infect Immun. 1991 Dec;59(12):4310–4317. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.12.4310-4317.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnenberg M. S., Tacket C. O., James S. P., Losonsky G., Nataro J. P., Wasserman S. S., Kaper J. B., Levine M. M. Role of the eaeA gene in experimental enteropathogenic Escherichia coli infection. J Clin Invest. 1993 Sep;92(3):1412–1417. doi: 10.1172/JCI116717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnenberg M. S., Yu J., Kaper J. B. A second chromosomal gene necessary for intimate attachment of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli to epithelial cells. J Bacteriol. 1993 Aug;175(15):4670–4680. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.15.4670-4680.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichelberg K., Ginocchio C. C., Galán J. E. Molecular and functional characterization of the Salmonella typhimurium invasion genes invB and invC: homology of InvC to the F0F1 ATPase family of proteins. J Bacteriol. 1994 Aug;176(15):4501–4510. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.15.4501-4510.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foubister V., Rosenshine I., Donnenberg M. S., Finlay B. B. The eaeB gene of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli is necessary for signal transduction in epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1994 Jul;62(7):3038–3040. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.7.3038-3040.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foubister V., Rosenshine I., Finlay B. B. A diarrheal pathogen, enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC), triggers a flux of inositol phosphates in infected epithelial cells. J Exp Med. 1994 Mar 1;179(3):993–998. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.3.993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galán J. E., Ginocchio C., Costeas P. Molecular and functional characterization of the Salmonella invasion gene invA: homology of InvA to members of a new protein family. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jul;174(13):4338–4349. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.13.4338-4349.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groisman E. A., Ochman H. Cognate gene clusters govern invasion of host epithelial cells by Salmonella typhimurium and Shigella flexneri. EMBO J. 1993 Oct;12(10):3779–3787. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06056.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale T. L. Genetic basis of virulence in Shigella species. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Jun;55(2):206–224. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.2.206-224.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerse A. E., Yu J., Tall B. D., Kaper J. B. A genetic locus of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli necessary for the production of attaching and effacing lesions on tissue culture cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):7839–7843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.7839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaniga K., Bossio J. C., Galán J. E. The Salmonella typhimurium invasion genes invF and invG encode homologues of the AraC and PulD family of proteins. Mol Microbiol. 1994 Aug;13(4):555–568. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb00450.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny B., Finlay B. B. Protein secretion by enteropathogenic Escherichia coli is essential for transducing signals to epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Aug 15;92(17):7991–7995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.17.7991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutton S., Baldwin T., Williams P. H., McNeish A. S. Actin accumulation at sites of bacterial adhesion to tissue culture cells: basis of a new diagnostic test for enteropathogenic and enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1290–1298. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1290-1298.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Bergquist E. J., Nalin D. R., Waterman D. H., Hornick R. B., Young C. R., Sotman S. Escherichia coli strains that cause diarrhoea but do not produce heat-labile or heat-stable enterotoxins and are non-invasive. Lancet. 1978 May 27;1(8074):1119–1122. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90299-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Kaper J. B., Lockman H., Black R. E., Clements M. L., Falkow S. Recombinant DNA risk assessment studies in humans: efficacy of poorly mobilizable plasmids in biologic containment. J Infect Dis. 1983 Oct;148(4):699–709. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.4.699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Nataro J. P., Karch H., Baldini M. M., Kaper J. B., Black R. E., Clements M. L., O'Brien A. D. The diarrheal response of humans to some classic serotypes of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli is dependent on a plasmid encoding an enteroadhesiveness factor. J Infect Dis. 1985 Sep;152(3):550–559. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.3.550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manjarrez-Hernandez H. A., Baldwin T. J., Aitken A., Knutton S., Williams P. H. Intestinal epithelial cell protein phosphorylation in enteropathogenic Escherichia coli diarrhoea. Lancet. 1992 Feb 29;339(8792):521–523. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)90340-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDaniel T. K., Jarvis K. G., Donnenberg M. S., Kaper J. B. A genetic locus of enterocyte effacement conserved among diverse enterobacterial pathogens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Feb 28;92(5):1664–1668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.5.1664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michiels T., Vanooteghem J. C., Lambert de Rouvroit C., China B., Gustin A., Boudry P., Cornelis G. R. Analysis of virC, an operon involved in the secretion of Yop proteins by Yersinia enterocolitica. J Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;173(16):4994–5009. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.16.4994-5009.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon H. W., Whipp S. C., Argenzio R. A., Levine M. M., Giannella R. A. Attaching and effacing activities of rabbit and human enteropathogenic Escherichia coli in pig and rabbit intestines. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1340–1351. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1340-1351.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ménard R., Sansonetti P. J., Parsot C. Nonpolar mutagenesis of the ipa genes defines IpaB, IpaC, and IpaD as effectors of Shigella flexneri entry into epithelial cells. J Bacteriol. 1993 Sep;175(18):5899–5906. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.18.5899-5906.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plano G. V., Barve S. S., Straley S. C. LcrD, a membrane-bound regulator of the Yersinia pestis low-calcium response. J Bacteriol. 1991 Nov;173(22):7293–7303. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.22.7293-7303.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenshine I., Donnenberg M. S., Kaper J. B., Finlay B. B. Signal transduction between enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) and epithelial cells: EPEC induces tyrosine phosphorylation of host cell proteins to initiate cytoskeletal rearrangement and bacterial uptake. EMBO J. 1992 Oct;11(10):3551–3560. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05438.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russel M. Phage assembly: a paradigm for bacterial virulence factor export? Science. 1994 Jul 29;265(5172):612–614. doi: 10.1126/science.8036510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmond G. P., Reeves P. J. Membrane traffic wardens and protein secretion in gram-negative bacteria. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Jan;18(1):7–12. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90080-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saraste M., Sibbald P. R., Wittinghofer A. The P-loop--a common motif in ATP- and GTP-binding proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Nov;15(11):430–434. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90281-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scaletsky I. C., Silva M. L., Trabulsi L. R. Distinctive patterns of adherence of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli to HeLa cells. Infect Immun. 1984 Aug;45(2):534–536. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.2.534-536.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straley S. C., Skrzypek E., Plano G. V., Bliska J. B. Yops of Yersinia spp. pathogenic for humans. Infect Immun. 1993 Aug;61(8):3105–3110. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.8.3105-3110.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Gijsegem F., Genin S., Boucher C. Conservation of secretion pathways for pathogenicity determinants of plant and animal bacteria. Trends Microbiol. 1993 Aug;1(5):175–180. doi: 10.1016/0966-842x(93)90087-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesan M. M., Buysse J. M., Oaks E. V. Surface presentation of Shigella flexneri invasion plasmid antigens requires the products of the spa locus. J Bacteriol. 1992 Mar;174(6):1990–2001. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.6.1990-2001.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogler A. P., Homma M., Irikura V. M., Macnab R. M. Salmonella typhimurium mutants defective in flagellar filament regrowth and sequence similarity of FliI to F0F1, vacuolar, and archaebacterial ATPase subunits. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(11):3564–3572. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.11.3564-3572.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. E., Saraste M., Runswick M. J., Gay N. J. Distantly related sequences in the alpha- and beta-subunits of ATP synthase, myosin, kinases and other ATP-requiring enzymes and a common nucleotide binding fold. EMBO J. 1982;1(8):945–951. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01276.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woestyn S., Allaoui A., Wattiau P., Cornelis G. R. YscN, the putative energizer of the Yersinia Yop secretion machinery. J Bacteriol. 1994 Mar;176(6):1561–1569. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.6.1561-1569.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]