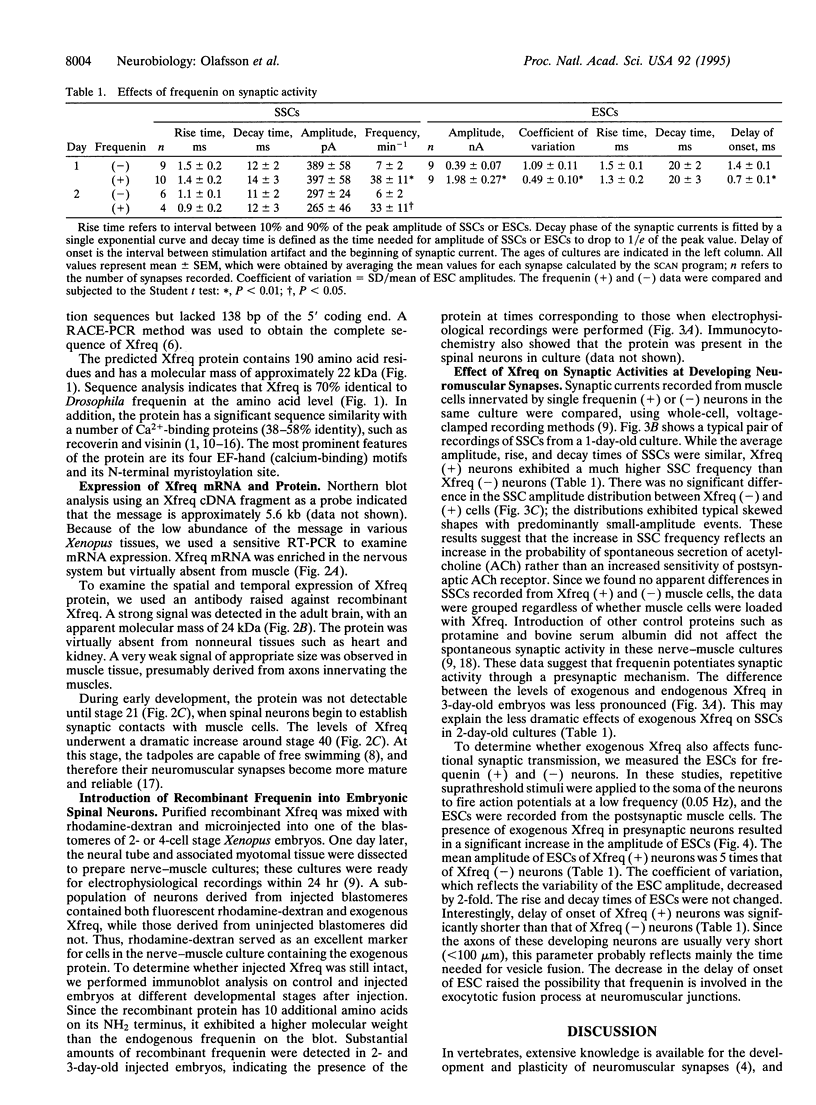
Abstract
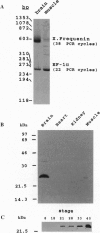
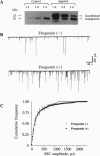
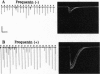
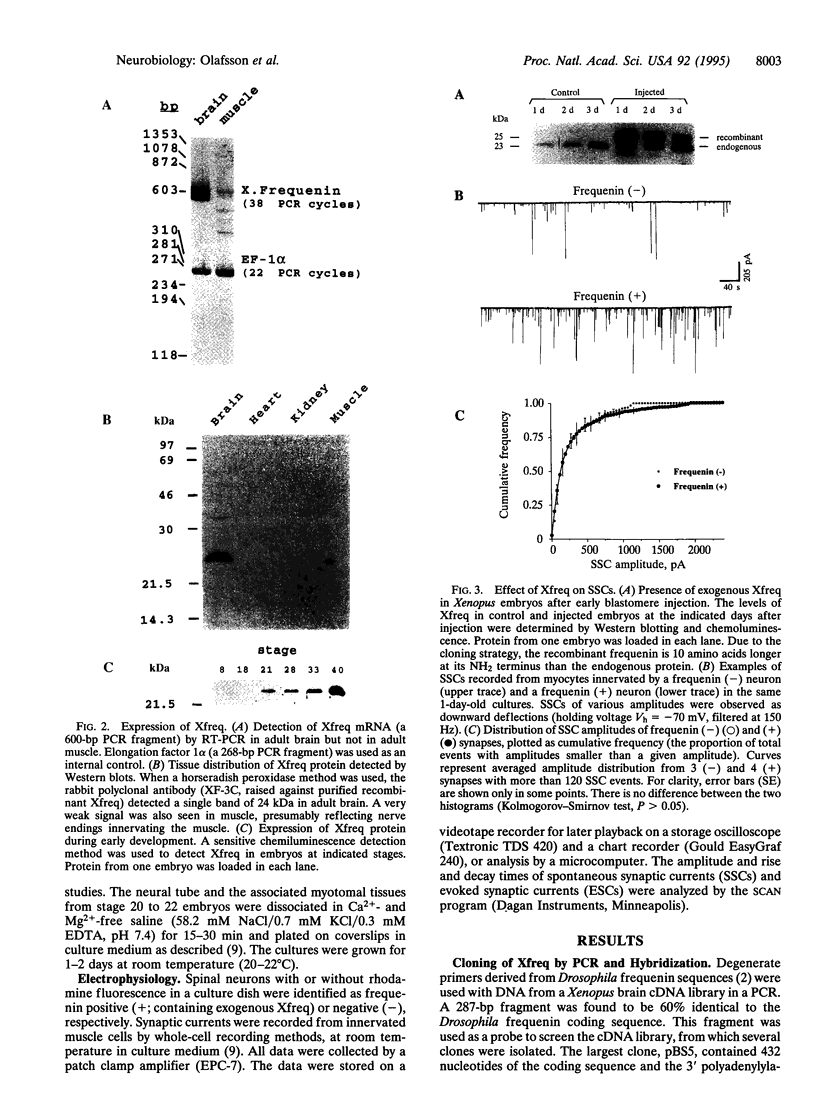
Frequenin was originally identified in Drosophila melanogaster as a Ca(2+)-binding protein facilitating transmitter release at the neuromuscular junction. We have cloned the Xenopus frequenin (Xfreq) by PCR using degenerate primers combined with low-stringency hybridization. The deduced protein has 70% identity with Drosophila frequenin and about 38-58% identity with other Ca(2+)-binding proteins. The most prominent features are the four EF-hands, Ca(2+)-binding motifs. Xfreq mRNA is abundant in the brain and virtually nondetectable from adult muscle. Western blot analysis indicated that Xfreq is highly concentrated in the adult brain and is absent from nonneural tissues such as heart and kidney. During development, the expression of the protein correlated well with the maturation of neuromuscular synapses. To determine the function of Xfreq at the developing neuromuscular junction, the recombinant protein was introduced into Xenopus embryonic spinal neurons by early blastomere injection. Synapses made by spinal neurons containing exogenous Xfreq exhibited a much higher synaptic efficacy. These results provide direct evidence that frequenin enhances transmitter release at the vertebrate neuromuscular synapse and suggest its potential role in synaptic development and plasticity.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baimbridge K. G., Celio M. R., Rogers J. H. Calcium-binding proteins in the nervous system. Trends Neurosci. 1992 Aug;15(8):303–308. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(92)90081-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Certa U., Bannwarth W., Stüber D., Gentz R., Lanzer M., Le Grice S., Guillot F., Wendler I., Hunsmann G., Bujard H. Subregions of a conserved part of the HIV gp41 transmembrane protein are differentially recognized by antibodies of infected individuals. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):3051–3056. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04605.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dizhoor A. M., Ray S., Kumar S., Niemi G., Spencer M., Brolley D., Walsh K. A., Philipov P. P., Hurley J. B., Stryer L. Recoverin: a calcium sensitive activator of retinal rod guanylate cyclase. Science. 1991 Feb 22;251(4996):915–918. doi: 10.1126/science.1672047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall Z. W., Sanes J. R. Synaptic structure and development: the neuromuscular junction. Cell. 1993 Jan;72 (Suppl):99–121. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80031-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahn R., Südhof T. C. Synaptic vesicles and exocytosis. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1994;17:219–246. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.17.030194.001251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidokoro Y. Two types of miniature endplate potentials in Xenopus nerve-muscle cultures. Neurosci Res. 1984 Jun;1(3):157–170. doi: 10.1016/s0168-0102(84)80013-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi M., Takamatsu K., Saitoh S., Miura M., Noguchi T. Molecular cloning of hippocalcin, a novel calcium-binding protein of the recoverin family exclusively expressed in hippocampus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Nov 30;189(1):511–517. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91587-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenz S. E., Henschel Y., Zopf D., Voss B., Gundelfinger E. D. VILIP, a cognate protein of the retinal calcium binding proteins visinin and recoverin, is expressed in the developing chicken brain. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1992 Sep;15(1-2):133–140. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(92)90160-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Sugimori M., Silver R. B. Microdomains of high calcium concentration in a presynaptic terminal. Science. 1992 May 1;256(5057):677–679. doi: 10.1126/science.1350109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu B., Greengard P., Poo M. M. Exogenous synapsin I promotes functional maturation of developing neuromuscular synapses. Neuron. 1992 Mar;8(3):521–529. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90280-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis J. F., Stepanik P. L., Baehr W., Subbaraya I., Lerious V. Cloning and sequencing of the 23 kDa mouse photoreceptor cell-specific protein. FEBS Lett. 1992 May 11;302(2):172–176. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80433-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okazaki K., Watanabe M., Ando Y., Hagiwara M., Terasawa M., Hidaka H. Full sequence of neurocalcin, a novel calcium-binding protein abundant in central nervous system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 May 29;185(1):147–153. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80968-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pongs O., Lindemeier J., Zhu X. R., Theil T., Engelkamp D., Krah-Jentgens I., Lambrecht H. G., Koch K. W., Schwemer J., Rivosecchi R. Frequenin--a novel calcium-binding protein that modulates synaptic efficacy in the Drosophila nervous system. Neuron. 1993 Jul;11(1):15–28. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90267-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivosecchi R., Pongs O., Theil T., Mallart A. Implication of frequenin in the facilitation of transmitter release in Drosophila. J Physiol. 1994 Jan 15;474(2):223–232. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer E., Alder J., Greengard P., Poo M. M. Synapsin IIa accelerates functional development of neuromuscular synapses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 26;91(9):3882–3886. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.9.3882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakamatsu Y., Watanabe Y., Shimono A., Kondoh H. Transition of localization of the N-Myc protein from nucleus to cytoplasm in differentiating neurons. Neuron. 1993 Jan;10(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90236-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang T., Xie K., Lu B. Neurotrophins promote maturation of developing neuromuscular synapses. J Neurosci. 1995 Jul;15(7 Pt 1):4796–4805. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-07-04796.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiechmann A. F., Hammarback J. A. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of a cDNA encoding recoverin from human retina. Exp Eye Res. 1993 Apr;56(4):463–470. doi: 10.1006/exer.1993.1059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamagata K., Goto K., Kuo C. H., Kondo H., Miki N. Visinin: a novel calcium binding protein expressed in retinal cone cells. Neuron. 1990 Mar;4(3):469–476. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90059-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]