Abstract
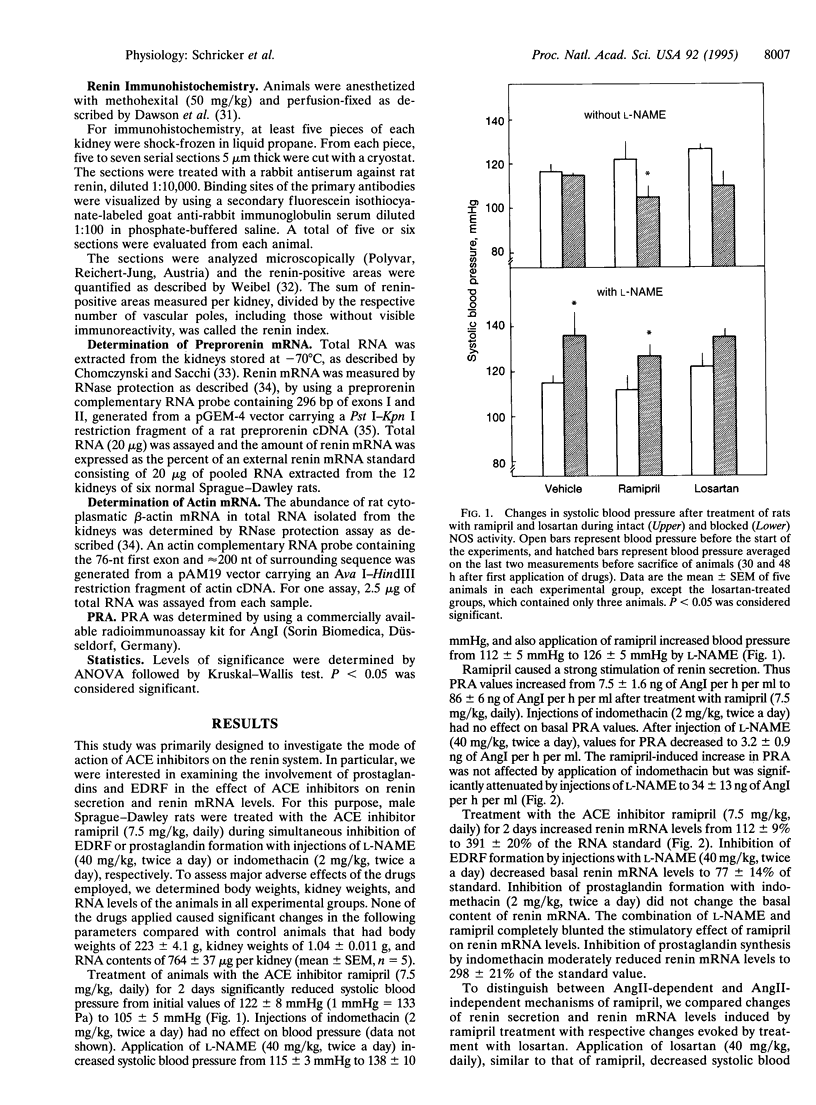
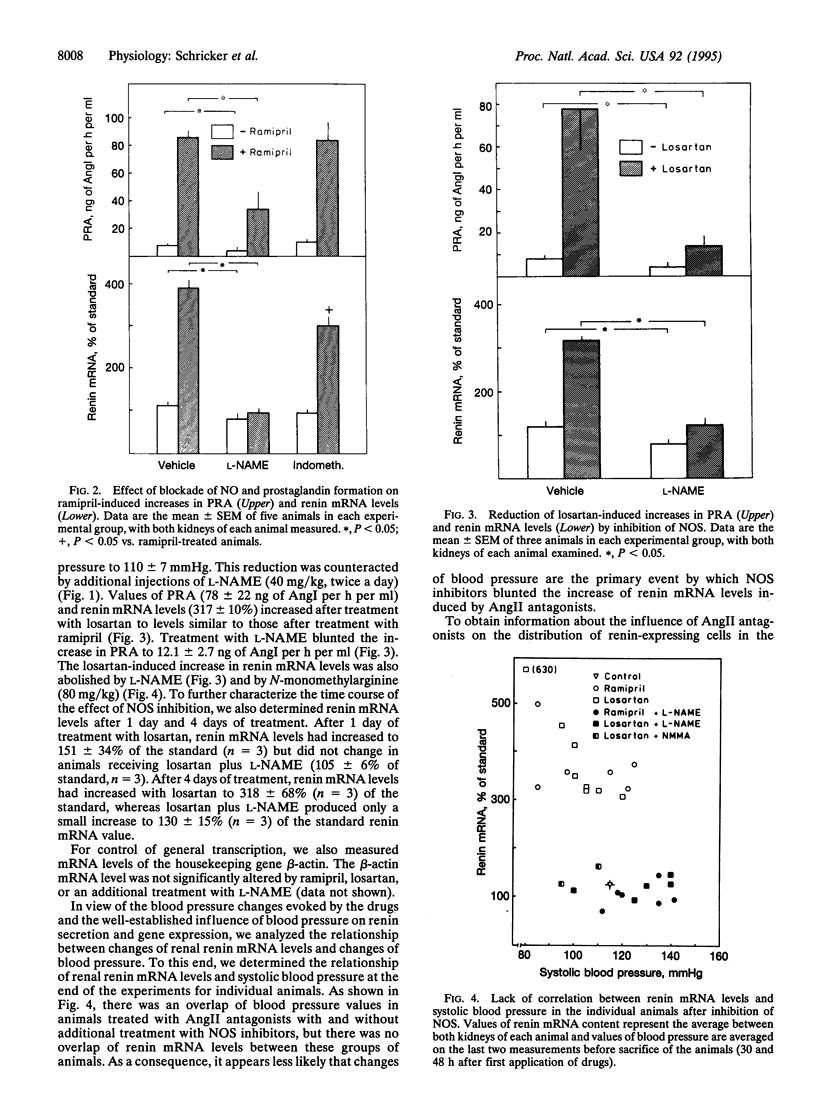
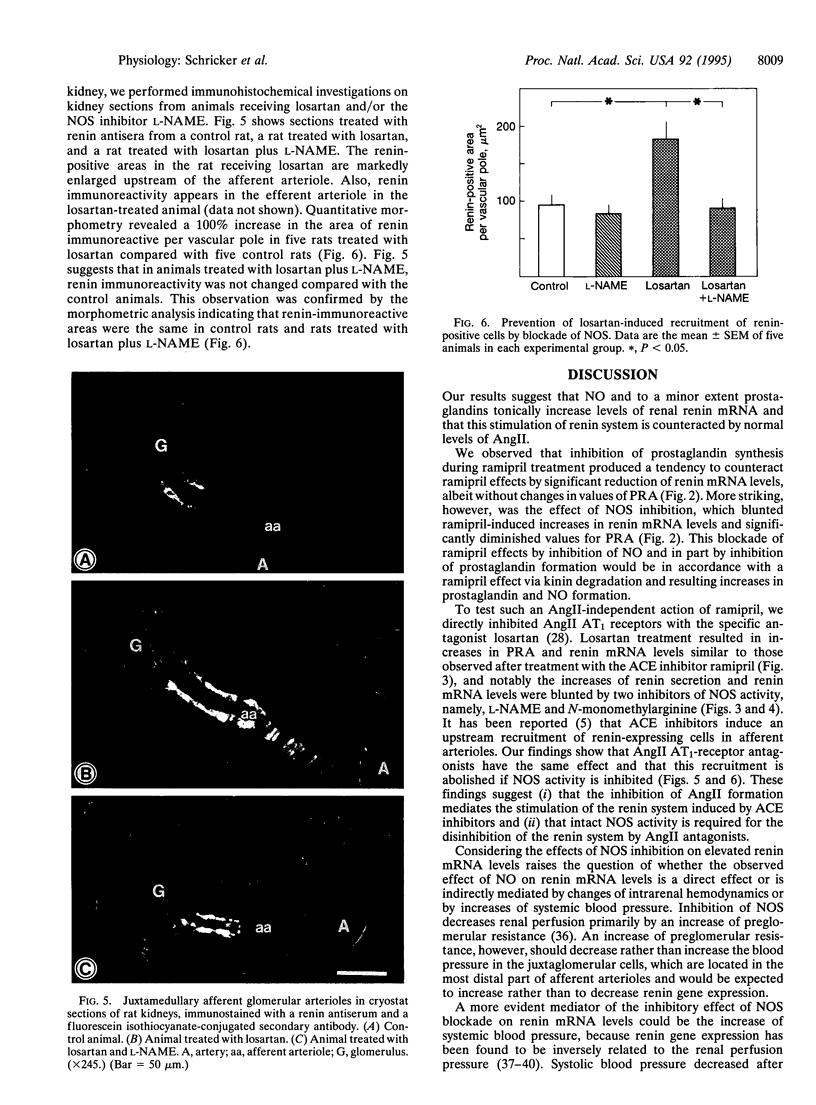
This study was designed to examine the possible involvement of prostaglandins and nitric oxide (NO) in the renin stimulatory effect of angiotensin II (AngII) antagonists. To this end, plasma renin activities (PRAs) and renal renin mRNA levels were assayed in rats that were treated with the Ang-converting enzyme inhibitor ramipril or with the AngII AT1-receptor antagonist losartan. Ramipril and losartan increased PRA values from 7.5 +/- 1.6 to 86 +/- 6 and 78 +/- 22 ng of AngI per h per ml and renin mRNA levels from 112 +/- 9% to 391 +/- 20% and 317 +/- 10%, respectively. Inhibition of prostaglandin formation with indomethacin did not influence basal or ramipril-affected PRA. Basal renin mRNA levels also were unchanged by indomethacin, while increases in renin mRNA levels after ramipril treatment were slightly reduced by indomethacin. Inhibition of NO synthase by nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME) reduced PRA values to 3.2 +/- 0.9, 34 +/- 13, and 12.1 +/- 2.7 ng of AngI per h per ml in control, ramipril-treated, and losartan-treated animals, respectively. Renin mRNA levels were reduced to 77 +/- 14% under basal conditions and ramipril- and losartan-induced increases in renin mRNA levels were completely blunted after addition of L-NAME. The AngII antagonists, furthermore, induced an upstream recruitment of renin-expressing cells in the renal afferent arterioles, which was also blunted by L-NAME. These findings suggest that renin mRNA levels are tonically increased by NO and that the action of NO is counteracted by AngII.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burnham C. E., Hawelu-Johnson C. L., Frank B. M., Lynch K. R. Molecular cloning of rat renin cDNA and its gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5605–5609. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson T. P., Gandhi R., Le Hir M., Kaissling B. Ecto-5'-nucleotidase: localization in rat kidney by light microscopic histochemical and immunohistochemical methods. J Histochem Cytochem. 1989 Jan;37(1):39–47. doi: 10.1177/37.1.2535703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flower R. J. Drugs which inhibit prostaglandin biosynthesis. Pharmacol Rev. 1974 Mar;26(1):33–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardes J., Gonzalez M. F., Alhenc-Gelas F., Ménard J. Influence of sodium diet on L-NAME effects on renin release and renal vasoconstriction. Am J Physiol. 1994 Nov;267(5 Pt 2):F798–F804. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1994.267.5.F798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardes J., Poux J. M., Gonzalez M. F., Alhenc-Gelas F., Menard J. Decreased renin release and constant kallikrein secretion after injection of L-NAME in isolated perfused rat kidney. Life Sci. 1992;50(14):987–993. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(92)90092-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez R. A., Lynch K. R., Chevalier R. L., Everett A. D., Johns D. W., Wilfong N., Peach M. J., Carey R. M. Renin and angiotensinogen gene expression and intrarenal renin distribution during ACE inhibition. Am J Physiol. 1988 Jun;254(6 Pt 2):F900–F906. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.254.6.F900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman J. C., Wall T. M., Hullinger T. G., Shebuski R. J. Reduction of myocardial infarct size in rabbits by ramiprilat: reversal by the bradykinin antagonist HOE 140. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1993 Jun;21(6):996–1003. doi: 10.1097/00005344-199306000-00022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmer S., Eckardt K. U., Aedtner O., LeHir M., Schricker K., Hamann M., Götz K., Riegger G., Moll W., Kurtz A. Which factor mediates reno-renal control of renin gene expression? J Hypertens. 1993 Oct;11(10):1011–1019. doi: 10.1097/00004872-199310000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johns D. W., Peach M. J., Gomez R. A., Inagami T., Carey R. M. Angiotensin II regulates renin gene expression. Am J Physiol. 1990 Dec;259(6 Pt 2):F882–F887. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.259.6.F882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. A., Freeman R. H. Renin release in rats during blockade of nitric oxide synthesis. Am J Physiol. 1994 Jun;266(6 Pt 2):R1723–R1729. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1994.266.6.R1723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohara K., Brosnihan K. B., Ferrario C. M., Milsted A. Peripheral and central angiotensin II regulates expression of genes of the renin-angiotensin system. Am J Physiol. 1992 May;262(5 Pt 1):E651–E657. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1992.262.5.E651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz A., Kaissling B., Busse R., Baier W. Endothelial cells modulate renin secretion from isolated mouse juxtaglomerular cells. J Clin Invest. 1991 Oct;88(4):1147–1154. doi: 10.1172/JCI115415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig G., Ganten D., Murakami K., Fasching U., Hackenthal E. Relationship between renin mRNA and renin secretion in adrenalectomized, salt-depleted, or converting enzyme inhibitor-treated rats. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1987 Apr;50(3):223–229. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(87)90020-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lückhoff A., Pohl U., Mülsch A., Busse R. Differential role of extra- and intracellular calcium in the release of EDRF and prostacyclin from cultured endothelial cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Sep;95(1):189–196. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb16564.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makrides S. C., Mulinari R., Zannis V. I., Gavras H. Regulation of renin gene expression in hypertensive rats. Hypertension. 1988 Oct;12(4):405–410. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.12.4.405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntyre T. M., Zimmerman G. A., Satoh K., Prescott S. M. Cultured endothelial cells synthesize both platelet-activating factor and prostacyclin in response to histamine, bradykinin, and adenosine triphosphate. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jul;76(1):271–280. doi: 10.1172/JCI111957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisel S., Shamiss A., Rosenthal T. Clinical pharmacokinetics of ramipril. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1994 Jan;26(1):7–15. doi: 10.2165/00003088-199426010-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moffett R. B., McGowan R. A., Gross K. W. Modulation of kidney renin messenger RNA levels during experimentally induced hypertension. Hypertension. 1986 Oct;8(10):874–882. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.8.10.874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mundel P., Bachmann S., Bader M., Fischer A., Kummer W., Mayer B., Kriz W. Expression of nitric oxide synthase in kidney macula densa cells. Kidney Int. 1992 Oct;42(4):1017–1019. doi: 10.1038/ki.1992.382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naess P. A., Christensen G., Kirkebøen K. A., Kiil F. Effect on renin release of inhibiting renal nitric oxide synthesis in anaesthetized dogs. Acta Physiol Scand. 1993 Jun;148(2):137–142. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1993.tb09543.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura A., Iwao H., Fukui K., Kimura S., Tamaki T., Nakanishi S., Abe Y. Regulation of liver angiotensinogen and kidney renin mRNA levels by angiotensin II. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jan;258(1 Pt 1):E1–E6. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1990.258.1.E1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura N., Soubrier F., Menard J., Panthier J. J., Rougeon F., Corvol P. Nonproportional changes in plasma renin concentration, renal renin content, and rat renin messenger RNA. Hypertension. 1985 Nov-Dec;7(6 Pt 1):855–859. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.7.6.855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama I., Kawahara Y., Tsuda T., Okuda M., Yokoyama M. Angiotensin II inhibits cytokine-stimulated inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 15;269(15):11628–11633. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson P. B., Baumann J. E., Ehmke H., Hackenthal E., Kirchheim H. R., Nafz B. Endothelium-derived NO stimulates pressure-dependent renin release in conscious dogs. Am J Physiol. 1993 Jun;264(6 Pt 2):F943–F947. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1993.264.6.F943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radermacher J., Förstermann U., Frölich J. C. Endothelium-derived relaxing factor influences renal vascular resistance. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jul;259(1 Pt 2):F9–17. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.259.1.F9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees D. D., Palmer R. M., Schulz R., Hodson H. F., Moncada S. Characterization of three inhibitors of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in vitro and in vivo. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov;101(3):746–752. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14151.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samani N. J., Godfrey N. P., Major J. S., Brammar W. J., Swales J. D. Kidney renin mRNA levels in the early and chronic phases of two-kidney, one clip hypertension in the rat. J Hypertens. 1989 Feb;7(2):105–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherf H., Pietsch R., Landsberg G., Kramer H. J., Düsing R. Converting enzyme inhibitor ramipril stimulates prostacyclin synthesis by isolated rat aorta: evidence for a kinin-dependent mechanism. Klin Wochenschr. 1986 Aug 15;64(16):742–745. doi: 10.1007/BF01734341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholz H., Kurtz A. Involvement of endothelium-derived relaxing factor in the pressure control of renin secretion from isolated perfused kidney. J Clin Invest. 1993 Mar;91(3):1088–1094. doi: 10.1172/JCI116266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schricker K., Ritthaler T., Krämer B. K., Kurtz A. Effect of endothelium-derived relaxing factor on renin secretion from isolated mouse renal juxtaglomerular cells. Acta Physiol Scand. 1993 Nov;149(3):347–354. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1993.tb09630.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schunkert H., Ingelfinger J. R., Jacob H., Jackson B., Bouyounes B., Dzau V. J. Reciprocal feedback regulation of kidney angiotensinogen and renin mRNA expressions by angiotensin II. Am J Physiol. 1992 Nov;263(5 Pt 1):E863–E869. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1992.263.5.E863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigmon D. H., Carretero O. A., Beierwaltes W. H. Endothelium-derived relaxing factor regulates renin release in vivo. Am J Physiol. 1992 Aug;263(2 Pt 2):F256–F261. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1992.263.2.F256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taugner R., Hackenthal E., Helmchen U., Ganten D., Kugler P., Marin-Grez M., Nobiling R., Unger T., Lockwald I., Keilbach R. The intrarenal renin-angiotensin-system. An immunocytochemical study on the localization of renin, angiotensinogen, converting enzyme and the angiotensins in the kidney of mouse and rat. Klin Wochenschr. 1982 Oct 1;60(19):1218–1222. doi: 10.1007/BF01716726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorup C., Sundler F., Ekblad E., Persson A. E. Resetting of the tubuloglomerular feedback mechanism by blockade of NO-synthase. Acta Physiol Scand. 1993 Jul;148(3):359–360. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1993.tb09569.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd P. A., Benfield P. Ramipril. A review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic efficacy in cardiovascular disorders. Drugs. 1990 Jan;39(1):110–135. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199039010-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tojo A., Gross S. S., Zhang L., Tisher C. C., Schmidt H. H., Wilcox C. S., Madsen K. M. Immunocytochemical localization of distinct isoforms of nitric oxide synthase in the juxtaglomerular apparatus of normal rat kidney. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1994 Jan;4(7):1438–1447. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V471438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tufro-McReddie A., Chevalier R. L., Everett A. D., Gomez R. A. Decreased perfusion pressure modulates renin and ANG II type 1 receptor gene expression in the rat kidney. Am J Physiol. 1993 Apr;264(4 Pt 2):R696–R702. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1993.264.4.R696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidal M. J., Romero J. C., Vanhoutte P. M. Endothelium-derived relaxing factor inhibits renin release. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 May 10;149(3):401–402. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90679-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiemer G., Schölkens B. A., Becker R. H., Busse R. Ramiprilat enhances endothelial autacoid formation by inhibiting breakdown of endothelium-derived bradykinin. Hypertension. 1991 Oct;18(4):558–563. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.18.4.558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox C. S., Welch W. J., Murad F., Gross S. S., Taylor G., Levi R., Schmidt H. H. Nitric oxide synthase in macula densa regulates glomerular capillary pressure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):11993–11997. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.11993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]