Abstract
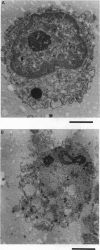
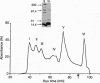
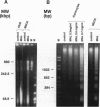
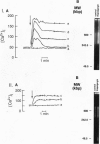
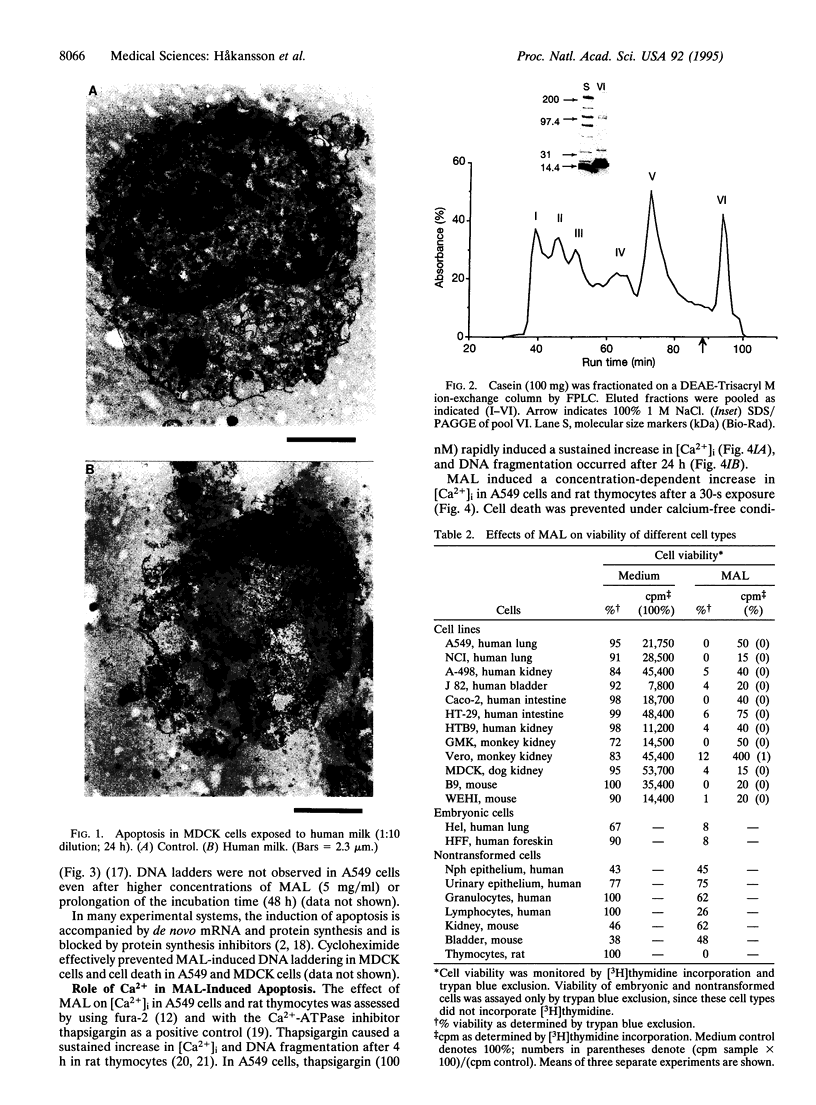
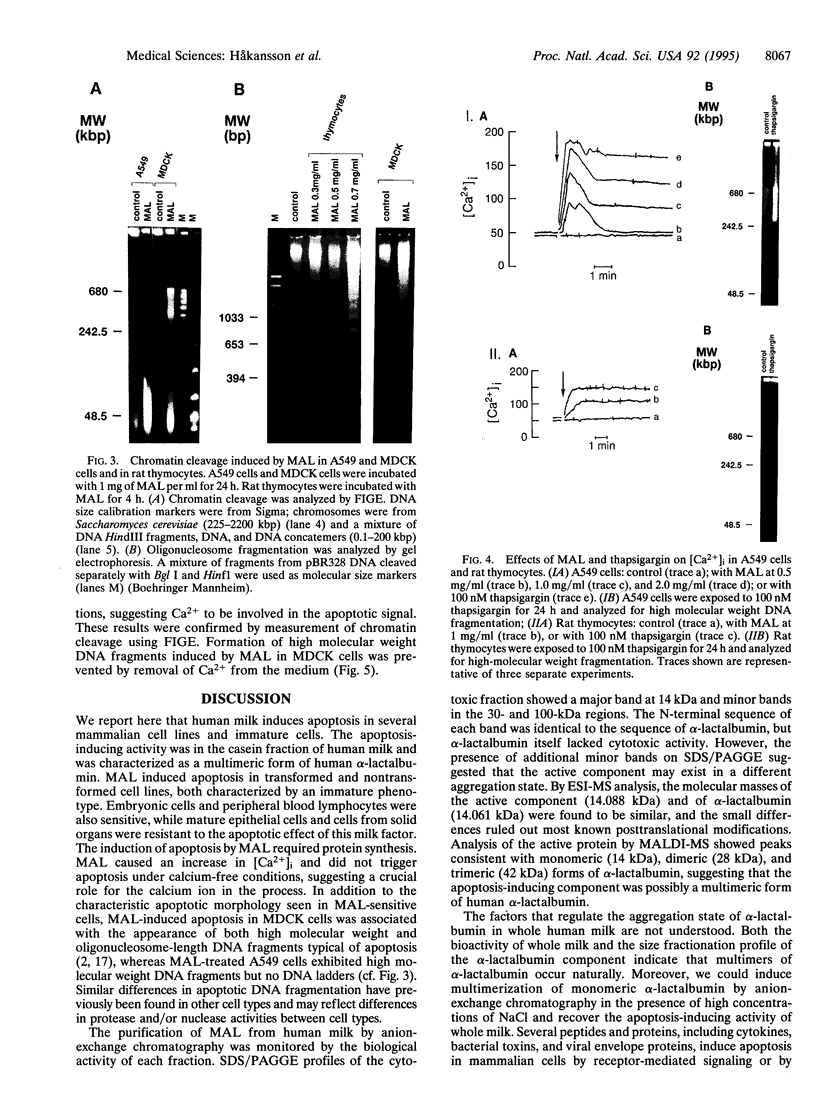
To the breast-fed infant, human milk is more than a source of nutrients; it furnishes a wide array of molecules that restrict microbes, such as antibodies, bactericidins, and inhibitors of bacterial adherence. However, it has rarely been considered that human milk may also contain substances bioactive toward host cells. While investigating the effect of human milk on bacterial adherence to a human lung cancer cell line, we were surprised to discover that the milk killed the cells. Analysis of this effect revealed that a component of milk in a particular physical state--multimeric alpha-lact-albumin--is a potent Ca(2+)-elevating and apoptosis-inducing agent with broad, yet selective, cytotoxic activity. Multimeric alpha-lactalbumin killed all transformed, embryonic, and lymphoid cells tested but spared mature epithelial elements. These findings raise the possibility that milk contributes to mucosal immunity not only by furnishing antimicrobial molecules but also by policing the function of lymphocytes and epithelium. Finally, analysis of the mechanism by which multimeric alpha-lactalbumin induces apoptosis in transformed epithelial cells could lead to the design of antitumor agents.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson B., Dahmén J., Frejd T., Leffler H., Magnusson G., Noori G., Edén C. S. Identification of an active disaccharide unit of a glycoconjugate receptor for pneumococci attaching to human pharyngeal epithelial cells. J Exp Med. 1983 Aug 1;158(2):559–570. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.2.559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banda N. K., Bernier J., Kurahara D. K., Kurrle R., Haigwood N., Sekaly R. P., Finkel T. H. Crosslinking CD4 by human immunodeficiency virus gp120 primes T cells for activation-induced apoptosis. J Exp Med. 1992 Oct 1;176(4):1099–1106. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.4.1099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beavis R. C., Chait B. T. Rapid, sensitive analysis of protein mixtures by mass spectrometry. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6873–6877. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellomo G., Perotti M., Taddei F., Mirabelli F., Finardi G., Nicotera P., Orrenius S. Tumor necrosis factor alpha induces apoptosis in mammary adenocarcinoma cells by an increase in intranuclear free Ca2+ concentration and DNA fragmentation. Cancer Res. 1992 Mar 1;52(5):1342–1346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiat A. M., Jollès P. Caseins of various origins and biologically active casein peptides and oligosaccharides: structural and physiological aspects. Mol Cell Biochem. 1989 May 4;87(1):5–30. doi: 10.1007/BF00421079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillin F. D., Reiner D. S., Wang C. S. Human milk kills parasitic intestinal protozoa. Science. 1983 Sep 23;221(4617):1290–1292. doi: 10.1126/science.6310751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Håkansson A., Kidd A., Wadell G., Sabharwal H., Svanborg C. Adenovirus infection enhances in vitro adherence of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1994 Jul;62(7):2707–2714. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.7.2707-2714.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang S., Chow S. C., Nicotera P., Orrenius S. Intracellular Ca2+ signals activate apoptosis in thymocytes: studies using the Ca(2+)-ATPase inhibitor thapsigargin. Exp Cell Res. 1994 May;212(1):84–92. doi: 10.1006/excr.1994.1121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas D., Walev I., Berger T., Liebetrau M., Palmer M., Bhakdi S. Novel path to apoptosis: small transmembrane pores created by staphylococcal alpha-toxin in T lymphocytes evoke internucleosomal DNA degradation. Infect Immun. 1994 Apr;62(4):1304–1312. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.4.1304-1312.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keough T., Takigiku R., Lacey M. P., Purdon M. Matrix-assisted laser desorption mass spectrometry of proteins isolated by capillary zone electrophoresis. Anal Chem. 1992 Jul 15;64(14):1594–1600. doi: 10.1021/ac00038a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl L., Vogel H. J. Metal-ion-dependent hydrophobic-interaction chromatography of alpha-lactalbumins. Anal Biochem. 1984 Aug 1;140(2):394–402. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90184-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mariggió M. A., Fulle S., Calissano P., Nicoletti I., Fanó G. The brain protein S-100ab induces apoptosis in PC12 cells. Neuroscience. 1994 May;60(1):29–35. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(94)90201-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews T. H., Nair C. D., Lawrence M. K., Tyrrell D. A. Antiviral activity in milk of possible clinical importance. Lancet. 1976 Dec 25;2(8000):1387–1389. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91922-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConkey D. J., Hartzell P., Amador-Pérez J. F., Orrenius S., Jondal M. Calcium-dependent killing of immature thymocytes by stimulation via the CD3/T cell receptor complex. J Immunol. 1989 Sep 15;143(6):1801–1806. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mincheva-Nilsson L., Hammarström M. L., Juto P., Hammarström S. Human milk contains proteins that stimulate and suppress T lymphocyte proliferation. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Mar;79(3):463–469. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb08113.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofek I., Mirelman D., Sharon N. Adherence of Escherichia coli to human mucosal cells mediated by mannose receptors. Nature. 1977 Feb 17;265(5595):623–625. doi: 10.1038/265623a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redhead K., Hill T., Mulloy B. Antimicrobial effect of human milk on Bordetella pertussis. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 Aug;58(3):269–273. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1990.tb13987.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz L. M., Osborne B. A. Programmed cell death, apoptosis and killer genes. Immunol Today. 1993 Dec;14(12):582–590. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90197-S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. J., Moritz R. L., Begg G. S., Rubira M. R., Nice E. C. Micropreparative procedures for high sensitivity sequencing of peptides and proteins. Anal Biochem. 1989 Mar;177(2):221–236. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90044-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinnakre M. G., Vilotte J. L., Soulier S., Mercier J. C. Creation and phenotypic analysis of alpha-lactalbumin-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 5;91(14):6544–6548. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.14.6544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svanborg C., Aniansson G., Mestecky J., Sabharwal H., Wold A. Anti-adhesive molecules in human milk. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1991;310:167–171. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-3838-7_20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viney J. L., Kilshaw P. J., MacDonald T. T. Cytotoxic alpha/beta+ and gamma/delta+ T cells in murine intestinal epithelium. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Jul;20(7):1623–1626. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie A. H. Glucocorticoid-induced thymocyte apoptosis is associated with endogenous endonuclease activation. Nature. 1980 Apr 10;284(5756):555–556. doi: 10.1038/284555a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhivotovsky B., Cedervall B., Jiang S., Nicotera P., Orrenius S. Involvement of Ca2+ in the formation of high molecular weight DNA fragments in thymocyte apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Jul 15;202(1):120–127. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhivotovsky B., Nicotera P., Bellomo G., Hanson K., Orrenius S. Ca2+ and endonuclease activation in radiation-induced lymphoid cell death. Exp Cell Res. 1993 Jul;207(1):163–170. doi: 10.1006/excr.1993.1176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhivotovsky B., Wade D., Gahm A., Orrenius S., Nicotera P. Formation of 50 kbp chromatin fragments in isolated liver nuclei is mediated by protease and endonuclease activation. FEBS Lett. 1994 Sep 5;351(2):150–154. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)00827-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]