Abstract
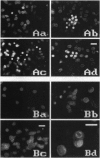
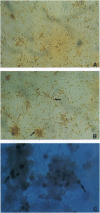
N-Methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor-mediated neurotoxicity may depend, in part, on the generation of nitric oxide (NO.) and superoxide anion (O2.-), which react to form peroxynitrite (OONO-). This form of neurotoxicity is thought to contribute to a final common pathway of injury in a wide variety of acute and chronic neurologic disorders, including focal ischemia, trauma, epilepsy, Huntington disease, Alzheimer disease, amyotrophic lateral scelerosis, AIDS dementia, and other neurodegenerative diseases. Here, we report that exposure of cortical neurons to relatively short durations or low concentrations of NMDA, S-nitrosocysteine, or 3-morpholinosydnonimine, which generate low levels of peroxynitrite, induces a delayed form of neurotoxicity predominated by apoptotic features. Pretreatment with superoxide dismutase and catalase to scavenge O2.- partially prevents the apoptotic process triggered by S-nitrosocysteine or 3-morpholinosydnonimine. In contrast, intense exposure to high concentrations of NMDA or peroxynitrite induces necrotic cell damage characterized by acute swelling and lysis, which cannot be ameliorated by superoxide dismutase and catalase. Thus, depending on the intensity of the initial insult, NMDA or nitric oxide/superoxide can result in either apoptotic or necrotic neuronal cell damage.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ankarcrona M., Dypbukt J. M., Brüne B., Nicotera P. Interleukin-1 beta-induced nitric oxide production activates apoptosis in pancreatic RINm5F cells. Exp Cell Res. 1994 Jul;213(1):172–177. doi: 10.1006/excr.1994.1187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckman J. S., Beckman T. W., Chen J., Marshall P. A., Freeman B. A. Apparent hydroxyl radical production by peroxynitrite: implications for endothelial injury from nitric oxide and superoxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1620–1624. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgoyne L. A., Hewish D. R., Mobbs J. Mammalian chromatin substructure studies with the calcium-magnesium endonuclease and two-dimensional polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis. Biochem J. 1974 Oct;143(1):67–72. doi: 10.1042/bj1430067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bursch W., Oberhammer F., Schulte-Hermann R. Cell death by apoptosis and its protective role against disease. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1992 Jun;13(6):245–251. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(92)90077-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson V. L., Dawson T. M., London E. D., Bredt D. S., Snyder S. H. Nitric oxide mediates glutamate neurotoxicity in primary cortical cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6368–6371. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dessi F., Charriaut-Marlangue C., Khrestchatisky M., Ben-Ari Y. Glutamate-induced neuronal death is not a programmed cell death in cerebellar culture. J Neurochem. 1993 May;60(5):1953–1955. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb13427.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duke R. C., Cohen J. J. IL-2 addiction: withdrawal of growth factor activates a suicide program in dependent T cells. Lymphokine Res. 1986 Fall;5(4):289–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis R. E., Yuan J. Y., Horvitz H. R. Mechanisms and functions of cell death. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:663–698. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.003311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavrieli Y., Sherman Y., Ben-Sasson S. A. Identification of programmed cell death in situ via specific labeling of nuclear DNA fragmentation. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(3):493–501. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.3.493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogg N., Darley-Usmar V. M., Wilson M. T., Moncada S. Production of hydroxyl radicals from the simultaneous generation of superoxide and nitric oxide. Biochem J. 1992 Jan 15;281(Pt 2):419–424. doi: 10.1042/bj2810419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr J. F., Wyllie A. H., Currie A. R. Apoptosis: a basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in tissue kinetics. Br J Cancer. 1972 Aug;26(4):239–257. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1972.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafon-Cazal M., Pietri S., Culcasi M., Bockaert J. NMDA-dependent superoxide production and neurotoxicity. Nature. 1993 Aug 5;364(6437):535–537. doi: 10.1038/364535a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lei S. Z., Pan Z. H., Aggarwal S. K., Chen H. S., Hartman J., Sucher N. J., Lipton S. A. Effect of nitric oxide production on the redox modulatory site of the NMDA receptor-channel complex. Neuron. 1992 Jun;8(6):1087–1099. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90130-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennon S. V., Martin S. J., Cotter T. G. Dose-dependent induction of apoptosis in human tumour cell lines by widely diverging stimuli. Cell Prolif. 1991 Mar;24(2):203–214. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.1991.tb01150.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linnik M. D., Zobrist R. H., Hatfield M. D. Evidence supporting a role for programmed cell death in focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Stroke. 1993 Dec;24(12):2002–2009. doi: 10.1161/01.str.24.12.2002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton S. A., Choi Y. B., Pan Z. H., Lei S. Z., Chen H. S., Sucher N. J., Loscalzo J., Singel D. J., Stamler J. S. A redox-based mechanism for the neuroprotective and neurodestructive effects of nitric oxide and related nitroso-compounds. Nature. 1993 Aug 12;364(6438):626–632. doi: 10.1038/364626a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton S. A., Rosenberg P. A. Excitatory amino acids as a final common pathway for neurologic disorders. N Engl J Med. 1994 Mar 3;330(9):613–622. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199403033300907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loo D. T., Copani A., Pike C. J., Whittemore E. R., Walencewicz A. J., Cotman C. W. Apoptosis is induced by beta-amyloid in cultured central nervous system neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 1;90(17):7951–7955. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.17.7951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacManus J. P., Buchan A. M., Hill I. E., Rasquinha I., Preston E. Global ischemia can cause DNA fragmentation indicative of apoptosis in rat brain. Neurosci Lett. 1993 Dec 24;164(1-2):89–92. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(93)90864-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff M. C. Social controls on cell survival and cell death. Nature. 1992 Apr 2;356(6368):397–400. doi: 10.1038/356397a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz L. M., Smith S. W., Jones M. E., Osborne B. A. Do all programmed cell deaths occur via apoptosis? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 1;90(3):980–984. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.3.980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sáez J. C., Kessler J. A., Bennett M. V., Spray D. C. Superoxide dismutase protects cultured neurons against death by starvation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):3056–3059. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.3056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie A. H., Kerr J. F., Currie A. R. Cell death: the significance of apoptosis. Int Rev Cytol. 1980;68:251–306. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62312-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]