Abstract
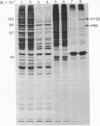
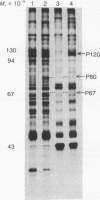
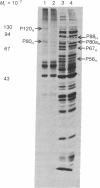
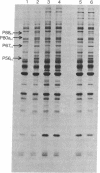
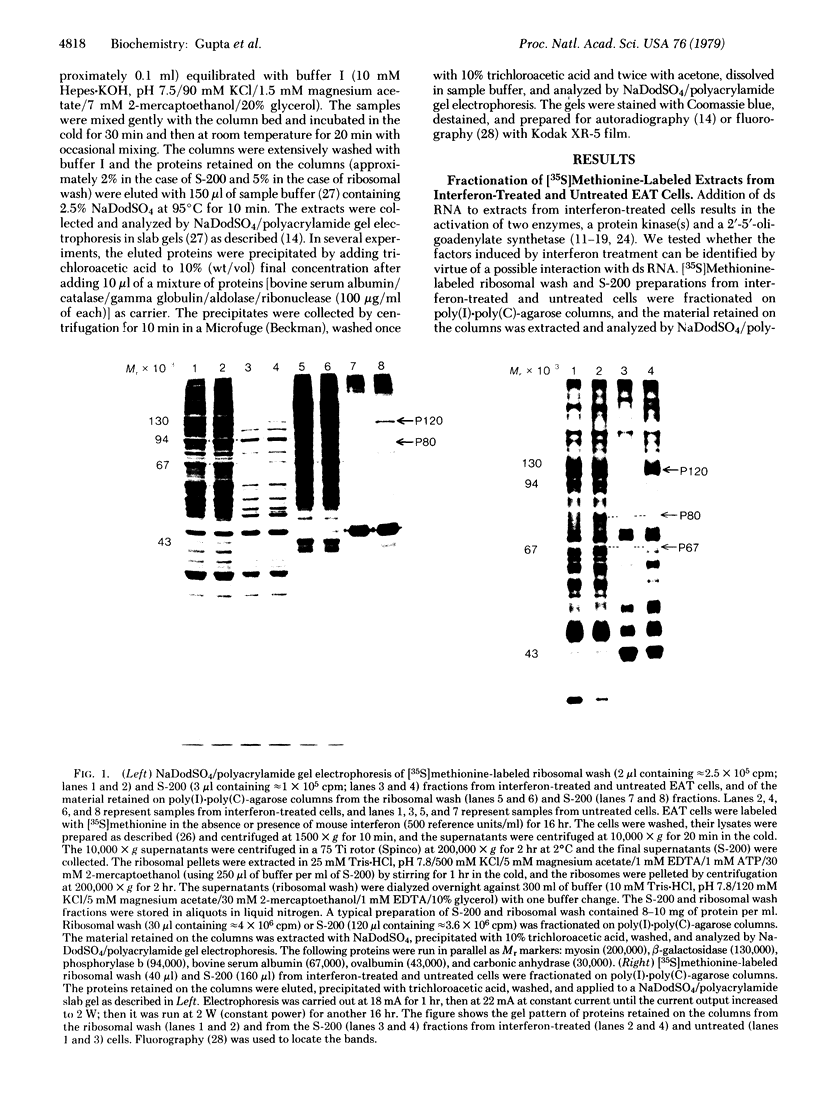
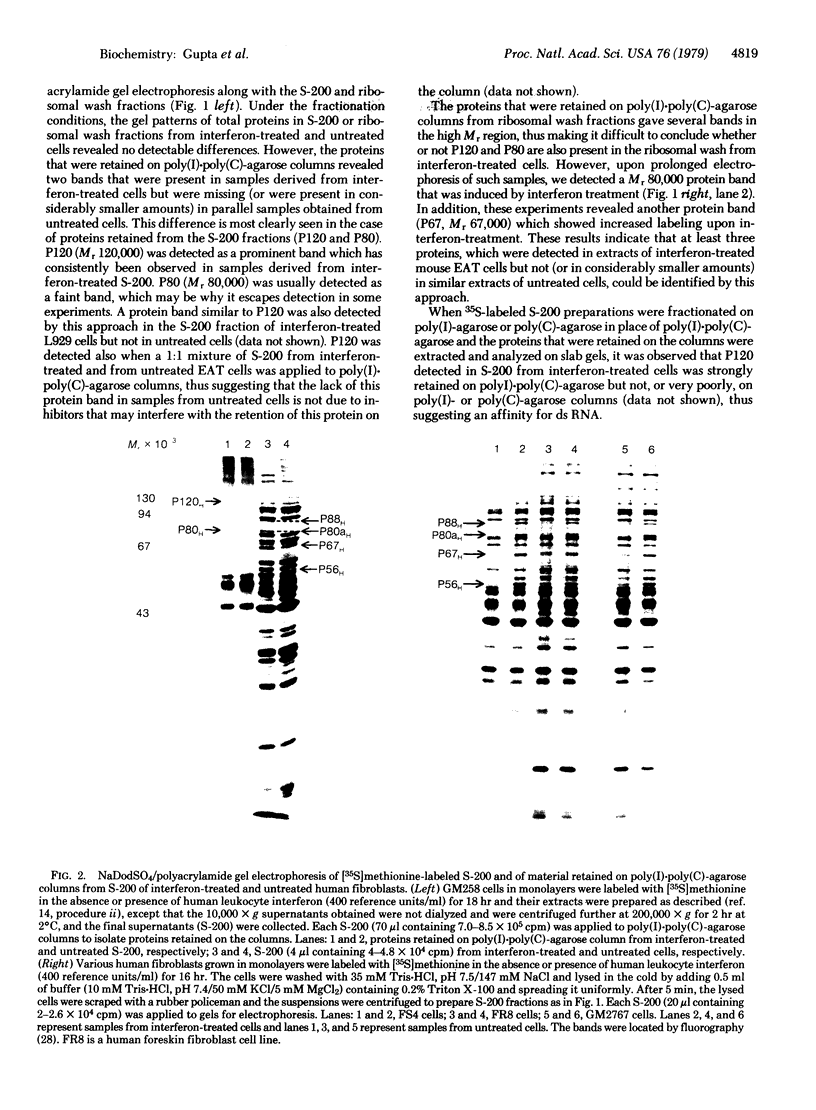
Treatment of mouse (Ehrlich ascites tumor and L929) and human (FS4, GM258, etc.) cells with homologous interferons results in the induction of several proteins. Extracts obtained from cells labeled with [35S]methionine in the absence or presence of interferon were fractionated on poly(I) . poly(C)-agarose columns. The proteins retained on the columns revealed, upon sodium dodecyl sulfate/polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, three protein bands in mouse cells (Mr 120,000; 80,000; and 67,000) and two in human cells (Mr 120,000 and 80,000) which were detected in the extracts of interferon-treated but not of untreated cells. These proteins were retained on double-stranded RNA [poly(I) . poly(C)-agarose] columns but very poorly, if at all, on single-stranded RNA [poly(I)- or poly(C)-agarose] columns, suggesting that they have an affinity for double-stranded RNA. In addition, interferon treatment of human fibroblasts greatly increased the labeling of three other protein bands (Mr 88,000; 67,000; and 56,000) which were detected in whole extracts but were not appreciably retained on poly(I) . poly(C)-agarose columns. The appearance of the induced proteins was blocked by actinomycin D if added together with interferon, indicating that transcription of certain genetic information is required. The possible correlation between the induced proteins described here and the elevated levels of certain enzymes in interferon-treated cells (a protein kinase and 2'-5'-oligoadenylate synthetase) is at present unclear.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baglioni C., Minks M. A., Maroney P. A. Interferon action may be mediated by activation of a nuclease by pppA2'p5'A2'p5'A. Nature. 1978 Jun 22;273(5664):684–687. doi: 10.1038/273684a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball L. A. Induction of 2'5'-oligoadenylate synthetase activity and a new protein by chick interferon. Virology. 1979 Apr 30;94(2):282–296. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90462-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball L. A., White C. N. Oligonucleotide inhibitor of protein synthesis made in extracts of interferon-treated chick embryo cells: comparison with the mouse low molecular weight inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1167–1171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemens M. J., Williams B. R. Inhibition of cell-free protein synthesis by pppA2'p5'A2'p5'A: a novel oligonucleotide synthesized by interferon-treated L cell extracts. Cell. 1978 Mar;13(3):565–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90329-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell P. J., Sen G. C., Dubois M. F., Ratner L., Slattery E., Lengyel P. Interferon action: two distinct pathways for inhibition of protein synthesis by double-stranded RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):5893–5897. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.5893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. M. Antiviral activity of interferons. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Sep;41(3):543–567. doi: 10.1128/br.41.3.543-567.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. M., Sonnabend J. A. Inhibition of interferon action by puromycin. J Immunol. 1965 Oct;95(4):696–703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresser I. On the varied biologic effects of interferon. Cell Immunol. 1977 Dec;34(2):406–415. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(77)90262-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S. L., Sopori M. L., Lengyel P. Inhibition of protein synthesis directed by added viral and cellular messenger RNAs in extracts of interferon-treated Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. Location and dominance of the inhibitor(s). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Sep 18;54(2):777–783. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91491-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S. L. Specific protein phosphorylation in interferon-treated uninfected and virus-infected mouse L929 cells: enhancement by double-stranded RNA. J Virol. 1979 Jan;29(1):301–311. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.1.301-311.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakita M., Cabrer B., Taira H., Rebello M., Slattery E., Weideli H., Lengyel P. Purification of interferon from mouse Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jan 25;253(2):598–602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr I. M., Brown R. E., Hovanessian A. G. Nature of inhibitor of cell-free protein synthesis formed in response to interferon and double-stranded RNA. Nature. 1977 Aug 11;268(5620):540–542. doi: 10.1038/268540a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr I. M., Brown R. E. pppA2'p5'A2'p5'A: an inhibitor of protein synthesis synthesized with an enzyme fraction from interferon-treated cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):256–260. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINE S. EFFECT OF ACTINOMYCIN D AND PUROMYCIN DIHYDROCHLORIDE ON ACTION OF INTERFERON. Virology. 1964 Dec;24:586–588. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90211-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebleu B., Sen G. C., Shaila S., Cabrer B., Lengyel P. Interferon, double-stranded RNA, and protein phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3107–3111. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radke K. L., Colby C., Kates J. R., Krider H. M., Prescott D. M. Establishment and maintenance of the interferon-induced antiviral state: studies in enucleated cells. J Virol. 1974 Mar;13(3):623–630. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.3.623-630.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratner L., Wiegand R. C., Farrell P. J., Sen G. C., Cabrer B., Lengyel P. Interferon, double-stranded RNA and RNA degradation. Fractionation of the endonucleaseINT system into two macromolecular components; role of a small molecule in nuclease activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Apr 14;81(3):947–954. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91443-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts W. K., Hovanessian A., Brown R. E., Clemens M. J., Kerr I. M. Interferon-mediated protein kinase and low-molecular-weight inhibitor of protein synthesis. Nature. 1976 Dec 2;264(5585):477–480. doi: 10.1038/264477a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt A., Zilberstein A., Shulman L., Federman P., Berissi H., Revel M. Interferon action: isolation of nuclease F, a translation inhibitor activated by interferon-induced (2'-5') oligo-isoadenylate. FEBS Lett. 1978 Nov 15;95(2):257–264. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)81006-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen G. C., Taira H., Lengyel P. Interferon, double-stranded RNA, and protein phosphorylation. Characteristics of a double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase system partially purified from interferon treated Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 10;253(17):5915–5921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. Inhibition of interferon action by actinomycin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1964;14:447–451. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(64)90084-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young C. S., Pringle C. R., Follett E. A. Action of interferon in enucleated cells. J Virol. 1975 Feb;15(2):428–429. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.2.428-429.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilberstein A., Federman P., Shulman L., Revel M. Specific phosphorylation in vitro of a protein associated with ribosomes of interferon-treated mouse L cells. FEBS Lett. 1976 Sep 15;68(1):119–124. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80418-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilberstein A., Kimchi A., Schmidt A., Revel M. Isolation of two interferon-induced translational inhibitors: a protein kinase and an oligo-isoadenylate synthetase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4734–4738. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]