Abstract
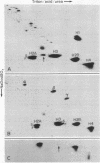
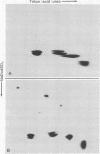
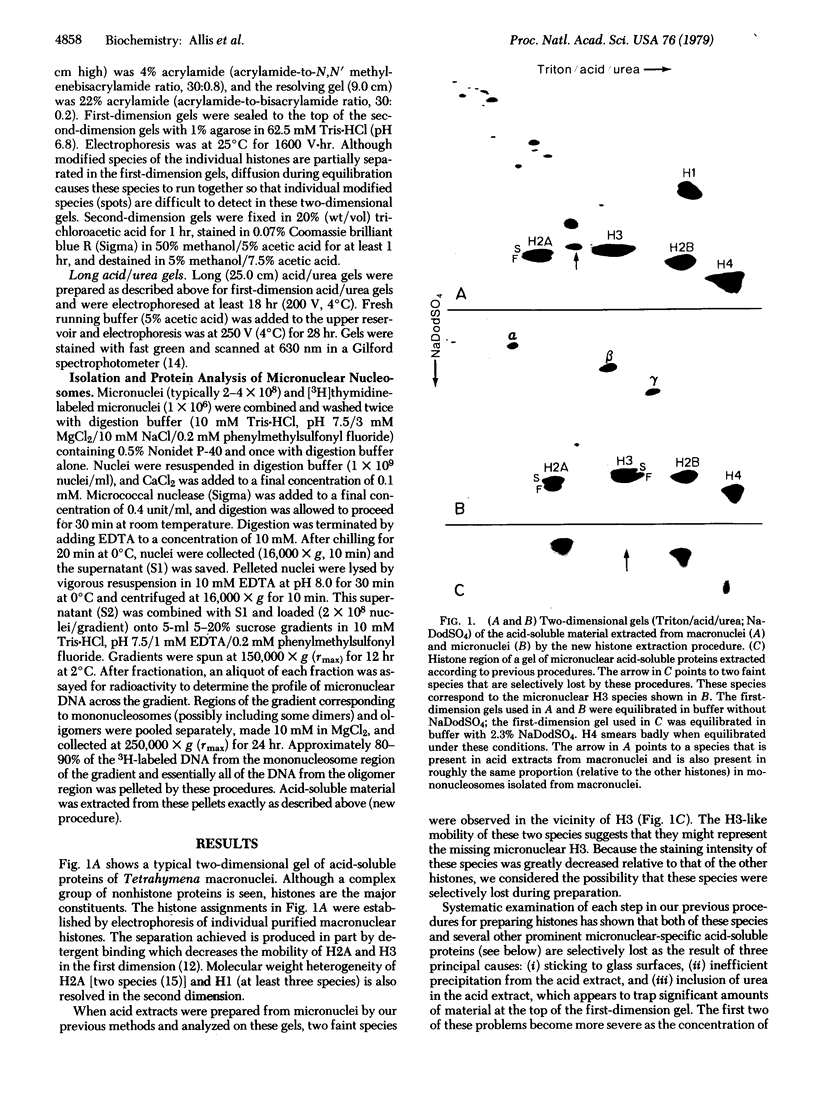
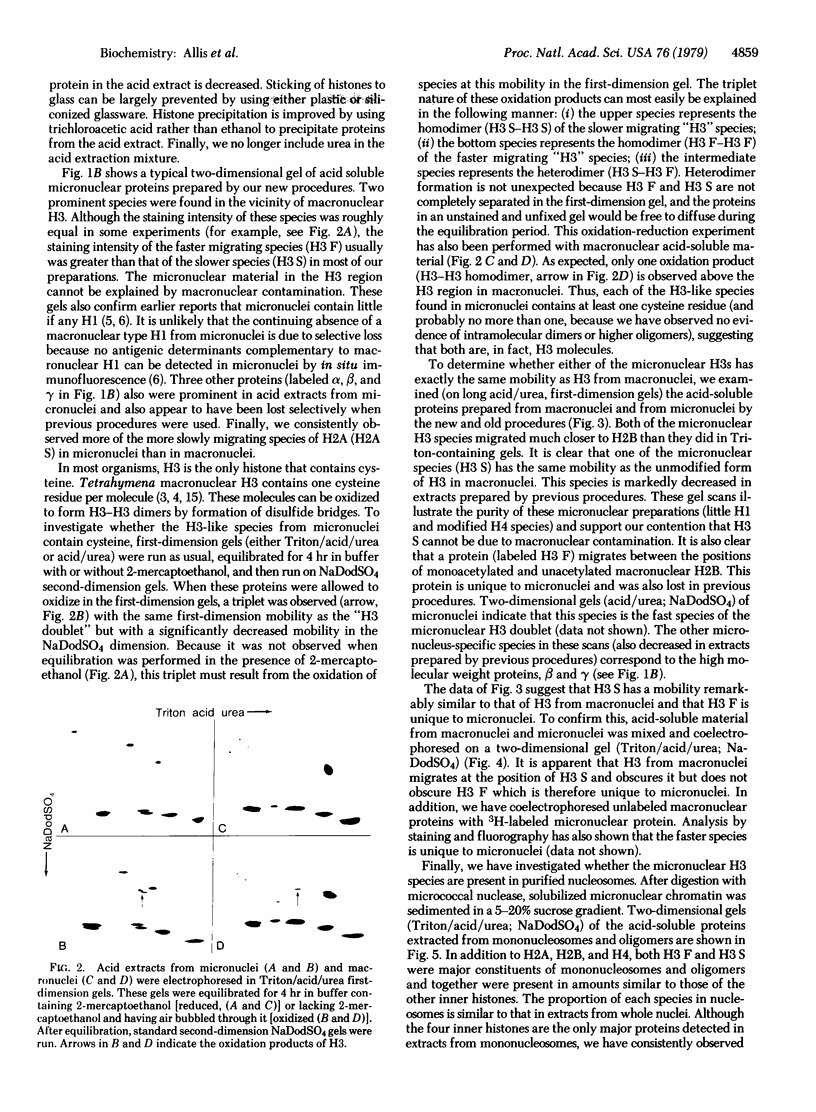
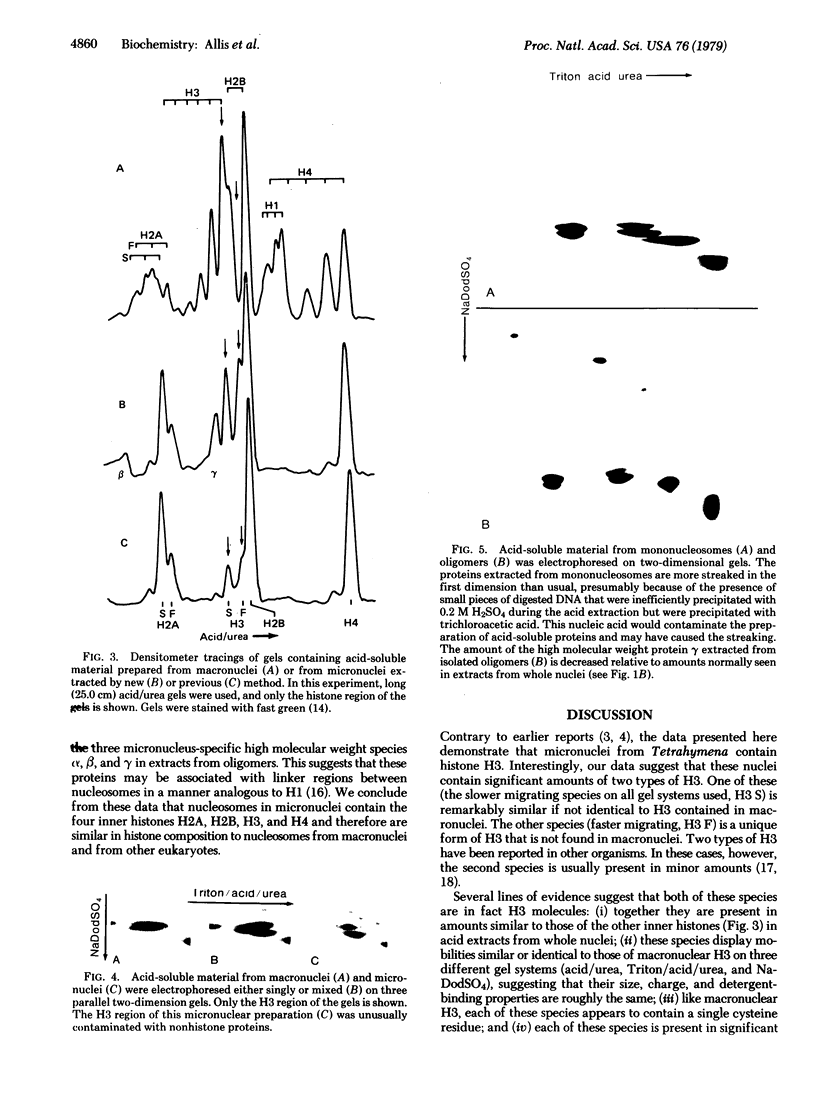
Evidence is presented that micronuclei of Tetrahymena thermophila contain significant amounts of two types of histone H3. One is indistinguishable from that found in macronuclei and the other is unique to micronuclei. The micronucleus-specific H3 has a slightly faster mobility than the common H3 in three different gel systems (both of these species were artifactually lost during procedures for histone preparation in previous studies). Both micronuclear H3s appear to contain a single cysteine residue and are present in sucrose gradient-purified nucleosomes. Acid extracts from micronuclei also contain three prominent high molecular weight proteins that also were lost during previous procedures. These proteins are present in extracts from oligomers but are not observed in extracts from mononucleosomes, suggesting that they may be associated with linker regions between nucleosomes.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alfageme C. R., Zweidler A., Mahowald A., Cohen L. H. Histones of Drosophila embryos. Electrophoretic isolation and structural studies. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 25;249(12):3729–3736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrard W. T. Two forms of rat liver histone H3. FEBS Lett. 1976 May 1;64(2):323–325. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80320-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glover C. V., Gorovsky M. A. Histone-histone interactions in a lower eukaryote, Tetrahymena thermophila. Biochemistry. 1978 Dec 26;17(26):5705–5713. doi: 10.1021/bi00619a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorovsky M. A., Carlson K., Rosenbaum J. L. Simple method for quantitive densitometry of polyacrylamide gels using fast green. Anal Biochem. 1970 Jun;35(2):359–370. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90196-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorovsky M. A., Glover C., Johmann C. A., Keevert J. B., Mathis D. J., Samuelson M. Histones and chromatin structure in Tetrahymena macro- and micronuclei. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 1):493–503. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorovsky M. A., Keevert J. B. Absence of histone F1 in a mitotically dividing, genetically inactive nucleus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2672–2676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorovsky M. A., Keevert J. B. Subunit structure of a naturally occurring chromatin lacking histones F1 and F3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3536–3540. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorovsky M. A. Macro- and micronuclei of Tetrahymena pyriformis: a model system for studying the structure and function of eukaryotic nuclei. J Protozool. 1973 Feb;20(1):19–25. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1973.tb05995.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorovsky M. A., Pleger G. L., Keevert J. B., Johmann C. A. Studies on histone fraction F2A1 in macro- and micronuclei of Tetrahymena pyriformis. J Cell Biol. 1973 Jun;57(3):773–781. doi: 10.1083/jcb.57.3.773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorovsky M. A., Yao M. C., Keevert J. B., Pleger G. L. Isolation of micro- and macronuclei of Tetrahymena pyriformis. Methods Cell Biol. 1975;9(0):311–327. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60080-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johmann C. A., Gorovsky M. A. Immunofluorescence evidence for the absence of histone H1 in a mitotically dividing, genetically inactive nucleus. J Cell Biol. 1976 Oct;71(1):89–95. doi: 10.1083/jcb.71.1.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johmann C. A., Gorovsky M. A. Purification and characterization of the histones associated with the macronucleus of Tetrahymena. Biochemistry. 1976 Mar 23;15(6):1249–1256. doi: 10.1021/bi00651a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg R. D. Structure of chromatin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:931–954. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.004435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marzluff W. F., Jr, Sanders L. A., Miller D. M., McCarty K. S. Two chemically and metabolically distinct forms of calf thymus histone F3. J Biol Chem. 1972 Apr 10;247(7):2026–2033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panyim S., Jensen R. H., Chalkley R. Proteolytic contamination of calf thymus nucleohistone and its inhibition. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jun 26;160(2):252–255. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(68)90095-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshavsky A. J., Bakayev V. V., Georgiev G. P. Heterogeneity of chromatin subunits in vitro and location of histone H1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Feb;3(2):477–492. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.2.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]