Abstract
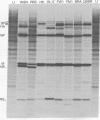
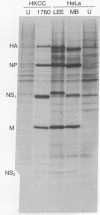
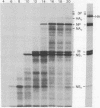
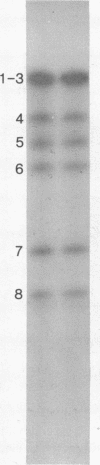
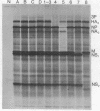
In previous studies we showed that a ninth polypeptide with a molecular weight of approximately 11,000 (NS2) found in influenza virus-infected cells was unique, that it could be synthesized in vitro, and that its expression in vivo required early protein synthesis. On the basis of these results we suggested that one of the eight genome RNA segments of influenza virus codes for two polypeptides [Lamb, R.A., Etkind, P.R. & Choppin, P.W. (1978) Virology 91, 60-78]. We describe here differences in the electrophoretic mobility of the NS2 polypeptides of different strains of influenza A virus. These results provided further evidence that NS2 is virus coded and also made possible genetic studies using recombinants between two virus strains (HK and PR8) whose NS2 polypeptides differ. These studies showed that the gene for NS2 reassorts with that of the nonstructural polypeptide NS1, which is coded by genome segment 8. A mRNA for NS2 has been separated from that of NS1 and the other viral polypeptides by centrifugation and has been translated in vitro. Hybridization of genome segment 8 to the total mRNAs from infected cells specifically prevented the synthesis of NS2 and NS1. These results indicate that influenza virus genome segment 8 is transcribed into two separate mRNAs that code for two polypeptides, NS1 and NS2. Possible mechanisms for the transcription of the two mRNAs from either contiguous or overlapping genes are discussed.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almond J. W., McGeoch D., Barry R. D. Method for assigning temperature-sensitive mutations of influenza viruses to individual segments of the genome. Virology. 1977 Aug;81(1):62–73. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90058-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrell B. G., Air G. M., Hutchison C. A., 3rd Overlapping genes in bacteriophage phiX174. Nature. 1976 Nov 4;264(5581):34–41. doi: 10.1038/264034a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry R. D., Mahy B. W. The influenza virus genome and its replication. Br Med Bull. 1979 Jan;35(1):39–46. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brzeski H., Kennedy S. I. Synthesis of alphavirus-specified RNA. J Virol. 1978 Feb;25(2):630–640. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.2.630-640.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choppin P. W. Replication of influenza virus in a continuous cell line: high yield of infective virus from cells inoculated at high multiplicity. Virology. 1969 Sep;39(1):130–134. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90354-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Contreras R., Rogiers R., Van de Voorde A., Fiers W. Overlapping of the VP2-VP3 gene and the VP1 gene in the SV40 genome. Cell. 1977 Oct;12(2):529–538. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90129-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimmock N. J. New virus-specific antigens in cells infected with influenza virus. Virology. 1969 Oct;39(2):224–234. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90042-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emtage J. S., Catlin G. H., Carey N. H. Polyadenylation and reverse transcription of influenza viral RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Apr;6(4):1221–1239. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.4.1221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etkind P. R., Krug R. M. Purification of influenza viral complementary RNA: its genetic content and activity in wheat germ cell-free extracts. J Virol. 1975 Dec;16(6):1464–1475. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.6.1464-1475.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Follett E. A., Pringle C. R., Wunner W. H., Skehel J. J. Virus replication in enucleate cells: vesicular stomatitis virus and influenza virus. J Virol. 1974 Feb;13(2):394–399. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.2.394-399.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay A. J., Lomniczi B., Bellamy A. R., Skehel J. J. Transcription of the influenza virus genome. Virology. 1977 Dec;83(2):337–355. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90179-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T. R., Hunt T., Knowland J., Zimmern D. Messenger RNA for the coat protein of tobacco mosaic virus. Nature. 1976 Apr 29;260(5554):759–764. doi: 10.1038/260759a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inglis S. C., Barrett T., Brown C. M., Almond J. W. The smallest genome RNA segment of influenza virus contains two genes that may overlap. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3790–3794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inglis S. C., Carroll A. R., Lamb R. A., Mahy B. W. Polypeptides specified by the influenza virus genome I. Evidence for eight distinct gene products specified by fowl plague virus. Virology. 1976 Oct 15;74(2):489–503. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90355-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inglis S. C., McGeoch D. J., Mahy B. W. Polypeptides specified by the influenza virus genoma. 2. Assignement of protein coding functions to individual genome segments by in vitro translation. Virology. 1977 May 15;78(2):522–536. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90128-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y., Joklik W. K. Temperature-sensitive mutants of reovirus. I. Patterns of gene expression by mutants of groups C, D, and E. Virology. 1972 Oct;50(1):189–201. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90359-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeppesen P. G., Barrell B. G., Sanger F., Coulson A. R. Nucleotide sequences of two fragments from the coat-protein cistron of bacteriophage R17 ribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1972 Aug;128(5):993–1006. doi: 10.1042/bj1280993h. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krug R. M., Soeiro R. Studies on the intranuclear localization of influenza virus-specific proteins. Virology. 1975 Apr;64(2):378–387. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90114-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb R. A., Choppin P. W. Synthesis of influenza virus proteins in infected cells: translation of viral polypeptides, including three P polypeptides, from RNA produced by primary transcription. Virology. 1976 Oct 15;74(2):504–519. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90356-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb R. A., Etkind P. R., Choppin P. W. Evidence for a ninth influenza viral polypeptide. Virology. 1978 Nov;91(1):60–78. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90355-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarowitz S. G., Compans R. W., Choppin P. W. Influenza virus structural and nonstructural proteins in infected cells and their plasma membranes. Virology. 1971 Dec;46(3):830–843. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90084-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubeck M. D., Palese P., Schulman J. L. Nonrandom association of parental genes in influenza A virus recombinants. Virology. 1979 May;95(1):269–274. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90430-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D., Fellner P., Newton C. Influenza virus genome consists of eight distinct RNA species. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3045–3049. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minor P. D., Dimmock N. J. Inhibition of synthesis of influenza virus proteins: evidence of two host-cell-dependent events during multiplication. Virology. 1975 Sep;67(1):114–123. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90409-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palese P., Ritchey M. B., Schulman J. L. P1 and P3 proteins of influenza virus are required for complementary RNA synthesis. J Virol. 1977 Mar;21(3):1187–1195. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.3.1187-1195.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palese P., Schulman J. L. Differences in RNA patterns of influenza A viruses. J Virol. 1976 Mar;17(3):876–884. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.3.876-884.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palese P. The genes of influenza virus. Cell. 1977 Jan;10(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90133-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plotch S. J., Krug R. M. Segments of influenza virus complementary RNA synthesized in vitro. J Virol. 1978 Feb;25(2):579–586. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.2.579-586.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pons M. W. A reexamination of influenza single-and double-stranded RNAs by gel electrophoresis. Virology. 1976 Feb;69(2):789–792. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90508-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Privalsky M. L., Penhoet E. E. Influenza virus proteins: identity, synthesis, and modification analyzed by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3625–3629. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchey M. B., Palese P., Schulman J. L. Mapping of the influenza virus genome. III. Identification of genes coding for nucleoprotein, membrane protein, and nonstructural protein. J Virol. 1976 Oct;20(1):307–313. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.1.307-313.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawicki D. L., Kaariainen L., Lambek C., Gomatos P. J. Mechanism for control of synthesis of Semliki Forest virus 26S and 42s RNA. J Virol. 1978 Jan;25(1):19–27. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.1.19-27.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholtissek C., Harms E., Rohde W., Orlich M., Rott R. Correlation between RNA fragments of fowl plague virus and their corresponding gene functions. Virology. 1976 Oct 15;74(2):332–344. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90340-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulman J. L., Palese P. Selection and identification of influenza virus recombinants of defined genetic composition. J Virol. 1976 Oct;20(1):248–254. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.1.248-254.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih D. S., Kaesberg P. Translation of brome mosaic viral ribonucleic acid in a cell-free system derived from wheat embryo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jun;70(6):1799–1803. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.6.1799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skehel J. J. Early polypeptide synthesis in influenza virus-infected cells. Virology. 1973 Nov;56(1):394–399. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90320-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skehel J. J. Polypeptide synthesis in influenza virus-infected cells. Virology. 1972 Jul;49(1):23–36. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(72)80004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleigh M. J., Both G. W., Brownlee G. G. A new method for the size estimation of the RNA genome segments of influenza virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Apr;6(4):1309–1321. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.4.1309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson J. R., Hay A. J., Skehel J. J. Characterization of virus-specific messenger RNAs from avian fibroblasts infected with fowl plague virus. J Gen Virol. 1977 Aug;36(2):237–248. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-36-2-237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]