Abstract
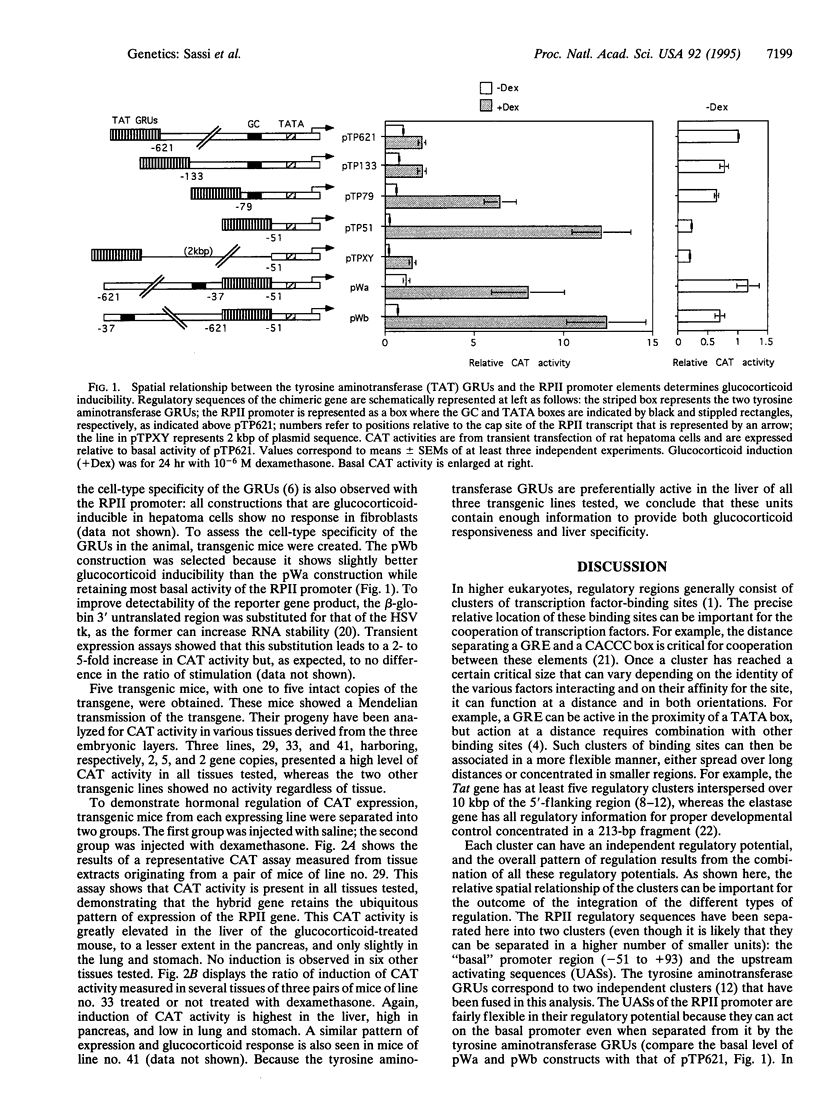
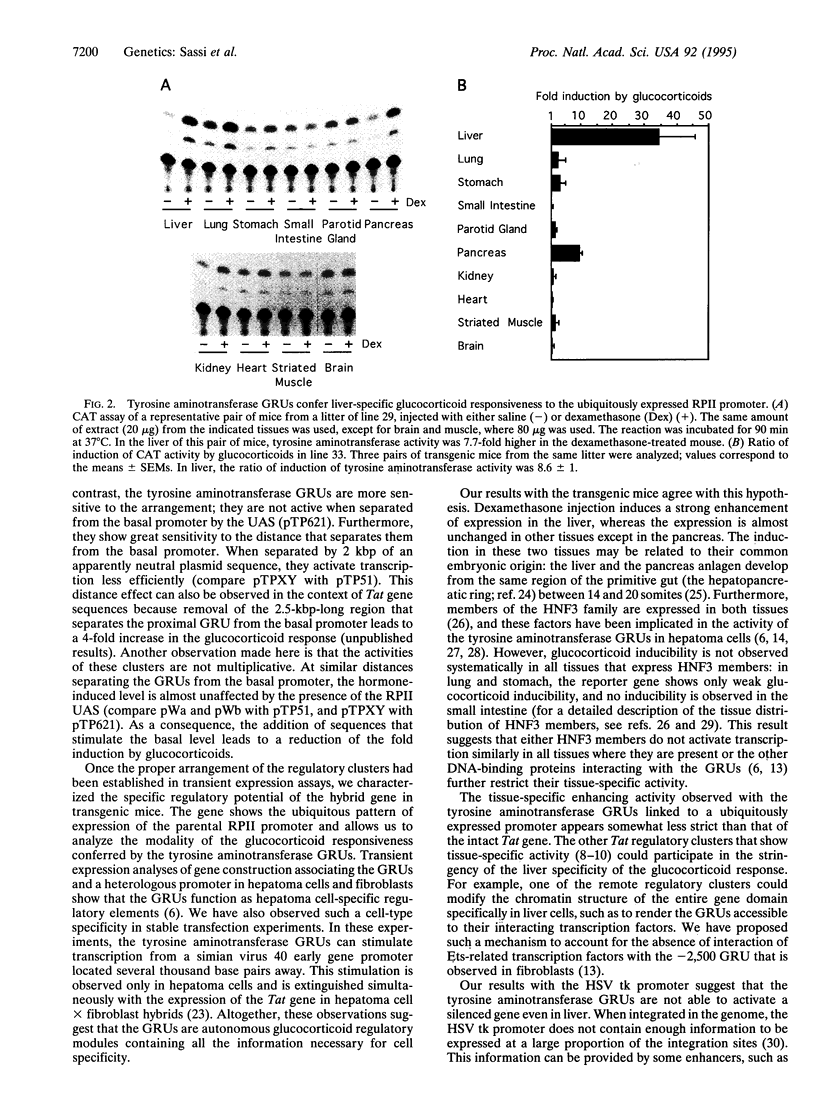
The glucocorticoid-responsive units (GRUs) of the rat tyrosine aminotransferase were associated with the regulatory sequences of a cellular gene expressed ubiquitously--that coding for the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II. In transient expression assays, glucocorticoid responsiveness of the hybrid regulatory regions depends on the spatial relationship and number of regulatory elements. Two parameters affect the ratio of induction by glucocorticoids: the basal level of the hybrid promoter that is affected by the RNA polymerase II regulatory sequences and the glucocorticoid-induced level that depends on the distance between the GRUs and the TATA box. A fully active glucocorticoid-responsive hybrid gene was used to generate transgenic mice. Results show that a composite regulatory pattern is obtained: ubiquitous basal expression characteristic of the RNA polymerase II gene and liver-specific glucocorticoid activation characteristic of the tyrosine aminotransferase GRUs. This result demonstrates that the activity of the tyrosine aminotransferase GRUs is cell-type-specific not only in cultured cells but also in the whole animal.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahearn J. M., Jr, Bartolomei M. S., West M. L., Cisek L. J., Corden J. L. Cloning and sequence analysis of the mouse genomic locus encoding the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10695–10705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen N. D., Cran D. G., Barton S. C., Hettle S., Reik W., Surani M. A. Transgenes as probes for active chromosomal domains in mouse development. Nature. 1988 Jun 30;333(6176):852–855. doi: 10.1038/333852a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ang S. L., Wierda A., Wong D., Stevens K. A., Cascio S., Rossant J., Zaret K. S. The formation and maintenance of the definitive endoderm lineage in the mouse: involvement of HNF3/forkhead proteins. Development. 1993 Dec;119(4):1301–1315. doi: 10.1242/dev.119.4.1301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beato M. Gene regulation by steroid hormones. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boshart M., Weih F., Schmidt A., Fournier R. E., Schütz G. A cyclic AMP response element mediates repression of tyrosine aminotransferase gene transcription by the tissue-specific extinguisher locus Tse-1. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):905–916. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90201-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuif M. H., Cognet M., Boquet D., Tremp G., Kahn A., Vaulont S. Elements responsible for hormonal control and tissue specificity of L-type pyruvate kinase gene expression in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;12(11):4852–4861. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.11.4852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S. Modularity in promoters and enhancers. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90393-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espinás M. L., Roux J., Ghysdael J., Pictet R., Grange T. Participation of Ets transcription factors in the glucocorticoid response of the rat tyrosine aminotransferase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jun;14(6):4116–4125. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.6.4116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grange T., Roux J., Fromont-Racine M., Pictet R. Positive and negative regulation of a transfected chimeric tyrosine aminotransferase gene: effect of copy number. Exp Cell Res. 1989 Jan;180(1):220–233. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(89)90226-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grange T., Roux J., Rigaud G., Pictet R. Cell-type specific activity of two glucocorticoid responsive units of rat tyrosine aminotransferase gene is associated with multiple binding sites for C/EBP and a novel liver-specific nuclear factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jan 11;19(1):131–139. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.1.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grange T., Roux J., Rigaud G., Pictet R. Two remote glucocorticoid responsive units interact cooperatively to promote glucocorticoid induction of rat tyrosine aminotransferase gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 11;17(21):8695–8709. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.21.8695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granner D. K., Hargrove J. L. Regulation of the synthesis of tyrosine aminotransferase: the relationship to mRNATAT. Mol Cell Biochem. 1983;53-54(1-2):113–128. doi: 10.1007/BF00225249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai E., Stromstedt P. E., Quinn P. G., Carlstedt-Duke J., Gustafsson J. A., Granner D. K. Characterization of a complex glucocorticoid response unit in the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4712–4719. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jantzen H. M., Strähle U., Gloss B., Stewart F., Schmid W., Boshart M., Miksicek R., Schütz G. Cooperativity of glucocorticoid response elements located far upstream of the tyrosine aminotransferase gene. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):29–38. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90752-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabnick K. S., Housman D. E. Determinants that contribute to cytoplasmic stability of human c-fos and beta-globin mRNAs are located at several sites in each mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3244–3250. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaestner K. H., Hiemisch H., Luckow B., Schütz G. The HNF-3 gene family of transcription factors in mice: gene structure, cDNA sequence, and mRNA distribution. Genomics. 1994 Apr;20(3):377–385. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luciw P. A., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E., Capecchi M. R. Location and function of retroviral and SV40 sequences that enhance biochemical transformation after microinjection of DNA. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitsch D., Boshart M., Schütz G. Activation of the tyrosine aminotransferase gene is dependent on synergy between liver-specific and hormone-responsive elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 15;90(12):5479–5483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.12.5479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitsch D., Stewart A. F., Boshart M., Mestril R., Weih F., Schütz G. Chromatin structures of the rat tyrosine aminotransferase gene relate to the function of its cis-acting elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3334–3342. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornitz D. M., Palmiter R. D., Hammer R. E., Brinster R. L., Swift G. H., MacDonald R. J. Specific expression of an elastase-human growth hormone fusion gene in pancreatic acinar cells of transgenic mice. Nature. 1985 Feb 14;313(6003):600–602. doi: 10.1038/313600a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rettinger S. D., Kennedy S. C., Wu X., Saylors R. L., Hafenrichter D. G., Flye M. W., Ponder K. P. Liver-directed gene therapy: quantitative evaluation of promoter elements by using in vivo retroviral transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Feb 15;91(4):1460–1464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.4.1460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigaud G., Roux J., Pictet R., Grange T. In vivo footprinting of rat TAT gene: dynamic interplay between the glucocorticoid receptor and a liver-specific factor. Cell. 1991 Nov 29;67(5):977–986. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90370-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roux J., Pictet R., Grange T. Hepatocyte nuclear factor 3 determines the amplitude of the glucocorticoid response of the rat tyrosine aminotransferase gene. DNA Cell Biol. 1995 May;14(5):385–396. doi: 10.1089/dna.1995.14.385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweizer-Groyer G., Groyer A., Cadepond F., Grange T., Baulieu E. E., Pictet R. Expression from the tyrosine aminotransferase promoter (nt -350 to +1) is liver-specific and dependent on the binding of both liver-enriched and ubiquitous trans-acting factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 May 11;22(9):1583–1592. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.9.1583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüle R., Muller M., Kaltschmidt C., Renkawitz R. Many transcription factors interact synergistically with steroid receptors. Science. 1988 Dec 9;242(4884):1418–1420. doi: 10.1126/science.3201230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüle R., Muller M., Otsuka-Murakami H., Renkawitz R. Cooperativity of the glucocorticoid receptor and the CACCC-box binding factor. Nature. 1988 Mar 3;332(6159):87–90. doi: 10.1038/332087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strähle U., Schmid W., Schütz G. Synergistic action of the glucocorticoid receptor with transcription factors. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3389–3395. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03212.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




