Abstract
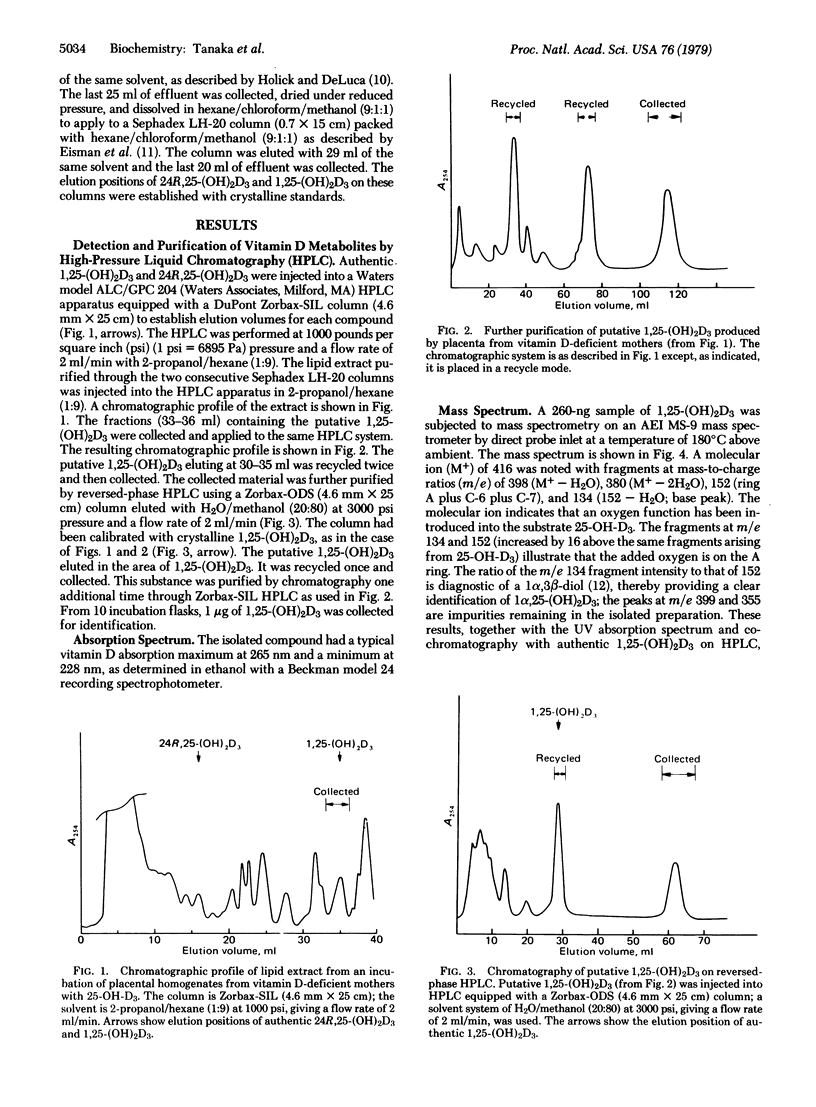
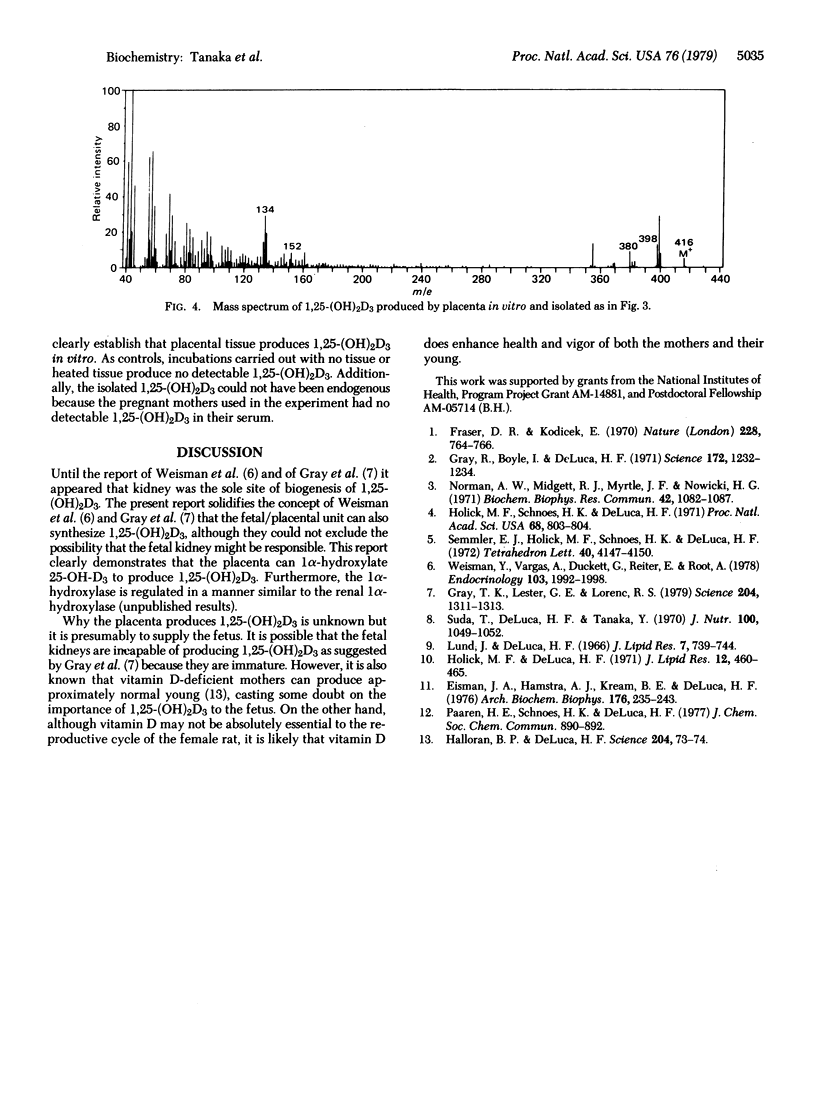
Weanling female rats were fed a vitamin D-deficient diet for 4 months until they reached maturity. They were mated with normal, vitamin D-replete male rats and, at 20 days of pregnancy, the female rats were killed and their placentae were removed, homogenzied, and incubated with 25-hydroxyvitamin D3. The incubation mixtures were extracted and the extracts were subjected to Sephadex LH-20 column chromatography followed by high-pressure liquid chromatography. The 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 region of the high-pressure liquid chromatogram was recycled to purity and the structure of the product was identified as 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 by ultraviolet absorption spectrophotometry and by mass spectrometry. Thus it is now evident that placenta, in addition to renal tissue, is capable of converting 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 to the hormonal form of vitamin D, 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Eisman J. A., Hamstra A. J., Kream B. E., DeLuca H. F. A sensitive, precise, and convenient method for determination of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D in human plasma. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Sep;176(1):235–243. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90161-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser D. R., Kodicek E. Unique biosynthesis by kidney of a biological active vitamin D metabolite. Nature. 1970 Nov 21;228(5273):764–766. doi: 10.1038/228764a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray R., Boyle I., DeLuca H. F. Vitamin D metabolism: the role of kidney tissue. Science. 1971 Jun 18;172(3989):1232–1234. doi: 10.1126/science.172.3989.1232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray T. K., Lester G. E., Lorenc R. S. Evidence for extra-renal 1 alpha-hydroxylation of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 in pregnancy. Science. 1979 Jun 22;204(4399):1311–1313. doi: 10.1126/science.451538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holick M. F., DeLuca H. F. A new chromatographic system for vitamin D3 and its metabolites: resoluation of a new vitamin D3 metabolite. J Lipid Res. 1971 Jul;12(4):460–465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holick M. F., Schnoes H. K., DeLuca H. F. Identification of 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol, a form of vitamin D3 metabolically active in the intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Apr;68(4):803–804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.4.803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund J., DeLuca H. F. Biologically active metabolite of vitamin D3 from bone, liver, and blood serum. J Lipid Res. 1966 Nov;7(6):739–744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman A. W., Midgett R. J., Myrtle J. F., Nowicki H. G. Studies on calciferol metabolism. I. Production of vitamin D metabolite 4B from 25-OH-cholecalciferol by kidney homogenates. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Mar 19;42(6):1082–1087. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90015-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suda T., DeLuca H. F., Tanaka Y. Biological activity of 25-hydroxyergocalciferol in rats. J Nutr. 1970 Sep;100(9):1049–1052. doi: 10.1093/jn/100.9.1049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisman Y., Vargas A., Duckett G., Reiter E., Root A. W. Synthesis of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D in the nephrectomized pregnant rat. Endocrinology. 1978 Dec;103(6):1992–1996. doi: 10.1210/endo-103-6-1992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



