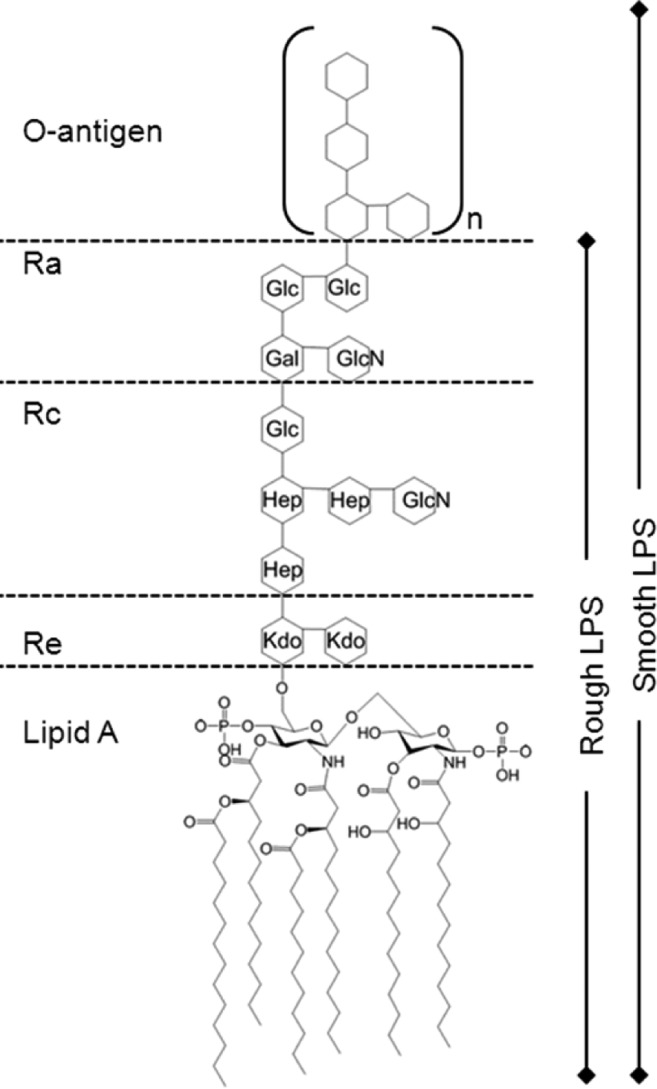
In the original publication, the schematic of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) from Escherichia coli in Figure 1 is incorrect. A corrected version of the figure and accompanying legend is below.
Figure 1.
Schematic of the organization of Escherichia coli LPS. LPS was from the rough mutant J5 strain of E. coli O111:B4, which produces an Rc chemotype with a core oligosaccharide as described by Müller-Loennies et al.1 The original R mutants, which defined the different chemotypes were from Salmonella minnesota, so in this paper we use the terms Ra/Rc to denote the chemotype of E. coli LPS used according to this convention. Kdo, 2-keto-3-deoxyoctonic acid; Hep, l-glycero-D-manno heptose; Glc, glucose; Gal, galactose; GlcN, glucosamine. The Lipid A tails consists of four (R)-3-hydroxy-mystic acids, one myristic acid, and one lauric acid. Additional phosphates and ethanolamines on Kdo and Hep have been omitted for clarity.
References
- Müller-Loennies S.; Holst O.; Lindner B.; Brade H. Eur. J. Biochem. 1999, 260, 235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]