Abstract
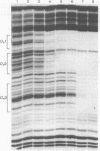
The λ phage repressor binds cooperatively to the three sites in the right operator (OR) according to the following pattern. If the DNA is wild type, OR1 and OR2 are filled coordinately because of interactions between repressor dimers bound to these two sites. Site OR3 is filled only at higher repressor concentrations. In contrast, if OR1 is mutant, OR2 and OR3 are filled coordinately because of interactions between repressors bound to these sites. In this case, the affinity of OR3 is increased and that of OR2 is decreased relative to the wild type. We infer that a repressor dimer bound to the middle site OR2 can interact either with another repressor dimer bound to OR1 (wild-type case) or, alternatively, with one bound to OR3 (mutant OR1 case). We argue that these repressor interactions are mediated by protein-protein contacts between adjacent repressor dimers, because the isolated amino-terminal domains of repressor bind to the operator sites noncooperatively. The cro protein of phage λ, a second regulatory protein, which recognizes the same three sites in OR as does repressor, binds non-cooperatively. Experiments performed in vivo show that regulation of gene expression by repressor can be influenced critically by cooperative interactions. We demonstrate that the effect of repressor in a lysogen on the activity of the promoter PRM can be changed from activation to repression by deletion of OR1. We explain this effect in terms of the alternative cooperative interactions described above.
Keywords: pairwise cooperativity, cro protein, DNA binding, amino- and carboxyl-terminal domains, operators and promoters
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Backman K., Ptashne M., Gilbert W. Construction of plasmids carrying the cI gene of bacteriophage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):4174–4178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.4174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flashman S. M. Mutational analysis of the operators of bacteriophage lambda. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Oct 25;166(1):61–73. doi: 10.1007/BF00379730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkmanis A., Takeda Y., Simuth J., Gussin G., Echols H. Purification and properties of a DNA-binding protein with characteristics expected for the Cro protein of bacteriophage lambda, a repressor essential for lytic growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2249–2253. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsiang M. W., Cole R. D., Takeda Y., Echols H. Amino acid sequence of Cro regulatory protein of bacteriophage lambda. Nature. 1977 Nov 17;270(5634):275–277. doi: 10.1038/270275a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humayun Z., Kleid D., Ptashne M. Sites of contact between lambda operators and lambda repressor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977;4(5):1595–1607. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.5.1595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A., Meyer B. J., Ptashne M. Mechanism of action of the cro protein of bacteriophage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1783–1787. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Enhanced autoradiographic detection of 32P and 125I using intensifying screens and hypersensitized film. FEBS Lett. 1977 Oct 15;82(2):314–316. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80609-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., Kleid D. G. Nucleotide sequence of the rightward operator of phage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Ptashne M., Backman K., Kield D., Flashman S., Jeffrey A., Maurer R. Recognition sequences of repressor and polymerase in the operators of bacteriophage lambda. Cell. 1975 Jun;5(2):109–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90018-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. H., Ganem D., Lu P., Schmitz A. Genetic studies of the lac repressor. I. Correlation of mutational sites with specific amino acid residues: construction of a colinear gene-protein map. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jan 15;109(2):275–298. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80034-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Sauer R. T., Sturtevant J. M., Ptashne M. The lambda repressor contains two domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1608–1612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M., Backman K., Humayun M. Z., Jeffrey A., Maurer R., Meyer B., Sauer R. T. Autoregulation and function of a repressor in bacteriophage lambda. Science. 1976 Oct 8;194(4261):156–161. doi: 10.1126/science.959843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs A. D., Suzuki H., Bourgeois S. Lac repressor-operator interaction. I. Equilibrium studies. J Mol Biol. 1970 Feb 28;48(1):67–83. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90219-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts T. M., Shimatake H., Brady C., Rosenberg M. Sequence of Cro gene of bacteriophage lambda. Nature. 1977 Nov 17;270(5634):274–275. doi: 10.1038/270274a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauer R. T., Anderegg R. Primary structure of the lambda repressor. Biochemistry. 1978 Mar 21;17(6):1092–1100. doi: 10.1021/bi00599a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauer R. T. DNA sequence of the bacteriophage gama cI gene. Nature. 1978 Nov 16;276(5685):301–302. doi: 10.1038/276301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauer R. T., Pabo C. O., Meyer B. J., Ptashne M., Backman K. C. Regulatory functions of the lambda repressor reside in the amino-terminal domain. Nature. 1979 May 31;279(5712):396–400. doi: 10.1038/279396a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda Y. Specific repression of in vitro transcription by the Cro repressor of bacteriophage lambda. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jan 15;127(2):177–189. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90238-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]