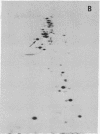
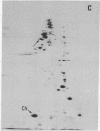
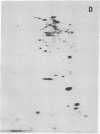
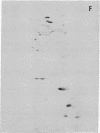
Abstract
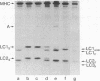
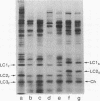
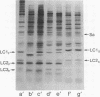
The nature of the myosin heavy chain in embryonic muscle tissue, cultured muscle cells, and several adult muscles was investigated. After denaturation with sodium dodecyl sulfate, purified rat myosins were subjected to partial proteolytic cleavage or immunological analysis using microcomplement fixation. Three types of myosin heavy chains could be demonstrated by both approaches. Whereas adult muscles contain fast- or slow-type myosin heavy chains, embryonic tissue and cultured muscle cells harbor a distinct embryonic form. The existence of this distinct form further characterizes the isozymic transitions of contractile proteins during muscle development.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnheim N. Immunochemical resemblance between human leukemia and hen egg-ehite lysozyme and their reduced carboxymethyl derivatives. J Mol Biol. 1971 Oct 14;61(1):237–250. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90220-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnon R., Maron E. An immunological approach to the structural relationship between hen egg-white lysozyme and bovine -lactalbumin. J Mol Biol. 1971 Oct 14;61(1):225–235. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90219-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
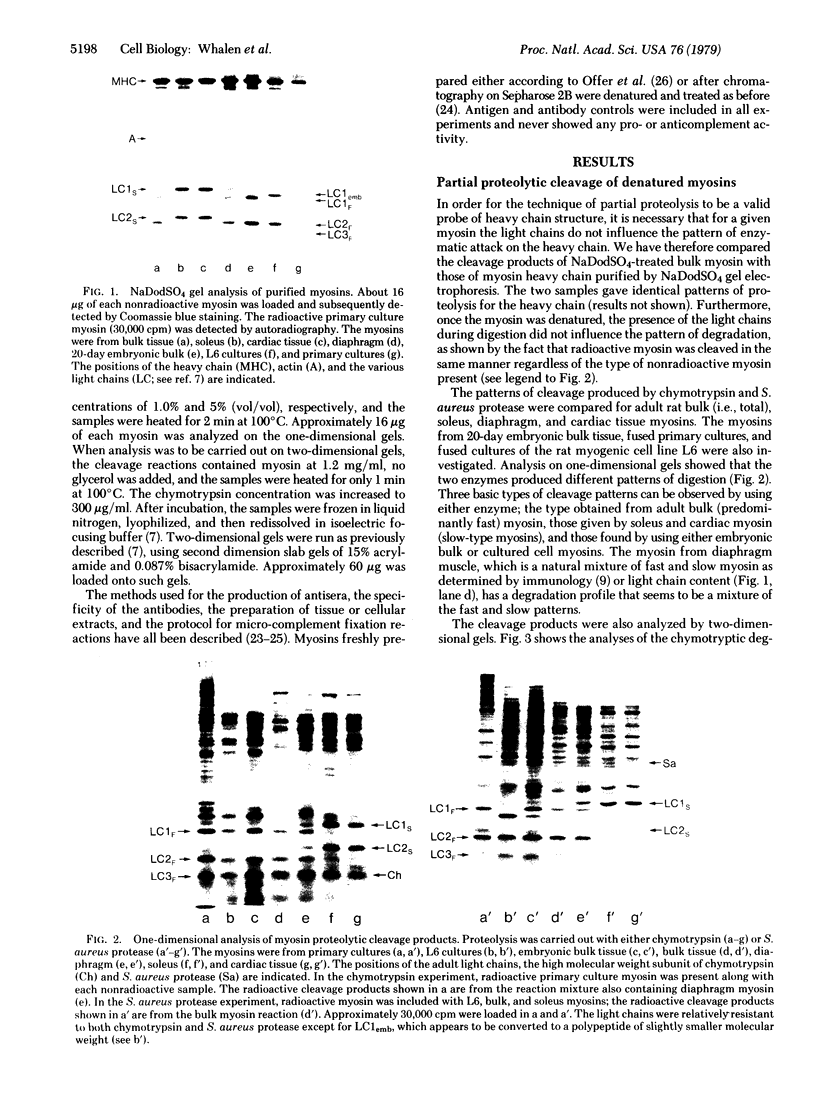
- Brevet A., Whalen R. G. Comparative structural analysis of myosin after limited tryptic hydrolysis by use of two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Biochimie. 1978 Sep 4;60(5):459–466. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(78)80860-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burridge K., Bray D. Purification and structural analysis of myosins from brain and other non-muscle tissues. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 25;99(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80154-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke M., Spudich J. A. Nonmuscle contractile proteins: the role of actin and myosin in cell motility and shape determination. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:797–822. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.004053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Close R. I. Dynamic properties of mammalian skeletal muscles. Physiol Rev. 1972 Jan;52(1):129–197. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1972.52.1.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devlin R. B., Emerson C. P., Jr Coordinate regulation of contractile protein synthesis during myoblast differentiation. Cell. 1978 Apr;13(4):599–611. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90211-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhoot G. K., Perry S. V. Distribution of polymorphic forms of troponin components and tropomyosin in skeletal muscle. Nature. 1979 Apr 19;278(5706):714–718. doi: 10.1038/278714a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrels J. I., Gibson W. Identification and characterization of multiple forms of actin. Cell. 1976 Dec;9(4 Pt 2):793–805. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90142-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
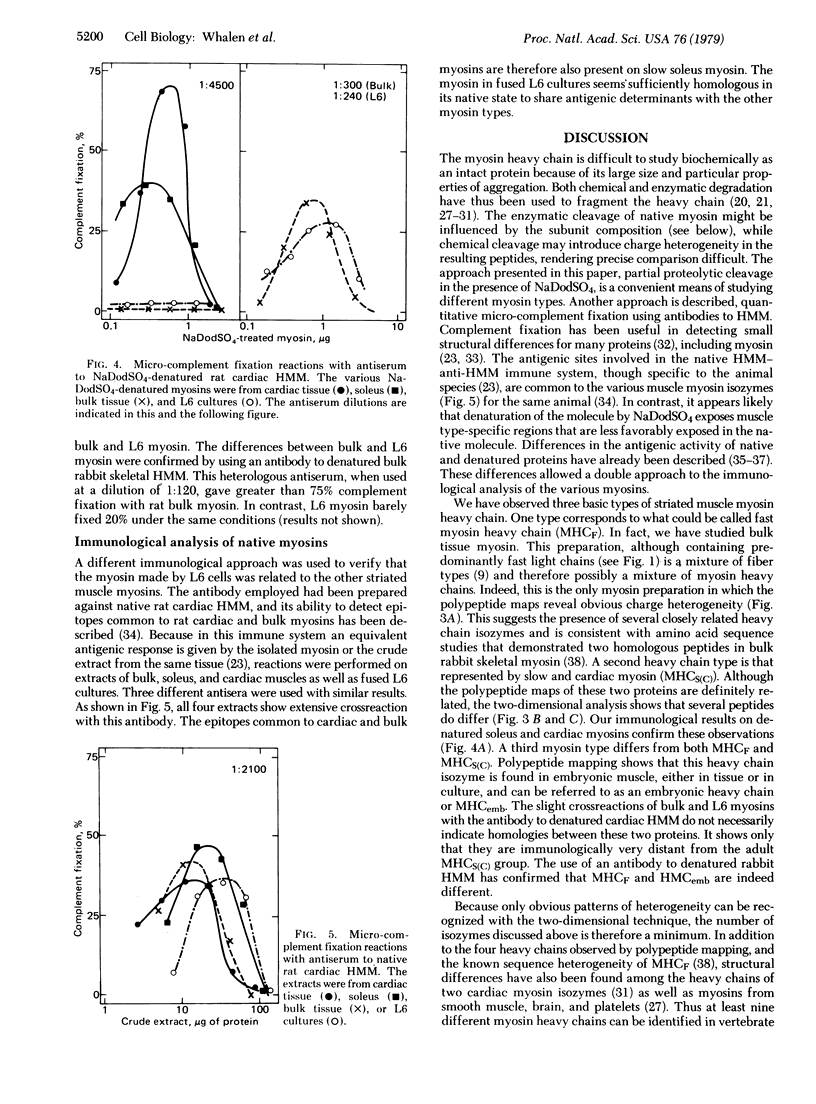
- Gauthier G. F., Lowey S. Distribution of myosin isoenzymes among skeletal muscle fiber types. J Cell Biol. 1979 Apr;81(1):10–25. doi: 10.1083/jcb.81.1.10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauthier G. F., Lowey S., Hobbs A. W. Fast and slow myosin in developing muscle fibres. Nature. 1978 Jul 6;274(5666):25–29. doi: 10.1038/274025a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoh J. F., Yeoh G. P., Thomas M. A., Higginbottom L. Structural differences in the heavy chains of rat ventricular myosin isoenzymes. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jan 15;97(2):330–334. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80115-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoh J. Y., McGrath P. A., White R. I. Electrophoretic analysis of multiple forms of myosin in fast-twitch and slow-twitch muscles of the chick. Biochem J. 1976 Jul 1;157(1):87–95. doi: 10.1042/bj1570087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huszar G. Developmental changes of the primary structure and histidine methylation in rabbit skeletal muscle myosin. Nat New Biol. 1972 Dec 27;240(104):260–264. doi: 10.1038/newbio240260a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huszar G., Elzinga M. Homologous methylated and nonmethylated histidine peptides in skeletal and cardiac myosins. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 10;247(3):745–753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lompre A. M., Bouveret P., Leger J., Schwartz K. Detection of antibodies specific to sodium dodecyl sulfate-treated proteins. J Immunol Methods. 1979;28(1-2):143–148. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90336-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLeod A. R., Waterston R. H., Brenner S. An internal deletion mutant of a myosin heavy chain in Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5336–5340. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masaki T., Yoshizaki C. Differentiation of myosin in chick embryos. J Biochem. 1974 Jul;76(1):123–131. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offer G., Moos C., Starr R. A new protein of the thick filaments of vertebrate skeletal myofibrils. Extractions, purification and characterization. J Mol Biol. 1973 Mar 15;74(4):653–676. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90055-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelloni-Müller G., Ermini M., Jenny E. Changes in myosin light and heavy chain stoichiometry during development of rabbit fast, slow, and cardiac muscle. FEBS Lett. 1976 Nov;70(1):113–117. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80738-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pette D., Vrbová G., Whalen R. C. Independent development of contractile properties and myosin light chains in embryonic chick fast and slow muscle. Pflugers Arch. 1979 Jan 31;378(3):251–257. doi: 10.1007/BF00592743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard T. D., Weihing R. R. Actin and myosin and cell movement. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1974 Jan;2(1):1–65. doi: 10.3109/10409237409105443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prager E. M., Wilson A. C. The dependence of immunological cross-reactivity upon sequence resemblance among lysozymes. I. Micro-complement fixation studies. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 10;246(19):5978–5989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein N. A., Pepe F. A., Holtzer H. Myosin types during the development of embryonic chicken fast and slow muscles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4524–4527. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sartore S., Pierobon-Bormioli S., Schiaffino S. Immunohistochemical evidence for myosin polymorphism in the chicken heart. Nature. 1978 Jul 6;274(5666):82–83. doi: 10.1038/274082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz K., Bouveret P., Bercovici J., Swynghedauw B. An immunochemical difference between myosins from normal and hypertrophied rat hearts. FEBS Lett. 1978 Sep 1;93(1):137–140. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80822-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz K., Bouveret P., Sebag C. Immunochemical evidence for structural homologies between mammalian cardiac and skeletal myosins. FEBS Lett. 1978 Mar 1;87(1):99–102. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80143-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz K., Bouveret P., Sebag C., Leger J., Swynghedauw B. Immunochemical evidence for the species-specificity of mammalian cardiac myosin and heavy meromyosin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Nov 25;495(1):24–36. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(77)90236-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sréter F. A., Bálint M., Gergely J. Structural and functional changes of myosin during development: comparison with adult fast, slow and cardiac myosin. Dev Biol. 1975 Oct;46(2):317–325. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(75)90108-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr R., Offer G. Polarity of the myosin molecule. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 25;81(1):17–31. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90244-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syrový I., Gutmann E. Differentiation of myosin in soleus and extensor digitorum longus muscle in differnt animal species during development. Pflugers Arch. 1977 May 6;369(1):85–89. doi: 10.1007/BF00580815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeds A. G., Burridge K. Myosin from cross-reinnervated cat muscles. Evidence for reciprocal transformation of heavy chains. FEBS Lett. 1975 Sep 15;57(2):203–208. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80717-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeds A. G., Pope B. Studies on the chymotryptic digestion of myosin. Effects of divalent cations on proteolytic susceptibility. J Mol Biol. 1977 Apr;111(2):129–157. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80119-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whalen R. G., Butler-Browne G. S., Gros F. Identification of a novel form of myosin light chain present in embryonic muscle tissue and cultured muscle cells. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 15;126(3):415–431. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90049-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whalen R. G., Butler-Browne G. S., Gros F. Protein synthesis and actin heterogeneity in calf muscle cells in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):2018–2022. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.2018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whalen R. G., Butler-Browne G. S., Sell S., Gros F. Transitions in contractile protein isozymes during muscle cell differentiation. Biochimie. 1979;61(5-6):625–632. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(79)80160-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yablonka Z., Yaffe D. Synthesis of myosin light chains and accumulation of translatable mRNA coding for light chain-like polypeptides in differentiating muscle cultures. Differentiation. 1977 Oct 13;8(3):133–143. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1977.tb00929.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakin M. M., Garel J. R., Dautry-Varsat A., Cohen G. N., Boulot G. Detection of the homology among proteins by immunochemical cross-reactivity between denatured antigens. Application to the threonine and methionine regulated aspartokinases-homoserine dehydrogenases from Escherichia coli K 12. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 3;17(20):4318–4323. doi: 10.1021/bi00613a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]