Abstract
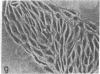
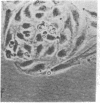
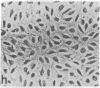
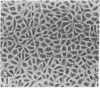
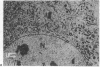
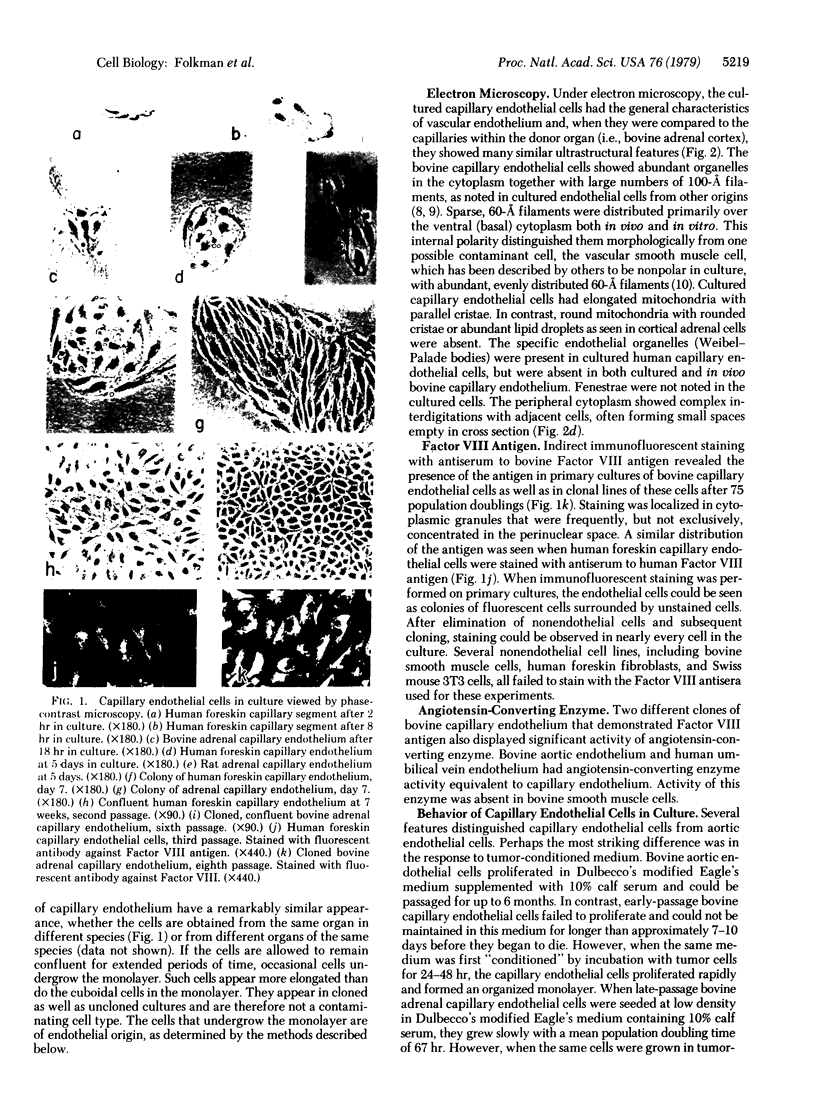
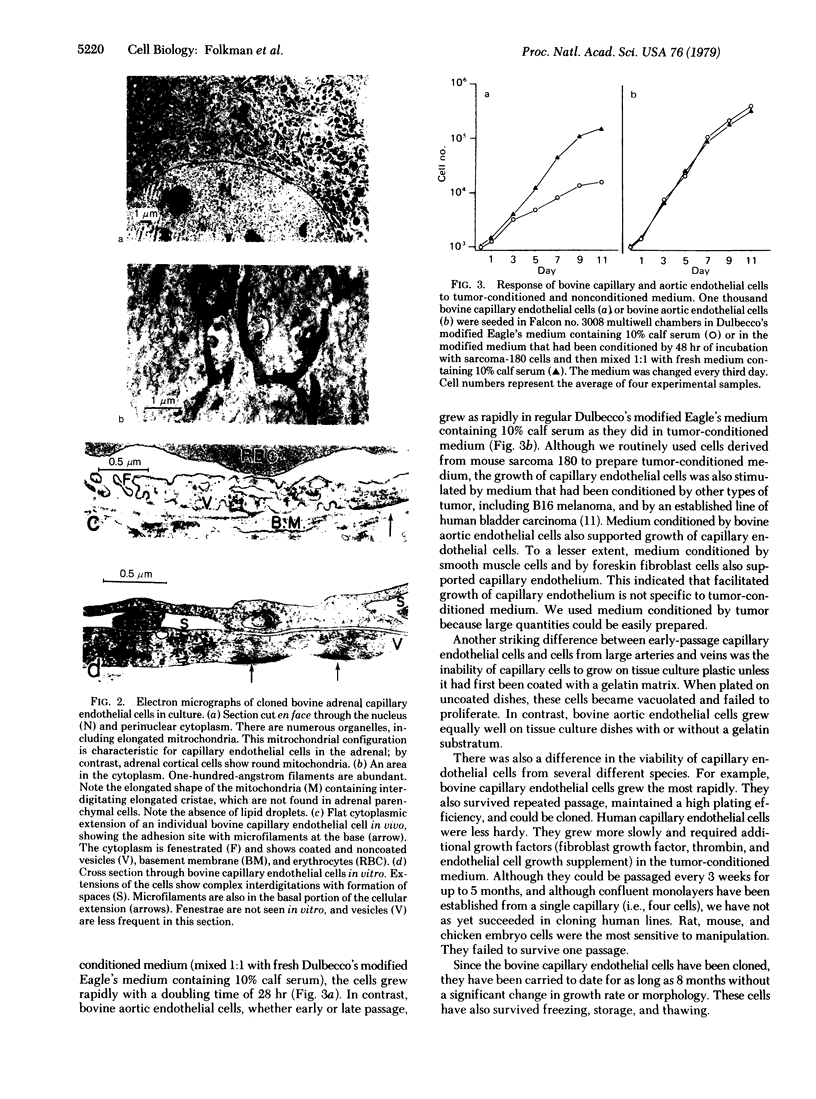
Capillary endothelial cells from rats, calves, and humans, have been carried in long-term culture. Bovine capillary endothelial cells have been cloned and maintained by serial passage for longer than 8 months. This prolonged culture was accomplished by using tumor-conditioned medium, gelatin-coated plates, and a method of enriching cells in primary culture. Cultured bovine capillary endothelial cells produce Factor VIII antigen and angiotensin-converting enzyme, but do not have Weibel-Palade bodies. Human cells do contain Weibel-Palade bodies. Capillary endothelial cells are distinguished from aortic endothelial cells by their requirement for conditioned medium. Bovine capillary endothelial cells in regular medium grow slowly with a mean doubling time of 67 hr and eventually die. In tumor-conditioned medium, these cells grow rapidly with a doubling time of 28 hr and continue to proliferate for as long as the tumor-conditioned medium is present. In contrast, bovine aortic endothelial cells grow as rapidly in regular medium as in tumor-conditioned medium. This method allows the production of pure capillary endothelial cells that may prove useful for studies of tumor angiogenesis, metastatic mechanisms, and the role of capillary endothelium in other pathologic states.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blose S. H., Shelanski M. L., Chacko S. Localization of bovine brain filament antibody on intermediate (100 A) filaments in guinea pig vascular endothelial cells and chick cardiac muscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):662–665. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booyse F. M., Sedlak B. J., Rafelson M. E., Jr Culture of arterial endothelial cells: characterization and growth of bovine aortic cells. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1975 Dec 15;34(3):825–839. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J. Angiogenesis in psoriasis: therapeutic implications. J Invest Dermatol. 1972 Jul;59(1):40–43. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12625746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J. Tumor angiogenesis. Adv Cancer Res. 1974;19(0):331–358. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60058-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedland J., Silverstein E. A sensitive fluorimetric assay for serum angiotensin-converting enzyme. Am J Clin Pathol. 1976 Aug;66(2):416–424. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/66.2.416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Cotran R. S., Folkman J. Human vascular endothelial cells in culture. Growth and DNA synthesis. J Cell Biol. 1974 Mar;60(3):673–684. doi: 10.1083/jcb.60.3.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Cotran R. S. Human vascular smooth muscle in culture. Growth and ultrastructure. Lab Invest. 1975 Jul;33(1):16–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Moran J., Braun D., Birdwell C. Clonal growth of bovine vascular endothelial cells: fibroblast growth factor as a survival agent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):4120–4124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.4120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haudenschild C. C., Cotran R. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Folkman J. Fine structure of vascular endothelium in culture. J Ultrastruct Res. 1975 Jan;50(1):22–32. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(75)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hial V., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Peyton M. P., Wilcox G. M., Pisano J. J. Angiotensin metabolism by cultured human vascular endothelial and smooth muscle cells. Microvasc Res. 1979 May;17(3 Pt 1):314–329. doi: 10.1016/s0026-2862(79)80007-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer L. W., De los Santos R. P., Hoyer J. R. Antihemophilic factor antigen. Localization in endothelial cells by immunofluorescent microscopy. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2737–2744. doi: 10.1172/JCI107469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Nachman R. L., Becker C. G., Minick C. R. Culture of human endothelial cells derived from umbilical veins. Identification by morphologic and immunologic criteria. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2745–2756. doi: 10.1172/JCI107470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klagsbrun M., Knighton D., Folkman J. Tumor angiogenesis activity in cells grown in tissue culture. Cancer Res. 1976 Jan;36(1):110–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer R., Brem H., Falterman K., Klein M., Folkman J. Isolations of a cartilage factor that inhibits tumor neovascularization. Science. 1976 Jul 2;193(4247):70–72. doi: 10.1126/science.935859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall C. J., Franks L. M., Carbonell A. W. Markers of neoplastic transformation in epithelial cell lines derived from human carcinomas. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1977 Jun;58(6):1743–1751. doi: 10.1093/jnci/58.6.1743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L., Brunson K. W., Fidler I. J. Specificity of arrest, survival, and growth of selected metastatic variant cell lines. Cancer Res. 1978 Nov;38(11 Pt 2):4105–4111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tripathi B., Ashton N., Knight G. Effect of oxygen on the developing retinal vessels of the rabbit. 3. Mode of growth of rabbit retinal vessels in tissue culture. Exp Eye Res. 1973 Mar;15(3):321–351. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(73)90149-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner R. C., Matthews M. A. The isolation and culture of capillary endothelium from epididymal fat. Microvasc Res. 1975 Nov;10(3):286–297. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(75)90033-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]