Abstract
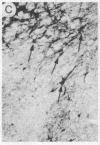
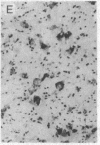
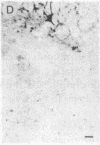
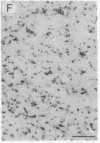
Unilateral stereotaxic injection of 3.5 nmol of kainic acid into the ventral globus pallidus of rats reduced biochemical cholinergic neuronal markers by 45-50% and virtually eliminated histochemical staining for acetylcholinesterase in neocortex ipsilateral to the lesion. At the lesion site, the large, multipolar neurons that stain densely for acetylcholinesterase were absent when compared with the uninjected side. Kainate was as effective as electrocoagulation for reducing cholinergic markers although it did not affect aminergic projections ascending through the lesioned area. The conclusion that the cholinergic projection originated in neuronal perikarya at the lesion site was supported by the failure of kainate or electrolytic lesions in contiguous regions to produce similar effects. These studies provide strong evidence for a cholinergic projection to neocortex from neurons in the forebrain in the nucleus basalis.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arikuni T., Ban T., Jr Subcortical afferents to the prefrontal cortex in rabbits. Exp Brain Res. 1978 May 12;32(1):69–75. doi: 10.1007/BF00237391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Ari Y., Le Gal La Salle G., Barbin G., Schwartz J. C., Garbarg M. Histamine synthesizing afferents within the amygdaloid complex and bed nucleus of the stria terminalis of the rat. Brain Res. 1977 Dec 16;138(2):285–294. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90746-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird S. J., Aghajanian G. K. The cholinergic pharmacology of hippocampal pyramidal cells: a microiontophoretic study. Neuropharmacology. 1976 May;15(5):273–282. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(76)90128-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bull G., Oderfeld-Nowak B. Standardization of a radiochemical assay of choline acetyltransferase and a study of the activation of the enzyme in rabbit brain. J Neurochem. 1971 Jun;18(6):935–941. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1971.tb12023.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butcher L. L., Talbot K., Bilezikjian L. Acetylcholinesterase neurons in dopamine-containing regions of the brain. J Neural Transm. 1975;37(2):127–153. doi: 10.1007/BF01663629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coyle J. T., Enna S. J. Neurochemical aspects of the ontogenesis of GABAnergic neurons in the rat brain. Brain Res. 1976 Jul 23;111(1):119–133. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)91053-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coyle J. T., Henry D. Catecholamines in fetal and newborn rat brain. J Neurochem. 1973 Jul;21(1):61–67. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb04225.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coyle J. T., Molliver M. E., Kuhar M. J. In situ injection of kainic acid: a new method for selectively lesioning neural cell bodies while sparing axons of passage. J Comp Neurol. 1978 Jul 15;180(2):301–323. doi: 10.1002/cne.901800208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coyle J. T. Tyrosine hydroxylase in rat brain--cofactor requirements, regional and subcellular distribution. Biochem Pharmacol. 1972 Jul 15;21(14):1935–1944. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(72)90006-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curzon G., Green A. R. Rapid method for the determination of 5-hydroxytryptamine and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid in small regions of rat brain. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 Jul;39(3):653–655. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1970.tb10373.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das G. D. Projections of the interstitial nerve cells surrounding the globus pallidus: a study of retrograde changes following cortical ablations in rabbits. Z Anat Entwicklungsgesch. 1971;133(2):135–160. doi: 10.1007/BF00528020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLong M. R. Activity of pallidal neurons during movement. J Neurophysiol. 1971 May;34(3):414–427. doi: 10.1152/jn.1971.34.3.414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Divac I. Magnocellular nuclei of the basal forebrain project to neocortex, brain stem, and olfactory bulb. Review of some functional correlates. Brain Res. 1975 Aug 15;93(3):385–398. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90178-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drachman D. A., Leavitt J. Human memory and the cholinergic system. A relationship to aging? Arch Neurol. 1974 Feb;30(2):113–121. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1974.00490320001001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fonnum F. Topographical and subcellular localization of choline acetyltransferase in rat hippocampal region. J Neurochem. 1970 Jul;17(7):1029–1037. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1970.tb02256.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A. M., McCaman R. E. The determination of picomole amounts of acetylcholine in mammalian brain. J Neurochem. 1973 Jan;20(1):1–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb12097.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham L. T., Jr, Aprison M. H. Fluorometric determination of aspartate, glutamate, and gamma-aminobutyrate in nerve tissue using enzymic methods. Anal Biochem. 1966 Jun;15(3):487–497. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90110-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEBB C. O. Biochemical evidence for the neural function of acetylcholine. Physiol Rev. 1957 Apr;37(2):196–220. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1957.37.2.196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoover D. B., Muth E. A., Jacobowitz D. M. A mapping of the distribution of acetycholine, choline acetyltransferase and acetylcholinesterase in discrete areas of rat brain. Brain Res. 1978 Sep 22;153(2):295–306. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90408-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt S., Schmidt J. Some observations on the binding patterns of alpha-bungarotoxin in the central nervous system of the rat. Brain Res. 1978 Nov 24;157(2):213–232. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobowitz D. M., Palkovits M. Topographic atlas of catecholamine and acetylcholinesterase-containing neurons in the rat brain. I. Forebrain (telencephalon, diencephalon). J Comp Neurol. 1974 Sep 1;157(1):13–28. doi: 10.1002/cne.901570103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston M. V., Coyle J. T. Histological and neurochemical effects of fetal treatment with methylazoxymethanol on rat neocortex in adulthood. Brain Res. 1979 Jul 6;170(1):135–155. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90946-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones E. G., Burton H., Saper C. B., Swanson L. W. Midbrain, diencephalic and cortical relationships of the basal nucleus of Meynert and associated structures in primates. J Comp Neurol. 1976 Jun 15;167(4):385–419. doi: 10.1002/cne.901670402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARNOVSKY M. J., ROOTS L. A "DIRECT-COLORING" THIOCHOLINE METHOD FOR CHOLINESTERASES. J Histochem Cytochem. 1964 Mar;12:219–221. doi: 10.1177/12.3.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly P. H., Moore K. E. Decrease of neocortical choline acetyltransferase after lesion of the globus pallidus in the rat. Exp Neurol. 1978 Sep 1;61(2):479–484. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(78)90263-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kievit J., Kuypers H. G. Basal forebrain and hypothalamic connection to frontal and parietal cortex in the Rhesus monkey. Science. 1975 Feb 21;187(4177):660–662. doi: 10.1126/science.1114317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krnjević K., Phillis J. W. Pharmacological properties of acetylcholine-sensitive cells in the cerebral cortex. J Physiol. 1963 May;166(2):328–350. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhar M. J., Sethy V. H., Roth R. H., Aghajanian G. K. Choline: selective accumulation by central cholinergic neurons. J Neurochem. 1973 Feb;20(2):581–593. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb12157.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann J., Fibiger H. C. Acetylcholinesterase in the substantia nigra and caudate-putamen of the rat: properties and localization in dopaminergic neurons. J Neurochem. 1978 Mar;30(3):615–624. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb07816.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeer E. G., Wada J. A., Terao A., Jung E. Amine synthesis in various brain regions with caudate or septal lesions. Exp Neurol. 1969 Jun;24(2):277–284. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(69)90021-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeer P. L., McGeer E. G., Singh V. K., Chase W. H. Choline acetyltransferase localization in the central nervous system by immunohistochemistry. Brain Res. 1974 Dec 6;81(2):373–379. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90955-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mesulam M. M., Van Hoesen G. W. Acetylcholinesterase-rich projections from the basal forebrain of the rhesus monkey to neocortex. Brain Res. 1976 Jun 4;109(1):152–157. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90385-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell J. F. The spontaneous and evoked release of acetylcholine from the cerebral cortex. J Physiol. 1963 Jan;165(1):98–116. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palkovits M., Richardson J. S., Jacobowitz D. M. A histochemical study of ventral tegmental acetylcholinesterase-containing pathway following destructive lesions. Brain Res. 1974 Nov 29;81(1):183–188. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90487-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramón-Moliner E., Nauta W. J. The isodendritic core of the brain stem. J Comp Neurol. 1966 Mar;126(3):311–335. doi: 10.1002/cne.901260301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribak C. E. Aspinous and sparsely-spinous stellate neurons in the visual cortex of rats contain glutamic acid decarboxylase. J Neurocytol. 1978 Aug;7(4):461–478. doi: 10.1007/BF01173991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossier J. Choline acetyltransferase: a review with special reference to its cellular and subcellular localization. Int Rev Neurobiol. 1977;20:283–337. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7742(08)60656-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal M., Dudai Y., Amsterdam A. Distribution of an alpha-bungarotoxin-binding cholinergic nicotinic receptor in rat brain. Brain Res. 1978 Jun 9;148(1):105–119. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90381-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shute C. C., Lewis P. R. The ascending cholinergic reticular system: neocortical, olfactory and subcortical projections. Brain. 1967 Sep;90(3):497–520. doi: 10.1093/brain/90.3.497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel J., Wang R. Y. Electroencephalographic, behavioral, and single-unit effects produced by stimulation of forebrain inhibitory structures in cats. Exp Neurol. 1974 Jan;42(1):28–50. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(74)90004-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spillane J. A., White P., Goodhardt W. J., Flack R. H., Bowen D. M., Davison A. N. Selective vulnerability of neurones in organic dementia. Nature. 1977 Apr 7;266(5602):558–559. doi: 10.1038/266558a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storm-Mathisen J. Quantitative histochemistry of acetylcholinesterase in rat hippocampal region correlated to histochemical staining. J Neurochem. 1970 Jun;17(6):739–750. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1970.tb03344.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ungerstedt U. Stereotaxic mapping of the monoamine pathways in the rat brain. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1971;367:1–48. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-201x.1971.tb10998.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittaker V. P. The application of subcellular fractionation techniques to the study of brain function. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1965;15:39–96. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(65)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson S. H., Schrier B. K., Farber J. L., Thompson E. J., Rosenberg R. N., Blume A. J., Nirenberg M. W. Markers for gene expression in cultured cells from the nervous system. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 25;247(10):3159–3169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamura H. I., Kuhar M. J., Snyder S. H. In vivo identification of muscarinic cholinergic receptor binding in rat brain. Brain Res. 1974 Nov 8;80(1):170–176. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90738-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]