Abstract
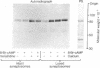
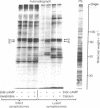
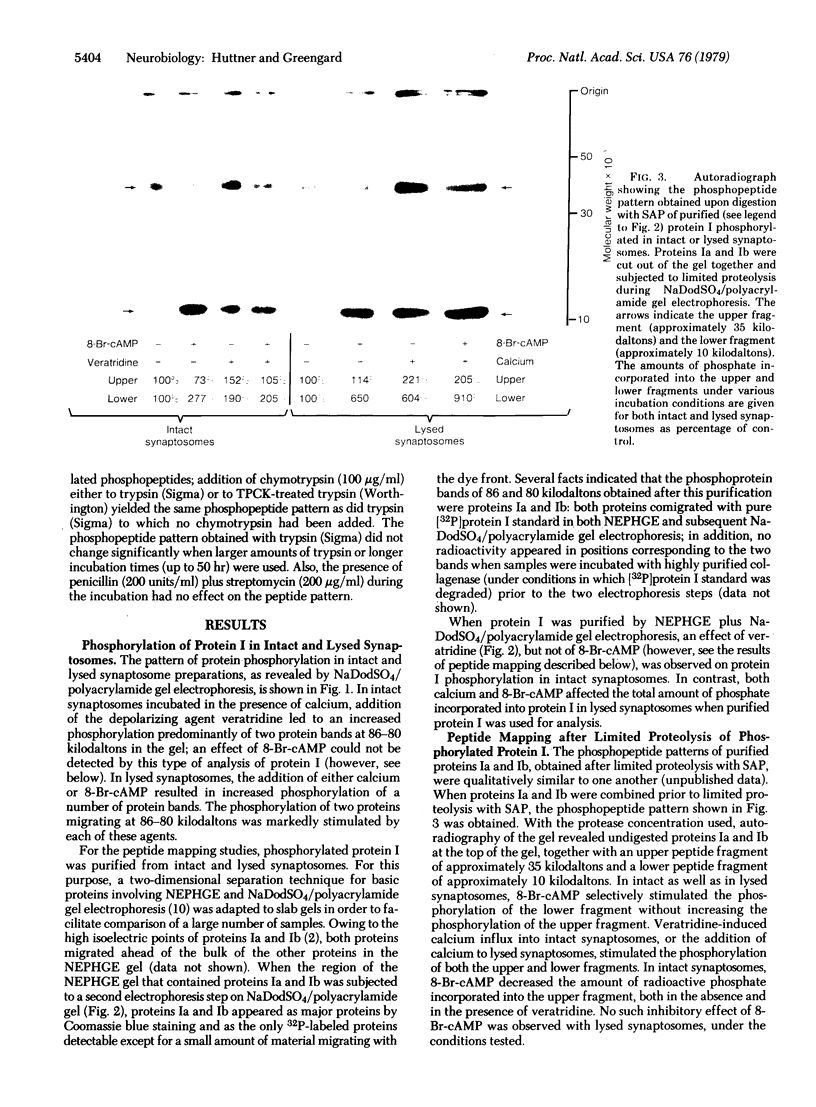
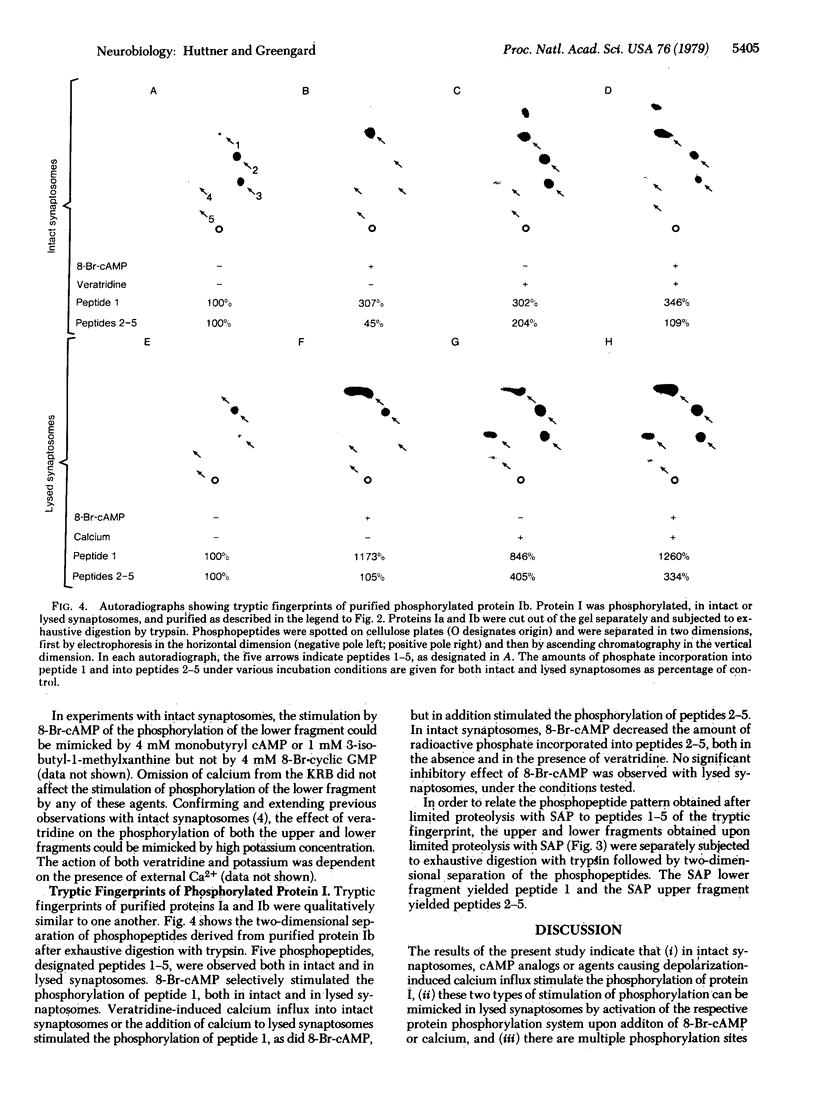
The phosphorylation of protein I, a specific neuronal protein, has been found to be regulated both by cyclic AMP (cAMP) and by calcium, in intact as well as in lysed synaptosome preparations from rat brain. In order to determine the phosphorylation site(s) of protein I that were regulated by cAMP and calcium, protein I was purified after it was phosphorylated under various conditions. This purified protein I was then subjected either to peptide mapping after limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate/polyacrylamide gels or to tryptic fingerprinting. 8-Br-cAMP selectively increased the phosphorylation of the same protein I peptide fragment in both intact and lysed synaptosomes. Depolarization-induced calcium influx into intact synaptosomes, or the addition of calcium to lysed synaptosomes, caused a stimulation of the phosphorylation not only of this peptide but also of other distinct peptides. Differential regulation by cAMP and calcium of the phosphorylation of multiple sites on the same neuronal protein may provide a molecular basis for interactions between these two second-messenger systems in certain nerve terminal functions.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axelrod N. Phosphoproteins of adenovirus 2. Virology. 1978 Jun 15;87(2):366–383. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90141-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. The role of cyclic-AMP-dependent protein kinase in the regulation of glycogen metabolism in mammalian skeletal muscle. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1978;14:117–196. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152814-0.50008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forn J., Greengard P. Depolarizing agents and cyclic nucleotides regulate the phosphorylation of specific neuronal proteins in rat cerebral cortex slices. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):5195–5199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.5195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly P. T., Cotman C. W. Synaptic proteins. Characterization of tubulin and actin and identification of a distinct postsynaptic density polypeptide. J Cell Biol. 1978 Oct;79(1):173–183. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.1.173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger B. K., Forn J., Greengard P. Depolarization-induced phosphorylation of specific proteins, mediated by calcium ion influx, in rat brain synaptosomes. J Biol Chem. 1977 Apr 25;252(8):2764–2773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. Z., Goodman H. M., O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of basic as well as acidic proteins. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):1133–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sieghart W., Forn J., Greengard P. Ca2+ and cyclic AMP regulate phosphorylation of same two membrane-associated proteins specific to nerve tissue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2475–2479. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strömbom U., Forn J., Dolphin A. C., Greengard P. Regulation of the state of phosphorylation of specific neuronal proteins in mouse brain by in vivo administration of anesthetic and convulsant agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4687–4690. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda T., Greengard P. Adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-regulated phosphoprotein system of neuronal membranes. I. Solubilization, purification, and some properties of an endogenous phosphoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 25;252(14):5155–5163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda T., Maeno H., Greengard P. Regulation of endogenous phosphorylation of specific proteins in synaptic membrane fractions from rat brain by adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate. J Biol Chem. 1973 Dec 10;248(23):8295–8305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]