Abstract
Membrane biofouling remains a severe problem to be addressed in wastewater treatment systems affecting reactor performance and economy. The finding that many wastewater bacteria rely on N-acyl homoserine lactone-mediated quorum sensing to synchronize their activities essential for biofilm formations; the quenching bacterial quorum sensing suggests a promising approach for control of membrane biofouling. A variety of quorum quenching compounds of both synthetic and natural origin have been identified and found effective in inhibition of membrane biofouling with much less environmental impact than traditional antimicrobials. Work over the past few years has demonstrated that enzymatic quorum quenching mechanisms are widely conserved in several prokaryotic organisms and can be utilized as a potent tool for inhibition of membrane biofouling. Such naturally occurring bacterial quorum quenching mechanisms also play important roles in microbe-microbe interactions and have been used to develop sustainable nonantibiotic antifouling strategies. Advances in membrane fabrication and bacteria entrapment techniques have allowed the implication of such quorum quenching bacteria for better design of membrane bioreactor with improved antibiofouling efficacies. In view of this, the present paper is designed to review and discuss the recent developments in control of membrane biofouling with special emphasis on quorum quenching bacteria that are applied in membrane bioreactors.
1. Introduction
Advanced wastewater treatment technology membrane bioreactor (MBR) combines the use of biological degradation process by activated sludge with a direct solid-liquid separation by micro- or ultrafiltration membranes of pore sizes ranging from 0.05 to 0.4 μm [1]. These membranes allow the complete retention of bacteria and suspended solids within bioreactor and only water with reusable quality gets released. As a result, the MBRs are increasingly emerging as an advanced treatment processes in industrial and municipal wastewaters [2]. Even though MBRs have been implemented in commercial applications for more than two decades, one of the major problems restricting their wide spread use is membrane biofouling [3]. Membrane biofouling is the accumulation of microorganisms and their metabolites produced such as extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) on membrane surfaces. This results in the unacceptable operational problems like decay in filtrate flux, pressure drop increase, and, thus, alteration on membranes [4]. The biofouling problem progresses throughout the treatment process, so the membranes have to be cleaned and eventually replaced [5]. Thus, biofouling is considered as the most severe problem in wastewater treatment systems resulting in greater loss in the economy.
Different physicochemical and biological practices have been tried to overcome the problem of membrane biofouling. These include physical cleaning of membrane surfaces with hot water, fabrication of biofouling resistant membranes, and incorporation of antibiotics or antimicrobial compounds in MBR [1, 6]. Indiscriminate use of antibiotics puts selection pressure on bacteria by interfering with their vital genomic functions like protein synthesis, RNA synthesis, and DNA synthesis [7, 8]. These result in the emergence of multidrug resistance among pathogenic bacteria and thus are considered as a serious and growing phenomenon in contemporary medicines used in human healthcare. In this scenario, it is necessary to use alternative approach to replace antibiotics for combating membrane biofouling.
Studies to mitigate membrane biofouling have suggested that biofilm formation is mostly associated with Gram-negative bacteria and their secreted metabolites [9]. Several species of Gram-negative bacteria communicate by synthesizing, secreting, and responding to small diffusible signal molecules N-acyl homoserine lactones (AHLs) through a mechanism called quorum sensing [10, 11]. The AHLs-mediated cell-to-cell signaling allows these bacteria to coordinate gene expression and regulate different phenotypes such as biofilm formation, secretion of EPS, and virulence factor [12–14]. Moreover, the AHL-mediated quorum sensing system is associated with almost all stages of biofilm formation such as initial surface attachment, bacterial growth, maturation, and detachment of aged cells [15, 16].
As quorum sensing plays significant roles in the establishment of biofilms by Gram-negative bacteria, disruption of AHL-based signaling has become the promising strategy to control membrane biofouling [17]. Three targets that can intercept AHL-based quorum sensing and modulate its controlled behaviors like biofilm formation are known, which include (i) inhibition of AHL synthesis by blocking synthase proteins [18], (ii) interference with signal receptors [19], and (iii) enzymatic degradation or alteration of AHLs molecules [20, 21]. Recently, some natural compounds such as vanillin, furanones, and curcumin have been found to intercept AHL-mediated quorum sensing system and thus inhibit membrane biofouling [22–24]. However, this approach is not feasible to use at commercial levels due to higher cost of natural compounds and the fact that more doses are required to achieve considerable biofouling inhibition. Another promising approach is that the enzymatic quorum quenching (in the form of a free enzyme or an immobilized form on a bead) has been successfully applied to mitigate biofouling in submerged membrane bioreactor treating wastewaters [25, 26]. But the higher cost of purified enzymes makes it difficult to use at commercial levels.
In view of this, a novel biological paradigm with the application of quorum quenching bacteria in MBRs has been investigated recently. This has proven more effective and economically feasible with membrane encapsulated and bead entrapped quorum quenching bacterial studies and suggested a new milestone towards widespread antibiofouling applications. Thus, in this review, we briefly overview the AHL-mediated biofilm formations by Gram-negative bacteria and elucidate the roles of enzymatic interference of AHLs by quorum quenching bacteria in inhibiting membrane biofouling.
2. Quorum Sensing for Coordinated Behaviors in Bacteria
Many Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria use quorum sensing signal circuits to coordinate a diverse array of physiological behaviors such as symbiosis, competence, virulence, conjugation, antibiotic production, sporulation, motility, and biofilm formation [27]. The quorum sensing system has been divided into two paradigmatic classes: oligopeptide/two component-type quorum sensing circuits in Gram-positive bacteria and Lux I/Lux R-type quorum sensing system in Gram-negative bacteria [28]. The difference in regulatory process depends on the chemical structure of signal molecule and its detection mechanism [29]. In general, Gram-positive bacteria use processed oligopeptides and Gram-negative bacteria use AHL as signal molecule to coordinate their behaviors. Furthermore, the molecular bases of the synthesis and perception of different quorum sensing signals and details of the signal transduction pathways have revealed their specific behaviors. As AHL-mediated quorum sensing system of Gram-negative bacteria is known to be involved in biofilm formations, we will only briefly address its mechanisms.
2.1. AHL-Mediated Quorum Sensing
Predominant Gram-negative Proteobacteria belonging to α, β, and γ subdivisions utilize AHL-mediated quorum sensing pathways to regulate their behaviors [30]. However, Gram-positive bacteria belonging to the Exiguobacterium genera have been recently identified as AHL producer [31]. AHLs are amphipathic in nature and are soluble in water and freely diffusible through cell membranes [32, 33].
The AHL-mediated quorum sensing system requires three major components to function: (i) the AHL signal molecule, (ii) AHL synthase protein to make the AHL signal, and (iii) a regulatory protein which responds to the surrounding concentration of AHLs [34]. A schematic representation of the AHL-mediated quorum sensing is shown in Figure 1. In AHL-mediated quorum sensing, a single synthase-regulator complex is responsible for the expression of specific genes. The signal molecules are produced by an AHL synthase gene Lux I at low concentration and are distributed in and around the cell. At lower cell densities, the Lux I is constitutively expressed at a low, basal level and thus AHLs get accumulated in the surrounding [35]. At high concentration of AHLs, the signal-receptor protein complex forms and gets activated. The activated signal-receptor complex in turn forms dimers or multimers with other activated AHL-lux R complexes and functions as transcriptional regulators controlling the expression of quorum sensing regulated target genes. At a certain cell density, also known as “quorum size,” the transcription of quorum sensing genes gets triggered and results in the expression of various phenotypes [36, 37]. Each individual quorum sensing regulated gene has its own specific quorum size to activate and there is no single population density at which all the genes are activated [38, 39].
Figure 1.
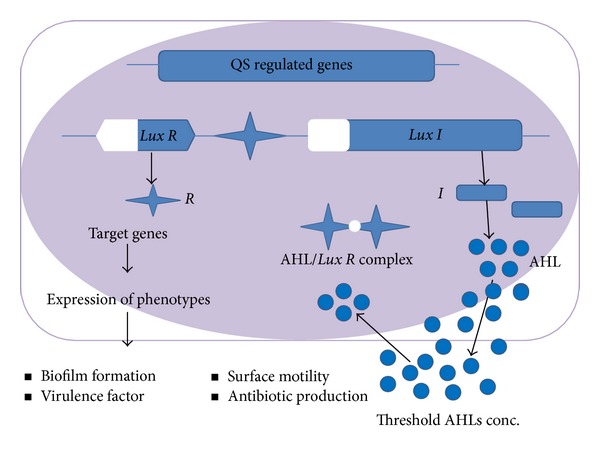
Schematic representation of the LuxR/AHL type quorum sensing system in Gram-negative bacteria. The “r” is a gene encoding Lux R-type transcription factor R and “i” is gene encoding Lux I-type AHL synthase I. Transcription of QS-regulated target genes appears by Lux R homologue proteins only when high AHL concentration is present, which required a threshold bacterial cell density.
AHL-mediated quorum sensing is the most widely studied and best understood model of cell-to-cell communication in Gram-negative bacteria regulating various phenotypes. In Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1, swarming motility, expression of virulence factors, and biofilm maturation are regulated by AHL-mediated quorum sensing system [40]. The AHL-based quorum sensing in Serratia liquefaciens regulates swarming motility which results in the maturation of heterogeneous biofilms [41]. Burkholderia cepacia, a common bacteria found in the membrane systems, has been shown to use cepI/R quorum sensing to control biofilm maturation [42]. In a natural inhabitant of waters, Vibrio cholerae, the transcriptional regulator hapRAHL, has been shown to be responsible for EPS synthesis and biofilm formation [43]. Moreover, some other Gram-negative bacteria, v.z. Aeromonas hydrophila, P. aeruginosa, and so forth, have been shown to use AHL-based quorum sensing system to regulate numerous phenotypes including biofilm formation [22, 44].
2.2. AHLs Production and Phenotypes Controlled
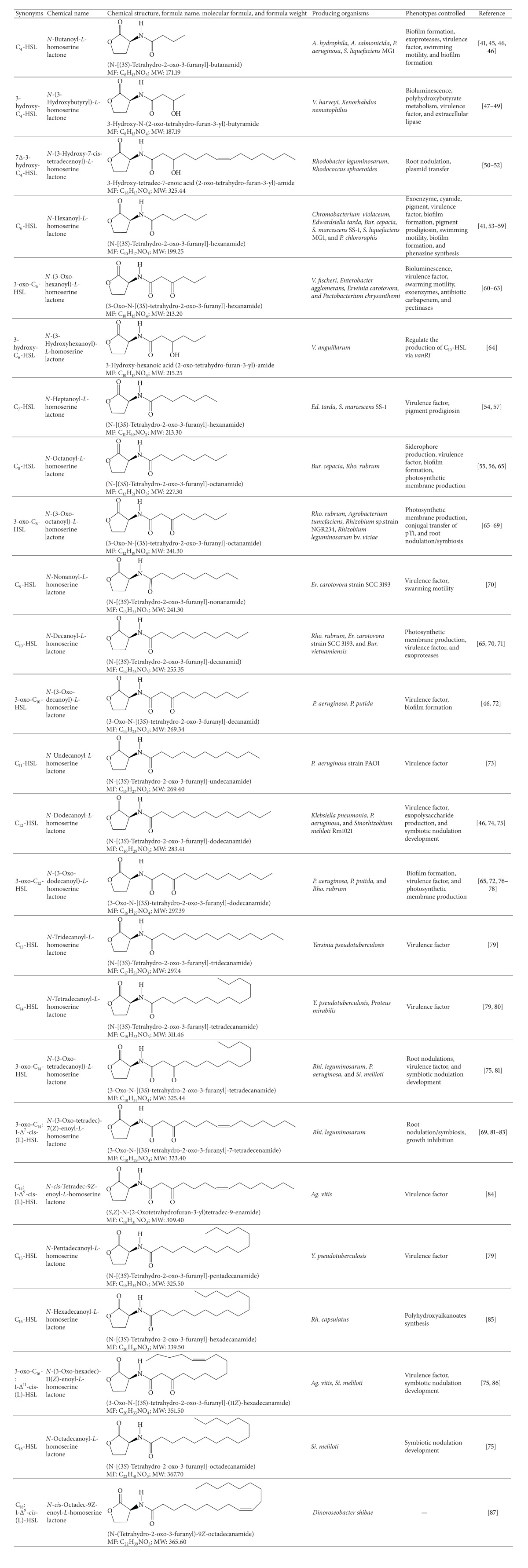
The AHLs which have been characterized so far consist of homoserine lactone (HSL) ring unsubstituted in the β- andγ-positions which is N-acylated with a fatty acyl group at theα-position [154]. The naturally occurring AHLs produced by Gram-negative bacteria exhibit varying lengths of acyl chain with 4 to 18 carbon atoms and contain either N-acyl, N-(3-oxoacyl), or N-(3-hydroxyacyl) classes [10, 73]. Some AHLs with unsaturation in the 5 and 7 positions in a chain of 12 or 14 carbon atoms have been also reported. The screening for putative AHL producers has revealed that Gram-negative bacteria belonging to different genera which occupy a wide variety of environmental sources produce AHLs. Some examples of AHLs producing bacteria include species of Acinetobacter, Aeromonas, Agrobacterium, Burkholderia, Erwinia, Enterobacter, Chromobacterium, Methylobacter, Paracoccus, Pseudomonas, Ralstonia, Rhodobacter, Rhizobium, Serratia, Sinorhizobium, Vibrio, and Yersinia [155]. Multiple AHLs have also been reported in these bacteria due to the presence of more than one AHL synthase. In addition, AHL signal production is a consequence of sloppy active site selection for the acyl chain and hence a single synthase will often make multiple AHL types. Thus, the presence of single or multiple AHL synthase in a single bacterium has resulted in the regulation of various quorum sensing phenotypes in one organism which includes virulence factor, exopolysaccharide production, swarming motility, antibiotic production, pigmentation, and biofilm formation. The detailed structural information of AHLs identified in Gram-negative bacteria and various phenotypes controlled is given in Table 1.
Table 1.
Structures of common N-acyl homoserine lactones produced by different Gram-negative bacteria and the phenotype controlled.
|
2.3. AHLs-Mediated Biofilm Formations in Wastewaters
Bacterial biofilms are present in many water and wastewater treatment systems, where they may play beneficial or detrimental roles [34]. Bacteria prefer to live in biofilms, as the mode of bacterial life in the form of biofilms confers many advantages over a planktonic mode of life, such as resistance to environmental stresses [156]. The formation of biofilms is a stepwise process involving the initial attachment of bacteria to surfaces, microcolonies growth and maturation into expanding structures, and further detachment of aged microorganisms [16]. In general, the transition from free-living individual cell to a sessile form initiated with the transportation and attachment of bacteria to specific substratum followed by adhesion, colonization, and setup of early biofilm structures [157]. It has been proposed that AHL-mediated quorum sensing system of Gram-negative bacteria is involved in almost all stages of biofilm formation such as swarming motility and dispersal of aggregates in S. liquefaciens and biofilm maturation in P. aeruginosa [15, 158, 159]. The influence of quorum sensing signal molecule 3-oxo-C12-HSL synthesis on biofilm maturation in P. aeruginosa has been described by Davies et al. [9]. It is also reported that quorum sensing regulated cell surface properties alteration seems to translate to a biofilm phenotype variation [15, 160]. The specific role of individual HSL in biofilm formation has been also reported, where C4-HSL was found to be involved in the initial surface attachment and maturation of A. hydrophila biofilms [161].
Several biofilm forming bacterial species have been identified in wastewater treatment systems and are known to possess AHL-mediated quorum sensing mechanism [162]. Moreover, a number of AHLs producing bacterial strains have been isolated from wastewaters and found to be involved in quorum sensing-mediated biofilm formation [88, 163–165]. Different AHLs have also been detected from wastewaters as produced by Gram-negative Proteobacteria belonging to α, β, and γ subdivisions [158]. Furthermore, a correlation between AHL production and biofilm formation has been found among wastewater bacterial isolates as accessed by biofilm formation assay [88]. It is suggested that, in Gram-negative bacterium S. liquefaciens, the AHL-mediated quorum sensing regulates swarming motility resulting in formations of heterogeneous biofilms [41]. The detection of C6-HSL and C8-HSL in the MBR biocake also indicates the involvement of AHLs producing bacteria in biofilm formation [17]. All these evidences suggest that the AHL-mediated quorum sensing system present in several Gram-negative wastewater bacteria is responsible for the formation of biofilms and thus by membrane biofouling.
The bacterial species identified in wastewater treatment systems possessing AHLs-mediated quorum sensing mechanisms are shown in Table 2. This list includes the only culturable bacteria that were identified in wastewater treatment systems and are involved in AHL-based membrane biofouling. However, the number of biofouling bacteria will obviously increase with further investigation of quorum sensing regulation and interspecies interaction. In addition to this, most of the wastewater bacteria are unculturable and have not been specifically studied so far to understand their genetic and physiological attributes. Advanced molecular biology techniques such as pyrosequencing will be used for detailed characterization of unculturable bacteria present in wastewater treatment systems and further study to understand the quorum sensing mechanism involved.
Table 2.
AHLs producing bacteria present in wastewater treatment systems and quorum sensing phenotypes regulated.
| Bacterial strains | AHLs produced | Phenotypes regulated | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| A. hydrophila subsp. hydrophila strain NA1, A. hydrophila subsp. dhakensis strain LBA2, A. media strain NA2, En. ludwigii strain SWA1, K. variicola strain SWA2, and S. marcescens strain SWA6 | Short- to medium-chain | Biofilm formation | [88] |
|
| |||
| Enterobacter sp. strain LBA3, En. cancerogenus strain LBA4, Raoultella ornithinolytica strain TSA7, P. japonica strain TSA3, and Citrobacter freundii strain R2A5 | Long-chain | Biofilm formation | [88] |
|
| |||
| A. hydrophila, A. media, A. punctate, A. sobria, A. veronii, A. jandaei, P. oryzihabitans, Ci. farmer, Ci. murliniae, and En. ludwigii | Short- to medium-chain | n.d. | [89] |
|
| |||
| A. punctata GC3, Aeromonas sp. GC5, A. hydrophila GC10, A. allosaccharophila GC15, A. media GC16, Citrobacter sp. GC20, Acinetobacter johnsonii GC23, Klebsiella sp. GC30, Shigella sp. GC37, Microbacterium paraoxydans GC42, Chitinimonas taiwanensis GC43, Pantoea agglomerans GC47, Ra. terrigena GC49,and Microbacterium sp. GC50 | Short- to medium-chain | n.d. | [90] |
|
| |||
| A. punctata GC4, Aeromonas sp. GC8, Aeromonadaceae sp. GC14, Citrobacter sp. GC19, Neisseria sp. GC34, Pseudomonas sp. GC35, and Malikia spinosa GC45 | Long-chain | n.d. | [90] |
|
| |||
| Ac. junii | Medium-chain | Biofilm formation | [91, 92] |
|
| |||
| A. hydrophila | Short-chain | n.d. | [93] |
|
| |||
| P. putida | Medium-chain | n.d. | [93] |
|
| |||
| Ed. tarda | Short- and medium-chain | Virulence factor | [54] |
n.d.: not determined; short-chain: C4-HSL and C6-HSL; medium-chain: C6-HSL, 3-oxo-C8-HSL, and C8-HSL; long-chain: C8-HSL, 3-oxo-C8-HSL, C10-HSL, C12-HSL, 3-oxo-C12-HSL, and C14-HSL.
3. Quorum Quenching Disrupts Quorum Sensing Phenotypes
The mechanism that can interfere with any phenotype regulated by quorum sensing is known as quorum quenching [166]. There are three basic components and thus targets for external intervention in AHL-mediated quorum sensing system have been identified which include Lux I-type synthase which generates AHL signals, the AHL ligand as signal itself, and the Lux R-type signal receptor [18, 167, 168]. Among all these targets, the enzymatic degradation of AHL signal molecules has been reported in a wide range of prokaryotes and a few eukaryotes [169]. Thus, one of the most important prerequisites for designing quorum quenching strategies is the screening of Gram-negative bacteria for putative AHLs production. In view of this, the simple AHL biosensors bacterial strains based on lux, lacZ, or gfp reporter gene fusion or pigment induction have been developed which can be used to detect the presence of broad range of AHLs among Gram-negative bacteria [170].
3.1. Bacterial Biosensors for Detection of AHLs
The detection of AHLs producing bacteria can be achieved by several methods. One common approach involving the use of biosensors strains is sensitive and convenient and allows real time detection of AHLs [171]. Biosensors strains contain quorum sensing regulatory promoters fused to lux operon or lacZ and lack AHL synthase enzyme. Such developed strains cannot produce AHLs but promoter activity gets induced by exogenous quorum sensing signals. Thus, the receptor gets activated and binds to its cognate LuxI promoter which initiates the expression of certain genes [45, 98]. The expression of relevant genes results in the display of specific phenotypes such as β-galactosidase production by Ag. tumefaciens NT1 [94], violacein pigmentation by C. violaceum CV026 [53], green fluorescent protein production by V. fischeri [105], and bioluminescence by P. putida 117 [101]. These biosensors strains can detect a narrow range of AHLs and thus more than one kind of such biosensors are required to test the wide range of AHLs produced by a single bacterium. Although biosensors were initially developed to detect the presence of AHLs in environmental isolates, they have also been used to investigate the activities of nonnative AHL analogues. The AHL detection bioassays are most commonly performed by overlay method while quantitative assays are performed by liquid cultures. A graphical representation for the construction of bacterial biosensor and its use to detect exogenous AHLs by means of different assay is shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2.
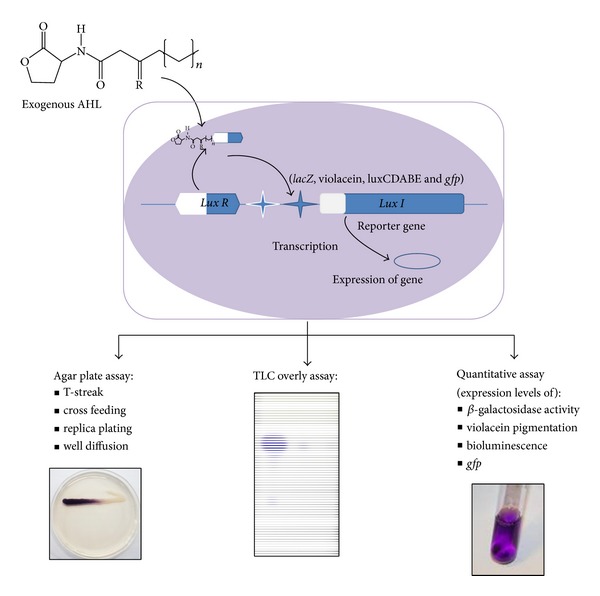
Construction of bacterial biosensor for the detection of exogenous AHLs. The bacterial biosensor is deficient in AHL production and when exogenous AHL interacts with LuxR protein, the transcription of reporter genes from LuxR-AHL regulated promoter initiated. This results in the display of specific phenotypes such as β-galactosidase activity, violacein pigmentation, bioluminescence, and green fluorescent protein production.
The most commonly used biosensor strain Ag. tumefaciens NT1 (traR, tra::lacZ749) contains a lacZ fusion in the tra1 gene of pTiC58 which is induced to produce blue colour from the hydrolysis of 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl-β-D-galactopyranoside by the β-galactosidase activity, in response to broad range of AHLs such as 3-oxo-HSLs with side chains ranging from C4 to C12, 3-unsubstituted-HSLs with side chains from C6 to C12, and 3-hydroxy-HSLs with side chains from C8 to C10 [94, 172]. Another equally sensitive biosensor strain for long chain AHLs detection is Ag. tumefaciens A136. It contains the traI-lacZ fusion in the (pCF218) (pCF372) plasmids and is capable of detecting the presence C8-HSL, 3-oxo-C8-HSL, C10-HSL, C12-HSL, 3-oxo-C12-HSL, and C14-HSL exogenous AHLs by β-galactosidase activity [17, 37, 148]. The second class of reporter strain required for identifying short-chain AHLs with acyl chains of C4 to C6 is represented by C. violaceum CV026. It is mini-Tn5 mutant of ATCC31532 containing LuxR homologue CviR regulating the production of violacein, a purple pigment when induced by short-chain exogenous AHLs [53, 96]. A more recent developed reporter strain for detecting long-chain AHLs ranging from 3-oxo-C6-HSL to C14-HSL is C. violaceum VIR24, an in-frame deletion mutant of the cvil gene encoding AHL synthase in C. violaceum ATCC12472 [97]. The use of P. putida 117 as bioluminescence sensor for detection of medium-chain C8-HSL is suggested by Steidle et al. [101]. The green fluorescent protein derivative GFPmut3∗ and its unstable variant have also proven effective biosensors for detecting the presence of AHLs [105]. The GFPmut3∗ emits fluorescent light in the presence of oxygen and does not require any additional substrate. In addition to this, the plasmid sensor pSB1075 based on Escherichia coli bioluminescence has also been reported to detect the presence of C10-HSL, C12-HSL, and their 3-oxo derivatives [98]. In addition to the above-mentioned biosensors, new biosensors have also been developed so far and are summarized and listed in Table 3.
Table 3.
The biosensors strains developed to detect AHLs produced by Gram-negative bacteria.
| Biosensor strain/plasmid | Responded AHLs | Reporter system | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ag. tumefaciens NT1 (pDCI41E33 containing traG::lacZ fusion) | C6-HSL, C8-HSL, C10-HSL, C12-HSL, C14-HSL, and AHLs with 3-oxo-, 3-hydroxy-, and 3-unsubstituted side chains |
β-Galactosidase activity | [94] |
|
| |||
| Ag. tumefaciens NT1 (pZLR4 containing Tral/R) | C6-HSL, C8-HSL, C10-HSL, C12-HSL, C14-HSL, 3-hydroxy-C6-HSL, 3-hydroxy-C8-HSL, 3-hydroxy-C10-HSL, and all AHLs with 3-oxo-side chains | β-Galactosidase activity | [95] |
|
| |||
| Ag. tumefaciens A136 (traI-lacZ fusion (pCF218) (pCF372)) | C6-HSL, C8-HSL, 3-oxo-C8-HSL, C10-HSL, C12-HSL, 3-oxo-C12-HSL, and C14-HSL | β-Galactosidase activity | [37] |
|
| |||
| C. violaceum CV026 (CviVR receptor) | C4-HSL, C6-HSL, and C8-HSL | Violacein pigmentation | [53, 96] |
|
| |||
| C. violaceum VIR24 (CviI receptor) | 3-Oxo-C6-HSL, C6-HSL, C7-HSL, 3-oxo-C8-HSL, C8-HSL, C10-HSL, C12-HSL, and C14-HSL | Violacein pigmentation | [97] |
|
| |||
| E. coli (luxCDABE cassette activated by Ahyl/R of A. hydrophila) | C4-HSL | Bioluminescence | [45] |
|
| |||
| E. coli (pSB401 containing LuxI/R of V. fischeri) | C6-HSL 3-Oxo-C8-HSL C8-HSL |
luxCDABE | [98] |
|
| |||
| E. coli (pHV2001 containing luxI/R) | C6-AHL C8-3-oxo-HSL C8-HSL |
luxCDABE |
[99] |
|
| |||
| E. coli (pSB1075 containing LusI/R of P. aeruginosa) | 3-Oxo-C12-HSL, C12-HSL | luxCDABE | [98] |
|
| |||
| E. coli (pHV2001-containing LuxI/R of V. fischeri) | C6-HSL, 3-oxo-C6-HSL, 3-oxo-C8-HSL, and C8-HSL | luxCDABE | [100] |
|
| |||
| E. coli (pKDT17 containing LusI/R of P. aeruginosa) | 3-Oxo-C10-HSL, C10-HSL, 3-oxo-C12-HSL, and C12-HSL | β-Galactosidase activity | [100] |
|
| |||
| P. putida 117 (pAS-C8-CepR receptor) | C8-HSL | Bioluminescence | [101] |
|
| |||
| P. aeruginosa (M71LZ containing Lasl/R) | 3-Oxo-C10-HSL, 3-oxo-C12-HSL | β-Galactosidase activity | [102] |
|
| |||
| P. aeruginosa (pSB406 containing RhlI/R) | C4-HSL, C6-HSL, C8-HSL, C10-HSL, C12-HSL, and C14-HSL with 3-oxo-side chains | luxCDABE | [98] |
|
| |||
| P. fluorescens (pSF105 + pSF107 containing Phzl/R) | 3-Hydroxy-C6-HSL, 3-hydroxy-C8-HSL | β-Galactosidase activity | [103] |
|
| |||
| Si. meliloti Rm41 (sinI::lacZ pJNSinR) | C14-HSL, 3-oxo-C14-HSL, C16-HSL, and 1-3-oxo-C16-HSL | β-Galactosidase activity | [104] |
|
| |||
| V. fischeri (pJBA88 and pJBA89 encoding luxR and Pluxl fusion of gfpmut3∗) | C6~C14-3-oxo-HSL C6~C12-HSL |
gfp | [105] |
3.2. Quorum Quenching and Biofilm Control
A large number of molecules capable of disrupting AHL-mediated quorum sensing system have been identified and their mechanisms are revealed, which includes halogenated furanones produced by seaweed Delisea pulchra and synthetic derivatives that target R proteins [173], synthetic AHL analogues that may compete with corresponding AHL signals [174], and quorum quenching enzymes such as AHL-acylase, AHL-lactonase, and oxidoreductases which degrade or modify AHL signals [20, 128, 153]. Such quorum quenching compounds and enzymes with different mechanisms have been widely used in quenching AHL-mediated quorum sensing and thus preventing bacterial biofilms.
A detailed summary of the known natural quorum quenching molecules derived from plant, fungi, algae, and bacteria is provided in our previous review [175]. These compounds have been widely investigated in disease to combat AHL-mediated quorum sensing trait biofilm formations. However, very little research has been done so far using natural compounds on the inhibition of biofilm formations in advanced wastewater treatment systems. Recently, vanillin has shown to interfere with A. hydrophila quorum sensing and inhibited biofilm formations on five different membrane surfaces in a CDC (Center for Disease Control) biofilm reactor study [22]. Two more natural quorum sensing inhibitory compounds, furanones and Piper betle, have also been found to inhibit membrane biofouling in wastewater treatment systems [23, 176]. However, such purified natural compounds are not feasible to use at real MBRs due to the higher cost incurred for its extraction and purification, narrow efficacy towards specific AHLs, and high quantity required to achieve considerable biofouling inhibition. For example, vanillin showed the inhibition of only short-chain C4-HSL and C6-HSL and medium-chain 3-oxo-C8-HSL and C8-HSL AHLs, while it failed to inhibit long-chain AHLs [22]. Moreover, the quantity required to achieve considerable inhibition of AHLs is also high; that is, 0.25 mg/mL of vanillin showed the highest QSI activity with C4-HSL (69%) followed by 3-Oxo-C8-HSL (59.8%), C6-HSL (32%), and C8-HSL (28%). In addition, only 46.3% of biofilm inhibition was observed at the tested higher concentration of 0.25 mg/mL vanillin. The only major advantage of this novel strategy for antibiofouling method is that it circumvents the problem of resistance which is linked to the use antibiotics, as it specifically interferes with the expression of phenotypes rather than impede growth [137].
Another nonantibiotic approach studied to mitigate bacterial biofilms is the use of enzymes which can interfere with AHL signals and thereby inhibit its phenotypes. This approach of enzymatic quorum quenching has been attempted by many researchers to control membrane biofouling in MBRs treating wastewaters. Paul et al. [177] demonstrated the potential of purified AHL-degrading enzyme acylase I (porcine kidney) to reduce biofilm formations by environmental strains A. hydrophila and P. putida on three different membrane surfaces. To avoid the loss of free enzymes and maintain their stability, various methods of enzyme carriers have been tried. Recently, Yeon et al. [17] prepared a magnetic enzyme carrier by immobilizing quorum quenching enzyme acylase on magnetic particles to overcome the limitation of free enzyme and demonstrated its potential to control biofouling in MBR. In another study, the immobilization of acylase was carried out onto the membrane surface and mitigation of membrane biofouling investigated [26]. These innovative approaches of enzymatic quorum quenching have proven its potential for the control of biofouling in MBR treating wastewaters. However, some practical issues related to the high cost of purified enzymes and its instability make it difficult to use at commercial level MBRs treating municipal and industrial wastewaters. As an alternative to enzymatic quenching, the use of bacteria that produce quorum quenching enzymes and also help to decompose wastewater pollutant has been suggested [17, 148, 178].
4. Quorum Quenching Bacteria
The discovery of quorum quenching mechanisms in several bacterial species represents a new milestone in quorum sensing and quorum quenching research. Considering the essential roles of AHL-mediated quorum sensing in biofilm formation by Gram-negative bacteria, degradation or disruption of AHLs signals with quorum quenching enzymes produced by other bacteria appears to be a promising alterative for controlling membrane biofouling [179]. Therefore, strategies of disrupting the AHL-mediated quorum sensing with special emphasis on the control of membrane biofouling by quorum quenching bacteria are discussed herein.
Over the last few years, a range of quorum quenching enzymes have been identified in various Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. These novel enzymes are key molecules for establishing the concept of quorum quenching in regulating quorum sensing phenotypes. The AHL-degrading or modifying enzymes are often classified into three groups: (i) AHL-acylases, (ii) AHL-lactonases, and (iii) oxidoreductases [20, 128, 153]. It has been known so far that four potential cleavage sites in the AHLs are likely cut off by quorum quenching enzymes following a catabolic digestion of carbon and nitrogen sources [124]. The crystal structural characterization of quorum quenching enzymes has also provided the valuable information to elucidate its catalytic mechanisms [166]. Additionally, the molecular biology techniques have identified the genes responsible for production of quorum quenching enzymes and its phenotypes regulated. The general mechanisms of these enzymes involved in the degradation or modification of AHL signals are shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3.
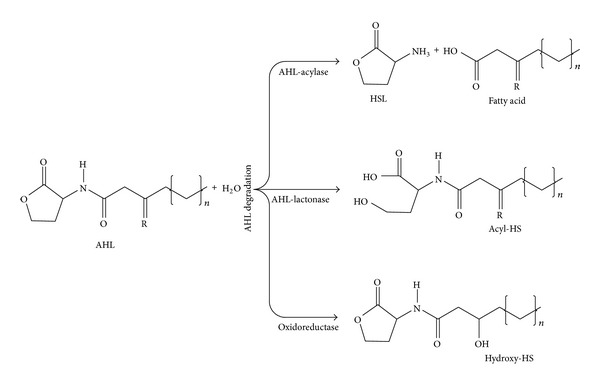
AHL-degradation or modification mechanism of quorum quenching enzymes: AHL-acylase, AHL-lactonase, and oxidoreductase.
AHL-acylases are known to irreversibly hydrolyze the amide linkage between the acyl chain and homoserine moiety of AHL signals resulting in the release of homoserine lactone and corresponding fatty acid, which do not exhibit further residual quorum sensing activity [20, 119]. The AHL-acylase was first reported in V. paradoxus strain VAI-C, which showed a wide range of degradation capacity against C4-HSL, 3-oxo-C6-HSL, C6-HSL, C8-HSL, C10-HSL, and C12-HSL [119]. Subsequently, several bacterial species have been reported to produce AHL-acylases such as AiiC in Anabaena sp. PCC7120 degrading C4-HSL to C14-HSL with 3-oxo and 3-hydroxy substitutions [106], QuiP in P. aeruginosa PAO1 degrading C8-HSL, C10-HSL, 3-oxo-C12-HSL, and C12-HSL [112], AiiD in Ralstonia sp. XJ12B degrading 3-oxo-C8-HSL, 3-oxo-C10-HSL, and 3-oxo-C12-HSL [20], and AhlM in Streptomyces sp. M664 degrading C8-HSL, C10-HSL, and 3-oxo-C12-HSL [117].
Another class of quorum quenching enzyme found in bacteria which degrades AHL molecule is AHL-lactonases [128]. This cleaves the homoserine lactone ring of AHLs in a hydrolytic and reversible manner to open the lactone ring, which makes the AHL incapable of binding to the target transcriptional regulator and attenuates its effectiveness [128]. The hydrolysis of lactone ring also appears at alkaline pH and can be reversed by acidification. Several AHL-lactonases have been identified from a range of bacterial species and are mentioned in some previous reviews [175, 180]. The first AHL-lactonase, encoded by aiiA gene of Bacillus sp. 240B1, was identified as AiiA240B1 by functional cloning of AHL signal as substrate in E. coli [128]. The AiiA240B1 has been shown to degrade C8-HSL and decreases the extracellular pectolytic enzyme activities and inhibition of virulence in Er. carotovora. It is reported that AiiA like lactonases hydrolytic activity is not affected by differences in the acyl chain length and substitutions in the AHLs [126, 181]. Another important class of AHL-lactonase is represented by the QsdA from Rh. erythropolis strain W2, which has been shown to degrade a wide range of AHLs including C6-HSL, C8-HSL, C10-HSL, C12-HSL, and C14-HSL with 3-oxo-substitutions [146]. The quorum quenching enzyme QsdA has been found to degrade the AHL-molecule and inhibits virulence factor in Pec. carotovorum strain PCC797. It is also reported that the QsdA lactonases belong to phosphotriesterase family which harbors lactonase, phosphotriesterase, or amidohydrolase activities [146]. Several other bacterial species including Ochrobactrum sp. T63, Ag. tumefaciens c58, P. aeruginosa PAO1, and Bacillus sp. 240B1 have been reported to encode AHL-acylase for degradation of AHLs which results in the inhibition of biofilm formation as listed in Table 4.
Table 4.
List of quorum quenching bacteria reported to degrade or modify AHLs.
| Quenching bacteria | Gene involved | AHLs degraded | Phenotypes regulated | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AHL-acylase mediated QQ | ||||
| Anabaena sp. PCC7120 | aiiC | C4-HSL, 3-oxo-C4-HSL, 3-hydoxo-C4-HSL, 3-oxo-C6-HSL, 3-hydoxo-C6-HSL, C6-HSL, 3-oxo-C8-HSL, 3-hydoxo-C8-HSL, C8-HSL, 3-oxo-C10-HSL, 3-hydoxo-C10-HSL, C10-HSL, 3-oxo-C12-HSL, 3-hydoxo-C12-HSL, C12-HSL, 3-oxo-C14-HSL, 3-hydoxo-C14-HSL, and C14-HSL | n.d. | [106] |
|
| ||||
| Acinetobacter sp. strain Ooi24 | Unknown | C10-HSL | n.d. | [89] |
|
| ||||
| B. pumilus S8-07 | Unknown | 3-Oxo-C12-HSL | Inhibit biofilm formation in P. aeruginosa PA01 | [107] |
|
| ||||
| Comamonas strain D1 | Unknown | C4-HSL, 3-oxo-C6-HSL, C6-HSL, 3-oxo-C8-HSL, C8-HSL, 3-oxo-C10-HSL, C10-HSL, 3-oxo-C12-HSL, C12-HSL, 3-oxo-C14-HSL, C14-HSL, and C16-HSL | Decreases virulence and antibiotic production in Pec. carotovorum strain Pcc797 | [108] |
|
| ||||
| P. aeruginosa | quiP | C6-HSL, C8-HSL, C10-HSL, and C12-HSL | Inhibits biofilm formation in Aeromonassp. | [109] |
|
| ||||
| P. aeruginosa PA01 | PA2385 | 3-Oxo-C12-HSL | Reduce virulence factor elastase and pyocyanin in P. aeruginosa PA01 | [73] |
|
| ||||
| P. syringae strain B728a | hacA | C8-HSL, C10-HSL, and C12-HSL | Influence biofilm formation | [110] |
|
| ||||
| P. syringae strain B728a | hacB | 3-Oxo-C6-HSL, C6-HSL, C8-HSL, C10-HSL, 3-oxo-C12-HSL, and C12-HSL | Influence biofilm formation | [110] |
|
| ||||
| P. aeruginosa PAO1 | PA2385 | C11-HSL, 3-oxo-C12-HSL, C12-HSL, 3-oxo-C14-HSL, and C14-HSL | Decreases elastolytic activity and pyocyanin production | [73] |
|
| ||||
| Pseudomonas sp. strain PAI-A | pvdQ | C10-HSL, 3-oxo-C12-HSL, C12-HSL, and C14-HSL | Inhibit virulence factor | [111] |
|
| ||||
| P. aeruginosa PAO1 | quiP | C8-HSL, C10-HSL, 3-oxo-C12-HSL, and C12-HSL | Inhibit virulence factor | [112] |
|
| ||||
| Pseudomonas sp. 1A1 | Unknown | C6-HSL, C8-HSL, 3-oxo-C8-HSL, 3-oxo-C10-HSL, C10-HSL, 3-oxo-C12-HSL, and C12-HSL | Inhibit biofilm formation in MBR | [113] |
|
| ||||
| Rho. erythropolis strain W2 | Unknown | C4-HSL, 3-oxo-C6-HSL, C6-HSL, C7-HSL, 3-oxo-C8-HSL, C8-HSL, and C10-HSL | Reduces pathogenicity of Pec. carotovorum subsp. carotovorum in plants | [114, 115] |
|
| ||||
| Ralstonia sp. XJ12B | aiiD | 3-Oxo-C8-HSL, 3-oxo-C10-HSL, and 3-oxo-C12-HSL | Decreases swarming ability and production of elastase and pyocyanin in P. aeruginosa PA01 | [20] |
|
| ||||
| Ralstonia solanacearum GMI1000 | aac | C7-HSL, C8-HSL, 3-oxo-C8-HSL, and C10-HSL | Inhibits violacein and chitinase activity in C. violaceum CV026 | [116] |
|
| ||||
| Streptomyces sp. strain M664 | ahlM | C8-HSL, C10-HSL, and 3-oxo-C12-HSL | Decreases virulence factor, elastase, protease, and LasA in P. aeruginosa | [117] |
|
| ||||
| Shewanella sp. strain MIB015 | aac | C8-HSL, C10-HSL, and C12-HSL | Reduces biofilm formation in V. anguillarum | [118] |
|
| ||||
| Variovorax paradoxus strain VAI-C | Unknown | C4-HSL, 3-oxo-C6-HSL, C6-HSL, C8-HSL, C10-HSL, and C12-HSL | n.d. | [119] |
|
| ||||
| AHL-lactonase mediated QQ | ||||
| Ag. tumefaciens c58 | attM | 3-Oxo-C8-HSL | Inhibit Ti plasmid conjugal transfer | [120] |
|
| ||||
| Ag. tumefaciens | aiiB | C4-HSL, 3-oxo-C6-HSL, C6-HSL, 3-oxo-C8-HSL, C8-HSL, and C10-HSL | n.d. | [121] |
|
| ||||
| Ag. tumefaciens C58 | aiiB | 3-Oxo-C6-HSL, C6-HSL, C8-HSL, C7-HSL, 3-oxo-C8-HSL, and C8-HSL | Reduces virulence of Erwinia strain 6276 | [122] |
|
| ||||
| Ag. tumefaciens K84 | aiiS | 3-Oxo-C6-HSL, C6-HSL, 3-oxo-C8-HSL, C8-HSL, 3-oxo-C10-HSL, C10-HSL, 3-oxo-C12-HSL, C12-HSL, 3-oxo-C14-HSL, and C14-HSL |
n.d. | [123, 124] |
|
| ||||
| Acinetobacter sp. strain C1010 | Unknown | C6-HSL, C8-HSL | Inhibit production of phenazines in P. chlororaphis O6 and virulence in Er. carotovora | [125] |
|
| ||||
| Acinetobacter sp. GG2 | Unknown | 3-Hydroxy-C4-HSL, C5-HSL, 3-hydroxy-C6-HSL, C6-HSL, C7-HSL, 3-oxo-C8-HSL, 3-hydroxy-C8-HSL, C8-HSL, C9-HSL, and 3-oxo-C10-HSL, 3-hydroxy-C10-HSL, C10-HSL, C11-HSL, 3-oxo-C12-HSL, 3-hydroxy-C12-HSL, C12-HSL, 3-oxo-C14-HSL, 3-hydroxy-C14-HSL, C14-HSL, Δ9-3-hydroxy-C14-HSL, Δ10-3-hydroxy-C14-HSL, Δ11-3-hydroxy-C14-HSL, and Δ13-3-hydroxy-C14-HSL | Attenuates virulence of P. aeruginosa and Er. carotovora | [109] |
|
| ||||
| Acidobacteria sp. | qIcA | 3-Oxo-C6-HSL, C6-HSL, C7-HSL, 3-oxo-C8-HSL, C8-HSL, 3-oxo-C10-HSL, and C10-HSL | Decreases virulence of Pec. carotovorum strain 6276 | [126] |
|
| ||||
| Arthrobacter sp. IBN110 | ahlD | C4-HSL, 3-oxo-C6-HSL, C6-HSL, C8-HSL, 3-oxo-C10-HSL, and C10-HSL | Decreases virulence of Er. carotovora N98 | [127] |
|
| ||||
| Bacillus sp. 240B1 | aiiA | C8-HSL | Decreases extracellular pectolytic enzyme activities and inhibits virulence in Er. carotovora | [128, 129] |
|
| ||||
| B. cereus | aiiA | C6-HSL, C8-HSL, and C10-HSL | Decreases virulence factor | [130] |
|
| ||||
| B. mycoides | aiiA | C6-HSL, C8-HSL, and C10-HSL | Decreases virulence factor | [130] |
|
| ||||
| Bacillus strain COT1 | aiiA | 3-Oxo-C6-HSL | Decreases virulence factor | [130] |
|
| ||||
| B. anthracis | aiiA | C6-HSL, C8-HSL, and C10-HSL | Decreases swarming in Bur. thailandensis | [131] |
|
| ||||
| B. pumilus SW9 | Unknown | n.d. | Inhibit biofouling on microfiltration membranes by Brevundimonas sp. SW1, Acidovorax sp. DB3, Acinetobacter sp. GS1, and Staphylococcus aureus SA1 | [132, 133] |
|
| ||||
| B. thuringiensis subspecies morrisoni | aiiA | 3-Oxo-C6-HSL | Attenuates the pathogenicity of Er. carotovora | [134] |
|
| ||||
| B. thuringiensis | aiiA | 3-Oxo-C6-HSL | Decreases virulence of Er. carotovora | [135] |
|
| ||||
| Bacillus sp. A24 | aiiA | C4-HSL, C6-HSL | Decreases production of elastase, rhamnolipids, and pyocyanin and inhibits swarming in P. aeruginosa PA01 | [136] |
|
| ||||
| En. asburiae VT65 | aiiA | C4-HSL, C6-HSL | n.d. | [137] |
|
| ||||
| Geobacillus kaustophilus strain HTA426 | GKL | C4-HSL, 3-oxo-C6-HSL, C6-HSL, 3-oxo-C8-HSL, C8-HSL, C10-HSL, and 3-oxo-C12-HSL | Thermostable antivirulence therapeutic agent | [138] |
|
| ||||
| K. pneumonia | ahlK | C6-HSL, 3-oxo-C6-HSL | Decreases virulence of Er. carotovora N98 | [127] |
|
| ||||
| M. testaceum StLB018 | Unknown | C6-HSL, 3-oxo-C6-HSL, C10-HSL, and 3-oxo-C10-HSL | Interrupts pathogenicity of Pec. carotovorum subsp. carotovorum | [139] |
|
| ||||
| Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis K-10 | MCP | C7-HSL, C8-HSL, 3-oxo-C8-HSL, C10-HSL, and C12-HSL | n.d. | [140] |
|
| ||||
| My. tuberculosis | AhlA, PPH | C4-HSL, 3-oxo-C8-HSL, and C10-HSL | n.d. | [141] |
|
| ||||
| M. testaceum StLB037 | aiiM | 3-Oxo-C6-HSL, C6-HSL, 3-oxo-C8-HSL, C8-HSL, 3-oxo-C10-HSL, and C10-HSL |
Reduces pectinase activity and virulence in Pec. carotovorum subsp. carotovorum | [142] |
|
| ||||
| Ochrobactrum sp. T63 | aidH | C4-HSL, C6-HSL, 3-oxo-C6-HSL, 3-oxo-C8-HSL, and C10-HSL | Reduce biofilm formation by P. fluorescens 2P24 and the pathogenicity of Pec. carotovorum | [143] |
|
| ||||
| Pichia pastoris | aiiA B546 | 3-Oxo-C6-HSL, C6-HSL, 3-oxo-C8-HSL, C8-HSL, C10-HSL, and C12-HSL | Attenuates the A. hydrophila infection in aquaculture | [144] |
|
| ||||
| Pseudoalteromonas byunsanensis strain 1A01261 | qsdH | C4-HSL, 3-oxo-C6-HSL, C6-HSL, 3-oxo-C8-HSL, C8-HSL, C10-HSL, C12-HSL, and C14-HSL | Attenuates the plant pathogenicity of Er. carotovora | [145] |
|
| ||||
| Rho. erythropolis W2 | qsdA | 3-Oxo-C6-HSL, C6-HSL, 3-oxo-C8-HSL, C8-HSL, 3-oxo-C10-HSL, C10-HSL, 3-oxo-C12-HSL, C12-HSL, 3-oxo-C14-HSL, and C14-HSL |
Decreases virulence of Pec. carotovorum strain PCC797 | [146] |
|
| ||||
| Rhodococcus strain LS31 | Unknown | C6-HSL, 3-oxo-C6-HSL, C10-HSL, and 3-oxo-C10-HSL | Reduces pectate lyase activity in Er. carotovora | [147] |
|
| ||||
| Rhodococcus strain PI33 | Unknown | C6-HSL, C10-HSL | Reduces pectate lyase activity in Er. carotovora | [147] |
|
| ||||
| Rhodococcus sp. BH4 | qsdA | 3-Oxo-C6-HSL, C6-HSL, 3-oxo-C8-HSL, C8-HSL, 3-oxo-C10-HSL, C10-HSL, 3-oxo-C12-HSL, and C12-HSL | Inhibit biofilm formation in MBR | [148, 149] |
|
| ||||
| Rhodococcus sp. A167 | Unknown | C6-HSL, 3-oxo-C8-HSL, and C8-HSL | Attenuates maceration ability of Pec. carotovorum subsp. carotovorum | [150] |
|
| ||||
| Solibacillus silvestris StLB046 | ahlS | C10-HSL | Attenuates maceration of plant pathogen Pec. carotovorum subsp. carotovorum | [151] |
|
| ||||
| Thalassomonas sp. PP2-459 | Unknown | C4-HSL, C6-HSL, C8-HSL, 3-oxo-C10-HSL, C10-HSL, and C12-HSL | Decreases pathogenicity of V. anguillarum ATCC 19264 | [152] |
|
| ||||
| Oxidoreductase mediated QQ | ||||
| B. megaterium CYP102A1 | P450BM3 | Oxidizes; C12-HSL, 3-oxo-C12-HSL, C14-HSL, 3-oxo-C14-HSL, C16-HSL, C18-HSL, and C20-HSL. | n.d. | [153] |
|
| ||||
| Rho. erythropolis W2 | Unknown | Oxidizes; 3-oxo-C10, 3-oxo-C12-HSL | n.d. | [115] |
n.d.: not determined.
Oxidoreductase is the third important class of quorum quenching enzymes found in limited number of bacterial species. The oxidoreductases are known to target the acyl side chain by oxidative or reductive manner and thus catalyze the structural modification of AHL signal without degradation [182]. This structural change in AHL signal thus affects its specificity and recognition which results in the disturbance of the activation of quorum sensing-mediated phenotypes by modified AHL [114]. The bacterial oxidoreductases are suggested to oxidize a range of long-chain AHLs with or without 3-oxo-substitutions [115, 153]. The first bacterial oxidoreductase P450BM3 has been isolated from Bacillus megaterium which showed the oxidation of C12-HSL, 3-oxo-C12-HSL, C14-HSL, 3-oxo-C14-HSL, C16-HSL, C18-HSL, and C20-HSL [153]. Another unknown quorum quenching enzyme has been reported from Rho. erythropolis W2 which showed the oxidation of 3-oxo-C10 and 3-oxo-C12-HSL [115]. Additionally, one more enzyme was found in Rho. erythropolis W2 which can reduce the 3-oxo substituent of 3-oxo-C14-HSL to yield the corresponding derivative 3-hydroxy-C14-HSL and results in the inhibition of quorum sensing phenotypes.
All these enzymatic quorum quenching mechanisms present in bacteria could be used as a potent antibiofouling tool in MBRs treating wastewaters. A detailed survey of literature on quorum quenching bacteria has been carried out and some strains with AHLs degradation or modification activities are presented in Table 4.
4.1. Application of Quorum Quenching Bacteria in MBR
Enzymatic quorum quenching has proven its potential as an effective approach for biofouling control in the MBRs for advanced wastewater treatment [178]. Several groups of bacteria known to produce quorum quenching enzymes have also been reported and could be further elaborated as economically feasible antibiofouling tool in MBR. This interspecies quorum quenching mechanism present in bacterial cells will thus help to resolve the practical issues concerned with extraction and purification cost of free enzyme as well as its stability. In view of this, the practical applicability of quorum quenching bacteria in the regulation of biofilm formations in wastewater treatment systems has been investigated recently. This will provide valuable information in addressing both the basic and connectional problems associated with membrane biofouling.
Oh et al. [178] investigated the inhibition of quorum sensing in MBR by two quorum quenching bacteria, a recombinant E. coli which produces AHL-lactonase and a real MBR isolate Rhodococcus sp. A quorum quenching microbial vessel prepared by encapsulating both the bacterial strains into a microporous membrane (polyethylene hollow fiber) has successfully inhibited the membrane biofouling by interspecies interference in MBR treating wastewater. Moreover, the continuous MBR operation in the presence of inserted microbial vessel has also inhibited biofouling as determined by substantial delay in the TMP rise-up without any deterioration of wastewater treatment performance. In another study with Rhodococcus sp. BH4 encapsulated microbial vessel, the quorum quenching activity has been found to coincide well with biofouling inhibition in the continuous MBR [149]. Additionally, the internal submerged MBR equipped with quorum quenching microbial vessel showed much lower biofouling than conventional MBR. The quorum quenching effect of the microbial vessel was found to be more pronounced when positioned nearer to the filtration membrane and also depends on recirculation rate of mixed liquor between the bioreactor and membrane tank [2]. It is also observed that the microbial vessel has mentioned its quorum quenching activity steadily over 100 days of MBR operation due to the continuous regeneration of quenching bacteria inside the vessel. This indicates its future potential in designing long-term cost effective antibiofouling strategies in real MBRs treating wastewaters. Recently, a microbial vessel encapsulated with indigenous sludge isolate Pseudomonas sp. 1A1 has been found effective in the inhibition of AHL-mediated membrane biofouling in a lab-scale MBR [113]. However, various factors such as vessel material, pore structure, inner volume of vessel, and amount of quorum quenching bacteria have been found to affect the microbial vessel performance and should be taken into account while designing further microbial vessel containing antibiofouling strategies. The microbial vessels have some limitations which need to be resolved before elaborating further for batch scale MBRs, which include the following: (i) as the quorum quenching microbial vessel has been submerged in a fixed place in the MBR, it could degrade only soluble AHLs that were able to diffuse into the vessel, and (ii) the mass transfer of AHLs from the mixed liquor to the inside of the microbial vessel is also limited [148].
To overcome the limitations of quorum quenching microbial vessel, Kim et al. [148] demonstrated cell entrapping beads (CEBs) as an alternative method of bacterial quorum quenching. The CEBs prepared by free-moving beads of alginate entrapped with Rhodococcus sp. BH4 have shown the mitigation of membrane biofouling as attributed by both physical (friction) and biological (quorum quenching) effects. The quorum quenching activity of CEBs has also inhibited generation of EPS in biofilm cells and thus formed loosely bound biofilms. This approach of bacterial quorum quenching with CFBs has shown its potential over microbial vessels and found more economically feasible than pure enzymatic quorum quenching. This new process of biofouling control with CFBs could open new horizons in the field of wastewater treatment technology. However, this approach needs further investigation using consortium of quorum quenching bacteria, as real MBR contains diversity of microorganisms which may vary AHLs regulating biofouling phenotype.
5. Future Perspectives
The existence of AHL-mediated quorum sensing system in Gram-negative bacteria and its potential role in the formation of biofilms has suggested the application of quorum quenching as an alternative approach for combating membrane biofouling. Recently, some bacterial species having the ability to produce AHL-degrading or modifying enzymes have been identified and successfully attempted in MBRs to reduce biofouling. These evidences strongly indicate that quorum quenching bacteria could be used to develop a potent tool for the control of membrane biofouling. However, the direct application of quorum quenching bacteria has not yet been tried in real MBRs treating municipal or industrial wastewaters. Since wastewaters are composed of diverse groups of biofilm forming bacteria, there is need to design a consortium quorum quenching bacterial system which can destruct a wide range of AHLs and will help to prevent multispecies biofouling in MBR. Additionally, this economically feasible approach needs to be explored further in real MBRs under natural conditions.
6. Conclusions
As most of the wastewater bacteria responsible for biofilm formations employ AHL-mediated quorum sensing mechanism to regulate their behaviours, the application of quorum quenching strategy suggests an alternative nontoxic approach for control of biofouling in MBR. The AHLs-mediated quorum quenching mechanisms exist in several Proteobacteria and could be explored further as a new version of antagonism for combating biofilms. Recently, the use of microbial vessel and bead entrapped quorum quenching bacteria has been found as an effective tool in controlling AHL-mediated biofouling in MBRs. These observations will help researchers to design the futuristic AHL-mediated biofouling control strategies in real MBRs treating industrial and municipal wastewaters. Since quorum quenching bacteria showed direct involvement in interfering with quorum sensing behaviours, their further therapeutic and bioindustrial applications should be evaluated in the near future.
Abbreviations
- Ac.:
Acinetobacter
- A.:
Aeromonas
- Ag.:
Agrobacterium
- B.:
Bacillus
- Bur.:
Burkholderia
- C.:
Chromobacterium
- Ci.:
Citrobacter
- Ed.:
Edwardsiella
- E.:
Escherichia
- En.:
Enterobacter
- Er.:
Erwinia
- K.:
Klebsiella
- M.:
Microbacterium
- My.:
Mycobacterium
- Pec.:
Pectobacterium
- P.:
Pseudomonas
- R.:
Ralstonia
- Ra.:
Raoultella
- Rhi.:
Rhizobium
- Rh.:
Rhodobacter
- Rho.:
Rhodococcus
- S.:
Serratia
- Si.:
Sinorhizobium
- V.:
Vibrio
- Y.:
Yersinia
- AHL:
N-Acyl homoserine lactone(s)
- HSL:
Homoserine lactone.
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
References
- 1.Le-Clech P, Chen V, Fane TAG. Fouling in membrane bioreactors used in wastewater treatment. Journal of Membrane Science. 2006;284(1-2):17–53. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Jahangir D, Oh H, Kim S, Park P, Lee C, Lee J. Specific location of encapsulated quorum quenching bacteria for biofouling control in an external submerged membrane bioreactor. Journal of Membrane Science. 2012;411-412:130–136. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kang I, Yoon S, Lee C. Comparison of the filtration characteristics of organic and inorganic membranes in a membrane-coupled anaerobic bioreactor. Water Research. 2002;36(7):1803–1813. doi: 10.1016/s0043-1354(01)00388-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Characklis WG, Marshall KC. Biofilms: a basis for an interdisciplinary approach. In: Characklis WG, Marshall KC, editors. Biofilms. Toronto, Canada: John Wiley & Sons; 1990. pp. 3–15. (Wiley Series in Ecological and Applied Microbiology). [Google Scholar]
- 5.Valladares Linares R, Bucs SS, Li Z, AbuGhdeeb M, Amy G, Vrouwenvelder JS. Impact of spacer thickness on biofouling in forward osmosis. Water Research. 2014;57:223–233. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2014.03.046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ramesh A, Lee DJ, Wang ML, et al. Biofouling in membrane bioreactor. Separation Science and Technology. 2006;41(7):1345–1370. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Asad S, Opal SM. Bench-to-bedside review: quorum sensing and the role of cell-to-cell communication during invasive bacterial infection. Critical care. 2008;12, article 236(6) doi: 10.1186/cc7101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Bhardwaj AK, Mohanty P. Bacterial efflux pumps involved in multidrug resistance and their inhibitors: rejuvinating the antimicrobial chemotherapy. Recent Patents on Anti-Infective Drug Discovery. 2012;7(1):73–89. doi: 10.2174/157489112799829710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Davies DG, Parsek MR, Pearson JP, Iglewski BH, Costerton JW, Greenberg EP. The involvement of cell-to-cell signals in the development of a bacterial biofilm. Science. 1998;280(5361):295–298. doi: 10.1126/science.280.5361.295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Williams P. Quorum sensing, communication and cross-kingdom signalling in the bacterial world. Microbiology. 2007;153(12):3923–3938. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.2007/012856-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ryan RP, Dow JM. Diffusible signals and interspecies communication in bacteria. Microbiology. 2008;154(7):1845–1858. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.2008/017871-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Fuqua C, Winans SC, Greenberg EP. Census and consensus in bacterial ecosystems: the LuxR-LuxI family of quorum-sensing transcriptional regulators. Annual Review of Microbiology. 1996;50:727–751. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.50.1.727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Dobretsov S, Teplitski M, Paul V. Mini-review: quorum sensing in the marine environment and its relationship to biofouling. Biofouling. 2009;25(5):413–427. doi: 10.1080/08927010902853516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Von Bodman SB, Farrand SK. Capsular polysaccharide biosynthesis and pathogenicity in Erwinia stewartii require induction by an N-acylhomoserine lactone autoinducer. Journal of Bacteriology. 1995;177(17):5000–5008. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.17.5000-5008.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Parsek MR, Greenberg EP. Sociomicrobiology: the connections between quorum sensing and biofilms. Trends in Microbiology. 2005;13(1):27–33. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2004.11.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hall-Stoodley L, Costerton JW, Stoodley P. Bacterial biofilms: from the natural environment to infectious diseases. Nature Reviews Microbiology. 2004;2(2):95–108. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Yeon KM, Cheong WS, Oh HS, et al. Quorum sensing: a new biofouling control paradigm in a membrane bioreactor for advanced wastewater treatment. Environmental Science and Technology. 2009;43(2):380–385. doi: 10.1021/es8019275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Geske GD, O'Neill JC, Blackwell HE. Expanding dialogues: from natural autoinducers to non-natural analogues that modulate quorum sensing in Gram-negative bacteria. Chemical Society Reviews. 2008;37(7):1432–1447. doi: 10.1039/b703021p. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Koch B, Liljefors T, Persson T, Nielsen J, Kjelleberg S, Givskov M. The LuxR receptor: the sites of interaction with quorum-sensing signals and inhibitors. Microbiology. 2005;151(11):3589–3602. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.27954-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Lin YH, Xu JL, Hu J, et al. Acyl-homoserine lactone acylase from Ralstonia strain XJ12B represents a novel and potent class of quorum-quenching enzymes. Molecular Microbiology. 2003;47(3):849–860. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2003.03351.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Yates EA, Philipp B, Buckley C, et al. N-acylhomoserine lactones undergo lactonolysis in a pH-, temperature-, and acyl chain length-dependent manner during growth of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis and Pseudomonas aeruginosa . Infection and Immunity. 2002;70(10):5635–5646. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.10.5635-5646.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ponnusamy K, Paul D, Kweon JH. Inhibition of quorum sensing mechanism and Aeromonas hydrophila biofilm formation by Vanillin. Environmental Engineering Science. 2009;26(8):1359–1363. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Ponnusamy K, Paul D, Kim YS, Kweon JH. 2(5H)-Furanone: a prospective strategy for biofouling-control in membrane biofilm bacteria by quorum sensing inhibition. Brazilian Journal of Microbiology. 2010;41(1):227–234. doi: 10.1590/S1517-838220100001000032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Rudrappa T, Bais HP. Curcumin, a known phenolic from Curcuma longa, attenuates the virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 in whole plant and animal pathogenicity models. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 2008;56(6):1955–1962. doi: 10.1021/jf072591j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Jiang W, Xia S, Liang J, Zhang Z, Hermanowicz SW. Effect of quorum quenching on the reactor performance, biofouling and biomass characteristics in membrane bioreactors. Water Research. 2013;47(1):187–196. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2012.09.050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kim JH, Choi DC, Yeon KM, Kim SR, Lee C. Enzyme-immobilized nanofiltration membrane to mitigate biofouling based on quorum quenching. Environmental Science and Technology. 2011;45(4):1601–1607. doi: 10.1021/es103483j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Miller MB, Bassler BL. Quorum sensing in bacteria. Annual Review of Microbiology. 2001;55:165–199. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.55.1.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Federle MJ, Bassler BL. Interspecies communication in bacteria. Journal of Clinical Investigation. 2003;112(9):1291–1299. doi: 10.1172/JCI20195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Fuqua C, Parsek MR, Greenberg EP. Regulation of gene expression by cell-to-cell communication: acyl-homoserine lactone quorum sensing. Annual Review of Genetics. 2001;35:439–468. doi: 10.1146/annurev.genet.35.102401.090913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Swift S, Williams P, Stewart GAB. N-acylhomoserine lactones and quorum sensing are widespread in the proteobacteria. In: Winans S, Dunny G, editors. Cell—Cell Signalling in Bacteria. Washington, DC, USA: ASM press; 1998. pp. 291–313. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Biswa P, Doble M. Production of acylated homoserine lactone by Gram-positive bacteria isolated from marine water. FEMS Microbiology Letters. 2013;343(1):34–41. doi: 10.1111/1574-6968.12123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Pearson JP, van Delden C, Iglewski BH. Active efflux and diffusion are involved in transport of Pseudomonas aeruginosa cell-to-cell signals. Journal of Bacteriology. 1999;181(4):1203–1210. doi: 10.1128/jb.181.4.1203-1210.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Evans K, Passador L, Srikumar R, Tsang E, Nezezon J, Poole K. Influence of the MexAB-OprM multidrug efflux system on quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Journal of Bacteriology. 1998;180(20):5443–5447. doi: 10.1128/jb.180.20.5443-5447.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Shrout JD, Nerenberg R. Monitoring bacterial twitter: does quorum sensing determine the behavior of water and wastewater treatment biofilms? Environmental Science & Technology. 2012;46(4):1995–2005. doi: 10.1021/es203933h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Rasmussen TB, Givskov M. Quorum sensing inhibitors: a bargain of effects. Microbiology. 2006;152(4):895–904. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.28601-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Eberl L. N-acyl homoserinelactone-mediated gene regulation in Gram-negative bacteria. Systematic and Applied Microbiology. 1999;22(4):493–506. doi: 10.1016/S0723-2020(99)80001-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Fuqua WC, Winans SC, Greenberg EP. Quorum sensing in bacteria: the LuxR-LuxI family of cell density- responsive transcriptional regulators. Journal of Bacteriology. 1994;176(2):269–275. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.2.269-275.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Wagner VE, Bushnell D, Passador L, Brooks AI, Iglewski BH. Microarray analysis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum-sensing regulons: Effects of growth phase and environment. Journal of Bacteriology. 2003;185(7):2080–2095. doi: 10.1128/JB.185.7.2080-2095.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Schuster M, Lostroh CP, Ogi T, Greenberg EP. Identification, timing, and signal specificity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum-controlled genes: a transcriptome analysis. Journal of Bacteriology. 2003;185(7):2066–2079. doi: 10.1128/JB.185.7.2066-2079.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Whitehead NA, Barnard AML, Slater H, Simpson NJL, Salmond GPC. Quorum-sensing in Gram-negative bacteria. FEMS Microbiology Reviews. 2001;25(4):365–404. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2001.tb00583.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Labbate M, Queck SY, Koh KS, Rice SA, Givskov M, Kjelleberg S. Quorum sensing-controlled biofilm development in Serratia liquefaciens MG1. Journal of Bacteriology. 2004;186(3):692–698. doi: 10.1128/JB.186.3.692-698.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Huber B, Riedel K, Hentzer M, et al. The cep quorum-sensing system of Burkholderia cepacia H111 controls biofilm formation and swarming motility. Microbiology. 2001;147(9):2517–2528. doi: 10.1099/00221287-147-9-2517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Hammer BK, Bassler BL. Quorum sensing controls biofilm formation in Vibrio cholerae . Molecular Microbiology. 2003;50(1):101–114. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2003.03688.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Vanysacker L, Denis C, Declerck P, Piasecka A, Vankelecom IFJ. Microbial adhesion and biofilm formation on microfiltration membranes: a detailed characterization using model organisms with increasing complexity. BioMed Research International. 2013;2013:12 pages. doi: 10.1155/2013/470867.470867 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Swift S, Karlyshev AV, Fish L, et al. Quorum sensing in Aeromonas hydrophila and Aeromonas salmonicida: identification of the Luxri homologs AhyRi and AsaRi and their cognate N-acylhomoserine lactone signal molecules. Journal of Bacteriology. 1997;179(17):5271–5281. doi: 10.1128/jb.179.17.5271-5281.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Gould TA, Herman J, Krank J, Murphy RC, Churchill MEA. Specificity of acyl-homoserine lactone synthases examined by mass spectrometry. Journal of Bacteriology. 2006;188(2):773–783. doi: 10.1128/JB.188.2.773-783.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Hanzelka BL, Parsek MR, Val DL, Dunlap PV, Cronan JE, Jr., Greenberg EP. Acylhomoserine lactone synthase activity of the Vibrio fischeri AinS protein. Journal of Bacteriology. 1999;181(18):5766–5770. doi: 10.1128/jb.181.18.5766-5770.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Bassler BL, Wright M, Silverman MR. Multiple signalling systems controlling expression of luminescence in Vibrio harveyi: Sequence and function of genes encoding a second sensory pathway. Molecular Microbiology. 1994;13(2):273–286. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb00422.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Dunphy G, Miyamoto C, Meighen E. A homoserine lactone autoinducer regulates virulence of an insect- pathogenic bacterium, Xenorhabdus nematophilus (Enterobacteriaceae) Journal of Bacteriology. 1997;179(17):5288–5291. doi: 10.1128/jb.179.17.5288-5291.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Schripsema J, De Rudder KEE, Van Vliet TB, et al. Bacteriocin small of Rhizobium leguminosarum belongs to the class of N-acyl-L-homoserine lactone molecules, known as autoinducers and as quorum sensing co-transcription factors. Journal of Bacteriology. 1996;178(2):366–371. doi: 10.1128/jb.178.2.366-371.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Laue BE, Jiang Y, Chhabra SR, et al. The biocontrol strain Pseudomonas fluorescens F113 produces the Rhizobium small bacteriocin, N-(3-hydroxy-7-cis-tetradecenoyl) homoserine lactone, via HdtS, a putative novel N-acylhomoserine lactone synthase. Microbiology. 2000;146(10):2469–2480. doi: 10.1099/00221287-146-10-2469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Puskas A, Greenberg EP, Kaplan S, Schaefer AL. A quorum-sensing system in the free-living photosynthetic bacterium Rhodobacter sphaeroides . Journal of Bacteriology. 1997;179(23):7530–7537. doi: 10.1128/jb.179.23.7530-7537.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.McClean KH, Winson MK, Fish L, et al. Quorum sensing and Chromobacterium violaceum: exploitation of violacein production and inhibition for the detection of N-acylhomoserine lactones. Microbiology. 1997;143(12):3703–3711. doi: 10.1099/00221287-143-12-3703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Morohoshi T, Inaba T, Kato N, Kanai K, Ikeda T. Identification of quorum-sensing signal molecules and the LuxRI homologs in fish pathogen Edwardsiella tarda . Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering. 2004;98(4):274–281. doi: 10.1016/S1389-1723(04)00281-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Riedel K, Hentzer M, Geisenberger O, et al. N-acylhomoserine-lactone-mediated communication between Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Burkholderia cepacia in mixed biofilms. Microbiology. 2001;147(12):3249–3262. doi: 10.1099/00221287-147-12-3249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Lewenza S, Conway B, Greenberg EP, Sokol PA. Quorum sensing in Burkholderia cepacia: identification of the LuxrI homologs CepRI. Journal of Bacteriology. 1999;181(3):748–756. doi: 10.1128/jb.181.3.748-756.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Horng Y, Deng S, Daykin M, et al. The LuxR family protein SpnR functions as a negative regulator of N-acylhomoserine lactone-dependent quorum sensing in Serratia marcescens . Molecular Microbiology. 2002;45(6):1655–1671. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.03117.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Rice SA, Koh KS, Queck SY, Labbate M, Lam KW, Kjelleberg S. Biofilm formation and sloughing in Serratia marcescens are controlled by quorum sensing and nutrient cues. Journal of Bacteriology. 2005;187(10):3477–3485. doi: 10.1128/JB.187.10.3477-3485.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Pierson LS, III, Keppenne VD, Wood DW. Phenazine antibiotic biosynthesis in Pseudomonas aureofaciens 30–84 is regulated by PhzR in response to cell density. Journal of Bacteriology. 1994;176(13):3966–3974. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.13.3966-3974.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Geske GD, O’Neill JC, Blackwell HE. N-phenylacetanoyl-L-homoserine lactones can strongly antagonize or superagonize quorum sensing in Vibrio fischeri . ACS Chemical Biology. 2007;2(5):315–319. doi: 10.1021/cb700036x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Swift S, Winson MK, Chan PF, et al. A novel strategy for the isolation of luxl homologues: evidence for the widespread distribution of a LuxR:LuxI superfamily in enteric bacteria. Molecular Microbiology. 1993;10(3):511–520. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb00923.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Bainton NJ, Stead P, Chhabra SR, et al. N-(3-Oxohexanoyl)-L-homoserine lactone regulates carbapenem antibiotic production in Erwinia carotovora . Biochemical Journal. 1992;288(3):997–1004. doi: 10.1042/bj2880997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Nasser W, Bouillant ML, Salmond G, Reverchon S. Characterization of the Erwinia chrysanthemi expl-expR locus directing the synthesis of two N-acyl-homoserine lactone signal molecules. Molecular Microbiology. 1998;29(6):1391–1405. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1998.01022.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Milton DL, Chalker VJ, Kirke D, Hardman A, Cámara M, Williams P. The luxM homologue vanM from Vibrio anguillarum directs the synthesis of N-(3-hydroxyhexanoyl)homoserine lactone and N-hexanoylhomoserine lactone. Journal of Bacteriology. 2001;183(12):3537–3547. doi: 10.1128/JB.183.12.3537-3547.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Carius L, Carius AB, McIntosh M, Grammel H. Quorum sensing influences growth and photosynthetic membrane production in high-cell-density cultivations of Rhodospirillum rubrum . BMC Microbiology. 2013;13(1) article 189 doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-13-189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Fuqua WC, Winans SC. A LuxR-LuxI type regulatory system activates Agrobacterium Ti plasmid conjugal transfer in the presence of a plant tumor metabolite. Journal of Bacteriology. 1994;176(10):2796–2806. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.10.2796-2806.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Haudecoeur E, Tannieres M, Cirou A, Raffoux A, Dessaux Y, Faure D. Different regulation and roles of lactonases AiiB and AttM in agrobacterium tumefaciens C58. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions. 2009;22(5):529–537. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-22-5-0529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.He X, Chang W, Pierce DL, Seib LO, Wagner J, Fuqua C. Quorum sensing in Rhizobium sp. Strain NGR234 regulates conjugal transfer (tra) gene expression and influences growth rate. Journal of Bacteriology. 2003;185(3):809–822. doi: 10.1128/JB.185.3.809-822.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Danino VE, Wilkinson A, Edwards A, Downie JA. Recipient-induced transfer of the symbiotic plasmid pRL1JI in Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. viciae is regulated by a quorum-sensing relay. Molecular Microbiology. 2003;50(2):511–525. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2003.03699.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Brader G, Sjöblom S, Hyytiäinen H, Sims-Huopaniemi K, Palva ET. Altering substrate chain length specificity of an acylhomoserine lactone synthase in bacterial communication. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2005;280(11):10403–10409. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M408603200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Conway B, Greenberg EP. Quorum-sensing signals and quorum-sensing genes in Burkholderia vietnamiensis . Journal of Bacteriology. 2002;184(4):1187–1191. doi: 10.1128/jb.184.4.1187-1191.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Steidle A, Allesen-Holm M, Riedel K, et al. Identification and characterization of an N-acylhomoserine lactone-dependent quorum-sensing system in Pseudomonas putida strain IsoF. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 2002;68(12):6371–6382. doi: 10.1128/AEM.68.12.6371-6382.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Sio CF, Otten LG, Cool RH, et al. Quorum quenching by an N-acyl-homoserine lactone acylase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Infection and Immunity. 2006;74(3):1673–1682. doi: 10.1128/IAI.74.3.1673-1682.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Yin WF, Purmal K, Chin S, et al. N-Acyl homoserine lactone production by Klebsiella pneumonia isolated from human tongue surface. Sensors. 2012;12(3):3472–3483. doi: 10.3390/s120303472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Marketon M, Gronquist MR, Eberhard A, Gonzalez JE. Characterization of the Sinorhizobium meliloti sinR/sinI locus and the production of novel N-acyl homoserine lactones. Journal of Bacteriology. 2002;184(20):5686–5695. doi: 10.1128/JB.184.20.5686-5695.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Karlsson T, Turkina MV, Yakymenko O, Magnusson K, Vikström E. The Pseudomonas aeruginosaN-acylhomoserine lactone quorum sensing molecules target IQGAP1 and modulate epithelial cell migration. PLoS Pathogens. 2012;8(10) doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002953.e1002953 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Chapon-Hervé V, Akrim M, Latifi A, Williams P, Lazdunski A, Bally M. Regulation of the xcp secretion pathway by multiple quorum-sensing modulons in Pseudomonas aeruginosa . Molecular Microbiology. 1997;24(6):1169–1178. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1997.4271794.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Bertani I, Venturi V. Regulation of the N-acyl homoserine lactone-dependent quorum-sensing system in rhizosphere Pseudomonas putida WCS358 and cross-talk with the stationary-phase rpoS sigma factor and the global regulator GacA. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 2004;70(9):5493–5502. doi: 10.1128/AEM.70.9.5493-5502.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Ortori CA, Atkinson S, Chhabra SR, Cámara M, Williams P, Barrett DA. Comprehensive profiling of N-acylhomoserine lactones produced by Yersinia pseudotuberculosis using liquid chromatography coupled to hybrid quadrupole-linear ion trap mass spectrometry. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry. 2007;387(2):497–511. doi: 10.1007/s00216-006-0710-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Stankowska D, Kwinkowski M, Kaca W. Quantification of Proteus mirabilis virulence factors and modulation by acylated homoserine lactones. Journal of Microbiology, Immunology and Infection. 2008;41(3):243–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Lithgow JK, Wilkinson A, Hardman A, et al. The regulatory locus cinRI in Rhizobium leguminosarum controls a network of quorum-sensing loci. Molecular Microbiology. 2000;37(1):81–97. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2000.01960.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Rodelas B, Lithgow JK, Wisniewski-Dye F, et al. Analysis of quorum-sensing-dependent control of rhizosphere-expressed (rhi) genes in Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. viciae . Journal of Bacteriology. 1999;181(12):3816–3823. doi: 10.1128/jb.181.12.3816-3823.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Wilkinson A, Danino V, Wisniewski-Dyé F, Lithgow JK, Downie JA. N-acyl-homoserine lactone inhibition of rhizobial growth is mediated by two quorum-sensing genes that regulate plasmid transfer. Journal of Bacteriology. 2002;184(16):4510–4519. doi: 10.1128/JB.184.16.4510-4519.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Li Y, Gronquist MR, Hao G, et al. Chromosome and plasmid-encoded N-acyl homoserine lactones produced by Agrobacterium vitis wildtype and mutants that differ in their interactions with grape and tobacco. Physiological and Molecular Plant Pathology. 2006;67(6):284–290. [Google Scholar]
- 85.Schaefer AL, Taylor TA, Beatty JT, Greenberg EP. Long-chain acyl-homoserine lactone quorum-sensing regulation of Rhodobacter capsulatus gene transfer agent production. Journal of Bacteriology. 2002;184(23):6515–6521. doi: 10.1128/JB.184.23.6515-6521.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Hao G, Burr TJ. Regulation of long-chain N-acyl-homoserine lactones in Agrobacterium vitis . Journal of Bacteriology. 2006;188(6):2173–2183. doi: 10.1128/JB.188.6.2173-2183.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Wagner-Döbler I, Thiel V, Eberl L, et al. Discovery of complex mixtures of novel long-chain quorum sensing signals in free-living and host-associated marine alphaproteobacteria. ChemBioChem. 2005;6(12):2195–2206. doi: 10.1002/cbic.200500189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Lade H, Paul D, Kweon JH. Isolation and molecular characterization of biofouling bacteria and profiling of quorum sensing signal molecules from membrane bioreactor activated sludge. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2014;15(2):2255–2273. doi: 10.3390/ijms15022255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Ochiai S, Morohoshi T, Kurabeishi A, et al. Production and degradation of N-acylhomoserine lactone quorum sensing signal molecules in bacteria isolated from activated sludge. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry. 2013;77(12):2436–2440. doi: 10.1271/bbb.130553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Chong G, Kimyon O, Rice SA, Kjelleberg S, Manefield M. The presence and role of bacterial quorum sensing in activated sludge. Microbial Biotechnology. 2012;5(5):621–633. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-7915.2012.00348.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Bhadra B, Nanda AK, Chakraborty R. Inducible nickel resistance in a river isolate of India phylogenetically ascertained as a novel strain of Acinetobacter junii . World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology. 2006;22(3):225–232. [Google Scholar]
- 92.Sarkar S, Chakraborty R. Quorum sensing in metal tolerance of Acinetobacter junii BB1A is associated with biofilm production. FEMS Microbiology Letters. 2008;282(2):160–165. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2008.01080.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Morgan-Sagastume F, Boon N, Dobbelaere S, Defoirdt T, Verstraete W. Production of acylated homoserine lactones by Aeromonas and Pseudomonas strains isolated from municipal activated sludge. Canadian Journal of Microbiology. 2005;51(11):924–933. doi: 10.1139/w05-077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Shaw PD, Ping G, Daly SL, et al. Detecting and characterizing N-acyl-homoserine lactone signal molecules by thin-layer chromatography. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1997;94(12):6036–6041. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.12.6036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Farrand SK, Qin Y, Oger P. Quorum-sensing system of Agrobacterium plasmids: analysis and utility. Methods in Enzymology. 2002;358:452–484. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(02)58108-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Ravn L, Christensen AB, Molin S, Givskov M, Gram L. Methods for detecting acylated homoserine lactones produced by Gram-negative bacteria and their application in studies of AHL-production kinetics. Journal of Microbiological Methods. 2001;44(3):239–251. doi: 10.1016/s0167-7012(01)00217-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Someya N, Morohoshi T, Okano N, et al. Distribution of N-acylhomoserine lactone-producing fluorescent pseudomonads in the phyllosphere and rhizosphere of potato (Solanum tuberosum l.) Microbes and Environments. 2009;24(4):305–314. doi: 10.1264/jsme2.me09155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Winson MK, Swift S, Fish L, et al. Construction and analysis of lux CDABE-based plasmid sensors for investigating N-acyl homoserine lactone-mediated quorum sensing. FEMS Microbiology Letters. 1998;163(2):185–192. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1998.tb13044.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Ralling G, Bodrug S, Linn T. Growth rate-dependent regulation of RNA polymerase synthesis in Escherichia coli . Molecular and General Genetics. 1985;201(3):379–386. doi: 10.1007/BF00331327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Pearson JP, Gray KM, Passador L, et al. Structure of the autoinducer required for expression of Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence genes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1994;91(1):197–201. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.1.197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Steidle A, Sigl K, Schuhegger R, et al. Visualization of N-acylhomoserine lactone-mediated cell–cell communication between bacteria colonizing the tomato rhizosphere. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 2001;67(12):5761–5770. doi: 10.1128/AEM.67.12.5761-5770.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Dong Y-H, Zhang X-F, Soo H-M, Greenberg E-P, Zhang L-H. The two-component response regulator PprB modulates quorum-sensing signal production and global gene expression in Pseudomonas aeruginosa . Molecular Microbiology. 2008;69(3):p. 780. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06351.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Khan SR, Mavrodi DV, Jog GJ, Suga H, Thomashow LS, Farrand SK. Activation of the phz operon of Pseudomonas fluorescens 2-79 requires the LuxR homolog PhzR, N-(3-OH-Hexanoyl)-L- homoserine lactone produced by the LuxI homolog PhzI , and a cis-acting phz box. Journal of Bacteriology. 2005;187(18):6517–6527. doi: 10.1128/JB.187.18.6517-6527.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Llamas I, Keshavan N, González JE. Use of Sinorhizobium meliloti as an indicator for specific detection of long-chain N-Acyl homoserine lactones. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 2004;70(6):3715–3723. doi: 10.1128/AEM.70.6.3715-3723.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Andersen JB, Heydorn A, Hentzer M, et al. gfp-based N-acyl homoserine-lactone sensor systems for detection of bacterial communication. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 2001;67(2):575–585. doi: 10.1128/AEM.67.2.575-585.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Romero M, Diggle SP, Heeb S, Cámara M, Otero A. Quorum quenching activity in Anabaena sp. PCC 7120: identification of AiiC, a novel AHL-acylase. FEMS Microbiology Letters. 2008;280(1):73–80. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2007.01046.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Nithya C, Aravindraja C, Pandian SK. Bacillus pumilus of Palk Bay origin inhibits quorum-sensing-mediated virulence factors in Gram-negative bacteria. Research in Microbiology. 2010;161(4):293–304. doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2010.03.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Uroz S, Oger P, Chhabra SR, Cámara M, Williams P, Dessaux Y. N-acyl homoserine lactones are degraded via an amidolytic activity in Comamonas sp. strain D1. Archives of Microbiology. 2007;187(3):249–256. doi: 10.1007/s00203-006-0186-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Chan K, Atkinson S, Mathee K, et al. Characterization of N-acylhomoserine lactone-degrading bacteria associated with the Zingiber officinale (ginger) rhizosphere: co-existence of quorum quenching and quorum sensing in Acinetobacter and Burkholderia . BMC Microbiology. 2011;11, article 51 doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-11-51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Shepherd RW, Lindow SE. Two dissimilar N-aeyl-homoserine lactone acylases of Pseudomonas syringae influence colony and biofilm morphology. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 2009;75(1):45–53. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01723-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Huang JJ, Han J, Zhang L, Leadbetter JR. Utilization of Acyl-Homoserine Lactone Quorum Signals for Growth by a Soil Pseudomonad and Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 2003;69(10):5941–5949. doi: 10.1128/AEM.69.10.5941-5949.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Huang JJ, Petersen A, Whiteley M, Leadbetter JR. Identification of QuiP, the product of gene PA1032, as the second acyl-homoserine lactone acylase of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 2006;72(2):1190–1197. doi: 10.1128/AEM.72.2.1190-1197.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Lee C, Cheong W, Moon Y, et al. Isolation and identification of indigenous quorum quenching bacteria, Pseudomonas sp. 1A1, for biofouling control in MBR. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research. 2013;52(31):10554–10560. [Google Scholar]
- 114.Uroz S, D'Angelo-Picard C, Carlier A, et al. Novel bacteria degrading N-acylhomoserine lactones and their use as quenchers of quorum-sensing-regulated functions of plant-pathogenic bacteria. Microbiology. 2003;149(8):1981–1989. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.26375-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Uroz S, Chhabra SR, Cámara M, Williams P, Oger P, Dessaux Y. N-acylhomoserine lactone quorum-sensing molecules are modified and degraded by Rhodococcus erythropolis W2 by both amidolytic and novel oxidoreductase activities. Microbiology. 2005;151(10):3313–3322. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.27961-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Chen C-N, Chen C-J, Liao C-T, Lee C-Y. A probable aculeacin A acylase from the Ralstonia solanacearum GMI1000 is N-acyl-homoserine lactone acylase with quorum-quenching activity. BMC Microbiology. 2009;9, article 89 doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-9-89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Park S, Kang H, Jang H, Lee J, Koo B, Yum D. Identification of extracellular N-acylhomoserine lactone acylase from a Streptomyces sp. and its application to quorum quenching. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 2005;71(5):2632–2641. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.5.2632-2641.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Morohoshi T, Nakazawa S, Ebata A, Kato N, Ikeda T. Identification and characterization of N-acylhomoserine lactone-acylase from the fish intestinal Shewanella sp. strain MIB015. Bioscience, Biotechnology and Biochemistry. 2008;72(7):1887–1893. doi: 10.1271/bbb.80139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Leadbetter JR, Greenberg EP. Metabolism of acyl-homoserine lactone quorum-sensing signals by Variovorax paradoxus . Journal of Bacteriology. 2000;182(24):6921–6926. doi: 10.1128/jb.182.24.6921-6926.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Zhang HB, Wang LH, Zhang LH. Genetic control of quorum-sensing signal turnover in Agrobacterium tumefaciens . Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2002;99(7):4638–4643. doi: 10.1073/pnas.022056699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Liu D, Thomas PW, Momb J, et al. Structure and specificity of a quorum-quenching lactonase (AiiB) from Agrobacterium tumefaciens . Biochemistry. 2007;46(42):11789–11799. doi: 10.1021/bi7012849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Carlier A, Uroz S, Smadja B, et al. The Ti plasmid of Agrobactetium tumefaciens harbors an attM-paralogous gene, aiiB, also encoding N-acyl homoserine lactonase activity. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 2003;69(8):4989–4993. doi: 10.1128/AEM.69.8.4989-4993.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Uroz S, Dessaux Y, Oger P. Quorum sensing and quorum quenching: the Yin and Yang of bacterial communication. ChemBioChem. 2009;10(2):205–216. doi: 10.1002/cbic.200800521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Chen F, Gao Y, Chen X, Yu Z, Li X. Quorum quenching enzymes and their application in degrading signal molecules to block quorum sensing-dependent infection. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2013;14(9):17477–17500. doi: 10.3390/ijms140917477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Kang BR, Lee JH, Ko SJ, et al. Degradation of acyl-homoserine lactone molecules by Acinetobacter sp. strain C1010. Canadian Journal of Microbiology. 2004;50(11):935–941. doi: 10.1139/w04-083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Riaz K, Elmerich C, Moreira D, Raffoux A, Dessaux Y, Faure D. A metagenomic analysis of soil bacteria extends the diversity of quorum-quenching lactonases. Environmental Microbiology. 2008;10(3):560–570. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2007.01475.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Park SY, Lee SJ, Oh TK, et al. AhlD, an N-acylhomoserine lactonase in Arthrobacter sp., and predicted homologues in other bacteria. Microbiology. 2003;149(6):1541–1550. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.26269-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Dong Y-H, Xu J-L, Li X-Z, Zhang L-H. AiiA, an enzyme that inactivates the acylhomoserine lactone quorum- sensing signal and attenuates the virulence of Erwinia carotovora . Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2000;97(7):3526–3531. doi: 10.1073/pnas.060023897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Wopperer J, Cardona ST, Huber B, Jacobi CA, Valvano MA, Eberl L. A quorum-quenching approach to investigate the conservation of quorum-sensing-regulated functions within the Burkholderia cepacia complex. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 2006;72(2):1579–1587. doi: 10.1128/AEM.72.2.1579-1587.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Dong Y, Gusti AR, Zhang Q, Xu J, Zhang L. Identification of quorum-quenching N-acyl homoserine lactonases from Bacillus species. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 2002;68(4):1754–1759. doi: 10.1128/AEM.68.4.1754-1759.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Ulrich RL. Quorum quenching: enzymatic disruption of N-acylhomoserine lactone-mediated bacterial communication in Burkholderia thailandensis. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 2004;70(10):6173–6180. doi: 10.1128/AEM.70.10.6173-6180.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Wu Z, Ye C, Guo F, Zhang S, Yu X. Evidence for broad-spectrum biofilm inhibition by the bacterium Bacillus sp. strain SW9. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 2013;79(5):1735–1738. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02796-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Zhang Y, Yu X, Gong S, Ye C, Fan Z, Lin H. Antibiofilm activity of Bacillus pumilus SW9 against initial biofouling on microfiltration membranes. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology. 2014;98(3):1309–1320. doi: 10.1007/s00253-013-4991-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Lee SJ, Park S, Lee J, Yum D, Koo B. Genes encoding the N-acyl homoserine lactone-degrading enzyme are widespread in many subspecies of Bacillus thuringiensis . Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 2002;68(8):3919–3924. doi: 10.1128/AEM.68.8.3919-3924.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Dong Y, Zhang X, Xu J, Zhang L. Insecticidal Bacillus thuringiensis silences Erwinia carotovora virulence by a new form of microbial antagonism, signal interference. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 2004;70(2):954–960. doi: 10.1128/AEM.70.2.954-960.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Reimmann C, Ginet N, Michel L, et al. Genetically programmed autoinducer destruction reduces virulence gene expression and swarming motility in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Microbiology. 2002;148(4):923–932. doi: 10.1099/00221287-148-4-923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Rajesh S, Rai VR. Molecular identification of aiiA homologous gene from endophytic Enterobacter species and in silico analysis of putative tertiary structure of AHL-lactonase. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 2014;443(1):290–295. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.11.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Chow JY, Xue B, Lee KH, et al. Directed evolution of a thermostable quorum-quenching lactonase from the amidohydrolase superfamily. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2010;285(52):40911–40920. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.177139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Morohoshi T, Someya N, Ikeda T. Novel N-acylhomoserine lactone-degrading bacteria isolated from the leaf surface of solarium tuberosum and their quorum-quenching properties. Bioscience, Biotechnology and Biochemistry. 2009;73(9):2124–2127. doi: 10.1271/bbb.90283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Jeng YC, Wu L, Wen SY. Directed evolution of a quorum-quenching lactonase from Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis K-10 in the amidohydrolase superfamily. Biochemistry. 2009;48(20):4344–4353. doi: 10.1021/bi9004045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Afriat L, Roodveldt C, Manco G, Tawfik DS. The latent promiscuity of newly identified microbial lactonases is linked to a recently diverged phosphotriesterase. Biochemistry. 2006;45(46):13677–13686. doi: 10.1021/bi061268r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Wang WZ, Morohoshi T, Ikenoya M, Someya N, Ikeda T. AiiM, a novel class ot N-acylhomosenne lactonase from the leaf-associated bacterium Microbacterium testaceum . Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 2010;76(8):2524–2530. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02738-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Mei G, Yan X, Turak A, Luo Z, Zhang L. AidH, an alpha/beta-hydrolase fold family member from an Ochrobactrum sp. strain,is a novel N-acylhomoserine lactonase. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 2010;76(15):4933–4942. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00477-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Chen R, Zhou Z, Cao Y, Bai Y, Yao B. High yield expression of an AHL-lactonase from Bacillus sp. B546 in Pichia pastoris and its application to reduce Aeromonas hydrophila mortality in aquaculture. Microbial Cell Factories. 2010;9(article 39) doi: 10.1186/1475-2859-9-39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Huang W, Lin Y, Yi S, et al. QsdH, a novel AHL lactonase in the RND-type inner membrane of marine Pseudoalteromonas byunsanensis strain 1A01261. PLoS ONE. 2012;7(10) doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046587.e46587 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Uroz S, Oger PM, Chapelle E, Adeline MT, Faure D, Dessaux Y. A Rhodococcus qsdA-encoded enzyme defines a novel class of large-spectrum quorum-quenching lactonases. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 2008;74(5):1357–1366. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02014-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Park SY, Hwang BJ, Shin M, Kim J, Kim H, Lee J. N-acylhomoserine lactonase-producing Rhodococcus spp. with different AHL-degrading activities. FEMS Microbiology Letters. 2006;261(1):102–108. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2006.00336.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Kim S, Oh H, Jo S, et al. Biofouling control with bead-entrapped quorum quenching bacteria in membrane bioreactors: physical and biological effects. Environmental Science and Technology. 2013;47(2):836–842. doi: 10.1021/es303995s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Oh HS, Kim SR, Cheong WS, Lee CH, Lee JK. Biofouling inhibition in MBR by Rhodococcus sp. BH4 isolated from real MBR plant. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology. 2013;97(23):10223–10231. doi: 10.1007/s00253-013-4933-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Jafra S, Przysowa J, Czajkowski R, Michta A, Garbeva P, Van Der Wolf JM. Detection and characterization of bacteria from the potato rhizosphere degrading N-acyl-homoserine lactone. Canadian Journal of Microbiology. 2006;52(10):1006–1015. doi: 10.1139/w06-062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Morohoshi T, Tominaga Y, Someya N, Ikeda T. Complete genome sequence and characterization of the N-acylhomoserine lactone-degrading gene of the potato leaf-associated Solibacillus silvestris. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering. 2012;113(1):20–25. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiosc.2011.09.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Torres M, Romero M, Prado S, et al. N-acylhomoserine lactone-degrading bacteria isolated from hatchery bivalve larval cultures. Microbiological Research. 2013;168(9):547–554. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2013.04.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Chowdhary PK, Keshavan N, Nguyen HQ, Peterson JA, González JE, Haines DC. Bacillus megaterium CYP102A1 oxidation of acyl homoserine lactones and acyl homoserines. Biochemistry. 2007;46(50):14429–14437. doi: 10.1021/bi701945j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Chhabra SR, Philipp B, Eberl L, Givskov M, Williams P, Cámara M. Extracellular communication in bacteria. In: Schulz S, editor. Chemistry of Pheromones and Other Semiochemicals 2. Berlin, Germany: Springer; 2005. pp. 279–315. [Google Scholar]
- 155.Williams P, Winzer K, Chan WC, Cámara M. Look who's talking: communication and quorum sensing in the bacterial world. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 2007;362(1483):1119–1134. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2007.2039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Koskinen R, Kämpfer P, Laurikkala M, et al. Characterization of Sphingomonas isolates from Finnish and Swedish drinking water distribution systems. Journal of Applied Microbiology. 2000;89(4):687–696. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2672.2000.01167.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Pang CM, Hong P, Guo H, Liu W. Biofilm formation characteristics of bacterial isolates retrieved from a reverse osmosis membrane. Environmental Science and Technology. 2005;39(19):7541–7550. doi: 10.1021/es050170h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Atkinson S, Camara M, Williams P. N-Acylhomoserine lactones, quorum sensing and biofilm development in Gram-negative bacteria. In: Kjellberg S, Givskov M, editors. The Biofilm Mode of Life. Mechanisms and Adaptations. Wymondham, UK: Horizon Bioscience; 2007. pp. 95–122. [Google Scholar]
- 159.Kjelleberg S, Molin S. Is there a role for quorum sensing signals in bacterial biofilms? Current Opinion in Microbiology. 2002;5(3):254–258. doi: 10.1016/s1369-5274(02)00325-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Irie Y, Parsek MR. Bacterial Biofilms. Vol. 322. Berlin, Germany: Springer; 2008. Quorum sensing and microbial biofilms; pp. 67–84. (Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Lynch MJ, Swift S, Kirke DF, Keevil CW, Dodd CER, Williams P. The regulation of biofilm development by quorum sensing in Aeromonas hydrophila . Environmental Microbiology. 2002;4(1):18–28. doi: 10.1046/j.1462-2920.2002.00264.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Feng L, Wu Z, Yu X. Quorum sensing in water and wastewater treatment biofilms. Journal of Environmental Biology. 2013;34(2):437–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Lim S, Kim S, Yeon K-M, Sang B-I, Chun J, Lee C-H. Correlation between microbial community structure and biofouling in a laboratory scale membrane bioreactor with synthetic wastewater. Desalination. 2012;287:209–215. [Google Scholar]
- 164.Xia S, Zhou L, Zhang Z, Li J. Influence and mechanism of N-(3-oxooxtanoyl)-L-homoserine lactone (C8-oxo-HSL) on biofilm behaviors at early stage. Journal of Environmental Sciences. 2012;24(12):2035–2040. doi: 10.1016/s1001-0742(11)61060-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Kim M, Lee S, Park H, Choi S, Hong S. Biofouling control by quorum sensing inhibition and its dependence on membrane surface. Water Science and Technology. 2012;66(7):1424–1430. doi: 10.2166/wst.2012.307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Dong Y, Wang L, Zhang L. Quorum-quenching microbial infections: Mechanisms and implications. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 2007;362(1483):1201–1211. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2007.2045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Rasmussen TB, Givskov M. Quorum-sensing inhibitors as anti-pathogenic drugs. International Journal of Medical Microbiology. 2006;296(2-3):149–161. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2006.02.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Galloway WRJD, Hodgkinson JT, Bowden SD, Welch M, Spring DR. Quorum sensing in Gram-negative bacteria: Small-molecule modulation of AHL and AI-2 quorum sensing pathways. Chemical Reviews. 2011;111(1):28–67. doi: 10.1021/cr100109t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169.Kalia VC, Purohit HJ. Quenching the quorum sensing system: potential antibacterial drug targets. Critical Reviews in Microbiology. 2011;37(2):121–140. doi: 10.3109/1040841X.2010.532479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170.Steindler L, Venturi V. Detection of quorum-sensing N-acyl homoserine lactone signal molecules by bacterial biosensors. FEMS Microbiology Letters. 2007;266(1):1–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2006.00501.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171.Kalia VC. Quorum sensing inhibitors: an overview. Biotechnology Advances. 2013;31(2):224–245. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2012.10.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172.Zhu J, Beaber JW, Moré MI, Fuqua C, Eberhard A, Winans SC. Analogs of the autoinducer 3-oxooctanoyl-homoserine lactone strongly inhibit activity of the TraR protein of Agrobacterium tumefaciens . Journal of Bacteriology. 1998;180(20):5398–5405. doi: 10.1128/jb.180.20.5398-5405.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 173.Givskov M, de Nys R, Manefield M, et al. Eukaryotic interference with homoserine lactone-mediated prokaryotic signalling. Journal of Bacteriology. 1996;178(22):6618–6622. doi: 10.1128/jb.178.22.6618-6622.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174.Lyon GJ, Mayville P, Muir TW, Novick RP. Rational design of a global inhibitor of the virulence response in Staphylococcus aureus, based in part on localization of the site of inhibition to the receptor-histidine kinase, AgrC. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2000;97(24):13330–13335. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.24.13330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175.Lade H, Paul D, Kweon JH. Quorum quenching mediated approaches for control of membrane biofouling. International Journal of Biological Sciences. 2014;10(5):547–562. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.9028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 176.Siddiqui MF, Singh L, Zularisam AW, Sakinah M. Biofouling mitigation using Piper betle extract in ultrafiltration MBR. Desalination and Water Treatment. 2013;51(37–39):6940–6951. [Google Scholar]
- 177.Paul D, Kim YS, Ponnusamy K, Kweon JH. Application of quorum quenching to inhibit biofilm formation. Environmental Engineering Science. 2009;26(8):1319–1324. [Google Scholar]
- 178.Oh H, Yeon K, Yang C, et al. Control of membrane biofouling in MBR for wastewater treatment by quorum quenching bacteria encapsulated in microporous membrane. Environmental Science and Technology. 2012;46(9):4877–4884. doi: 10.1021/es204312u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 179.Xiong Y, Liu Y. Biological control of microbial attachment: a promising alternative for mitigating membrane biofouling. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology. 2010;86(3):825–837. doi: 10.1007/s00253-010-2463-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 180.Dong YH, Zhang LH. Quorum sensing and quorum-quenching enzymes. Journal of Microbiology. 2005;43:101–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 181.Kim MH, Choi W, Kang HO, et al. The molecular structure and catalytic mechanism of a quorum-quenching N-acyl-L-homoserine lactone hydrolase. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2005;102(49):17606–17611. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0504996102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 182.Chan K, Atkinson S, Mathee K, et al. Characterization of N-acylhomoserine lactone-degrading bacteria associated with the Zingiber officinale (ginger) rhizosphere: co-existence of quorum quenching and quorum sensing in Acinetobacter and Burkholderia . BMC Microbiology. 2011;11(article 51) doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-11-51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


