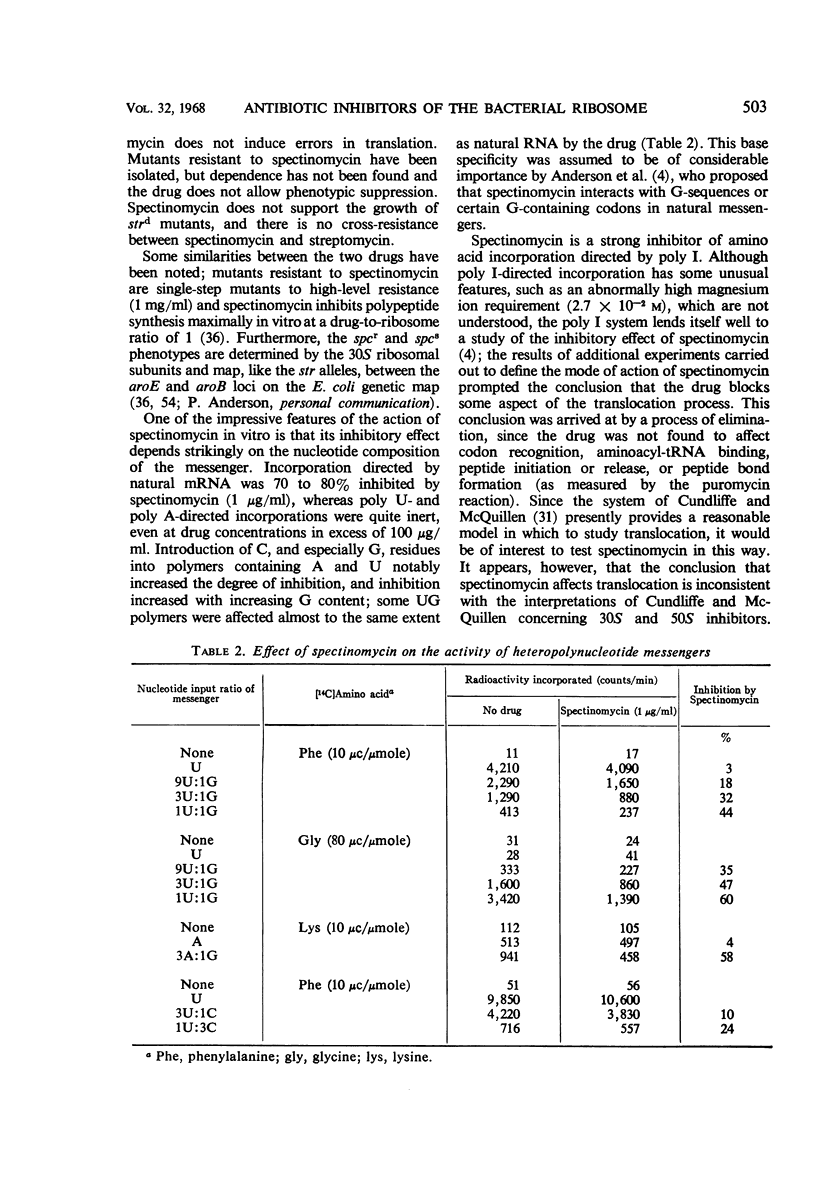
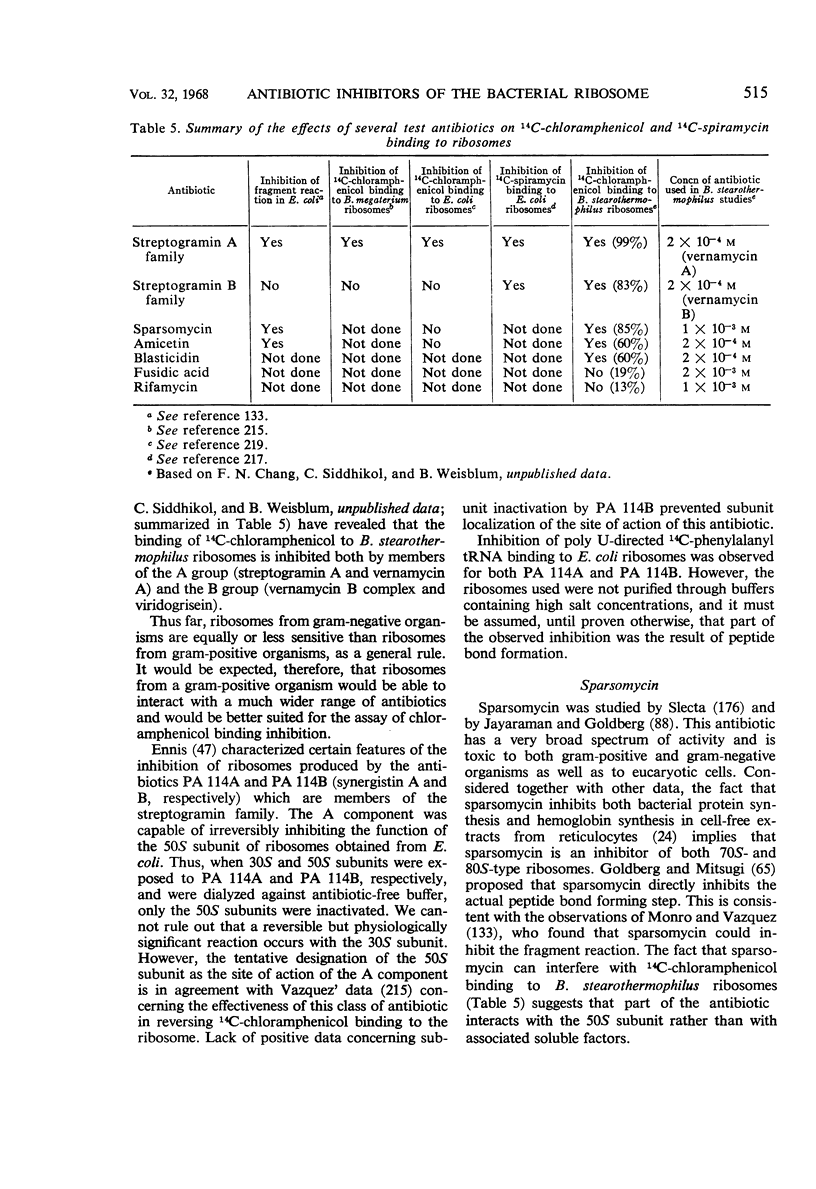
Full text
PDF

































Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMBROSE C. T., COONS A. H. Studies on antibody production. VIII. The inhibitory effect of chloramphenicol on the synthesis of antibody in tissue culture. J Exp Med. 1963 Jun 1;117:1075–1088. doi: 10.1084/jem.117.6.1075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANAND N., DAVIS B. D. Damage by streptomycin to the cell membrane of Escherichia coli. Nature. 1960 Jan 2;185:22–23. doi: 10.1038/185022a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANGEVINE D. M., HARTMANN H. A. Pseudomembranous colitis complicating prolonged antibiotic therapy. Am J Med Sci. 1956 Dec;232(6):667–673. doi: 10.1097/00000441-195612000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams J. M., Capecchi M. R. N-formylmethionyl-sRNA as the initiator of protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jan;55(1):147–155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.1.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson P., Davies J., Davis B. D. Effect of spectinomycin on polypeptide synthesis in extracts of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1967 Oct 14;29(1):203–215. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90191-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson W. F., Gorini L., Breckenridge L. Role of ribosomes in streptomycin-activated suppression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Oct;54(4):1076–1083. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.4.1076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apirion D., Schlessinger D. Coresistance to neomycin and kanamycin by mutations in an Escherichia coli locus that affects ribosomes. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):768–776. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.768-776.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apirion D., Schlessinger D. Mapping and complementation of three genes specifying 30S ribosomal components in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):1431–1432. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.1431-1432.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apirion D., Schlessinger D. Reversion from streptomycin dependence in Escherichia coli by a further change in the ribosome. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):1275–1276. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.1275-1276.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apirion D., Schlessinger D. The loss of phenotypic suppression in streptomycin-resistant mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jul;58(1):206–212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.1.206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apirion D. Three genes that affect Escherichia coli ribosomes. J Mol Biol. 1967 Dec 14;30(2):255–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARBER M., WATERWORTH P. M. ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY OF LINCOMYCIN AND PRISTINAMYCIN: A COMPARISON WITH ERYTHROMYCIN. Br Med J. 1964 Sep 5;2(5409):603–606. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5409.603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUSSARD A., NAONO S., GROS F., MONOD J. [Effects of an analog of uracil on the properties of an enzymatic protein synthesized in its presence]. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1960 Jun 13;250:4049–4051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloch A., Coutsogeorgopoulos C. Inhibition of protein synthesis by amicetin, a nucleoside antibiotic. Biochemistry. 1966 Oct;5(10):3345–3351. doi: 10.1021/bi00874a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boardman N. K., Francki R. I., Wildman S. G. Protein synthesis by cell-free extracts of tobacco leaves. 3. Comparison of the physical properties and protein synthesizing activities of 70 s chloroplast and 80 s cytoplasmic ribosomes. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jun;17(2):470–487. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80157-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher M. S. Translocation in protein synthesis: a hybrid structure model. Nature. 1968 May 18;218(5142):675–677. doi: 10.1038/218675a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. C., Doty P. Protein factor requirement for binding of messenger RNA to ribosomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Feb 15;30(3):284–291. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90448-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownstein B. L., Lewandowski L. J. A mutation suppressing streptomycin dependence. I. An effect on ribosome function. J Mol Biol. 1967 Apr 14;25(1):99–109. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90281-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHABBERT Y. Antagonisme in vitro entre l'érythromycine et la spiramycine. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1956 Jun;90(6):787–790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHABBERT Y. Etudes in vitro sur la spiramycine; activité, résistance, antibiogramme, concentrations humorales. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1955 Oct;89(4):434–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONNAMACHER R. H., MANDEL H. G. BINDING OF TETRACYCLINE TO THE 30S RIBOSOMES AND TO POLYURIDYLIC ACID. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Jun 18;20:98–103. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90954-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONWAY T. W., LIPMANN F. CHARACTERIZATION OF A RIBOSOME-LINKED GUANOSINE TRIPHOSPHATASE IN ESCHERICHIA COLI EXTRACTS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Dec;52:1462–1469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.6.1462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COX E. C., WHITE J. R., FLAKS J. G. STREPTOMYCIN ACTION AND THE RIBOSOME. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Apr;51:703–709. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.4.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cammarata A. An apparent correlation between the in vitro activity of chloramphenicol analogs and electronic polarizability. J Med Chem. 1967 Jul;10(4):525–527. doi: 10.1021/jm00316a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang F. N., Sih C. J., Weisblum B. Lincomycin, an inhibitor of aminoacyl sRNA binding to ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Feb;55(2):431–438. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.2.431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark-Walker G. D., Linnane A. W. In vivo differentiation of yeast cytoplasmic and mitochondrial protein synthesis with antibiotics. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Oct 5;25(1):8–13. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90631-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. S., Hoffner N., Jansen M., Moore M., Raina A. POLYAMINES, RNA SYNTHESIS, AND STREPTOMYCIN LETHALITY IN A RELAXED MUTANT OF E. coli STRAIN 15 TAU. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Mar;57(3):721–728. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.3.721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colombo B., Felicetti L., Baglioni C. Inhibition of protein synthesis in reticulocytes by antibiotics. I. Effects on polysomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Apr 18;119(1):109–119. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90043-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connamacher R. H., Mandel H. G. Studies on the intracellular localization of tetracycline in bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Sep 24;166(2):475–486. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90235-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coutsogeorgopoulos C. Amino acylaminonucleoside inhibitors of protein synthesis. The effect of amino acyl ribonucleic acid on the inhibition. Biochemistry. 1967 Jun;6(6):1704–1711. doi: 10.1021/bi00858a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couturier M., Desmet L., Thomas R. High pleiotropy of streptomycin mutations in Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1964 Jun 15;16(3):244–248. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(64)90333-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cundliffe E., McQuillen K. Bacterial protein synthesis: the effects of antibiotics. J Mol Biol. 1967 Nov 28;30(1):137–146. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90249-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutler R. G., Evans J. E. Relative transcription activity of different segments of the genome throughout the cell division cycle of Escherichia coli. The mapping of ribosomal and transfer RNA and the determination of the direction of replication. J Mol Biol. 1967 May 28;26(1):91–105. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90263-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIES J. E. STUDIES ON THE RIBOSOMES OF STREPTOMYCIN-SENSITIVE AND RESISTANT STRAINS OF ESCHERICHIA COLI. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Apr;51:659–664. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.4.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIES J., GILBERT W., GORINI L. STREPTOMYCIN, SUPPRESSION, AND THE CODE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 May;51:883–890. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.5.883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DJORDJEVIC B., SZYBALSKI W. Genetics of human cell lines. III. Incorporation of 5-bromo- and 5-iododeoxyuridine into the deoxyribonucleic acid of human cells and its effect on radiation sensitivity. J Exp Med. 1960 Sep 1;112:509–531. doi: 10.1084/jem.112.3.509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das H. K., Goldstein A., Kanner L. C. Inhibition by chlorampenicol of the growth of nascent protein chains in Escherichia coli. Mol Pharmacol. 1966 Mar;2(2):158–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J., Anderson P., Davis B. D. Inhibition of protein synthesis by spectinomycin. Science. 1965 Sep 3;149(3688):1096–1098. doi: 10.1126/science.149.3688.1096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J., Davis B. D. Misreading of ribonucleic acid code words induced by aminoglycoside antibiotics. The effect of drug concentration. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jun 25;243(12):3312–3316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J., Gorini L., Davis B. D. Misreading of RNA codewords induced by aminoglycoside antibiotics. Mol Pharmacol. 1965 Jul;1(1):93–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J., Jones D. S., Khorana H. G. A further study of misreading of codons induced by streptomycin and neomycin using ribopolynucleotides containing two nucleotides in alternating sequence as templates. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jun;18(1):48–57. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80075-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. Streptomycin and the genetic code. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1966;31:665–670. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1966.031.01.085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day L. E. Tetracycline inhibition of cell-free protein synthesis. I. Binding of tetracycline to components of the system. J Bacteriol. 1966 May;91(5):1917–1923. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.5.1917-1923.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day L. E. Tetracycline inhibition of cell-free protein synthesis. II. Effect of the binding of tetracycline to the components of the system. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jul;92(1):197–203. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.1.197-203.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle R. J., Woodside E. E., Fishel C. W. Protein-polyelectrolyte interactions. The concanavalin A precipitin reaction with polyelectrolytes and polysaccharide derivatives. Biochem J. 1968 Jan;106(1):35–40. doi: 10.1042/bj1060035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubnau D., Goldthwaite C., Smith I., Marmur J. Genetic mapping in Bacillus subtilis. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jul 14;27(1):163–185. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90358-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERDOS T., ULLMANN A. Effect of streptomycin on the incorporation of amino-acids labelled with carbon-14 into ribonucleic acid and protein in a cell-free system of a Mycobacterium. Nature. 1959 Feb 28;183(4661):618–619. doi: 10.1038/183618a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebringer L. Macrolide antibiotics as bleaching factors for Euglena gracillis. Naturwissenschaften. 1965 Dec;52(24):666–666. doi: 10.1007/BF00589640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ennis H. L. Inhibition of protein synthesis by polypeptide antibiotics. 3. Ribosomal site of inhibition. Mol Pharmacol. 1966 Sep;2(5):444–453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erbe R. W., Leder P. Initiation and protein synthesis: translation of di- and tri-codon messengers. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Jun 10;31(5):798–803. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90633-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ertel R., Brot N., Redfield B., Allende J. E., Weissbach H. Binding of guanosine 5'-triphosphate by soluble factors required for polypeptide synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Mar;59(3):861–868. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.3.861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezekiel D. H., Elkins B. N. The stimulation of ribonucleic acid synthesis by ribosome inhibitors in amino acid-starved Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Sep 24;166(2):466–474. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90234-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLAKS J. G., COX E. C., WHITE J. R. Inhibition of polypeptide synthesis by streptomycin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 May 11;7:385–389. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90320-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLAKS J. G., COX E. C., WITTING M. L., WHITE J. R. Polypeptide synthesis with ribosomes from streptomycin-resistant and dependent E. coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 May 11;7:390–393. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90321-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKLIN T. J. The inhibition of incorporation of leucine into protein of cell-free systems from rat liver and Escherichia coli by chlortetracycline. Biochem J. 1963 Jun;87:449–453. doi: 10.1042/bj0870449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felicetti L., Colombo B., Baglioni C. Inhibition of protein synthesis in reticulocytes by antibiotics. II. The site of action of cycloheximide, streptovitacin A and pactamycin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Apr 18;119(1):120–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flaks J. G., Leboy P. S., Birge E. A., Kurland C. G. Mutations and genetics concerned with the ribosome. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1966;31:623–631. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1966.031.01.081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser S. J., McDonald W. C. Analysis of mutations from streptomycin dependence to nondependence in Bacillus subtilis by transformation. J Bacteriol. 1966 Nov;92(5):1582–1583. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.5.1582-1583.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freda C. E., Cohen S. S. Nature of ribonucleic acid stimulated by streptomycin in the absence of protein synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1966 Dec;92(6):1680–1688. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.6.1680-1688.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GADO I., HORVATH I. THE EFFECT OF METHANOL ON THE GROWTH OF A STREPTOMYCIN-DEPENDENT STRAIN OF ESCHERICHIA COLI IN STREPTOMYCIN-FREE MEDIA. Life Sci. 1963 Oct;10:741–744. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(63)90080-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GALE E. F., FOLKES J. P. The assimilation of amino-acids by bacteria. XV. Actions of antibiotics on nucleic acid and protein synthesis in Staphylococcus aureus. Biochem J. 1953 Feb;53(3):493–498. doi: 10.1042/bj0530493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARROD L. P. The erythromycin group of antibiotics. Br Med J. 1957 Jul 13;2(5036):57–63. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5036.57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILBERT W. Polypeptide synthesis in Escherichia coli. II. The polypeptide chain and S-RNA. J Mol Biol. 1963 May;6:389–403. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80051-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDSCHMIDT E. P., MATNEY T. S., BAUSUM H. T. Genetic analyses of mutations from streptomycin dependence to independence in Salmonella typhimurium. Genetics. 1962 Nov;47:1475–1487. doi: 10.1093/genetics/47.11.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDSTEIN A. The origin of streptomycin-dependent variants of Escherichia coli. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1954 Nov;112(3):326–340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORINI L., KATAJA E. PHENOTYPIC REPAIR BY STREPTOMYCIN OF DEFECTIVE GENOTYPES IN E. COLI. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Mar;51:487–493. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.3.487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORINI L., KATAJA E. STREPTOMYCIN-INDUCED OVERSUPPRESSION IN E. COLI. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Jun;51:995–1001. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.6.995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRIFFITH L. J., OSTRANDER W. E., MULLINS C. G., BESWICK D. E. DRUG ANTAGONISM BETWEEN LINCOMYCIN AND ERYTHROMYCIN. Science. 1965 Feb 12;147(3659):746–747. doi: 10.1126/science.147.3659.746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartner T. K., Orias E. Effects of mutations to streptomycin resistance on the rate of translation of mutant genetic information. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):1021–1028. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.1021-1028.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg I. H., Mitsugi K. Inhibition by sparsomycin and other antibiotics of the puromycin-induced release of polypeptide from ribosomes. Biochemistry. 1967 Feb;6(2):383–391. doi: 10.1021/bi00854a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman R. E., Spotts C. R. Effects of streptomycin deprivation on enzyme synthesis in streptomycin-dependent Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):1154–1161. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.1154-1161.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. A stepwise reaction yielding a complex between a supernatant fraction from E. coli, guanosine 5'-triphosphate, and aminoacyl-sRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jan;59(1):179–183. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.1.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. Interaction of guanosine 5'-triphosphate with a supernatant fraction from E. coli and aminoacyl-sRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Oct;58(4):1574–1578. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.4.1574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorini L., Davies J. The effect of streptomycin on ribosomal function. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1968;44:100–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorini L., Rosset R., Zimmermann R. A. Phenotype masking and streptomycin dependence. Science. 1967 Sep 15;157(3794):1314–1317. doi: 10.1126/science.157.3794.1314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman M. E. Reaction of ribosome-bound peptidyl transfer ribonucleic acid with aminoacyl transfer ribonucleic acid or puromycin. J Biol Chem. 1967 Dec 10;242(23):5564–5571. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIEROWSKI M. INHIBITION OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS BY CHLORTETRACYCLINE IN THE E. COLI IN VITRO SYSTEM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Mar;53:594–599. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.3.594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey C. L., Knight S. G., Sih C. J. On the mode of action of fusidic acid. Biochemistry. 1966 Oct;5(10):3320–3327. doi: 10.1021/bi00874a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto K. Streptomycin Resistance in Escherichia Coli Analyzed by Transduction. Genetics. 1960 Jan;45(1):49–62. doi: 10.1093/genetics/45.1.49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofemeister J., Böhme H. Streptomycin-abhängige Mutanten von Proteus mirabilis: Ihre Genetik, Suppression und Modifikation. Mol Gen Genet. 1967;99(3):219–247. doi: 10.1007/BF01797728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang M., Biggs D. R., Clark-Walker G. D., Linnane A. W. Chloramphenicol inhibition of the formation of particulate mitochondrial enzymes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 21;114(2):434–436. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90330-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JULIAN G. R. (14C)LYSINE PEPTIDES SYNTHESIZED IN AN IN VITRO ESCHERICHIA COLI SYSTEM IN THE PRESENCE OF CHLORAMPHENICOL. J Mol Biol. 1965 May;12:9–16. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80277-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayaraman J., Goldberg I. H. Localization of sparsomycin action to the peptide-bond-forming step. Biochemistry. 1968 Jan;7(1):418–421. doi: 10.1021/bi00841a053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaji H., Kaji A. Specific binding of sRNA to ribosomes: effect of streptomycin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Jul;54(1):213–219. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.1.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaji H., Suzuka I., Kaji A. Binding of specific soluble ribonucleic acid to ribosomes. Binding of soluble ribonucleic acid to the template-30 S subunits complex. J Biol Chem. 1966 Mar 25;241(6):1251–1256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaji H., Tanaka Y. Binding of dihydrostreptomycin to ribosomal subunits. J Mol Biol. 1968 Mar 14;32(2):221–230. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90006-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo S., Okanishi M., Utahara R., Maeda K., Umezawa H. Isolation of kanamycin and paromamine inactivated by E. coli carrying R factor. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1968 Jan;21(1):22–29. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.21.22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krembel J., Apirion D. Changes in ribosomal proteins associated with mutants in a locus that affects Escherichia coli ribosomes. J Mol Biol. 1968 Apr 28;33(2):363–368. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90194-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroon A. M., Jansen R. J. The effect of low concentrations of chlorampheicol on beating rat-heart cells in tissue culture. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Feb 26;155(2):629–632. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90212-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger R. G. Properties of antibodies synthesized by cells in vitro in the presence and absence of streptomycin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 May;55(5):1206–1213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.5.1206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger R. G. The effect of Streptomycin on antibody synthesis in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Jul;54(1):144–152. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.1.144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwano M., Ishizawa M., Endo H. Su-II-specific restriction of amber suppression by mutation to streptomycin resistance. J Mol Biol. 1968 Apr 28;33(2):513–516. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90209-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Küntzel H., Noll H. Mitochondrial and cytoplasmic polysomes from Neurospora crassa. Nature. 1967 Sep 23;215(5108):1340–1345. doi: 10.1038/2151340a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEBOY P. S., COX E. C., FLAKS J. G. THE CHROMOSOMAL SITE SPECIFYING A RIBOSOMAL PROTEIN IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Dec;52:1367–1374. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.6.1367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEDERBERG E. M., CAVALLI-SFORZA L., LEDERBERG J. INTERACTION OF STREPTOMYCIN AND A SUPPRESSOR FOR GALACTOSE FERMENTATION IN E. COLI K-12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Apr;51:678–682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.4.678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEDERBERG J. Streptomycin resistance; a genetically recessive mutation. J Bacteriol. 1951 May;61(5):549–550. doi: 10.1128/jb.61.5.549-550.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEDERBERG S. Suppression of the multiplication of heterologous bacteriophages in lysogenic bacteria. Virology. 1957 Jun;3(3):496–513. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(57)90006-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskin A. I., May Chan W. Inhibition by tetracyclines of polyuridylic acid directed phenylalanine incorporation in Escherichia coli cell-free systems. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1964;14:137–142. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(64)90243-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lekover T. E., Kurland C. G. Ribosomes from a streptomycin-dependent strain of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1967 May 14;25(3):497–504. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90201-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis C. Antiplasmodial activity of halogenated lincomycin analogues in Plasmodium berghei-infected mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1967;7:537–542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Likover T. E., Kurland C. G. The contribution of DNA to translation errors induced by streptomycin in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Dec;58(6):2385–2392. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.6.2385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linnane A. W., Lamb A. J., Christodoulou C., Lukins H. B. The biogenesis of mitochondria, VI. Biochemical basis of the resistance of Saccharomyces cerevisiae toward antibiotics which specifically inhibit mitochondrial protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Apr;59(4):1288–1293. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.4.1288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linnane A. W., Stewart P. R. The inhibition of chlorophyll formation in Euglena by antibiotics which inhibit bacterial and mitochondrial protein synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Jun 9;27(5):511–516. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(67)80016-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas-Lenard J., Haenni A. L. Requirement of granosine 5'-triphosphate for ribosomal binding of aminoacyl-SRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Feb;59(2):554–560. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.2.554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas-Lenard J., Lipmann F. Separation of three microbial amino acid polymerization factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jun;55(6):1562–1566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.6.1562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luzzatto L., Apirion D., Schlessinger D. Mechanism of action of streptomycin in E. coli: interruption of the ribosome cycle at the initiation of protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jul;60(3):873–880. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.3.873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luzzatto L., Schlessinger D., Apirion D. Escherichia coli: high resistance or dependence on streptomycin produced by the same allele. Science. 1968 Aug 2;161(3840):478–479. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3840.478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIYAMURA S. [Chloramphenicolase in dysentery bacilli, with special reference to chloramphenicol resistance]. Nihon Saikingaku Zasshi. 1961 Feb;16:115–119. doi: 10.3412/jsb.16.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOSKOWITZ M. DIFFERENCES IN PRECIPITABILITY OF NUCLEIC ACIDS WITH STREPTOMYCIN AND DIHYDROSTREPTOMYCIN. Nature. 1963 Oct 26;200:335–337. doi: 10.1038/200335a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOSKOWITZ M., KELKER N. E. Sensitivity of culture mammalian cells to streptomycin and dihydrostreptomycin. Science. 1963 Aug 16;141(3581):647–648. doi: 10.1126/science.141.3581.647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOSKOWITZ M., KELKER N. AMINO-ACID CONTROL OF STREPTOMYCIN ACTION ON MAMMALIAN CELLS. Nature. 1965 Jan 30;205:476–477. doi: 10.1038/205476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magerlein B. J., Birkenmeyer R. D., Kagan F. Chemical modification of lincomycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1966;6:727–736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maitra U., Cohen S. N., Hurwitz J. Specificity of initiation and synthesis of RNA from DNA templates. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1966;31:113–122. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1966.031.01.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangiarotti G., Schlessinger D. Polyribosome metabolism in Escherichia coli. I. Extraction of polyribosomes and ribosomal subunits from fragile, growing Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1966 Sep;20(1):123–143. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90122-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao J. C. The stoichiometry of erythromycin binding to ribosomal particles of Staphylococcus aureus. Biochem Pharmacol. 1967 Dec;16(12):2441–2443. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(67)90232-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masukawa H., Tanaka N. Miscoding activity of amino sugars. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1968 Jan;21(1):70–72. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.21.70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell I. H. Studies of the binding of tetracycline to ribosomes in vitro. Mol Pharmacol. 1968 Jan;4(1):25–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayuga C., Meier D., Wang T. Escherichia coli: the K 12 ribosomal protein and the streptomycin region of the chromosome. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Oct 24;33(2):203–206. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90768-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy B. J., Holland J. J., Buck C. A. Single-stranded DNA as a template for in vitro protein synthesis. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1966;31:683–691. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1966.031.01.087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meynell E., Meynell G. G., Datta N. Phylogenetic relationships of drug-resistance factors and other transmissible bacterial plasmids. Bacteriol Rev. 1968 Mar;32(1):55–83. doi: 10.1128/br.32.1.55-83.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monro R. E. Catalysis of peptide bond formation by 50 S ribosomal subunits from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1967 May 28;26(1):147–151. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90271-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monro R. E., Marcker K. A. Ribosome-catalysed reaction of puromycin with a formylmethionine-containing oligonucleotide. J Mol Biol. 1967 Apr 28;25(2):347–350. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90146-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monro R. E., Vazquez D. Ribosome-catalysed peptidyl transfer: effects of some inhibitors of protein synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1967 Aug 28;28(1):161–165. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(67)80085-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan A. R., Wells R. D., Khorana H. G. Studies on polynucleotides. LXXIV. Direct translation in vitro of single-stranded DNA-like polymers with repeating nucleotide sequences in the presence of neomycin B. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 28;26(3):477–497. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90316-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEWCOMBE H. B., NYHOLM M. H. The inheritance of streptomycin resistance and dependence in crosses of Escherichia coli. Genetics. 1950 Nov;35(6):603–611. doi: 10.1093/genetics/35.6.603b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIRENBERG M., LEDER P. RNA CODEWORDS AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. THE EFFECT OF TRINUCLEOTIDES UPON THE BINDING OF SRNA TO RIBOSOMES. Science. 1964 Sep 25;145(3639):1399–1407. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3639.1399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newcombe H. B., Hawirko R. SPONTANEOUS MUTATION TO STREPTOMYCIN RESISTANCE AND DEPENDENCE IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Bacteriol. 1949 May;57(5):565–572. doi: 10.1128/jb.57.5.565-572.1949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikolov T. K., Stantchev B. D., Boyadjiev S. I. Influence des antibiotiques sur la formation des anticorps in vitro. I. Etude comparée de l'influence inhibitrice des tétracyclines et du chloramphénicol. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1966 Mar;110(3 Suppl):181–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y., Lipmann F. Comparison of guanosine triphosphate split and polypeptide synthesis with a purified E. coli system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jan;55(1):212–219. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.1.212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura M., Lowry C. V. PHAGE f2 RNA-DIRECTED BINDING OF FORMYLMETHIONYL-TRNA TO RIBOSOMES AND THE ROLE OF 30S RIBOSOMAL SUBUNITS IN INITIATION OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Sep;58(3):946–953. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.3.946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura M., Traub P., Bechmann H. Hybrid 30S ribosomal particles reconstituted from components of different bacterial origins. Nature. 1968 Aug 24;219(5156):793–799. doi: 10.1038/219793b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta T., Thach R. E. Binding of formylmethionyl-tRNA and aminoacyl-tRNA to ribosomes. Nature. 1968 Jul 20;219(5151):238–243. doi: 10.1038/219238a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto S., Suzuki Y. Chloramphenicol-, dihydrostreptomycin-, and kanamycin-inactivating enzymes from multiple drug-resistant Escherichia coli carrying episome 'R'. Nature. 1965 Dec 25;208(5017):1301–1303. doi: 10.1038/2081301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okanishi K., Kondo S., Utahara R., Umezawa H. Phosphorylation and inactivation of aminoglycosidic antibiotics by E. coli carrying R factor. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1968 Jan;21(1):13–21. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.21.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orias E., Gartner T. K. Suppression of amber and ochre rII mutants of bacteriophage T4 by streptomycin. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jun;91(6):2210–2215. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.6.2210-2215.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsuji N., Aono H. Effect of mutation to streptomycin resistance on amber suppressor genes. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jul;96(1):43–50. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.1.43-50.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PESTKA S., MARSHALL R., NIRENBERG M. RNA CODEWORDS AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. V. EFFECT OF STREPTOMYCIN ON THE FORMATION OF RIBOSOME-SRNA COMPLEXES. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Mar;53:639–646. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.3.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PLOTZ P. H., DAVIS B. D. Absence of a chloramphenicol-insensitive phase of streptomycin action. J Bacteriol. 1962 Apr;83:802–805. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.4.802-805.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PROVASOLI L., HUTNER S. H., PINTNER I. J. Destruction of chloroplasts by streptomycin. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1951;16:113–120. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1951.016.01.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S., Nirenberg M. Codeword recognition on 30 S ribosomes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1966;31:641–656. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1966.031.01.083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S. Studies on the formation of transfer ribonucleic acid-ribosome complexes. I. The effect of streptomycin and ribosomal dissociation on 14-C-aminoacyl transfer ribonucleic acid binding to ribosomes. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jan 25;241(2):367–372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S. Studies on the formation of trensfer ribonucleic acid-ribosome complexes. V. On the function of a soluble transfer factor in protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Oct;61(2):726–733. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.2.726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S. The action of streptomycin on protein synthesis in vitro. Bull N Y Acad Med. 1967 Feb;43(2):126–148. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RENDI R., OCHOA S. Effect of chloramphenicol on protein synthesis in cell-free preparations of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1962 Dec;237:3711–3713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROTHEIM M. B., RAVIN A. W. The mapping of genetic loci affecting streptomycin resistance in Pneumococcus. Genetics. 1961 Dec;46:1619–1634. doi: 10.1093/genetics/46.12.1619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravel J. M. Demonstration of a guanosine triphosphate-dependent enzymatic binding of aminoacyl-ribonucleic acid to Escherichia coli ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jun;57(6):1811–1816. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.6.1811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravel J. M., Shorey R. L., Shive W. Evidence for a guanine nucleotide-aminoacyl-RNA complex as an intermediate in the enzymatic transfer of aminoacyl-RNA to ribosomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Oct 11;29(1):68–73. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90542-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravin A. W., Mishra A. K. Relative frequencies of different kinds of spontaneous and induced mutants of pneumococci and streptococci capable of growth in the presence of streptomycin. J Bacteriol. 1965 Nov;90(5):1161–1173. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.5.1161-1173.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revel M., Herzberg M., Becarevic A., Gros F. Role of protein factor in the functional binding of ribosomes to natural messenger RNA. J Mol Biol. 1968 Apr 14;33(1):231–249. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90291-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rychlík I. Release of lysine peptides by puromycin from polylysyl-transfer ribonucleic acid in the presence of ribosomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 21;114(2):425–427. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90327-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAGER R. Genetic systems in Chlamydomonas. Science. 1960 Nov 18;132(3438):1459–1465. doi: 10.1126/science.132.3438.1459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOKOLSKI W. T., YEAGER R. L., CHIDESTER C. G. Cross-dependence between neamine and other basic antibiotics. Nature. 1962 Nov 24;196:776–777. doi: 10.1038/196776b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOKOLSKI W. T., YEAGER R. L., McCOY J. K. Cross-resistance studies with neomycin antibiotics. Nature. 1962 Aug 11;195:623–624. doi: 10.1038/195623a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPEYER J. F., LENGYEL P., BASILIO C. Ribosomal localization of streptomycin sensitivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Apr 15;48:684–686. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.4.684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPOTTS C. R. Physiological and biochemical studies on streptomycin dependence in Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1962 Jun;28:347–365. doi: 10.1099/00221287-28-2-347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPOTTS C. R., STANIER R. Y. Mechanism of streptomycin action on bacteria: a unitary hypothesis. Nature. 1961 Nov 18;192:633–637. doi: 10.1038/192633a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salas M., Hille M. B., Last J. A., Wahba A. J., Ochoa S. Translation of the genetic message, ii. Effect of initiation factors on the binding of formyl-methionyl-trna to ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Feb;57(2):387–394. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.2.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson K. E. Revised linkage map of Salmonella typhimurium. Bacteriol Rev. 1967 Dec;31(4):354–372. doi: 10.1128/br.31.4.354-372.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar S., Thach R. E. Inhibition of formylmethionyl-transfer RNA binding to ribosomes by tetracycline. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Aug;60(4):1479–1486. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.4.1479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J. H. An effect of streptomycin on the biosynthesis of the coat protein of coliphage f2 by extract of E. coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 May;53(5):1133–1140. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.5.1133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweet R., Heintz R. Protein synthesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1966;35:723–758. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.35.070166.003451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scolnick E., Tompkins R., Caskey T., Nirenberg M. Release factors differing in specificity for terminator codons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Oct;61(2):768–774. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.2.768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw W. V., Brodsky R. F. Characterization of chloramphenicol acetyltransferase from chloramphenicol-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jan;95(1):28–36. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.1.28-36.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw W. V. The enzymatic acetylation of chloramphenicol by extracts of R factor-resistant Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1967 Feb 25;242(4):687–693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw W. V., Unowsky J. Mechanism of R factor-mediated chloramphenicol resistance. J Bacteriol. 1968 May;95(5):1976–1978. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.5.1976-1978.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silengo L., Schlessinger D., Mangiarotti G., Apirion D. Induction of mutations to streptomycin and spectinomycin resistance in Escherichia coli by N-methyl-N'-nitroso-N-nitroguanidine and acridine half-mustard ICR-191. Mutat Res. 1967 Sep-Oct;4(5):701–703. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(67)90056-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sippel A., Hartmann G. Mode of action of rafamycin on the RNA polymerase reaction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Mar 18;157(1):218–219. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90286-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. H. R factors mediate resistance to mercury, nickel, and cobalt. Science. 1967 May 26;156(3778):1114–1116. doi: 10.1126/science.156.3778.1114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith I., Dubnau D., Morrell P., Marmur J. Chromosomal location of DNA base sequences complementary to transfer RNA and to 5 s, 16 s and 23 s ribosomal RNA in Bacillus subtilis. J Mol Biol. 1968 Apr 14;33(1):123–140. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90285-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staehelin T., Meselson M. Determination of streptomycin sensitivity by a subunit of the 30S ribosome of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1966 Aug;19(1):207–210. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80062-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern J. L., Barner H. D., Cohen S. S. The lethality of streptomycin and the stimulation of RNA synthesis in the absence of protein synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1966 May;17(1):188–217. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80103-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suhara Y., Maeda K., Umezawa H. Chemical studies on kasugamycin. V. The structure of kasugamycin. Tetrahedron Lett. 1966 Mar;12:1239–1244. doi: 10.1016/s0040-4039(01)99701-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuka I., Kaji H., Kaji A. Binding of specific sRNA to 30S ribosomal subunits: effect of 50S ribosomal subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jun;55(6):1483–1490. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.6.1483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki Y., Okamoto S. The enzymatic acetylation of chloramphenicol by the multiple drug-resistant Escherichia coli carrying R factor. J Biol Chem. 1967 Oct 25;242(20):4722–4730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKANAMI M., OKAMOTO T. INTERACTION OF RIBOSOMES AND SYNTHETIC POLYRIBONUCLEOTIDES. J Mol Biol. 1963 Oct;7:323–333. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80027-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRAUT R. R., MONRO R. E. THE PUROMYCIN REACTION AND ITS RELATION TO PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. J Mol Biol. 1964 Oct;10:63–72. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80028-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takasawa S., Utahara R., Okanishi M., Maeda K., Umezawa H. Studies on adenylylstreptomycin, a product of streptomycin inactivation by E. coli carrying the R-factor. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1968 Aug;21(8):477–484. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.21.477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Teraoka H., Nagira T., Tamaki M. [14C]erythromycin-ribosome complex formation and non-enzymatic binding of aminoacyl-transfer RNA to ribosome-messenger RNA complex. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Aug 17;123(2):435–437. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90300-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka N., Igusa S. Effects of viomycin and polymyxin B on protein synthesis in vitro. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1968 Mar;21(3):239–240. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.21.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka N., Kinoshita T., Masukawa H. Mechanism of protein synthesis inhibition by fusidic acid and related antibiotics. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Feb 15;30(3):278–283. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90447-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka N., Nishimura T., Yamaguchi H., Yamamoto C., Yoshida Y., Sashikata K., Umezawa H. Mechanism of action of kasugamycin. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1965 Jul;18(4):139–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka N., Sashikata K., Yamaguchi H., Umezawa H. Inhibition of protein synthesis by bottromycin A2 and its hydrazide. J Biochem. 1966 Oct;60(4):405–410. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka N., Yamaguchi H., Umezawa H. Mechanism of kasugamycin action on polypeptide synthesis. J Biochem. 1966 Oct;60(4):429–434. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka N., Yamaki H., Lin Y. C., Umezawa H. Further studies on inhibition of protein synthesis by fusidic and helvolinic acids. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1967 Jul;20(3):156–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka Y., Kaji H. The role of ribosomal protein for the binding of dihydrostreptomycin to ribosomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Jul 26;32(2):313–319. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90387-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taubman S. B., Jones N. R., Young F. E., Corcoran J. W. Sensitivity and resistance to erythromycin in Bacillus subtilis 168: the ribosomal binding of erythromycin and chloramphenicol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Aug 17;123(2):438–440. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90301-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A. L., Trotter C. D. Revised linkage map of Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1967 Dec;31(4):332–353. doi: 10.1128/br.31.4.332-353.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub P., Hosokawa K., Nomura M. Streptomycin sensitivity and the structural components of the 30S ribosomes of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1966 Aug;19(1):211–214. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80063-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub P., Nomura M. Streptomycin resistance mutation in Escherichia coli: altered ribosomal protein. Science. 1968 Apr 12;160(3824):198–199. doi: 10.1126/science.160.3824.198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub P., Nomura M. Structure and function of E. coli ribosomes. V. Reconstitution of functionally active 30S ribosomal particles from RNA and proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Mar;59(3):777–784. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.3.777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treffers H. P., Spinelli V., Belser N. O. A Factor (or Mutator Gene) Influencing Mutation Rates in Escherichia Coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1954 Nov;40(11):1064–1071. doi: 10.1073/pnas.40.11.1064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umezawa H., Mizuno S., Yamazaki H., Nitta K. Inhibition of DNA-dependent RNA synthesis by rifamycins. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1968 Mar;21(3):234–236. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.21.234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umezawa H., Takasawa S., Okanishi M., Utahara R. Adenylylstreptomycin, a product of streptomycin inactivated by E. coli carrying R factor. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1968 Jan;21(1):81–82. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.21.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unowsky J., Rachmeler M. Mechanisms of antibiotic resistance determined by resistance-transfer factors. J Bacteriol. 1966 Aug;92(2):358–365. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.2.358-365.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN KNIPPENBERGP, VAN CLAASENJ, GRIJM-VOS M., VELDSTRA H., BOSCH L. STIMULATION AND INHIBITION OF POLYPEPTIDE SYNTHESIS BY STREPTOMYCIN IN RIBOSOMAL SYSTEMS OF ESCHERICHIA COLI, PROGRAMMED WITH VARIOUS MESSENGERS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Mar 15;95:461–473. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(65)90192-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez D. Antibiotics affecting chloramphenicol uptake by bacteria. Their effect on amino acid incorporation in a cell-free system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 21;114(2):289–295. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90310-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez D. Binding of chloramphenicol to ribosomes. The effect of a number of antibiotics. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 21;114(2):277–288. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90309-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez D. Binding to ribosomes and inhibitory effect on protein synthesis of the spiramycin antibiotics. Life Sci. 1967 Apr 15;6(8):845–853. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(67)90287-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez D., Monro R. E. Effects of some inhibitors of protein synthesis on the binding of aminoacyl tRNA to ribosomal subunits. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Jun 20;142(1):155–173. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(67)90524-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez D. The binding of chloramphenicol by ribosomes from Bacillus megaterium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1964 Apr 22;15(5):464–468. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(64)90487-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verly W. G., Barbason H., Dusart J., Petitpas-Dewandre A. A comparative study of the action of ethyl methane sulfonate and HNO2 on the mutation to streptomycin resistance of Escherichia coli I 12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967;145(3):752–762. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(67)90134-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATANABE T. Infective heredity of multiple drug resistance in bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1963 Mar;27:87–115. doi: 10.1128/br.27.1.87-115.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATSON J. D. THE SYNTHESIS OF PROTEINS UPON RIBOSOMES. Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1964;46:1399–1425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITE J. R., WHITE H. L. STREPTOMYCINOID ANTIBIOTICS: SYNERGISM BY PUROMYCIN. Science. 1964 Nov 6;146(3645):772–774. doi: 10.1126/science.146.3645.772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wehrli W., Knüsel F., Schmid K., Staehelin M. Interaction of rifamycin with bacterial RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Oct;61(2):667–673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.2.667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitfield H. J., Jr, Martin R. G., Ames B. N. Classification of aminotransferase (C gene) mutants in the histidine operon. J Mol Biol. 1966 Nov 14;21(2):335–355. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90103-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe A. D., Hahn F. E. Stability of ribosomes from streptomycin-exposed Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Jun 28;31(6):945–949. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90544-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfgang R. W., Lawrence N. L. Intracellular distribution of 3H-dihydrostreptomycin in a streptomycin-dependent strain of Bacillus megaterium. J Bacteriol. 1968 Apr;95(4):1295–1299. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.4.1295-1299.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YAMAKI H., TANAKA N. EFFECTS OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS INHIBITORS ON THE LETHAL ACTION OF KANAMYCIN AND STREPTOMYCIN. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1963 Nov;16:222–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YUNIS A. A., BLOOMBERG G. R. CHLORAMPHENICOL TOXICITY: CLINICAL FEATURES AND PATHOGENESIS. Prog Hematol. 1964;4:138–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada T., Tipper D., Davies J. Enzymatic inactivation of streptomycin by R factor-resistant Escherichia coli. Nature. 1968 Jul 20;219(5151):288–291. doi: 10.1038/219288a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi H., Tanaka N. Inhibition of protein synthesis by blasticidin S. II. Studies on the site of action in E. coli polypeptide synthesizing systems. J Biochem. 1966 Dec;60(6):632–642. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanofsky C., Cox E. C., Horn V. The unusual mutagenic specificity of an E. Coli mutator gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Feb;55(2):274–281. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.2.274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh S. D., Shils M. E. Tetracycline and incorporation of amino acids into proteins of rat tissues. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Mar;121(3):729–734. doi: 10.3181/00379727-121-30872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



