Abstract
The reduction of geraniol to citronellol is the first step for the synthesis of natural phytol in the production of tocopherols and natural vitamin K. Baker’s yeast was used in the bioreduction described above as a whole-cell biocatalyst. However, the enzyme responsible for the reduction of geraniol to citronellol is not yet known. Four old yellow enzyme (OYE) genes were cloned from yeast and plants, and expressed in Escherichia coli for a high level of recombinant proteins. The recombinant protein displayed a catalytic activity of converting geraniol to citronellol as a sole product verified by GC-MS analyses. The recombinant OYE2 intact cells were found to show 3.7 and 1.9-fold higher activity than that of yeast cells and the recombinant crude extracts, respectively. Compared to the recombinant fusion enzyme, the entrokinase-cleaved enzyme displayed nearly identical activity for geraniol reduction. To our knowledge, this is the first enzyme identified to catalyze the formation of citronellol from geraniol by reducing the allylic alcohol double bond, which is normally known as inactivating group for the old yellow enzymes. 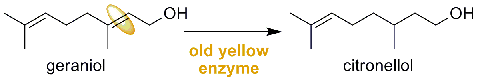
Electronic Supplementary Material
Supplementary material is available for this article at 10.1007/s13659-011-0032-6 and is accessible for authorized users.
Keywords: allylic alcohol, citronellol, geraniol, old yellow enzyme, reduction
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary material, approximately 398 KB.
Footnotes
This article is published with open access at Springerlink.com
References
- [1].Gramatica P., Manitto P., Ranzi B. M., Delbianco A., Francavilla M. Experientia. 1982;38:775–776. doi: 10.1007/BF01972264. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- [2].Gramatica P., Manitto P., Monti D., Speranza G. Tetrahedron. 1987;43:4481–4486. doi: 10.1016/S0040-4020(01)90325-4. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- [3].Toogood H. S., Gardiner J. M., Scrutton N. S. ChemCatChem. 2010;2:892–914. doi: 10.1002/cctc.201000094. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- [4].Stuermer R., Hauer B., Hall M., Faber K. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2007;11:203–213. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2007.02.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [5].Swiderska M. A., Stewart J. D. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2006;42:52–54. doi: 10.1016/j.molcatb.2006.06.023. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- [6].Hall M., Stueckler C., Hauer B., Stuermer R., Friedrich T., Breuer M., Kroutil W., Faber K. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2008;9:1511–1516. doi: 10.1002/ejoc.200701208. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- [7].Brenna E., Fronza G., Fuganti C., Monti D., Parmeggiani F. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2011;73:17–21. [Google Scholar]
- [8].Wada M., Yoshizumi A., Noda Y., Kataoka M., Shimizu S., Takagi H., Nakamori S. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003;69:933–937. doi: 10.1128/AEM.69.2.933-937.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [9].Kataoka M., Kotaka A., Thiwthong R., Wada M., Nakamori S., Shimizu S. J. Biotechnol. 2004;114:1–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2004.04.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [10].Hall M., Stueckler C., Ehammer H., Pointner E., Oberdorfer G., Gruber K., Hauer B., Stuermer R., Kroutil W., Macheroux P., Faber K. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2008;350:411–418. doi: 10.1002/adsc.200700458. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- [11].Hall M., Stueckler C., Kroutil W., Macheroux P., Faber K. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007;46:3934–3937. doi: 10.1002/anie.200605168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [12].Schaller F., Biesgen C., Müssig C., Altmann T., Weiler E. W. Planta. 2000;210:979–984. doi: 10.1007/s004250050706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [13].Schlieben N. H., Niefind K., Müller J., Riebel B., Hummel W., Schomburg D. J. Mol. Biol. 2005;349:801–813. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2005.04.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary material, approximately 398 KB.


