Abstract
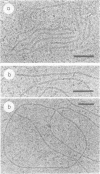
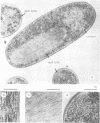
When recA protein is enzymatically inactive in vitro, it adopts a more compact helical polymer form than that of the active protein polymerized onto DNA in the presence of ATP. Here we describe some aspects of this structure. By cryo-electron microscopy, a pitch of 76 A is found for both the self-polymer and the inactive complex with ssDNA. A smaller pitch of 64 A is observed in conventional electron micrographs. The contour length of complexes with ssDNA was used to estimate the binding stoichiometry in the compact complex, 6 +/- 1 nt/recA. In addition, the compact structure was observed in vivo in Escherichia coli: inclusion bodies produced upon induction of recA expression in an overproducing strain have a fibrous morphology with the structural parameters of the compact polymer.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amos L., Klug A. Arrangement of subunits in flagellar microtubules. J Cell Sci. 1974 May;14(3):523–549. doi: 10.1242/jcs.14.3.523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant F. R., Taylor A. R., Lehman I. R. Interaction of the recA protein of Escherichia coli with single-stranded DNA. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):1196–1202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cazenave C., Toulmé J. J., Hélène C. Binding of RecA protein to single-stranded nucleic acids: spectroscopic studies using fluorescent polynucleotides. EMBO J. 1983;2(12):2247–2251. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01730.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. F., Rankert D. A., Jeng T. W., Morgan D. G., Schmid M. F., Chiu W. Cryo electron microscopy of unstained, unfixed RecA-cssDNA complexes. J Ultrastruct Mol Struct Res. 1988 Aug;100(2):166–172. doi: 10.1016/0889-1605(88)90023-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig N. L., Roberts J. W. E. coli recA protein-directed cleavage of phage lambda repressor requires polynucleotide. Nature. 1980 Jan 3;283(5742):26–30. doi: 10.1038/283026a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Capua E., Engel A., Stasiak A., Koller T. Characterization of complexes between recA protein and duplex DNA by electron microscopy. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):87–103. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90514-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiCapua E., Cuillel M., Hewat E., Schnarr M., Timmins P. A., Ruigrok R. W. Activation of recA protein. The open helix model for LexA cleavage. J Mol Biol. 1992 Aug 5;226(3):707–719. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90627-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiCapua E., Schnarr M., Ruigrok R. W., Lindner P., Timmins P. A. Complexes of RecA protein in solution. A study by small angle neutron scattering. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jul 20;214(2):557–570. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90198-U. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egelman E. H., Stasiak A. Structure of helical RecA-DNA complexes. Complexes formed in the presence of ATP-gamma-S or ATP. J Mol Biol. 1986 Oct 20;191(4):677–697. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90453-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flory J., Tsang S. S., Muniyappa K. Isolation and visualization of active presynaptic filaments of recA protein and single-stranded DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7026–7030. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith J., Shores C. G. RecA protein rapidly crystallizes in the presence of spermidine: a valuable step in its purification and physical characterization. Biochemistry. 1985 Jan 1;24(1):158–162. doi: 10.1021/bi00322a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuser J., Griffith J. Visualization of RecA protein and its complexes with DNA by quick-freeze/deep-etch electron microscopy. J Mol Biol. 1989 Dec 5;210(3):473–484. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90124-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewat E. A., Ruigrok R. W., DiCapua E. Activation of recA protein: the pitch of the helical complex with single-stranded DNA. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2695–2698. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07813.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobot J. A., Villiger W., Escaig J., Maeder M., Ryter A., Kellenberger E. Shape and fine structure of nucleoids observed on sections of ultrarapidly frozen and cryosubstituted bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jun;162(3):960–971. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.3.960-971.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalczykowski S. C. Biochemistry of genetic recombination: energetics and mechanism of DNA strand exchange. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1991;20:539–575. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.20.060191.002543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. W., Mount D. W. The SOS regulatory system of Escherichia coli. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):11–22. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay D. B., Steitz T. A., Weber I. T., West S. C., Howard-Flanders P. Crystallization of monomeric recA protein. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 25;255(14):6662–6662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menetski J. P., Kowalczykowski S. C. Interaction of recA protein with single-stranded DNA. Quantitative aspects of binding affinity modulation by nucleotide cofactors. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jan 20;181(2):281–295. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90092-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roca A. I., Cox M. M. The RecA protein: structure and function. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1990;25(6):415–456. doi: 10.3109/10409239009090617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata T., DasGupta C., Cunningham R. P., Radding C. M. Purified Escherichia coli recA protein catalyzes homologous pairing of superhelical DNA and single-stranded fragments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1638–1642. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver M. S., Fersht A. R. Direct observation of complexes formed between recA protein and a fluorescent single-stranded deoxyribonucleic acid derivative. Biochemistry. 1982 Nov 23;21(24):6066–6072. doi: 10.1021/bi00267a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slilaty S. N., Little J. W. Lysine-156 and serine-119 are required for LexA repressor cleavage: a possible mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):3987–3991. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.3987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stasiak A., Egelman E. H. Structure and Dynamics of recA Protein-DNA Complexes as Determined by Image Analysis of Electron Micrographs. Biophys J. 1986 Jan;49(1):5–7. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83569-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Story R. M., Weber I. T., Steitz T. A. The structure of the E. coli recA protein monomer and polymer. Nature. 1992 Jan 23;355(6358):318–325. doi: 10.1038/355318a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Kubista M., Nordén B. Binding stoichiometry and structure of RecA-DNA complexes studied by flow linear dichroism and fluorescence spectroscopy. Evidence for multiple heterogeneous DNA co-ordination. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jan 5;205(1):137–147. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90371-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Schnarr M. Investigation of RecA--polynucleotide interactions from the measurement of LexA repressor cleavage kinetics. Presence of different types of complex. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Aug 15;183(3):617–622. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb21091.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmins P. A., Ruigrok R. W., DiCapua E. The solution structure of recA filaments by small angle neutron scattering. Biochimie. 1991 Feb-Mar;73(2-3):227–230. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(91)90206-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang S. S., Chow S. A., Radding C. M. Networks of DNA and RecA protein are intermediates in homologous pairing. Biochemistry. 1985 Jun 18;24(13):3226–3232. doi: 10.1021/bi00334a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. C., Spengler S. J. Fibers of RecA protein and complexes of RecA protein and single-stranded phi X174 DNA as visualized by negative-stain electron microscopy. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jan 5;187(1):109–118. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90410-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrigley N. G. The lattice spacing of crystalline catalase as an internal standard of length in electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res. 1968 Sep;24(5):454–464. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(68)80048-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu X., Egelman E. H. Image analysis reveals that Escherichia coli RecA protein consists of two domains. Biophys J. 1990 Mar;57(3):555–566. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82571-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu X., Egelman E. H. Structural data suggest that the active and inactive forms of the RecA filament are not simply interconvertible. J Mol Biol. 1992 Sep 5;227(1):334–346. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90702-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]