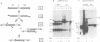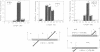Abstract
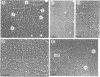
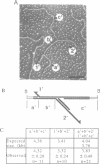
Several molecular mechanisms have been proposed to account for nonconservative homologous recombination. This type of recombination is particularly efficient in Xenopus oocytes when appropriate DNA substrates are injected. To distinguish between possible models, we have investigated recombination intermediates from oocytes by direct observation in the electron microscope. Partially recombined DNA was crosslinked with a psoralen derivative after incubation in oocytes to limit the branch migration that might occur during recovery procedures and alter the structures that were initially present. Branched structures, which we interpret as intermediates, represented approximately 10% of the DNA recovered and were readily analyzed. We did not observe any structures with internal loops predicted by invasion mechanisms. The majority of intermediates had one or two single-stranded branches on product-sized molecules, as predicted for incomplete junctions in the resection-annealing mechanism. Detailed length measurements confirmed the expectations of that model. When recovered DNA was not crosslinked, or when annealed junctions were prepared in vitro, we saw branched structures that indicated the occurrence of extensive branch migration. Comparison with the crosslinked sample confirmed the effectiveness of the crosslinking in preserving structures created in the oocytes. Our results strongly support a resection-annealing mechanism of recombination in oocytes.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baur M., Potrykus I., Paszkowski J. Intermolecular homologous recombination in plants. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):492–500. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brouillette S., Chartrand P. Intermolecular recombination assay for mammalian cells that produces recombinants carrying both homologous and nonhomologous junctions. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;7(6):2248–2255. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.6.2248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll D., Wright S. H., Wolff R. K., Grzesiuk E., Maryon E. B. Efficient homologous recombination of linear DNA substrates after injection into Xenopus laevis oocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2053–2061. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassuto E., Radding C. M. Mechanism for the action of lambda exonuclease in genetic recombination. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jan 6;229(1):13–16. doi: 10.1038/newbio229013a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R. Alkaline gel electrophoresis of deoxyribonucleic acid photoreacted with trimethylpsoralen: rapid and sensitive detection of interstrand cross-links. Biochemistry. 1981 Mar 17;20(6):1431–1437. doi: 10.1021/bi00509a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R., Pardue M. L. Electron microscopy of DNA crosslinked with trimethylpsoralen: test of the secondary structure of eukaryotic inverted repeat sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2644–2648. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti S., Joffe S., Seidman M. M. Recombination and deletion of sequences in shuttle vector plasmids in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;5(9):2265–2271. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.9.2265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortese R., Harland R., Melton D. Transcription of tRNA genes in vivo: single-stranded compared to double-stranded templates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4147–4151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale R. M., McClure B. A., Houchins J. P. A rapid single-stranded cloning strategy for producing a sequential series of overlapping clones for use in DNA sequencing: application to sequencing the corn mitochondrial 18 S rDNA. Plasmid. 1985 Jan;13(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(85)90053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty M. J., Morrison P. T., Kolodner R. Genetic recombination of bacterial plasmid DNA. Physical and genetic analysis of the products of plasmid recombination in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jul 5;167(3):539–560. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80097-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn K., Chrysogelos S., Griffith J. Electron microscopic visualization of recA-DNA filaments: evidence for a cyclic extension of duplex DNA. Cell. 1982 Apr;28(4):757–765. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90055-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman-Lobell J., Rudin N., Haber J. E. Two alternative pathways of double-strand break repair that are kinetically separable and independently modulated. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):1292–1303. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.1292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folger K. R., Thomas K., Capecchi M. R. Nonreciprocal exchanges of information between DNA duplexes coinjected into mammalian cell nuclei. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):59–69. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goedecke W., Vielmetter W., Pfeiffer P. Activation of a system for the joining of nonhomologous DNA ends during Xenopus egg maturation. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):811–816. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruss C., Gutierrez C., Burhans W. C., DePamphilis M. L., Koller T., Sogo J. M. Nucleosome assembly in mammalian cell extracts before and after DNA replication. EMBO J. 1990 Sep;9(9):2911–2922. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07482.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grzesiuk E., Carroll D. Recombination of DNAs in Xenopus oocytes based on short homologous overlaps. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 11;15(3):971–985. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.3.971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurdon J. B., Wickens M. P. The use of Xenopus oocytes for the expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:370–386. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01028-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh P., Camerini-Otero C. S., Camerini-Otero R. D. Pairing of homologous DNA sequences by proteins: evidence for three-stranded DNA. Genes Dev. 1990 Nov;4(11):1951–1963. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.11.1951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeong-Yu S. J., Carroll D. Test of the double-strand-break repair model of recombination in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):112–119. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura Y., Yoshikura H., Kobayashi I. Homologous recombination in a mammalian plasmid. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Jul;222(2-3):185–191. doi: 10.1007/BF00633816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin F. L., Sperle K., Sternberg N. Model for homologous recombination during transfer of DNA into mouse L cells: role for DNA ends in the recombination process. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;4(6):1020–1034. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.6.1020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
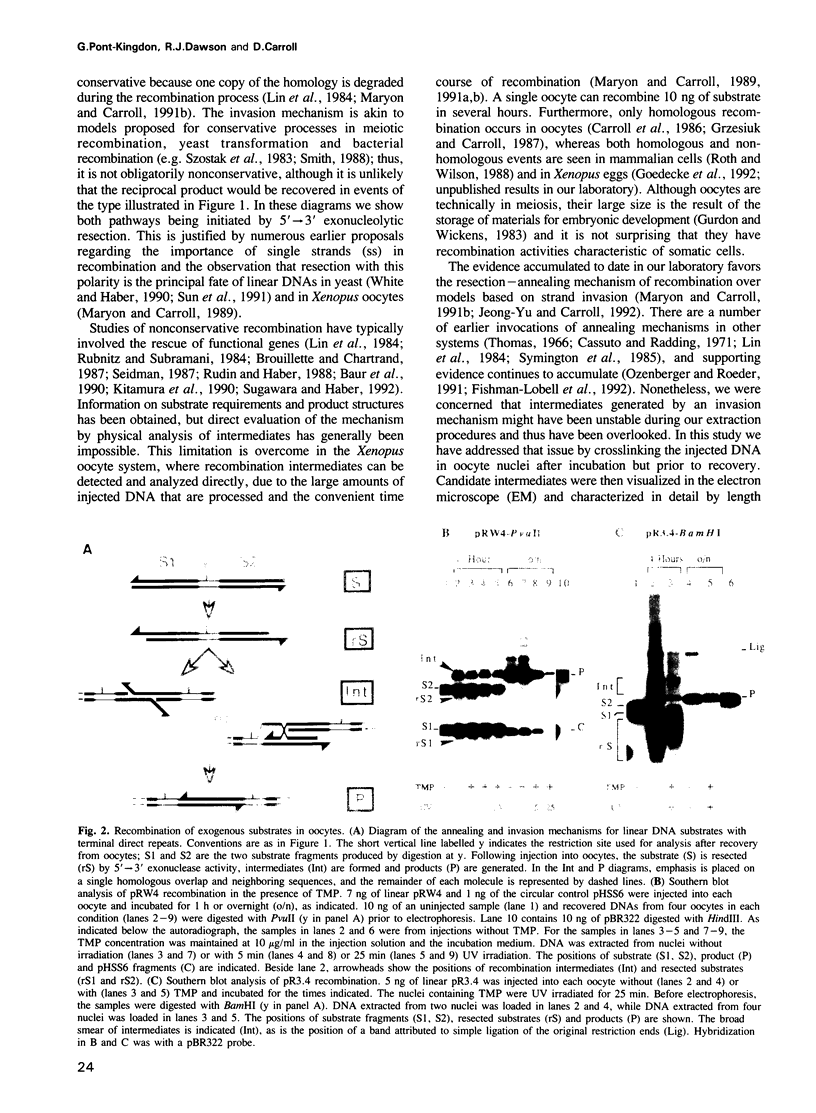
- Maryon E., Carroll D. Characterization of recombination intermediates from DNA injected into Xenopus laevis oocytes: evidence for a nonconservative mechanism of homologous recombination. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):3278–3287. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.3278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maryon E., Carroll D. Degradation of linear DNA by a strand-specific exonuclease activity in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4862–4871. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maryon E., Carroll D. Involvement of single-stranded tails in homologous recombination of DNA injected into Xenopus laevis oocyte nuclei. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):3268–3277. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.3268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEntee K., Weinstock G. M., Lehman I. R. Initiation of general recombination catalyzed in vitro by the recA protein of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2615–2619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozenberger B. A., Roeder G. S. A unique pathway of double-strand break repair operates in tandemly repeated genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1222–1231. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennington S. L., Wilson J. H. Gene targeting in Chinese hamster ovary cells is conservative. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9498–9502. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plessis A., Perrin A., Haber J. E., Dujon B. Site-specific recombination determined by I-SceI, a mitochondrial group I intron-encoded endonuclease expressed in the yeast nucleus. Genetics. 1992 Mar;130(3):451–460. doi: 10.1093/genetics/130.3.451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao B. J., Dutreix M., Radding C. M. Stable three-stranded DNA made by RecA protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):2984–2988. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.2984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Register J. C., 3rd, Griffith J. The direction of RecA protein assembly onto single strand DNA is the same as the direction of strand assimilation during strand exchange. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):12308–12312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revet B., Benichou D. Electron microscopy of AD5 replicating molecules after in vivo photocrosslinking with trioxsalen. Virology. 1981 Oct 15;114(1):60–70. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90252-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubnitz J., Subramani S. The minimum amount of homology required for homologous recombination in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2253–2258. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudin N., Haber J. E. Efficient repair of HO-induced chromosomal breaks in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by recombination between flanking homologous sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3918–3928. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidman M. M. Intermolecular homologous recombination between transfected sequences in mammalian cells is primarily nonconservative. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3561–3565. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifert H. S., Chen E. Y., So M., Heffron F. Shuttle mutagenesis: a method of transposon mutagenesis for Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):735–739. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
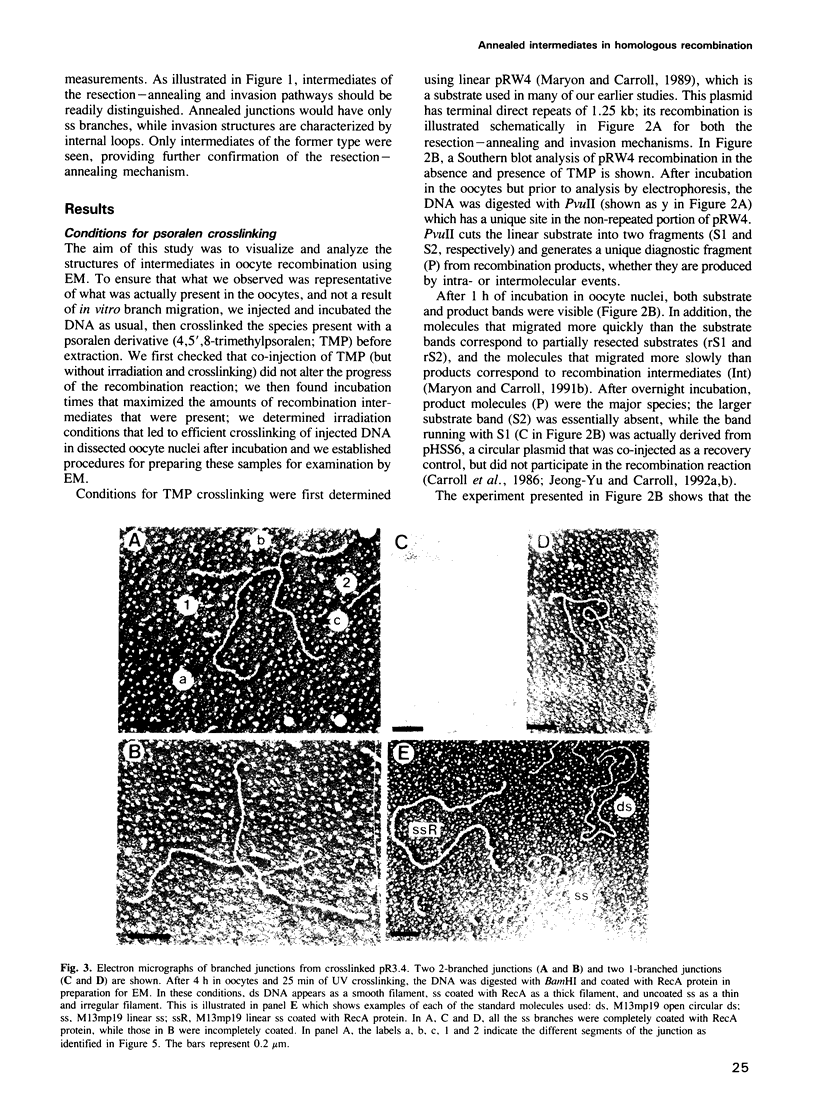
- Shibata T., DasGupta C., Cunningham R. P., Radding C. M. Purified Escherichia coli recA protein catalyzes homologous pairing of superhelical DNA and single-stranded fragments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1638–1642. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. R. Homologous recombination in procaryotes. Microbiol Rev. 1988 Mar;52(1):1–28. doi: 10.1128/mr.52.1.1-28.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugawara N., Haber J. E. Characterization of double-strand break-induced recombination: homology requirements and single-stranded DNA formation. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):563–575. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun H., Treco D., Szostak J. W. Extensive 3'-overhanging, single-stranded DNA associated with the meiosis-specific double-strand breaks at the ARG4 recombination initiation site. Cell. 1991 Mar 22;64(6):1155–1161. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90270-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symington L. S., Morrison P., Kolodner R. Intramolecular recombination of linear DNA catalyzed by the Escherichia coli RecE recombination system. J Mol Biol. 1985 Dec 5;186(3):515–525. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90126-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
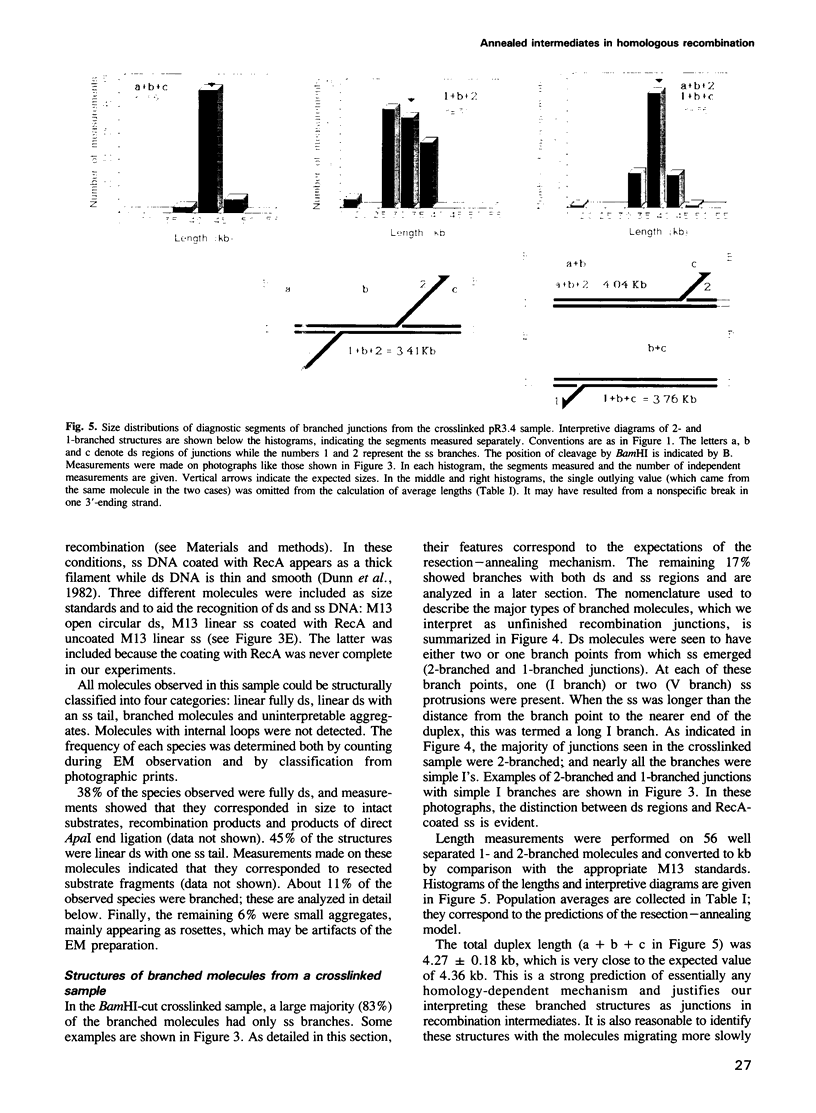
- Szostak J. W., Orr-Weaver T. L., Rothstein R. J., Stahl F. W. The double-strand-break repair model for recombination. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):25–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90331-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas C. A., Jr Recombination of DNA molecules. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1966;5:315–337. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60237-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umlauf S. W., Cox M. M., Inman R. B. Triple-helical DNA pairing intermediates formed by recA protein. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):16898–16912. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. A., Jared D. W., Dumont J. N., Sega M. W. Protein incorporation by isolated amphibian oocytes. 3. Optimum incubation conditions. J Exp Zool. 1973 Jun;184(3):321–333. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401840305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West S. C. Processing of recombination intermediates in vitro. Bioessays. 1990 Apr;12(4):151–154. doi: 10.1002/bies.950120402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White C. I., Haber J. E. Intermediates of recombination during mating type switching in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):663–673. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08158.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]