Abstract
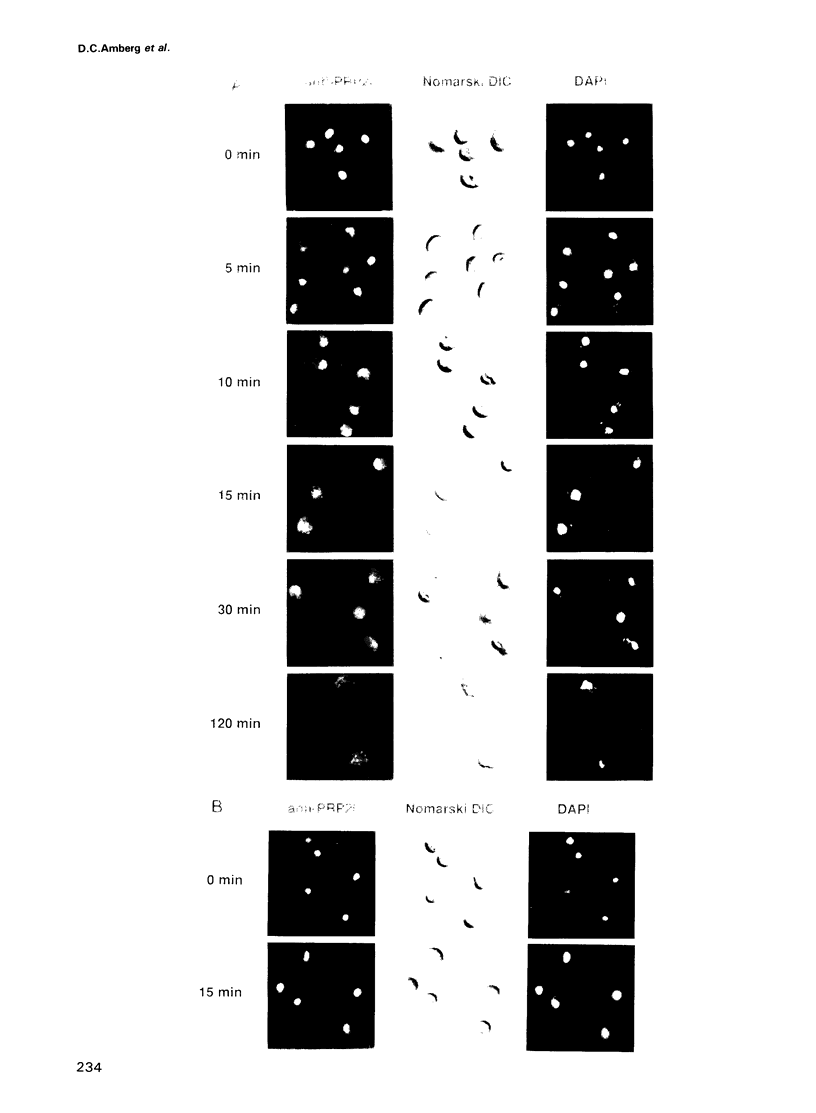
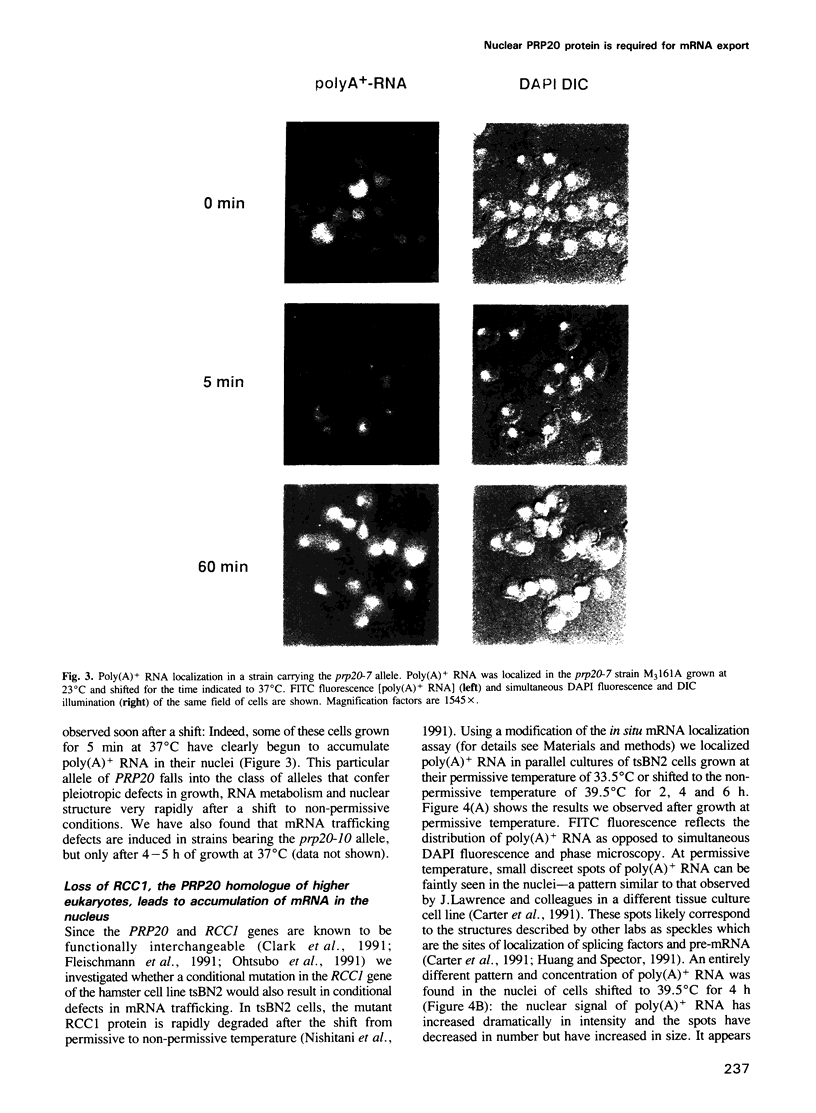
The yeast PRP20 protein is highly homologous in structure and function to the RCC1 protein of higher eukaryotes. The RCC1 protein is involved in the regulation of the onset of mitosis, whereas the PRP20 protein was shown to be required for accurate and efficient mRNA metabolism. The first observable phenotype in mutant prp20 cells when shifted from permissive to non-permissive temperature is a loss of nuclear PRP20 protein. Concomitantly, an accumulation of poly(A)+ RNA in the nucleus is observed. The temperature-sensitive RCC1 allele in the mutant hamster cell line tsBN2 leads to a similar accumulation of mRNA in the nucleus.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aebi M., Clark M. W., Vijayraghavan U., Abelson J. A yeast mutant, PRP20, altered in mRNA metabolism and maintenance of the nuclear structure, is defective in a gene homologous to the human gene RCC1 which is involved in the control of chromosome condensation. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Oct;224(1):72–80. doi: 10.1007/BF00259453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amberg D. C., Goldstein A. L., Cole C. N. Isolation and characterization of RAT1: an essential gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae required for the efficient nucleocytoplasmic trafficking of mRNA. Genes Dev. 1992 Jul;6(7):1173–1189. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.7.1173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bischoff F. R., Maier G., Tilz G., Ponstingl H. A 47-kDa human nuclear protein recognized by antikinetochore autoimmune sera is homologous with the protein encoded by RCC1, a gene implicated in onset of chromosome condensation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8617–8621. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bischoff F. R., Ponstingl H. Catalysis of guanine nucleotide exchange on Ran by the mitotic regulator RCC1. Nature. 1991 Nov 7;354(6348):80–82. doi: 10.1038/354080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bischoff F. R., Ponstingl H. Mitotic regulator protein RCC1 is complexed with a nuclear ras-related polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10830–10834. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., LaCroute F., Fink G. R. A positive selection for mutants lacking orotidine-5'-phosphate decarboxylase activity in yeast: 5-fluoro-orotic acid resistance. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;197(2):345–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00330984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter K. C., Taneja K. L., Lawrence J. B. Discrete nuclear domains of poly(A) RNA and their relationship to the functional organization of the nucleus. J Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;115(5):1191–1202. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.5.1191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark K. L., Ohtsubo M., Nishimoto T., Goebl M., Sprague G. F., Jr The yeast SRM1 protein and human RCC1 protein share analogous functions. Cell Regul. 1991 Oct;2(10):781–792. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.10.781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark K. L., Sprague G. F., Jr Yeast pheromone response pathway: characterization of a suppressor that restores mating to receptorless mutants. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2682–2694. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark M. W. Nucleolar-specific positive stains for optical and electron microscopy. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:717–728. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94053-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enoch T., Nurse P. Coupling M phase and S phase: controls maintaining the dependence of mitosis on chromosome replication. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):921–923. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90542-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischmann M., Clark M. W., Forrester W., Wickens M., Nishimoto T., Aebi M. Analysis of yeast prp20 mutations and functional complementation by the human homologue RCC1, a protein involved in the control of chromosome condensation. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Jul;227(3):417–423. doi: 10.1007/BF00273932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasch M. The maternally expressed Drosophila gene encoding the chromatin-binding protein BJ1 is a homolog of the vertebrate gene Regulator of Chromatin Condensation, RCC1. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1225–1236. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08064.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall M. N., Craik C., Hiraoka Y. Homeodomain of yeast repressor alpha 2 contains a nuclear localization signal. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):6954–6958. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.6954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H., Weinert T. A. Checkpoints: controls that ensure the order of cell cycle events. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):629–634. doi: 10.1126/science.2683079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang S., Spector D. L. Nascent pre-mRNA transcripts are associated with nuclear regions enriched in splicing factors. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12A):2288–2302. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12a.2288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence J. B., Singer R. H., Marselle L. M. Highly localized tracks of specific transcripts within interphase nuclei visualized by in situ hybridization. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):493–502. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90924-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto T., Beach D. Premature initiation of mitosis in yeast lacking RCC1 or an interacting GTPase. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):347–360. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90624-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimoto T., Eilen E., Basilico C. Premature of chromosome condensation in a ts DNA- mutant of BHK cells. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):475–483. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90017-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishitani H., Kobayashi H., Ohtsubo M., Nishimoto T. Cloning of Xenopus RCC1 cDNA, a homolog of the human RCC1 gene: complementation of tsBN2 mutation and identification of the product. J Biochem. 1990 Feb;107(2):228–235. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishitani H., Ohtsubo M., Yamashita K., Iida H., Pines J., Yasudo H., Shibata Y., Hunter T., Nishimoto T. Loss of RCC1, a nuclear DNA-binding protein, uncouples the completion of DNA replication from the activation of cdc2 protein kinase and mitosis. EMBO J. 1991 Jun;10(6):1555–1564. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07675.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtsubo M., Kai R., Furuno N., Sekiguchi T., Sekiguchi M., Hayashida H., Kuma K., Miyata T., Fukushige S., Murotsu T. Isolation and characterization of the active cDNA of the human cell cycle gene (RCC1) involved in the regulation of onset of chromosome condensation. Genes Dev. 1987 Aug;1(6):585–593. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.6.585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtsubo M., Okazaki H., Nishimoto T. The RCC1 protein, a regulator for the onset of chromosome condensation locates in the nucleus and binds to DNA. J Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;109(4 Pt 1):1389–1397. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.4.1389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtsubo M., Yoshida T., Seino H., Nishitani H., Clark K. L., Sprague G. F., Jr, Frasch M., Nishimoto T. Mutation of the hamster cell cycle gene RCC1 is complemented by the homologous genes of Drosophila and S.cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1265–1273. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08068.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRESCOTT D. M., BENDER M. A. Synthesis of RNA and protein during mitosis in mammalian tissue culture cells. Exp Cell Res. 1962 Mar;26:260–268. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(62)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. D., Fink G. R. KAR1, a gene required for function of both intranuclear and extranuclear microtubules in yeast. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):1047–1060. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90712-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth P., Grätz K., Sailer H. Syndrome de Gorlin-Goltz. Swiss Dent. 1991;12(5):37-8, 40-1, 43 passim. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs A. B., Bond M. W., Kornberg R. D. A single gene from yeast for both nuclear and cytoplasmic polyadenylate-binding proteins: domain structure and expression. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):827–835. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90557-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shermoen A. W., O'Farrell P. H. Progression of the cell cycle through mitosis leads to abortion of nascent transcripts. Cell. 1991 Oct 18;67(2):303–310. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90182-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR J. H. Nucleic acid synthesis in relation to the cell division cycle. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Oct 7;90:409–421. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb23259.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vijayraghavan U., Company M., Abelson J. Isolation and characterization of pre-mRNA splicing mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genes Dev. 1989 Aug;3(8):1206–1216. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.8.1206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner J. R. Labeling of RNA and phosphoproteins in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:423–428. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94033-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wintersberger U., Smith P., Letnansky K. Yeast chromatin. Preparation from isolated nuclei, histone composition and transcription capacity. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Feb 15;33(1):123–130. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02663.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xing Y. G., Lawrence J. B. Preservation of specific RNA distribution within the chromatin-depleted nuclear substructure demonstrated by in situ hybridization coupled with biochemical fractionation. J Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;112(6):1055–1063. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.6.1055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeitlin S., Parent A., Silverstein S., Efstratiadis A. Pre-mRNA splicing and the nuclear matrix. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):111–120. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeitlin S., Wilson R. C., Efstratiadis A. Autonomous splicing and complementation of in vivo-assembled spliceosomes. J Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;108(3):765–777. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.3.765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







