Abstract
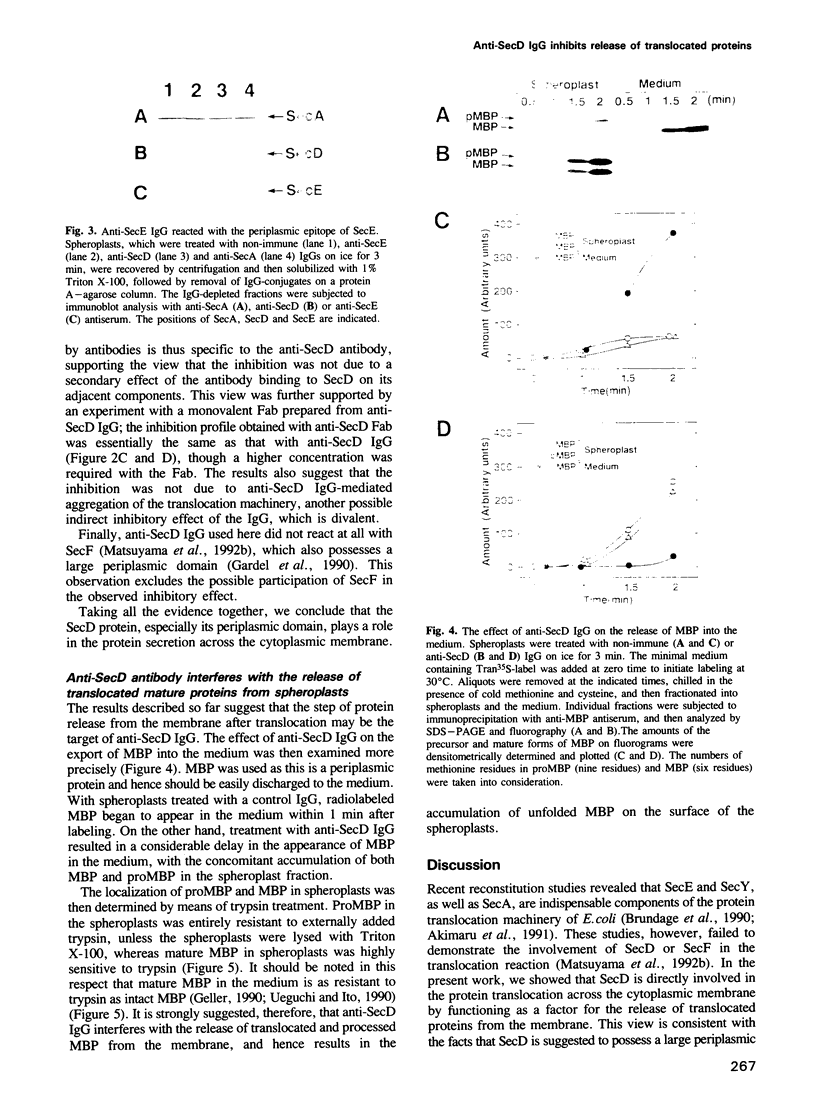
The SecD protein is one of the components that has been suggested from genetic studies to be involved in the protein secretion across the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli. We examined the effect of anti-SecD IgG on protein secretion using spheroplasts. Inhibition of the secretion of OmpA and maltose-binding protein (MBP) by this IgG was observed with concomitant accumulation of their precursor and mature forms in spheroplasts. This effect was specific to anti-SecD IgG. Anti-SecE and anti-SecY IgGs, of which the epitopes are located at the periplasmic domains of SecE and SecY, respectively, did not interfere with the secretion. Time-course experiments investigating the processing of proMBP and the release of MBP from spheroplasts revealed that anti-SecD IgG interfered with the release of the translocated mature MBP. The mature form of MBP thus accumulated was sensitive to trypsin, which was externally added to spheroplasts, whereas MBP released into the medium was resistant to trypsin as the native MBP is. The precursor form of MBP accumulated in spheroplasts was also trypsin resistant. We conclude that SecD is directly involved in protein secretion and important for the release of proteins that have been translocated across the cytoplasmic membrane.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akimaru J., Matsuyama S., Tokuda H., Mizushima S. Reconstitution of a protein translocation system containing purified SecY, SecE, and SecA from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6545–6549. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akita M., Sasaki S., Matsuyama S., Mizushima S. SecA interacts with secretory proteins by recognizing the positive charge at the amino terminus of the signal peptide in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):8164–8169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bardwell J. C., McGovern K., Beckwith J. Identification of a protein required for disulfide bond formation in vivo. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):581–589. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90532-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bieker-Brady K., Silhavy T. J. Suppressor analysis suggests a multistep, cyclic mechanism for protein secretion in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1992 Sep;11(9):3165–3174. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05393.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brundage L., Hendrick J. P., Schiebel E., Driessen A. J., Wickner W. The purified E. coli integral membrane protein SecY/E is sufficient for reconstitution of SecA-dependent precursor protein translocation. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):649–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90111-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabelli R. J., Chen L., Tai P. C., Oliver D. B. SecA protein is required for secretory protein translocation into E. coli membrane vesicles. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):683–692. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90227-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabelli R. J., Dolan K. M., Qian L. P., Oliver D. B. Characterization of membrane-associated and soluble states of SecA protein from wild-type and SecA51(TS) mutant strains of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 25;266(36):24420–24427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J. Transposition and fusion of the lac genes to selected promoters in Escherichia coli using bacteriophage lambda and Mu. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jul 5;104(3):541–555. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90119-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emr S. D., Hanley-Way S., Silhavy T. J. Suppressor mutations that restore export of a protein with a defective signal sequence. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):79–88. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90272-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardel C., Benson S., Hunt J., Michaelis S., Beckwith J. secD, a new gene involved in protein export in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1286–1290. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1286-1290.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardel C., Johnson K., Jacq A., Beckwith J. The secD locus of E.coli codes for two membrane proteins required for protein export. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3209–3216. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07519.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geller B. L. Electrochemical potential releases a membrane-bound secretion intermediate of maltose-binding protein in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):4870–4876. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.4870-4876.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halegoua S., Inouye M. Translocation and assembly of outer membrance proteins of Escherichia coli. Selective accumulation of precursors and novel assembly intermediates caused by phenethyl alcohol. J Mol Biol. 1979 May 5;130(1):39–61. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90551-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrick J. P., Wickner W. SecA protein needs both acidic phospholipids and SecY/E protein for functional high-affinity binding to the Escherichia coli plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 25;266(36):24596–24600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito K., Wittekind M., Nomura M., Shiba K., Yura T., Miura A., Nashimoto H. A temperature-sensitive mutant of E. coli exhibiting slow processing of exported proteins. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):789–797. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90065-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamitani S., Akiyama Y., Ito K. Identification and characterization of an Escherichia coli gene required for the formation of correctly folded alkaline phosphatase, a periplasmic enzyme. EMBO J. 1992 Jan;11(1):57–62. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05027.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawasaki H., Matsuyama S., Sasaki S., Akita M., Mizushima S. SecA protein is directly involved in protein secretion in Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jan 2;242(2):431–434. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80516-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura E., Akita M., Matsuyama S., Mizushima S. Determination of a region in SecA that interacts with presecretory proteins in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6600–6606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumamoto C. A., Beckwith J. Mutations in a new gene, secB, cause defective protein localization in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):253–260. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.253-260.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumamoto C. A. SecB protein: a cytosolic export factor that associates with nascent exported proteins. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1990 Jun;22(3):337–351. doi: 10.1007/BF00763171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lill R., Cunningham K., Brundage L. A., Ito K., Oliver D., Wickner W. SecA protein hydrolyzes ATP and is an essential component of the protein translocation ATPase of Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):961–966. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03458.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lill R., Dowhan W., Wickner W. The ATPase activity of SecA is regulated by acidic phospholipids, SecY, and the leader and mature domains of precursor proteins. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):271–280. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90742-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama S., Akimaru J., Mizushima S. SecE-dependent overproduction of SecY in Escherichia coli. Evidence for interaction between two components of the secretory machinery. FEBS Lett. 1990 Aug 20;269(1):96–100. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81128-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama S., Fujita Y., Mizushima S. Large-scale production of membrane proteins fused to a truncated SecA in Escherichia coli. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 1992 Sep;56(9):1512–1514. doi: 10.1271/bbb.56.1512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama S., Fujita Y., Sagara K., Mizushima S. Overproduction, purification and characterization of SecD and SecF, integral membrane components of the protein translocation machinery of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Jul 13;1122(1):77–84. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(92)90130-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama S., Kimura E., Mizushima S. Complementation of two overlapping fragments of SecA, a protein translocation ATPase of Escherichia coli, allows ATP binding to its amino-terminal region. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 25;265(15):8760–8765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minsky A., Summers R. G., Knowles J. R. Secretion of beta-lactamase into the periplasm of Escherichia coli: evidence for a distinct release step associated with a conformational change. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4180–4184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishiyama K., Kabuyama Y., Akimaru J., Matsuyama S., Tokuda H., Mizushima S. SecY is an indispensable component of the protein secretory machinery of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 May 31;1065(1):89–97. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(91)90015-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver D. B., Beckwith J. E. coli mutant pleiotropically defective in the export of secreted proteins. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):765–772. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90184-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M. J., Gander J. E., Parisi E., Carson J. Mechanism of assembly of the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium. Isolation and characterization of cytoplasmic and outer membrane. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3962–3972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs P. D., Derman A. I., Beckwith J. A mutation affecting the regulation of a secA-lacZ fusion defines a new sec gene. Genetics. 1988 Apr;118(4):571–579. doi: 10.1093/genetics/118.4.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiebel E., Driessen A. J., Hartl F. U., Wickner W. Delta mu H+ and ATP function at different steps of the catalytic cycle of preprotein translocase. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):927–939. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90317-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen K., Nikaido H. In vitro trimerization of OmpF porin secreted by spheroplasts of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):743–747. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinkai A., Mei L. H., Tokuda H., Mizushima S. The conformation of SecA, as revealed by its protease sensitivity, is altered upon interaction with ATP, presecretory proteins, everted membrane vesicles, and phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 25;266(9):5827–5833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stader J., Gansheroff L. J., Silhavy T. J. New suppressors of signal-sequence mutations, prlG, are linked tightly to the secE gene of Escherichia coli. Genes Dev. 1989 Jul;3(7):1045–1052. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.7.1045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuda H., Akimaru J., Matsuyama S., Nishiyama K., Mizushima S. Purification of SecE and reconstitution of SecE-dependent protein translocation activity. FEBS Lett. 1991 Feb 25;279(2):233–236. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80156-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueguchi C., Ito K. Escherichia coli sec mutants accumulate a processed immature form of maltose-binding protein (MBP), a late-phase intermediate in MBP export. J Bacteriol. 1990 Oct;172(10):5643–5649. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.10.5643-5649.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J. B., Ray P. H., Bassford P. J., Jr Purified secB protein of Escherichia coli retards folding and promotes membrane translocation of the maltose-binding protein in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8978–8982. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada H., Matsuyama S., Tokuda H., Mizushima S. A high concentration of SecA allows proton motive force-independent translocation of a model secretory protein into Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18577–18581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]