Abstract
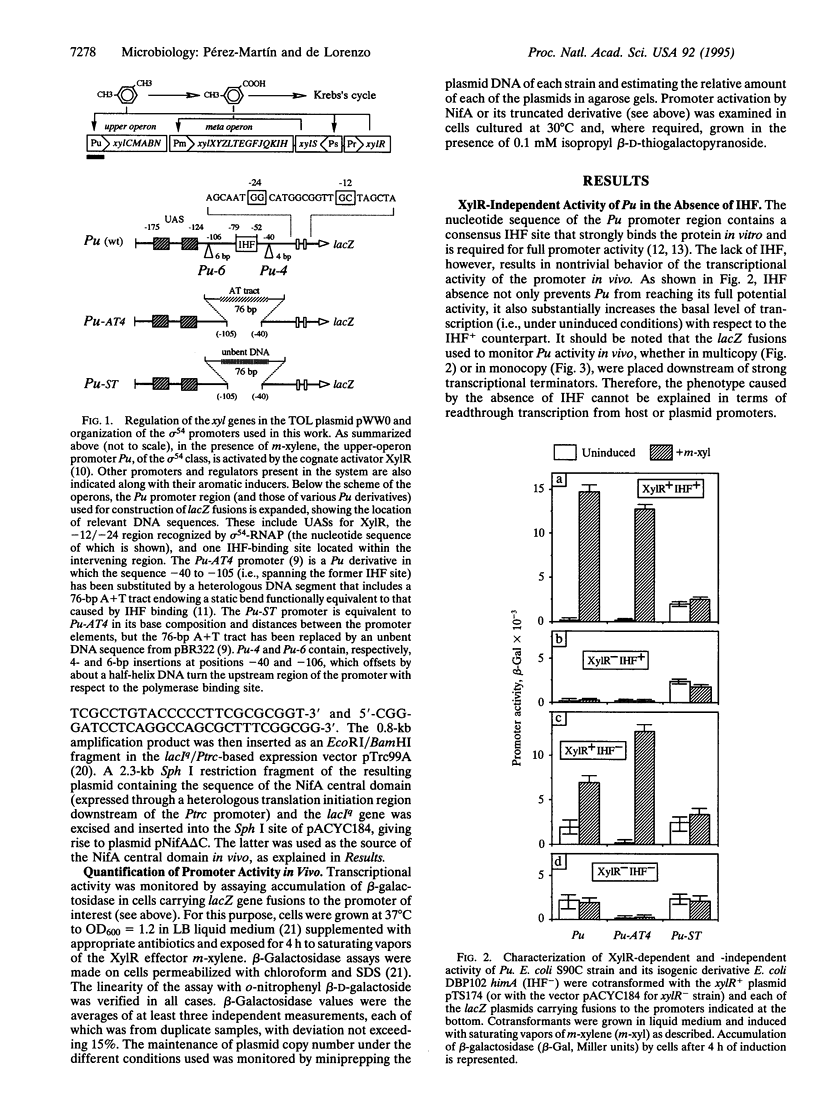
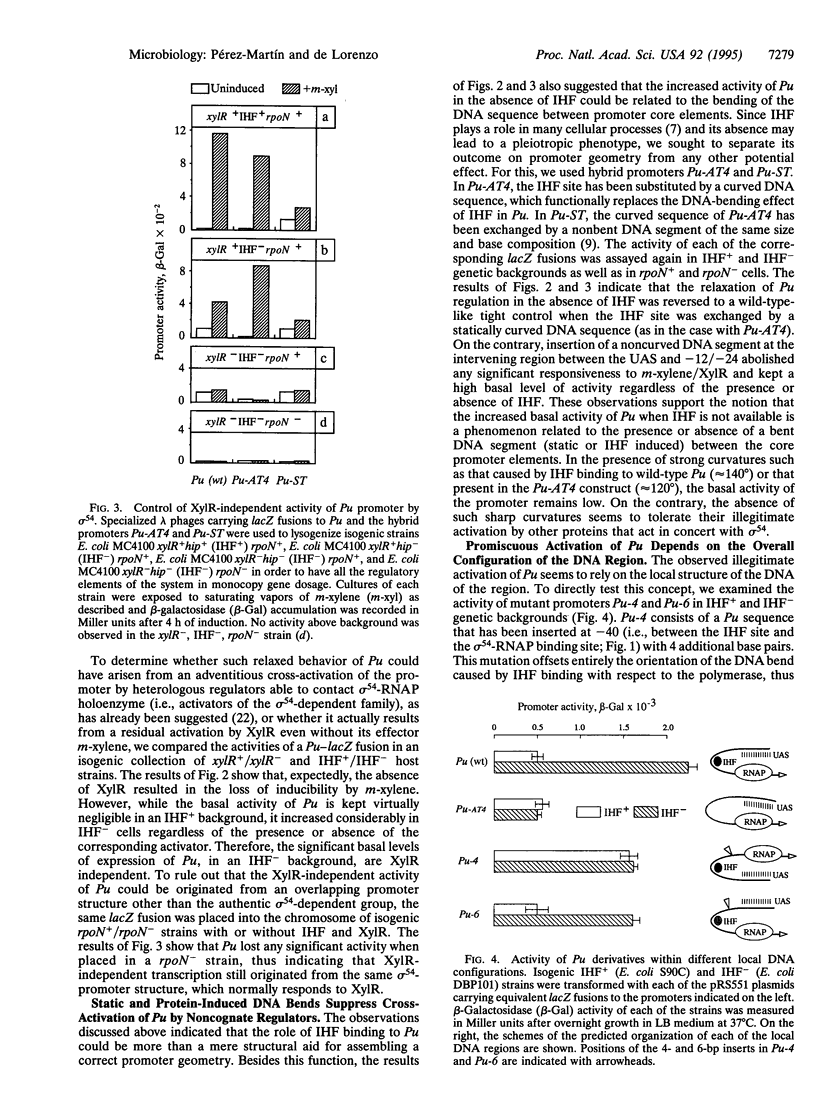
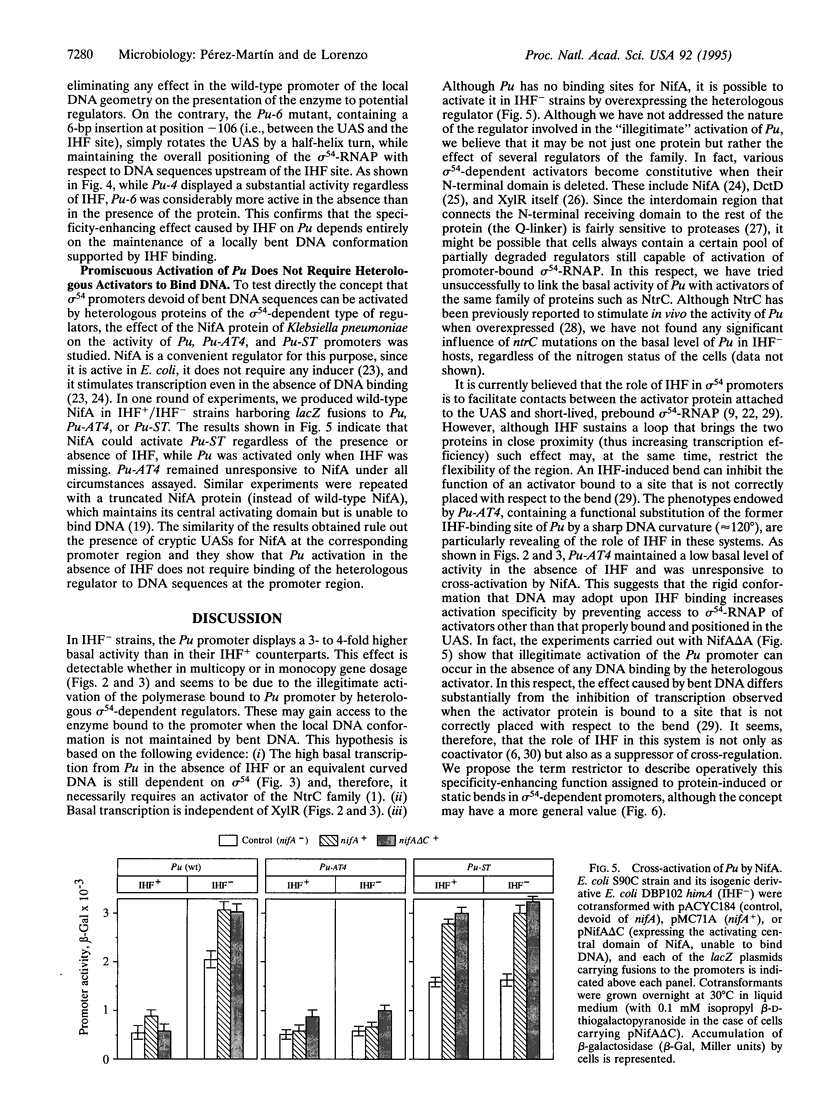
In the presence of m-xylene, the Pu promoter of the TOL plasmid of Pseudomonas putida is activated by the prokaryotic enhancer-binding protein XylR. The intervening DNA segment between the upstream activating sequences (UASs) and those for RNA polymerase binding contains an integration host factor (IHF) attachment site that is required for full transcriptional activity. In the absence of IHF, the Pu promoter can be cross-activated by other members of the sigma 54-dependent family of regulatory proteins. Such illegitimate activation does not require the binding of the heterologous regulators to DNA and it is suppressed by bent DNA structures, either static or protein induced, between the promoter core elements (UAS and RNA polymerase recognition sequence). The role of IHF in some sigma 54 promoters is, therefore, not only a structural aid for assembling a correct promoter geometry but also that of an active suppressor (restrictor) of promiscuous activation by heterologous regulators for increased promoter specificity.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abril M. A., Buck M., Ramos J. L. Activation of the Pseudomonas TOL plasmid upper pathway operon. Identification of binding sites for the positive regulator XylR and for integration host factor protein. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15832–15838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abril M. A., Ramos J. L. Physical organization of the upper pathway operon promoter of the Pseudomonas TOL plasmid. Sequence and positional requirements for XylR-dependent activation of transcription. Mol Gen Genet. 1993 May;239(1-2):281–288. doi: 10.1007/BF00281629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amann E., Ochs B., Abel K. J. Tightly regulated tac promoter vectors useful for the expression of unfused and fused proteins in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1988 Sep 30;69(2):301–315. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90440-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austin S., Buck M., Cannon W., Eydmann T., Dixon R. Purification and in vitro activities of the native nitrogen fixation control proteins NifA and NifL. J Bacteriol. 1994 Jun;176(12):3460–3465. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.12.3460-3465.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger D. K., Narberhaus F., Kustu S. The isolated catalytic domain of NIFA, a bacterial enhancer-binding protein, activates transcription in vitro: activation is inhibited by NIFL. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jan 4;91(1):103–107. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.1.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan-Wollaston V., Cannon M. C., Beynon J. L., Cannon F. C. Role of the nifA gene product in the regulation of nif expression in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Nature. 1981 Dec 24;294(5843):776–778. doi: 10.1038/294776a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler M., Galas D. J. Cointegrate formation mediated by Tn9. II. Activity of IS1 is modulated by external DNA sequences. J Mol Biol. 1983 Oct 15;170(1):61–91. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80227-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claverie-Martin F., Magasanik B. Positive and negative effects of DNA bending on activation of transcription from a distant site. J Mol Biol. 1992 Oct 20;227(4):996–1008. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90516-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. The xylABC promoter from the Pseudomonas putida TOL plasmid is activated by nitrogen regulatory genes in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Apr;203(1):129–136. doi: 10.1007/BF00330393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond M. H., Contreras A., Mitchenall L. A. The function of isolated domains and chimaeric proteins constructed from the transcriptional activators NifA and NtrC of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Jan;4(1):29–37. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb02012.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernández S., de Lorenzo V., Pérez-Martín J. Activation of the transcriptional regulator XylR of Pseudomonas putida by release of repression between functional domains. Mol Microbiol. 1995 Apr;16(2):205–213. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1995.tb02293.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman D. I. Integration host factor: a protein for all reasons. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):545–554. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90213-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartenberg M. R., Crothers D. M. Synthetic DNA bending sequences increase the rate of in vitro transcription initiation at the Escherichia coli lac promoter. J Mol Biol. 1991 May 20;219(2):217–230. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90563-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giladi H., Igarashi K., Ishihama A., Oppenheim A. B. Stimulation of the phage lambda pL promoter by integration host factor requires the carboxy terminus of the alpha-subunit of RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1992 Oct 20;227(4):985–990. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90514-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman S. D., Nicholson S. C., Nash H. A. Deformation of DNA during site-specific recombination of bacteriophage lambda: replacement of IHF protein by HU protein or sequence-directed bends. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):11910–11914. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.11910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins C. F., Hinton J. C., Hulton C. S., Owen-Hughes T., Pavitt G. D., Seirafi A. Protein H1: a role for chromatin structure in the regulation of bacterial gene expression and virulence? Mol Microbiol. 1990 Dec;4(12):2007–2012. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00559.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoover T. R., Santero E., Porter S., Kustu S. The integration host factor stimulates interaction of RNA polymerase with NIFA, the transcriptional activator for nitrogen fixation operons. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):11–22. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90284-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huala E., Ausubel F. M. The central domain of Rhizobium meliloti NifA is sufficient to activate transcription from the R. meliloti nifH promoter. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jun;171(6):3354–3365. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.3354-3365.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huala E., Stigter J., Ausubel F. M. The central domain of Rhizobium leguminosarum DctD functions independently to activate transcription. J Bacteriol. 1992 Feb;174(4):1428–1431. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.4.1428-1431.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S., Nakazawa A., Nakazawa T. Molecular cloning of regulatory gene xylR and operator-promoter regions of the xylABC and xylDEGF operons of the TOL plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1983 Sep;155(3):1192–1199. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.3.1192-1199.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kustu S., North A. K., Weiss D. S. Prokaryotic transcriptional enhancers and enhancer-binding proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Nov;16(11):397–402. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90163-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marqués S., Ramos J. L. Transcriptional control of the Pseudomonas putida TOL plasmid catabolic pathways. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Sep;9(5):923–929. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01222.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninfa A. J., Reitzer L. J., Magasanik B. Initiation of transcription at the bacterial glnAp2 promoter by purified E. coli components is facilitated by enhancers. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1039–1046. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90170-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North A. K., Klose K. E., Stedman K. M., Kustu S. Prokaryotic enhancer-binding proteins reflect eukaryote-like modularity: the puzzle of nitrogen regulatory protein C. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jul;175(14):4267–4273. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.14.4267-4273.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Martín J., Rojo F., de Lorenzo V. Promoters responsive to DNA bending: a common theme in prokaryotic gene expression. Microbiol Rev. 1994 Jun;58(2):268–290. doi: 10.1128/mr.58.2.268-290.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Martín J., Timmis K. N., de Lorenzo V. Co-regulation by bent DNA. Functional substitutions of the integration host factor site at sigma 54-dependent promoter Pu of the upper-TOL operon by intrinsically curved sequences. J Biol Chem. 1994 Sep 9;269(36):22657–22662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitzer L. J., Magasanik B. Transcription of glnA in E. coli is stimulated by activator bound to sites far from the promoter. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):785–792. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90553-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richet E., Vidal-Ingigliardi D., Raibaud O. A new mechanism for coactivation of transcription initiation: repositioning of an activator triggered by the binding of a second activator. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1185–1195. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90041-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santero E., Hoover T. R., North A. K., Berger D. K., Porter S. C., Kustu S. Role of integration host factor in stimulating transcription from the sigma 54-dependent nifH promoter. J Mol Biol. 1992 Oct 5;227(3):602–620. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90211-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons R. W., Houman F., Kleckner N. Improved single and multicopy lac-based cloning vectors for protein and operon fusions. Gene. 1987;53(1):85–96. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90095-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su W., Porter S., Kustu S., Echols H. DNA-looping and enhancer activity: association between DNA-bound NtrC activator and RNA polymerase at the bacterial glnA promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5504–5508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wootton J. C., Drummond M. H. The Q-linker: a class of interdomain sequences found in bacterial multidomain regulatory proteins. Protein Eng. 1989 May;2(7):535–543. doi: 10.1093/protein/2.7.535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuber F., Kotlarz D., Rimsky S., Buc H. Modulated expression of promoters containing upstream curved DNA sequences by the Escherichia coli nucleoid protein H-NS. Mol Microbiol. 1994 Apr;12(2):231–240. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb01012.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Lorenzo V., Herrero M., Metzke M., Timmis K. N. An upstream XylR- and IHF-induced nucleoprotein complex regulates the sigma 54-dependent Pu promoter of TOL plasmid. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1159–1167. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08056.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]