Abstract
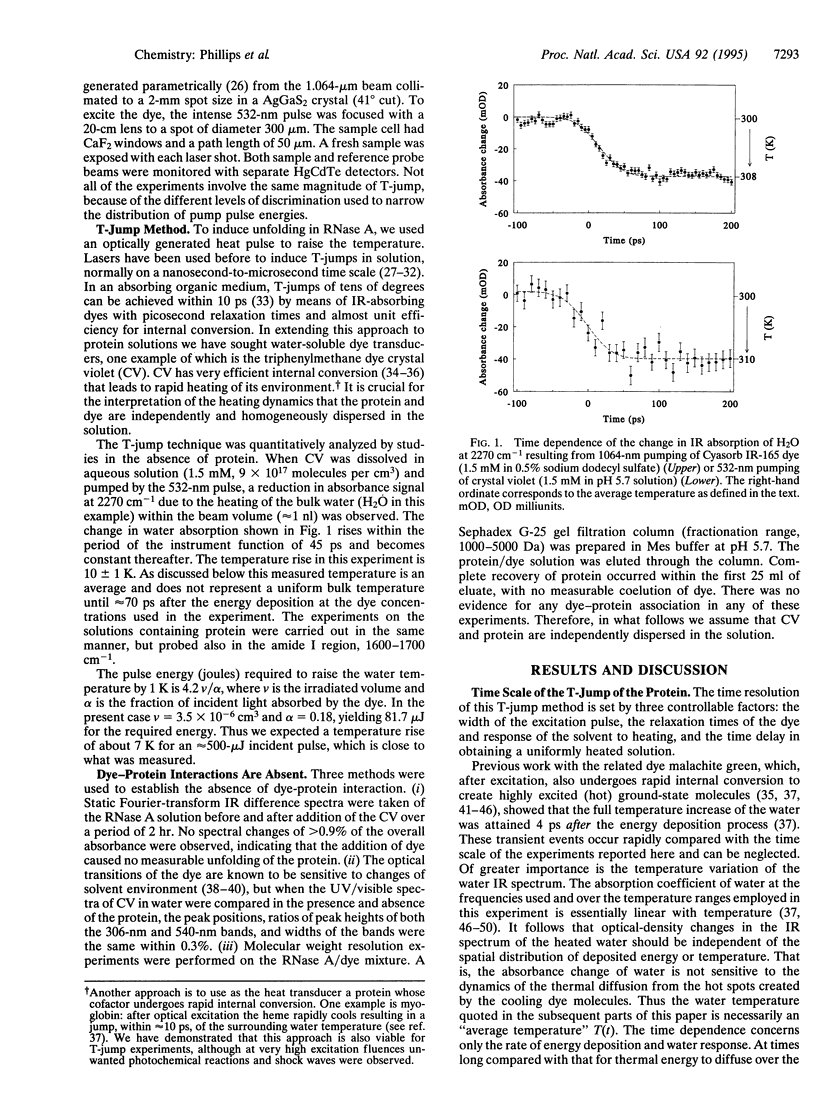
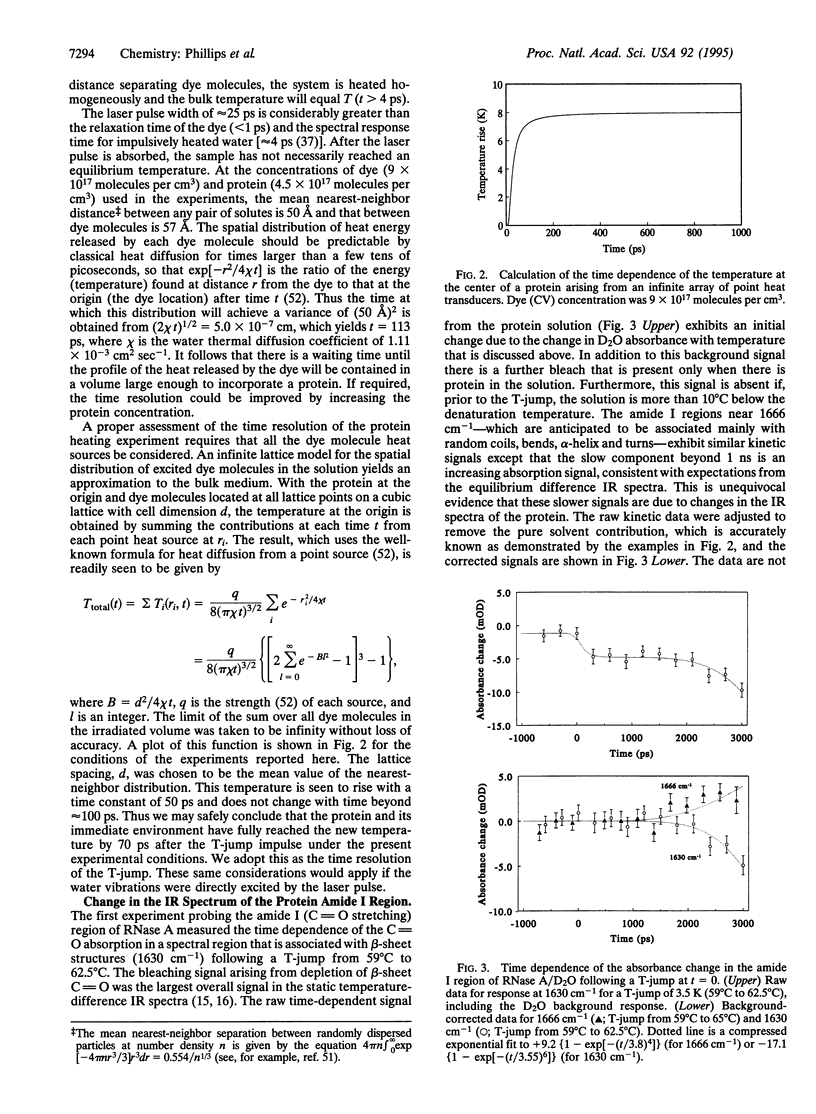
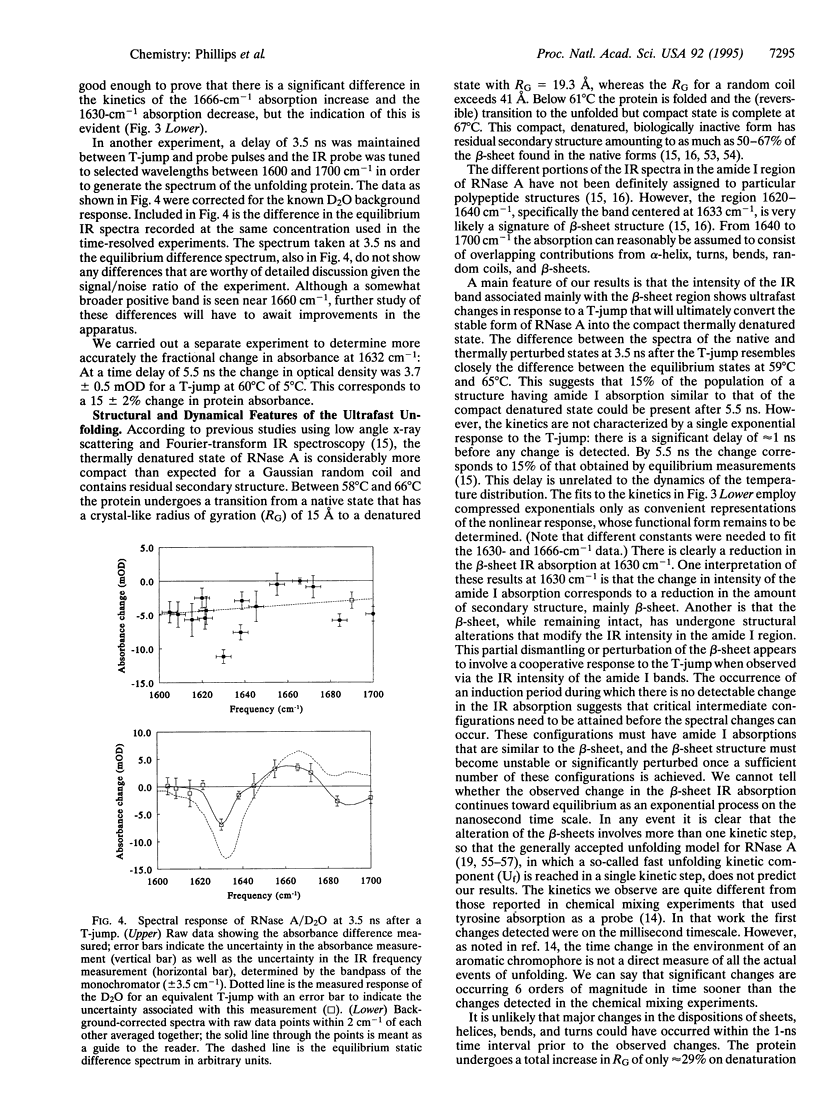
A temperature jump (T-jump) method capable of initiating thermally induced processes on the picosecond time scale in aqueous solutions is introduced. Protein solutions are heated by energy from a laser pulse that is absorbed by homogeneously dispersed molecules of the dye crystal violet. These act as transducers by releasing the energy as heat to cause a T-jump of up to 10 K with a time resolution of 70 ps. The method was applied to the unfolding of RNase A. At pH 5.7 and 59 degrees C, a T-jump of 3-6 K induced unfolding which was detected by picosecond transient infrared spectroscopy of the amide I region between 1600 and 1700 cm-1. The difference spectral profile at 3.5 ns closely resembled that found for the equilibrium (native-unfolded) states. The signal at 1633 cm-1, corresponding to the beta-sheet structure, achieved 15 +/- 2% of the decrease found at equilibrium, within 5.5 ns. However, no decrease in absorbance was detected until 1 ns after the T-ump. The disruption of beta-sheet therefore appears to be subject to a delay of approximately 1 ns. Prior to 1 ns after the T-jump, water might be accessing the intact hydrophobic regions.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akasaka K., Naito A., Nakatani H. Temperature-jump NMR study of protein folding: ribonuclease A at low pH. J Biomol NMR. 1991 May;1(1):65–70. doi: 10.1007/BF01874569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anfinrud P. A., Han C., Hochstrasser R. M. Direct observations of ligand dynamics in hemoglobin by subpicosecond infrared spectroscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8387–8391. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caflisch A., Karplus M. Molecular dynamics simulation of protein denaturation: solvation of the hydrophobic cores and secondary structure of barnase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 1;91(5):1746–1750. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.5.1746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen M. C., Lord R. C. Laser Raman spectroscopic studies of the thermal unfolding of ribonuclease A. Biochemistry. 1976 May 4;15(9):1889–1897. doi: 10.1021/bi00654a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Englander S. W., Mayne L. Protein folding studied using hydrogen-exchange labeling and two-dimensional NMR. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1992;21:243–265. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.21.060192.001331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink A. L., Painter B. Characterization of the unfolding of ribonuclease A in aqueous methanol solvents. Biochemistry. 1987 Mar 24;26(6):1665–1671. doi: 10.1021/bi00380a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman K. A., Jr The structure of water and the stability of the secondary structure in biological molecules. An infrared and proton magnetic resonance study. J Phys Chem. 1966 Jan;70(1):270–276. doi: 10.1021/j100873a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houry W. A., Rothwarf D. M., Scheraga H. A. A very fast phase in the refolding of disulfide-intact ribonuclease A: implications for the refolding and unfolding pathways. Biochemistry. 1994 Mar 8;33(9):2516–2530. doi: 10.1021/bi00175a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W. C., Jr Secondary structure of proteins through circular dichroism spectroscopy. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1988;17:145–166. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.17.060188.001045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. M., Henry E. R., Hu Y., Chan C. K., Luck S. D., Bhuyan A., Roder H., Hofrichter J., Eaton W. A. Fast events in protein folding initiated by nanosecond laser photolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 15;90(24):11860–11864. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.24.11860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kereiakes D. J., Ports T. A., Botvinick E. H., Schiller N. B., Turley K., Chatterjee K. Right ventricular myocardial infarction with ventricular septal rupture. Am Heart J. 1984 Jun;107(6):1257–1259. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(84)90286-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim P. S., Baldwin R. L. Intermediates in the folding reactions of small proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:631–660. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krimm S., Bandekar J. Vibrational spectroscopy and conformation of peptides, polypeptides, and proteins. Adv Protein Chem. 1986;38:181–364. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60528-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loncharich R. J., Brooks B. R. Temperature dependence of dynamics of hydrated myoglobin. Comparison of force field calculations with neutron scattering data. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):439–455. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(05)80363-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lustig B., Fink A. L. The thermal denaturation of ribonuclease A in aqueous-methanol solvents. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Feb 26;1119(2):205–210. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(92)90393-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayo S. L., Baldwin R. L. Guanidinium chloride induction of partial unfolding in amide proton exchange in RNase A. Science. 1993 Nov 5;262(5135):873–876. doi: 10.1126/science.8235609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nall B. T., Garel J. R., Baldwin R. L. Test of the extended two-state model for the kinetic intermediates observed in the folding transition of ribonuclease A. J Mol Biol. 1978 Jan 25;118(3):317–330. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90231-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Privalov P. L., Tiktopulo E. I., Venyaminov SYu, Griko YuV, Makhatadze G. I., Khechinashvili N. N. Heat capacity and conformation of proteins in the denatured state. J Mol Biol. 1989 Feb 20;205(4):737–750. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90318-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson A. D., Baldwin R. L. Hydrogen exchange in thermally denatured ribonuclease A. Biochemistry. 1991 Oct 15;30(41):9907–9914. doi: 10.1021/bi00105a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sali A., Shakhnovich E., Karplus M. How does a protein fold? Nature. 1994 May 19;369(6477):248–251. doi: 10.1038/369248a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid F. X., Baldwin R. L. The rate of interconversion between the two unfolded forms of ribonuclease A does not depend on guanidinium chloride concentration. J Mol Biol. 1979 Sep 15;133(2):285–287. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90536-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid F. X. Mechanism of folding of ribonuclease A. Slow refolding is a sequential reaction via structural intermediates. Biochemistry. 1983 Sep 27;22(20):4690–4696. doi: 10.1021/bi00289a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholtz J. M., Baldwin R. L. Perchlorate-induced denaturation of ribonuclease A: investigation of possible folding intermediates. Biochemistry. 1993 May 4;32(17):4604–4608. doi: 10.1021/bi00068a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seshadri S., Oberg K. A., Fink A. L. Thermally denatured ribonuclease A retains secondary structure as shown by FTIR. Biochemistry. 1994 Feb 15;33(6):1351–1355. doi: 10.1021/bi00172a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnick J., Kolinski A., Godzik A. From independent modules to molten globules: observations on the nature of protein folding intermediates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2099–2100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soman K. V., Karimi A., Case D. A. Molecular dynamics analysis of a ribonuclease C-peptide analogue. Biopolymers. 1993 Oct;33(10):1567–1580. doi: 10.1002/bip.360331007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sosnick T. R., Trewhella J. Denatured states of ribonuclease A have compact dimensions and residual secondary structure. Biochemistry. 1992 Sep 8;31(35):8329–8335. doi: 10.1021/bi00150a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tirado-Rives J., Jorgensen W. L. Molecular dynamics simulations of the unfolding of an alpha-helical analogue of ribonuclease A S-peptide in water. Biochemistry. 1991 Apr 23;30(16):3864–3871. doi: 10.1021/bi00230a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udgaonkar J. B., Baldwin R. L. Early folding intermediate of ribonuclease A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8197–8201. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udgaonkar J. B., Baldwin R. L. NMR evidence for an early framework intermediate on the folding pathway of ribonuclease A. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):694–699. doi: 10.1038/335694a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


