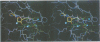Abstract
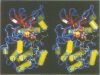
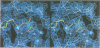
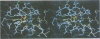
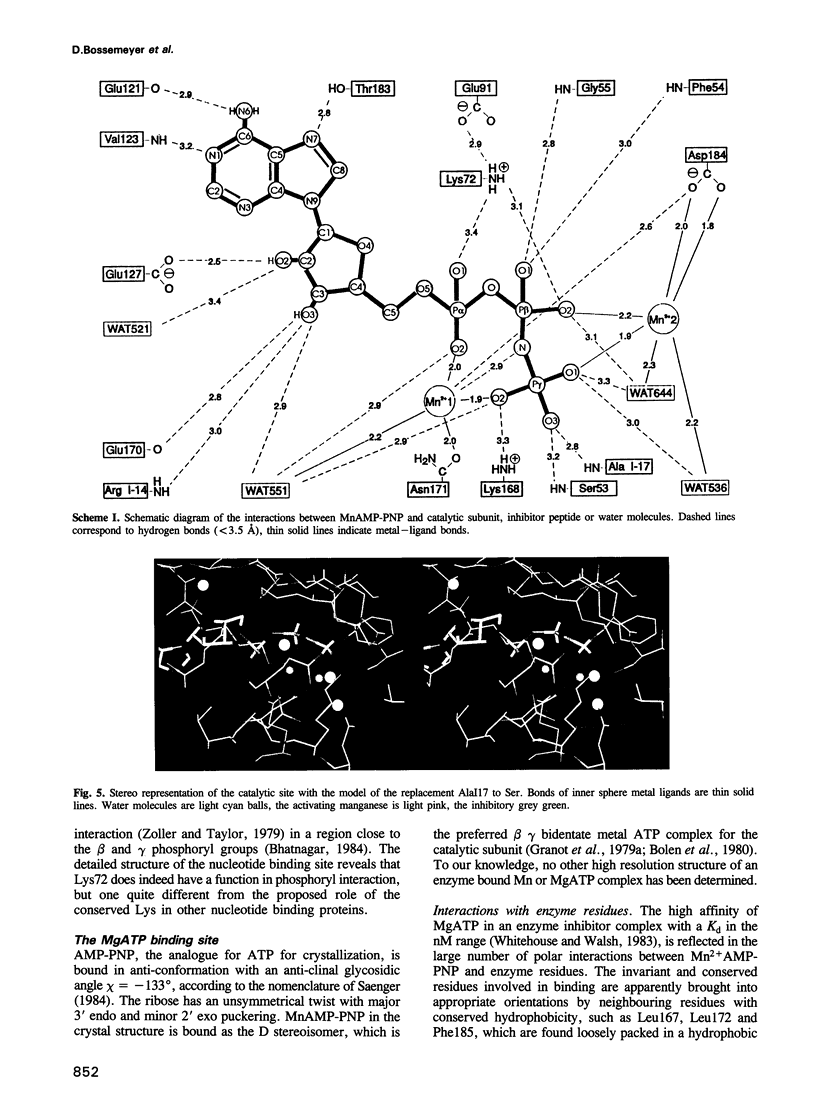
The crystal structure of the porcine heart catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase in a ternary complex with the MgATP analogue MnAMP-PNP and a pseudosubstrate inhibitor peptide, PKI(5-24), has been solved at 2.0 A resolution from monoclinic crystals of the catalytic subunit isoform CA. The refinement is presently at an R factor of 0.194 and the active site of the molecule is well defined. The glycine-rich phosphate anchor of the nucleotide binding fold motif of the protein kinase is a beta ribbon acting as a flap with conformational flexibility over the triphosphate group. The glycines seem to be conserved to avoid steric clash with ATP. The known synergistic effects of substrate binding can be explained by hydrogen bonds present only in the ternary complex. Implications for the kinetic scheme of binding order are discussed. The structure is assumed to represent a phosphotransfer competent conformation. The invariant conserved residue Asp166 is proposed to be the catalytic base and Lys168 to stabilize the transition state. In some tyrosine kinases Lys168 is functionally replaced by an Arg displaced by two residues in the primary sequence, suggesting invariance in three-dimensional space. The structure supports an in-line transfer with a pentacoordinate transition state at the phosphorus with very few nuclear movements.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams J. A., Taylor S. S. Energetic limits of phosphotransfer in the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase as measured by viscosity experiments. Biochemistry. 1992 Sep 15;31(36):8516–8522. doi: 10.1021/bi00151a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adavani S. R., Schwarz M., Showers M. O., Maurer R. A., Hemmings B. A. Multiple mRNA species code for the catalytic subunit of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase from LLC-PK1 cells. Evidence for two forms of the catalytic subunit. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Sep 1;167(2):221–226. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13326.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong R. N., Kondo H., Granot J., Kaiser E. T., Mildvan A. S. Magnetic resonance and kinetic studies of the manganese(II) ion and substrate complexes of the catalytic subunit of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate dependent protein kinase from bovine heart. Biochemistry. 1979 Apr 3;18(7):1230–1238. doi: 10.1021/bi00574a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong R. N., Kondo H., Kaiser E. T. Cyclic AMP-dependent ATPase activity of bovine heart protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):722–725. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benner S. A., Gerloff D. Patterns of divergence in homologous proteins as indicators of secondary and tertiary structure: a prediction of the structure of the catalytic domain of protein kinases. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1991;31:121–181. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(91)90012-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett W. S., Huber R. Structural and functional aspects of domain motions in proteins. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1984;15(4):291–384. doi: 10.3109/10409238409117796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhatnagar D., Hartl F. T., Roskoski R., Jr, Lessor R. A., Leonard N. J. Adenosine cyclic 3',5'-monophosphate dependent protein kinase: nucleotide binding to the chemically modified catalytic subunit. Biochemistry. 1984 Sep 11;23(19):4350–4357. doi: 10.1021/bi00314a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolen D. W., Stingelin J., Bramson H. N., Kaiser E. T. Stereochemical and kinetic studies on the action of the catalytic subunit of bovine cardiac muscle adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate dependent protein kinase using metal ion complexes of ATP beta S. Biochemistry. 1980 Mar 18;19(6):1176–1182. doi: 10.1021/bi00547a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bramson H. N., Kaiser E. T., Mildvan A. S. Mechanistic studies of cAMP-dependent protein kinase action. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1984;15(2):93–124. doi: 10.3109/10409238409102298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner S. Phosphotransferase sequence homology. Nature. 1987 Sep 3;329(6134):21–21. doi: 10.1038/329021a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brünger A. T. Crystallographic refinement by simulated annealing. Application to a 2.8 A resolution structure of aspartate aminotransferase. J Mol Biol. 1988 Oct 5;203(3):803–816. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90211-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buechler J. A., Taylor S. S. Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide cross-links two conserved residues, Asp-184 and Lys-72, at the active site of the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Biochemistry. 1989 Mar 7;28(5):2065–2070. doi: 10.1021/bi00431a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buechler J. A., Taylor S. S. Identification of aspartate-184 as an essential residue in the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Biochemistry. 1988 Sep 20;27(19):7356–7361. doi: 10.1021/bi00419a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buechler J. A., Vedvick T. A., Taylor S. S. Differential labeling of the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase with acetic anhydride: substrate-induced conformational changes. Biochemistry. 1989 Apr 4;28(7):3018–3024. doi: 10.1021/bi00433a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng H. C., Kemp B. E., Pearson R. B., Smith A. J., Misconi L., Van Patten S. M., Walsh D. A. A potent synthetic peptide inhibitor of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):989–992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrivia J. C., Uhler M. D., McKnight G. S. Characterization of genomic clones coding for the C alpha and C beta subunits of mouse cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5739–5744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg C. H., Ran W., Uhler M. D., McKnight G. S. A mutation in the catalytic subunit of protein kinase A prevents myristylation but does not inhibit biological activity. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 25;264(33):20140–20146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook P. F., Neville M. E., Jr, Vrana K. E., Hartl F. T., Roskoski R., Jr Adenosine cyclic 3',5'-monophosphate dependent protein kinase: kinetic mechanism for the bovine skeletal muscle catalytic subunit. Biochemistry. 1982 Nov 9;21(23):5794–5799. doi: 10.1021/bi00266a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreusicke D., Schulz G. E. The glycine-rich loop of adenylate kinase forms a giant anion hole. FEBS Lett. 1986 Nov 24;208(2):301–304. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81037-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs C. S., Knighton D. R., Sowadski J. M., Taylor S. S., Zoller M. J. Systematic mutational analysis of cAMP-dependent protein kinase identifies unregulated catalytic subunits and defines regions important for the recognition of the regulatory subunit. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 5;267(7):4806–4814. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs C. S., Zoller M. J. Identification of electrostatic interactions that determine the phosphorylation site specificity of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Biochemistry. 1991 Jun 4;30(22):5329–5334. doi: 10.1021/bi00236a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs C. S., Zoller M. J. Rational scanning mutagenesis of a protein kinase identifies functional regions involved in catalysis and substrate interactions. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):8923–8931. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass D. B., Cheng H. C., Mende-Mueller L., Reed J., Walsh D. A. Primary structural determinants essential for potent inhibition of cAMP-dependent protein kinase by inhibitory peptides corresponding to the active portion of the heat-stable inhibitor protein. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8802–8810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granot J., Kondo H., Armstrong R. N., Mildvan A. S., Kaiser E. T. Nuclear magnetic resonance studies of the conformation of tetraamminecobalt (III)--ATP bound at the active site of bovine heart protein kinase. Biochemistry. 1979 May 29;18(11):2339–2345. doi: 10.1021/bi00578a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granot J., Mildvan A. S., Bramson H. N., Kaiser E. T. Magnetic resonance measurements of intersubstrate distances at the active site of protein kinase using substitution-inert cobalt(III) and chromium(III) complexes of adenosine 5'-(beta, gamma-methylenetriphosphate). Biochemistry. 1980 Jul 22;19(15):3537–3543. doi: 10.1021/bi00556a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granot J., Mildvan A. S., Bramson H. N., Thomas N., Kaiser E. T. Nuclear magnetic resonance studies of the conformation and kinetics of the peptide-substrate at the active site of bovine heart protein kinase. Biochemistry. 1981 Feb 3;20(3):602–610. doi: 10.1021/bi00506a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granot J., Mildvan A. S., Brown E. M., Kondo H., Bramson H. N., Kaiser E. T. Specificity of bovine heart protein kinase for the delta-stereoisomer of the metal--ATP complex. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jul 15;103(2):265–269. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81342-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):42–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3291115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M. Protein kinase catalytic domain sequence database: identification of conserved features of primary structure and classification of family members. Methods Enzymol. 1991;200:38–62. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)00126-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hotz A., König N., Taniguchi H., Chrivia J. C., Kinzel V. Catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase from bovine heart: several isoforms demonstrated by high resolution focusing in immobilized pH gradient. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Apr 28;160(2):596–601. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92474-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T. Protein kinase classification. Methods Enzymol. 1991;200:3–37. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)00125-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. R., Cox A. D., Solski P. A., Devadas B., Adams S. P., Leimgruber R. M., Heuckeroth R. O., Buss J. E., Gordon J. I. Functional analysis of protein N-myristoylation: metabolic labeling studies using three oxygen-substituted analogs of myristic acid and cultured mammalian cells provide evidence for protein-sequence-specific incorporation and analog-specific redistribution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8511–8515. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. A., Zou J. Y., Cowan S. W., Kjeldgaard M. Improved methods for building protein models in electron density maps and the location of errors in these models. Acta Crystallogr A. 1991 Mar 1;47(Pt 2):110–119. doi: 10.1107/s0108767390010224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KREBS E. G., FISCHER E. H. The phosphorylase b to a converting enzyme of rabbit skeletal muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1956 Apr;20(1):150–157. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(56)90273-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabsch W., Mannherz H. G., Suck D., Pai E. F., Holmes K. C. Atomic structure of the actin:DNase I complex. Nature. 1990 Sep 6;347(6288):37–44. doi: 10.1038/347037a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabsch W., Sander C. Dictionary of protein secondary structure: pattern recognition of hydrogen-bonded and geometrical features. Biopolymers. 1983 Dec;22(12):2577–2637. doi: 10.1002/bip.360221211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Sefton B. M. Neither arginine nor histidine can carry out the function of lysine-295 in the ATP-binding site of p60src. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;6(3):751–757. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.3.751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp B. E., Graves D. J., Benjamini E., Krebs E. G. Role of multiple basic residues in determining the substrate specificity of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 25;252(14):4888–4894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knighton D. R., Zheng J. H., Ten Eyck L. F., Ashford V. A., Xuong N. H., Taylor S. S., Sowadski J. M. Crystal structure of the catalytic subunit of cyclic adenosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. Science. 1991 Jul 26;253(5018):407–414. doi: 10.1126/science.1862342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knighton D. R., Zheng J. H., Ten Eyck L. F., Xuong N. H., Taylor S. S., Sowadski J. M. Structure of a peptide inhibitor bound to the catalytic subunit of cyclic adenosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. Science. 1991 Jul 26;253(5018):414–420. doi: 10.1126/science.1862343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kong C. T., Cook P. F. Isotope partitioning in the adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate dependent protein kinase reaction indicates a steady-state random kinetic mechanism. Biochemistry. 1988 Jun 28;27(13):4795–4799. doi: 10.1021/bi00413a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letwin K., Mizzen L., Motro B., Ben-David Y., Bernstein A., Pawson T. A mammalian dual specificity protein kinase, Nek1, is related to the NIMA cell cycle regulator and highly expressed in meiotic germ cells. EMBO J. 1992 Oct;11(10):3521–3531. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05435.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin L. R., Zoller M. J. Association of catalytic and regulatory subunits of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase requires a negatively charged side group at a conserved threonine. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):1066–1075. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.1066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moll G. W., Jr, Kaiser E. T. Phosphorylation of histone catalyzed by a bovine brain protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jul 10;251(13):3993–4000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai E. F., Krengel U., Petsko G. A., Goody R. S., Kabsch W., Wittinghofer A. Refined crystal structure of the triphosphate conformation of H-ras p21 at 1.35 A resolution: implications for the mechanism of GTP hydrolysis. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2351–2359. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07409.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. B., Kemp B. E. Protein kinase phosphorylation site sequences and consensus specificity motifs: tabulations. Methods Enzymol. 1991;200:62–81. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)00127-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters K. A., Demaille J. G., Fischer E. H. Adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate dependent protein kinase from bovine heart. Characterization of the catalytic subunit. Biochemistry. 1977 Dec 27;16(26):5691–5697. doi: 10.1021/bi00645a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponder J. W., Richards F. M. Tertiary templates for proteins. Use of packing criteria in the enumeration of allowed sequences for different structural classes. J Mol Biol. 1987 Feb 20;193(4):775–791. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90358-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J., De Ropp J. S., Trewhella J., Glass D. B., Liddle W. K., Bradbury E. M., Kinzel V., Walsh D. A. Conformational analysis of PKI(5-22)amide, the active inhibitory fragment of the inhibitor protein of the cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. Biochem J. 1989 Dec 1;264(2):371–380. doi: 10.1042/bj2640371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J., Kinzel V., Cheng H. C., Walsh D. A. Circular dichroic investigations of secondary structure in synthetic peptide inhibitors of cAMP-dependent protein kinase: a model for inhibitory potential. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 1;26(24):7641–7647. doi: 10.1021/bi00398a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J., Kinzel V., Kemp B. E., Cheng H. C., Walsh D. A. Circular dichroic evidence for an ordered sequence of ligand/binding site interactions in the catalytic reaction of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Biochemistry. 1985 Jun 4;24(12):2967–2973. doi: 10.1021/bi00333a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J., Kinzel V. Ligand binding site interaction in adenosine cyclic 3',5'-monophosphate dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit: circular dichroic evidence for intramolecular transmission of conformational change. Biochemistry. 1984 Feb 28;23(5):968–973. doi: 10.1021/bi00300a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J., Kinzel V. Near- and far-ultraviolet circular dichroism of the catalytic subunit of adenosine cyclic 5'-monophosphate dependent protein kinase. Biochemistry. 1984 Mar 27;23(7):1357–1362. doi: 10.1021/bi00302a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringheim G. E., Taylor S. S. Dissecting the domain structure of the regulatory subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase I and elucidating the role of MgATP. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 25;265(9):4800–4808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salerno A., Mendelow M., Prorok M., Lawrence D. S. Noncovalent active site interactions enhance the affinity and control the binding order of reversible inhibitors of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 25;265(30):18079–18082. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. D., Glaccum M. B., Fischer E. H., Krebs E. G. Primary-structure requirements for inhibition by the heat-stable inhibitor of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1613–1616. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirakihara Y., Evans P. R. Crystal structure of the complex of phosphofructokinase from Escherichia coli with its reaction products. J Mol Biol. 1988 Dec 20;204(4):973–994. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90056-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoji S., Titani K., Demaille J. G., Fischer E. H. Sequence of two phosphorylated sites in the catalytic subunit of bovine cardiac muscle adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 25;254(14):6211–6214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. S. Sarcoplasmic reticulum ATPase catalyzes hydrolysis of adenyl-5'-yl imidodiphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 10;256(19):9793–9795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelen M., Rosen A., Nairn A. C., Aderem A. Regulation by phosphorylation of reversible association of a myristoylated protein kinase C substrate with the plasma membrane. Nature. 1991 May 23;351(6324):320–322. doi: 10.1038/351320a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas N. E., Bramson H. N., Miller W. T., Kaiser E. T. Role of enzyme-peptide substrate backbone hydrogen bonding in determining protein kinase substrate specificities. Biochemistry. 1987 Jul 14;26(14):4461–4466. doi: 10.1021/bi00388a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90801-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Patten S. M., Fletcher W. H., Walsh D. A. The inhibitor protein of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase-catalytic subunit interaction. Parameters of complex formation. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 25;261(12):5514–5523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh D. A., Perkins J. P., Krebs E. G. An adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependant protein kinase from rabbit skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jul 10;243(13):3763–3765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehouse S., Feramisco J. R., Casnellie J. E., Krebs E. G., Walsh D. A. Studies on the kinetic mechanism of the catalytic subunit of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3693–3701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehouse S., Walsh D. A. Mg X ATP2-dependent interaction of the inhibitor protein of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase with the catalytic subunit. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3682–3692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoon M. Y., Cook P. F. Chemical mechanism of the adenosine cyclic 3',5'-monophosphate dependent protein kinase from pH studies. Biochemistry. 1987 Jun 30;26(13):4118–4125. doi: 10.1021/bi00387a056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Taylor S. S. Affinity labeling of the nucleotide binding site of the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase using p-fluorosulfonyl-[14C]benzoyl 5'-adenosine. Identification of a modified lysine residue. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8363–8368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]