Abstract
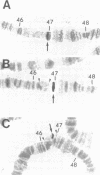
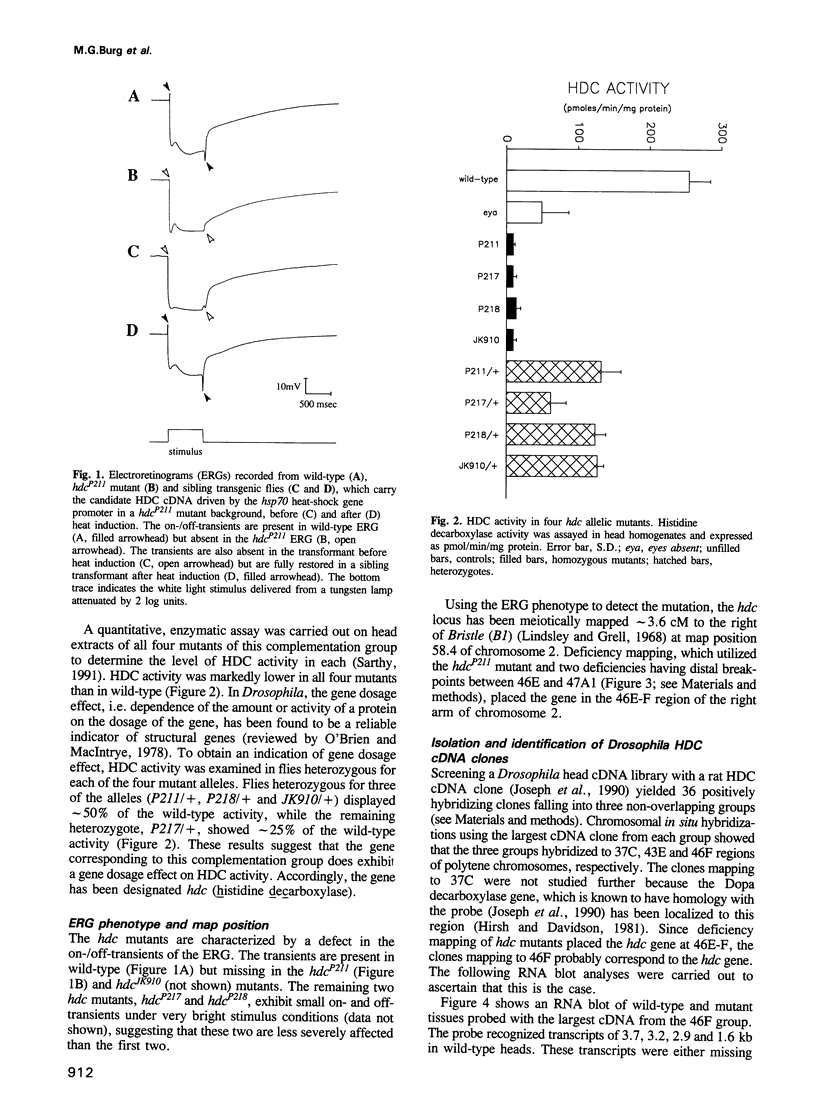
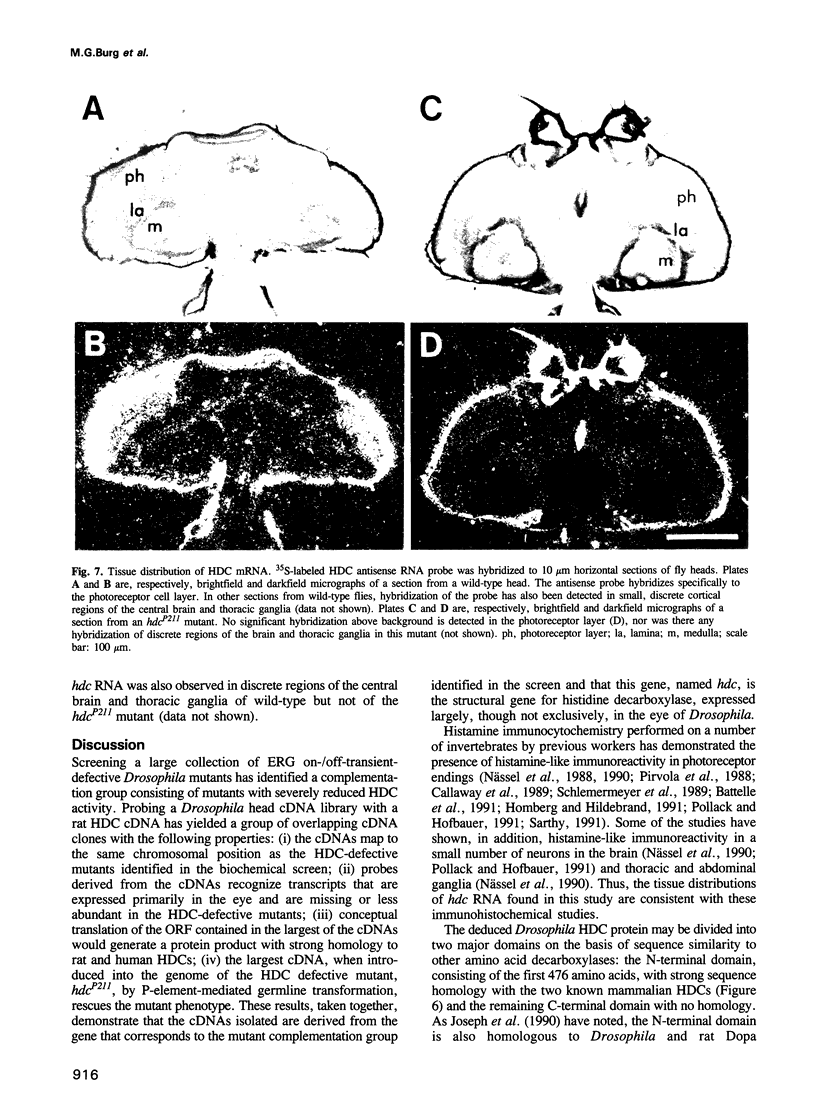
Drosophila mutants of a single complementation group with defective on-/off-transients of the electroretinogram (ERG) were found to be deficient in synthesis of the photoreceptor transmitter, histamine, in a gene-dosage dependent manner, suggesting that the gene identified by the mutants (hdc) might be the structural gene for Drosophila histidine decarboxylase (HDC). A rat HDC cDNA was used to isolate a Drosophila homolog which shows approximately 60% sequence identity with mammalian HDCs over a region of 476 amino acids. In RNA blots, the Drosophila homolog detects four transcripts that are expressed primarily in the eye and are severely reduced in hdc mutants. The cloned Drosophila cDNA hybridizes to the 46F region of the chromosome, to which hdc mutations have been mapped, and rescues the hdc mutant phenotype in transgenic flies generated by P element-mediated germline transformation. The results thus show that the Drosophila homolog corresponds to the histidine decarboxylase gene, identified by the hdc mutants, and that mutations in the gene disrupt photoreceptor synaptic transmission.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Battelle B. A., Calman B. G., Andrews A. W., Grieco F. D., Mleziva M. B., Callaway J. C., Stuart A. E. Histamine: a putative afferent neurotransmitter in Limulus eyes. J Comp Neurol. 1991 Mar 22;305(4):527–542. doi: 10.1002/cne.903050402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchner E. Genes expressed in the adult brain of Drosophila and effects of their mutations on behavior: a survey of transmitter- and second messenger-related genes. J Neurogenet. 1991;7(4):153–192. doi: 10.3109/01677069109167432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callaway J. C., Stuart A. E. Biochemical and physiological evidence that histamine is the transmitter of barnacle photoreceptors. Vis Neurosci. 1989 Oct;3(4):311–325. doi: 10.1017/s0952523800005502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callaway J. C., Stuart A. E., Edwards J. S. Immunocytochemical evidence for the presence of histamine and GABA in photoreceptors of the barnacle (Balanus nubilus). Vis Neurosci. 1989 Oct;3(4):289–299. doi: 10.1017/s0952523800005484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavener D. R. Comparison of the consensus sequence flanking translational start sites in Drosophila and vertebrates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 25;15(4):1353–1361. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.4.1353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias M. S., Evans P. D. Histamine in the insect nervous system: distribution, synthesis and metabolism. J Neurochem. 1983 Aug;41(2):562–568. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb04776.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eveleth D. D., Gietz R. D., Spencer C. A., Nargang F. E., Hodgetts R. B., Marsh J. L. Sequence and structure of the dopa decarboxylase gene of Drosophila: evidence for novel RNA splicing variants. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2663–2672. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04549.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fyrberg E. A., Mahaffey J. W., Bond B. J., Davidson N. Transcripts of the six Drosophila actin genes accumulate in a stage- and tissue-specific manner. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):115–123. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90340-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garbarg M., Barbin G., Rodergas E., Schwartz J. C. Inhibition of histamine synthesis in brain by alpha-fluoromethylhistidine, a new irreversible inhibitor: in vitro and in vivo studies. J Neurochem. 1980 Nov;35(5):1045–1052. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb07858.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gribskov M., Burgess R. R., Devereux J. PEPPLOT, a protein secondary structure analysis program for the UWGCG sequence analysis software package. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 10;14(1):327–334. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.1.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardie R. C. A histamine-activated chloride channel involved in neurotransmission at a photoreceptor synapse. Nature. 1989 Jun 29;339(6227):704–706. doi: 10.1038/339704a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardie R. C. Is histamine a neurotransmitter in insect photoreceptors? J Comp Physiol A. 1987 Aug;161(2):201–213. doi: 10.1007/BF00615241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsh J., Davidson N. Isolation and characterization of the dopa decarboxylase gene of Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Jun;1(6):475–485. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.6.475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homberg U., Hildebrand J. G. Histamine-immunoreactive neurons in the midbrain and suboesophageal ganglion of sphinx moth Manduca sexta. J Comp Neurol. 1991 May 22;307(4):647–657. doi: 10.1002/cne.903070410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph D. R., Sullivan P. M., Wang Y. M., Kozak C., Fenstermacher D. A., Behrendsen M. E., Zahnow C. A. Characterization and expression of the complementary DNA encoding rat histidine decarboxylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):733–737. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kollonitsch J., Perkins L. M., Patchett A. A., Doldouras G. A., Marburg S., Duggan D. E., Maycock A. L., Aster S. D. Selective inhibitors of biosynthesis of aminergic neurotransmitters. Nature. 1978 Aug 31;274(5674):906–908. doi: 10.1038/274906a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman D. J., Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive protein similarity searches. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1435–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.2983426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lis J. T., Simon J. A., Sutton C. A. New heat shock puffs and beta-galactosidase activity resulting from transformation of Drosophila with an hsp70-lacZ hybrid gene. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):403–410. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90173-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montell C., Jones K., Hafen E., Rubin G. Rescue of the Drosophila phototransduction mutation trp by germline transformation. Science. 1985 Nov 29;230(4729):1040–1043. doi: 10.1126/science.3933112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan B. A., Johnson W. A., Hirsh J. Regulated splicing produces different forms of dopa decarboxylase in the central nervous system and hypoderm of Drosophila melanogaster. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3335–3342. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04648.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morino Y., Nagashima F. Pyridoxal phosphate-binding site in enzymes; reduction and comparison of sequences. Methods Enzymol. 1984;106:116–137. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(84)06012-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount D. W., Conrad B. Improved programs for DNA and protein sequence analysis on the IBM personal computer and other standard computer systems. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 10;14(1):443–454. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.1.443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nässel D. R., Holmqvist M. H., Hardie R. C., Håkanson R., Sundler F. Histamine-like immunoreactivity in photoreceptors of the compound eyes and ocelli of the flies Calliphora erythrocephala and Musca domestica. Cell Tissue Res. 1988 Sep;253(3):639–646. doi: 10.1007/BF00219755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nässel D. R., Pirvola U., Panula P. Histaminelike immunoreactive neurons innervating putative neurohaemal areas and central neuropil in the thoraco-abdominal ganglia of the flies Drosophila and Calliphora. J Comp Neurol. 1990 Jul 22;297(4):525–536. doi: 10.1002/cne.902970406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pak W. L., Grossfield J., White N. V. Nonphototactic mutants in a study of vision of Drosophila. Nature. 1969 Apr 26;222(5191):351–354. doi: 10.1038/222351a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirvola U., Tuomisto L., Yamatodani A., Panula P. Distribution of histamine in the cockroach brain and visual system: an immunocytochemical and biochemical study. J Comp Neurol. 1988 Oct 22;276(4):514–526. doi: 10.1002/cne.902760406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack I., Hofbauer A. Histamine-like immunoreactivity in the visual system and brain of Drosophila melanogaster. Cell Tissue Res. 1991 Nov;266(2):391–398. doi: 10.1007/BF00318195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M., Spradling A. C. Genetic transformation of Drosophila with transposable element vectors. Science. 1982 Oct 22;218(4570):348–353. doi: 10.1126/science.6289436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarthy P. V. Histamine: a neurotransmitter candidate for Drosophila photoreceptors. J Neurochem. 1991 Nov;57(5):1757–1768. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb06378.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlemermeyer E., Schütte M., Ammermüller J. Immunohistochemical and electrophysiological evidence that locust ocellar photoreceptors contain and release histamine. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Apr 24;99(1-2):73–78. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90267-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneuwly S., Klemenz R., Gehring W. J. Redesigning the body plan of Drosophila by ectopic expression of the homoeotic gene Antennapedia. 1987 Feb 26-Mar 4Nature. 325(6107):816–818. doi: 10.1038/325816a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheets M. D., Ogg S. C., Wickens M. P. Point mutations in AAUAAA and the poly (A) addition site: effects on the accuracy and efficiency of cleavage and polyadenylation in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 11;18(19):5799–5805. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.19.5799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shortridge R. D., Yoon J., Lending C. R., Bloomquist B. T., Perdew M. H., Pak W. L. A Drosophila phospholipase C gene that is expressed in the central nervous system. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 5;266(19):12474–12480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka T., Horio Y., Taketoshi M., Imamura I., Ando-Yamamoto M., Kangawa K., Matsuo H., Kuroda M., Wada H. Molecular cloning and sequencing of a cDNA of rat dopa decarboxylase: partial amino acid homologies with other enzymes synthesizing catecholamines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):8142–8146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.8142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thummel C. S., Boulet A. M., Lipshitz H. D. Vectors for Drosophila P-element-mediated transformation and tissue culture transfection. Gene. 1988 Dec 30;74(2):445–456. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90177-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb J. D., Burg J. G., Knapp F. W. Moxidectin evaluation against Solenoptes capillatus (Anoplura: Linognathidae), Bovicola bovis (Mallophaga: trichodectidae), and Musca autumnalis (Diptera: Muscidae) on cattle. J Econ Entomol. 1991 Aug;84(4):1266–1269. doi: 10.1093/jee/84.4.1266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinreich D., Rubin L. Irreversible inhibitors of histidine decarboxylase in Aplysia ganglia: a tool for the identification of histaminergic synapses. Comp Biochem Physiol C. 1981;69(2):383–385. doi: 10.1016/0306-4492(81)90155-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamauchi K., Sato R., Tanno Y., Ohkawara Y., Maeyama K., Watanabe T., Satoh K., Yoshizawa M., Shibahara S., Takishima T. Nucleotide sequence of the cDNA encoding L-histidine decarboxylase derived from human basophilic leukemia cell line, KU-812-F. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 11;18(19):5891–5891. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.19.5891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoon J., Shortridge R. D., Bloomquist B. T., Schneuwly S., Perdew M. H., Pak W. L. Molecular characterization of Drosophila gene encoding G0 alpha subunit homolog. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18536–18543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Signal sequences. The limits of variation. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jul 5;184(1):99–105. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90046-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]