Abstract
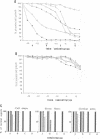
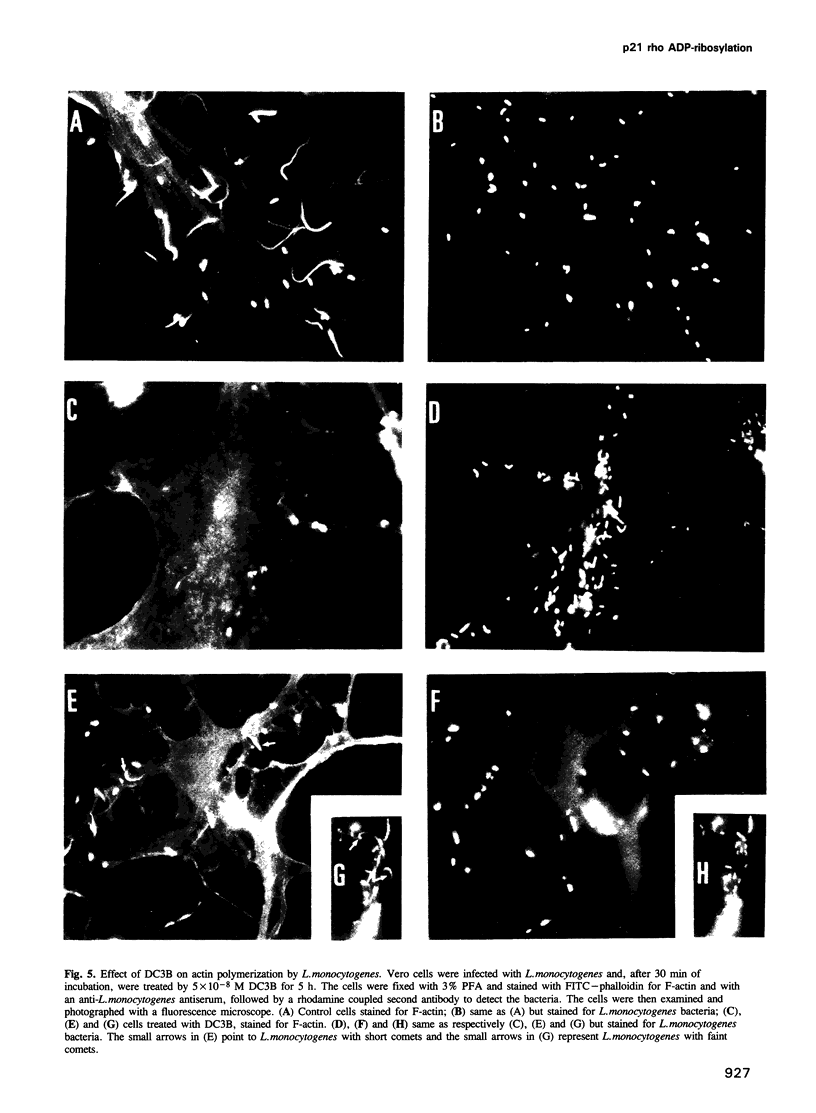
We have developed a new tool for studying the role of rho in actin stress fibre formation. Clostridium botulinum exoenzyme C3 which affects actin microfilament assembly by ADP-ribosylation of p21 rho was genetically fused in various ways to diphtheria toxin (DT). The resulting chimeric toxins were tested on Vero cells. Chimeras of C3 and both the A and B fragments of diphtheria toxin had reduced cell binding activities but were apparently able to penetrate into Vero cells by the same mechanism as DT. Upon exposure to low pH, DC3B, a fusion protein of C3 and DT B fragment, had a high affinity for the DT receptor, but was apparently not able to translocate to the cytosol upon acidification. In spite of this, addition of picomolar concentrations of DC3B to the growth medium caused disruption of the cell microfilament system associated with vinculin and blocked cell growth efficiently, indicating that the C3 part of DC3B reached the cytosol, albeit by a different mechanism than that of whole diphtheria toxin. The chimeric DC3B toxin was also applied to Vero cells infected by Listeria monocytogenes, a pathogenic bacterium that uses an unknown mechanism of actin polymerization to move rapidly in the cytosol. DC3B inhibited the bacterially induced microfilament assembly indicating that L. monocytogenes utilizes a cellular rho dependent mechanism in this process.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abo A., Pick E., Hall A., Totty N., Teahan C. G., Segal A. W. Activation of the NADPH oxidase involves the small GTP-binding protein p21rac1. Nature. 1991 Oct 17;353(6345):668–670. doi: 10.1038/353668a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adamson P., Paterson H. F., Hall A. Intracellular localization of the P21rho proteins. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(3):617–627. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.3.617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aktories K., Weller U., Chhatwal G. S. Clostridium botulinum type C produces a novel ADP-ribosyltransferase distinct from botulinum C2 toxin. FEBS Lett. 1987 Feb 9;212(1):109–113. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81566-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amann E., Brosius J. "ATG vectors' for regulated high-level expression of cloned genes in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1985;40(2-3):183–190. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90041-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blount P., Merlie J. P. BIP associates with newly synthesized subunits of the mouse muscle nicotinic receptor. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;113(5):1125–1132. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.5.1125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Sanders D. A., McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: a conserved switch for diverse cell functions. Nature. 1990 Nov 8;348(6297):125–132. doi: 10.1038/348125a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burridge K., Fath K., Kelly T., Nuckolls G., Turner C. Focal adhesions: transmembrane junctions between the extracellular matrix and the cytoskeleton. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:487–525. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.002415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buss F., Temm-Grove C., Henning S., Jockusch B. M. Distribution of profilin in fibroblasts correlates with the presence of highly dynamic actin filaments. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1992;22(1):51–61. doi: 10.1002/cm.970220106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chardin P., Boquet P., Madaule P., Popoff M. R., Rubin E. J., Gill D. M. The mammalian G protein rhoC is ADP-ribosylated by Clostridium botulinum exoenzyme C3 and affects actin microfilaments in Vero cells. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1087–1092. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03477.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chardin P., Madaule P., Tavitian A. Coding sequence of human rho cDNAs clone 6 and clone 9. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 25;16(6):2717–2717. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.6.2717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chardin P. The ras superfamily proteins. Biochimie. 1988 Jul;70(7):865–868. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(88)90226-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhary V. K., FitzGerald D. J., Pastan I. A proper amino terminus of diphtheria toxin is important for cytotoxicity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Oct 31;180(2):545–551. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81099-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choe S., Bennett M. J., Fujii G., Curmi P. M., Kantardjieff K. A., Collier R. J., Eisenberg D. The crystal structure of diphtheria toxin. Nature. 1992 May 21;357(6375):216–222. doi: 10.1038/357216a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Didsbury J., Weber R. F., Bokoch G. M., Evans T., Snyderman R. rac, a novel ras-related family of proteins that are botulinum toxin substrates. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16378–16382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draper R. K., Simon M. I. The entry of diphtheria toxin into the mammalian cell cytoplasm: evidence for lysosomal involvement. J Cell Biol. 1980 Dec;87(3 Pt 1):849–854. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.3.849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannini G., Rappuoli R., Ratti G. The amino-acid sequence of two non-toxic mutants of diphtheria toxin: CRM45 and CRM197. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 25;12(10):4063–4069. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.10.4063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt-Clermont P. J., Janmey P. A. Profilin, a weak CAP for actin and RAS. Cell. 1991 Aug 9;66(3):419–421. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90002-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall A. The cellular functions of small GTP-binding proteins. Science. 1990 Aug 10;249(4969):635–640. doi: 10.1126/science.2116664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen M. B., Nielsen S. E., Berg K. Re-examination and further development of a precise and rapid dye method for measuring cell growth/cell kill. J Immunol Methods. 1989 May 12;119(2):203–210. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(89)90397-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata K., Kikuchi A., Sasaki T., Kuroda S., Kaibuchi K., Matsuura Y., Seki H., Saida K., Takai Y. Involvement of rho p21 in the GTP-enhanced calcium ion sensitivity of smooth muscle contraction. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 5;267(13):8719–8722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. I., Pringle J. R. Molecular characterization of CDC42, a Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene involved in the development of cell polarity. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;111(1):143–152. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Just I., Mohr C., Schallehn G., Menard L., Didsbury J. R., Vandekerckhove J., van Damme J., Aktories K. Purification and characterization of an ADP-ribosyltransferase produced by Clostridium limosum. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 25;267(15):10274–10280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagan B. L., Finkelstein A., Colombini M. Diphtheria toxin fragment forms large pores in phospholipid bilayer membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4950–4954. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K., Groman N. B. Mode of inhibition of diphtheria toxin by ammonium chloride. J Bacteriol. 1965 Dec;90(6):1557–1562. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.6.1557-1562.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kocks C., Gouin E., Tabouret M., Berche P., Ohayon H., Cossart P. L. monocytogenes-induced actin assembly requires the actA gene product, a surface protein. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):521–531. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90188-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madaule P., Axel R. A novel ras-related gene family. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90058-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madaule P., Axel R., Myers A. M. Characterization of two members of the rho gene family from the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):779–783. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis R. L., Wilson L. Opposite end assembly and disassembly of microtubules at steady state in vitro. Cell. 1978 Jan;13(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90132-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCaffrey M., Johnson J. S., Goud B., Myers A. M., Rossier J., Popoff M. R., Madaule P., Boquet P. The small GTP-binding protein Rho1p is localized on the Golgi apparatus and post-Golgi vesicles in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;115(2):309–319. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekada E., Uchida T. Binding properties of diphtheria toxin to cells are altered by mutation in the fragment A domain. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):12148–12153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middlebrook J. L., Dorland R. B., Leppla S. H. Association of diphtheria toxin with Vero cells. Demonstration of a receptor. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 25;253(20):7325–7330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montecucco C., Schiavo G., Tomasi M. pH-dependence of the phospholipid interaction of diphtheria-toxin fragments. Biochem J. 1985 Oct 1;231(1):123–128. doi: 10.1042/bj2310123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskaug J. O., Sandvig K., Olsnes S. Cell-mediated reduction of the interfragment disulfide in nicked diphtheria toxin. A new system to study toxin entry at low pH. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10339–10345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moya M., Dautry-Varsat A., Goud B., Louvard D., Boquet P. Inhibition of coated pit formation in Hep2 cells blocks the cytotoxicity of diphtheria toxin but not that of ricin toxin. J Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;101(2):548–559. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.2.548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naglich J. G., Metherall J. E., Russell D. W., Eidels L. Expression cloning of a diphtheria toxin receptor: identity with a heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor precursor. Cell. 1992 Jun 12;69(6):1051–1061. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90623-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsnes S., Sandvig K., Petersen O. W., van Deurs B. Immunotoxins--entry into cells and mechanisms of action. Immunol Today. 1989 Sep;10(9):291–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papini E., Schiavo G., Tomasi M., Colombatti M., Rappuoli R., Montecucco C. Lipid interaction of diphtheria toxin and mutants with altered fragment B. 2. Hydrophobic photolabelling and cell intoxication. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Dec 15;169(3):637–644. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13655.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastan I., Willingham M. C., FitzGerald D. J. Immunotoxins. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):641–648. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90506-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson H. F., Self A. J., Garrett M. D., Just I., Aktories K., Hall A. Microinjection of recombinant p21rho induces rapid changes in cell morphology. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):1001–1007. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.1001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard T. D., Cooper J. A. Actin and actin-binding proteins. A critical evaluation of mechanisms and functions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:987–1035. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popoff M. R., Hauser D., Boquet P., Eklund M. W., Gill D. M. Characterization of the C3 gene of Clostridium botulinum types C and D and its expression in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1991 Oct;59(10):3673–3679. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.10.3673-3679.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popoff M., Boquet P., Gill D. M., Eklund M. W. DNA sequence of exoenzyme C3, an ADP-ribosyltransferase encoded by Clostridium botulinum C and D phages. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Mar 11;18(5):1291–1291. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.5.1291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley A. J., Hall A. The small GTP-binding protein rho regulates the assembly of focal adhesions and actin stress fibers in response to growth factors. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):389–399. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90163-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley A. J., Paterson H. F., Johnston C. L., Diekmann D., Hall A. The small GTP-binding protein rac regulates growth factor-induced membrane ruffling. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):401–410. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90164-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin E. J., Gill D. M., Boquet P., Popoff M. R. Functional modification of a 21-kilodalton G protein when ADP-ribosylated by exoenzyme C3 of Clostridium botulinum. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):418–426. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandvig K., Olsnes S. Diphtheria toxin entry into cells is facilitated by low pH. J Cell Biol. 1980 Dec;87(3 Pt 1):828–832. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.3.828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder T. E. Actin in dividing cells: contractile ring filaments bind heavy meromyosin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jun;70(6):1688–1692. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.6.1688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekine A., Fujiwara M., Narumiya S. Asparagine residue in the rho gene product is the modification site for botulinum ADP-ribosyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8602–8605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryer L., Bourne H. R. G proteins: a family of signal transducers. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:391–419. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.002135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theriot J. A., Mitchison T. J. Actin microfilament dynamics in locomoting cells. Nature. 1991 Jul 11;352(6331):126–131. doi: 10.1038/352126a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theriot J. A., Mitchison T. J. The nucleation-release model of actin filament dynamics in cell motility. Trends Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;2(8):219–222. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(92)90298-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theriot J. A., Mitchison T. J., Tilney L. G., Portnoy D. A. The rate of actin-based motility of intracellular Listeria monocytogenes equals the rate of actin polymerization. Nature. 1992 May 21;357(6375):257–260. doi: 10.1038/357257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida T., Pappenheimer A. M., Jr, Greany R. Diphtheria toxin and related proteins. I. Isolation and properties of mutant proteins serologically related to diphtheria toxin. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 10;248(11):3838–3844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida T., Pappenheimer A. M., Jr, Harper A. A. Diphtheria toxin and related proteins. II. Kinetic studies on intoxication of HeLa cells by diphtheria toxin and related proteins. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 10;248(11):3845–3850. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y. L. Exchange of actin subunits at the leading edge of living fibroblasts: possible role of treadmilling. J Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;101(2):597–602. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.2.597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissbach H., Ochoa S. Soluble factors required for eukaryotic protein synthesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:191–216. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.001203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedlocha A., Madshus I. H., Mach H., Middaugh C. R., Olsnes S. Tight folding of acidic fibroblast growth factor prevents its translocation to the cytosol with diphtheria toxin as vector. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):4835–4842. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05589.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeramian P., Chardin P., Madaule P., Tavitian A. Nucleotide sequence of human rho cDNA clone 12. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 25;15(4):1869–1869. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.4.1869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Duve C., de Barsy T., Poole B., Trouet A., Tulkens P., Van Hoof F. Commentary. Lysosomotropic agents. Biochem Pharmacol. 1974 Sep 15;23(18):2495–2531. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(74)90174-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]