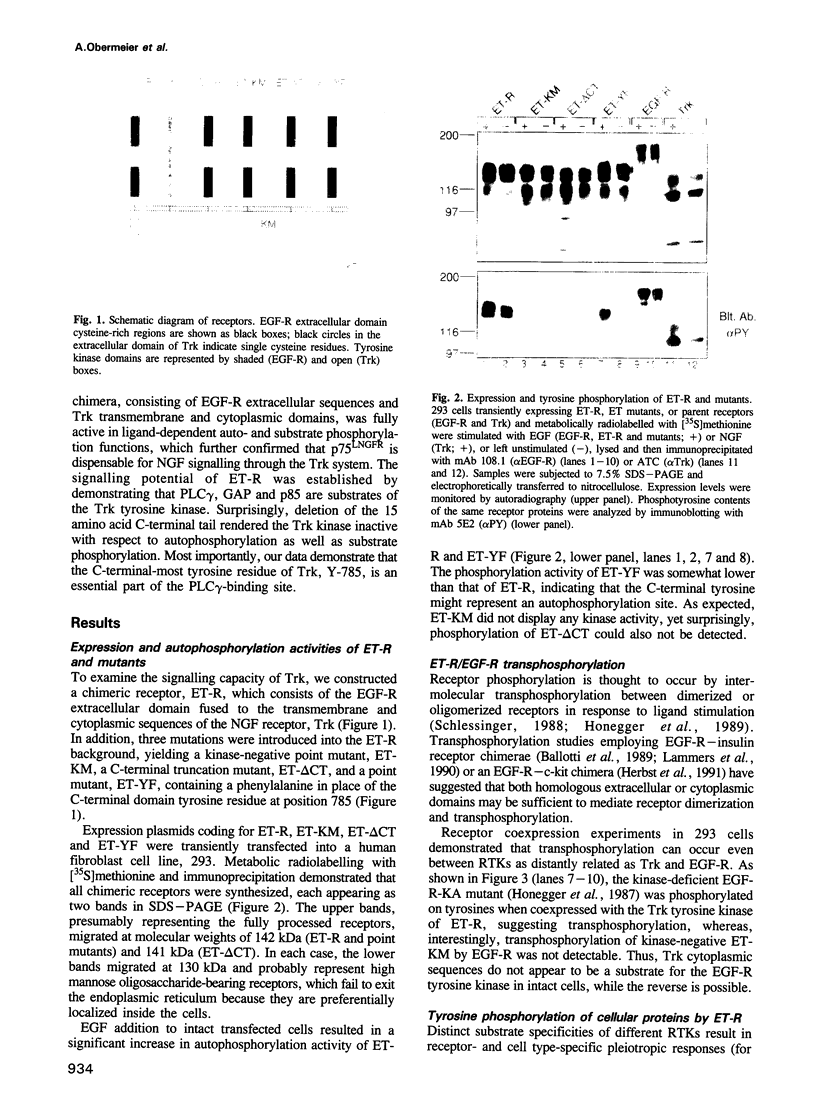
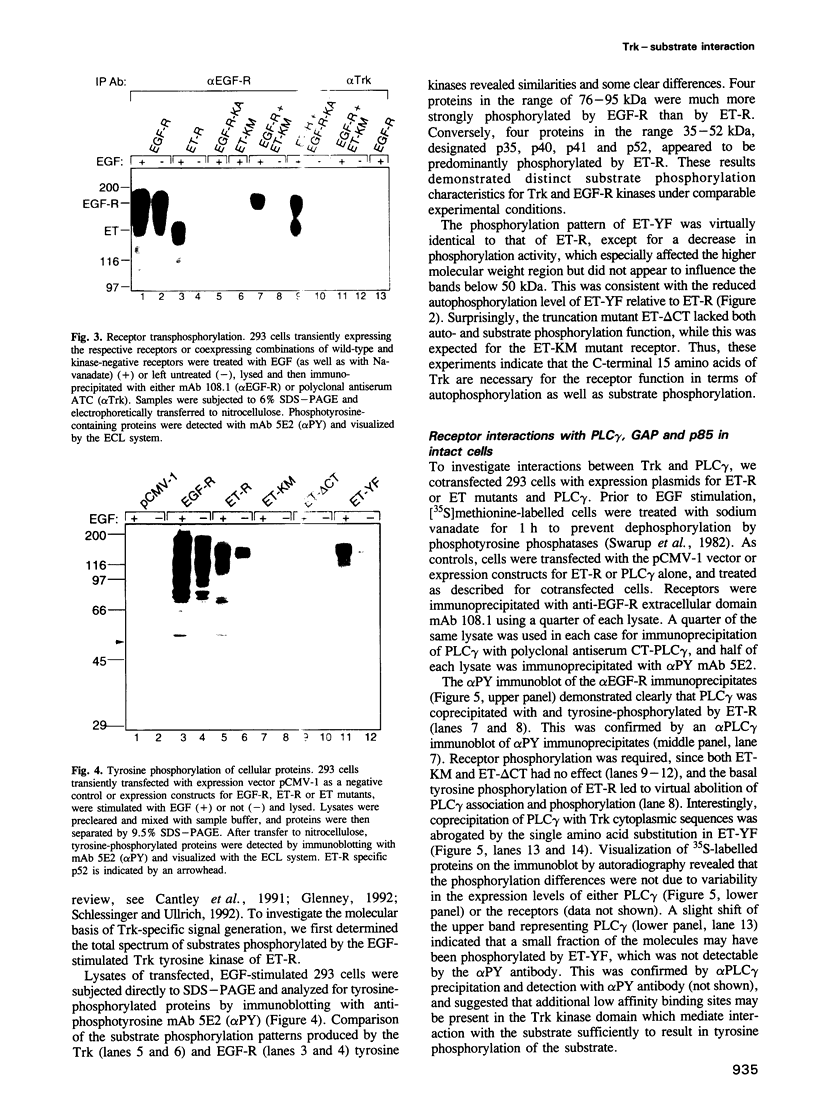
Abstract
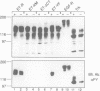
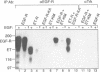
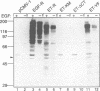
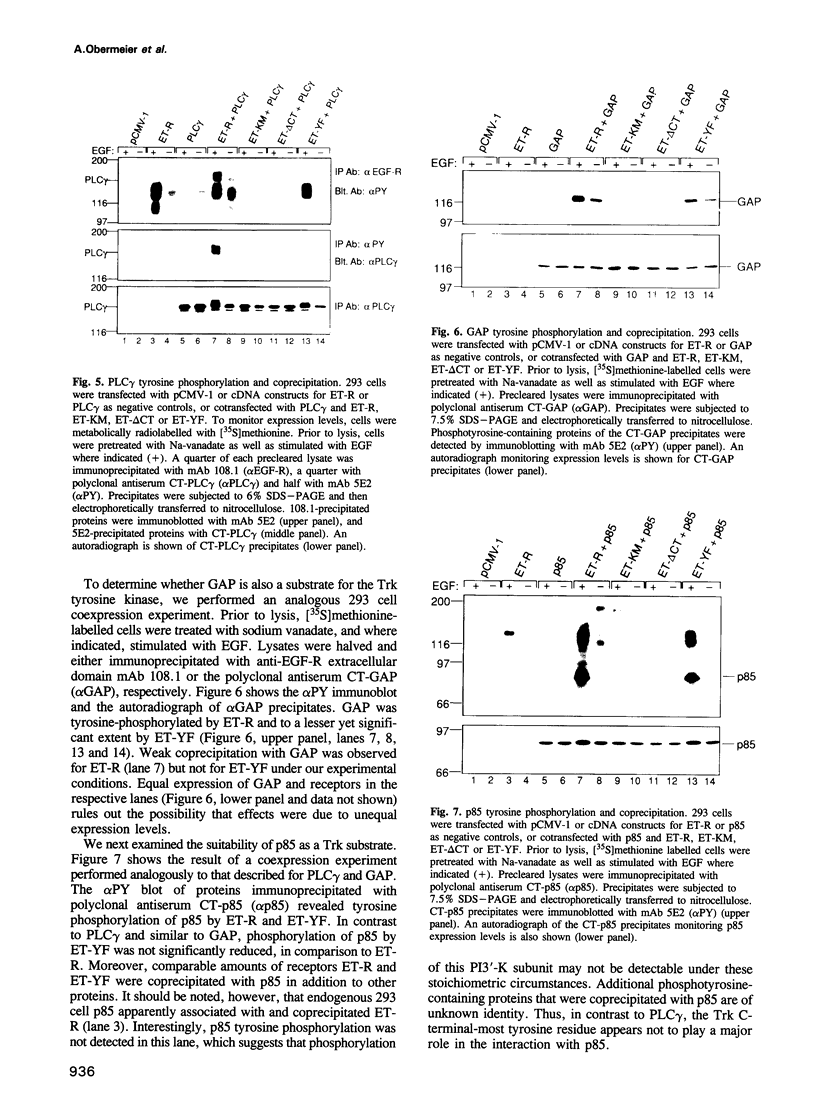
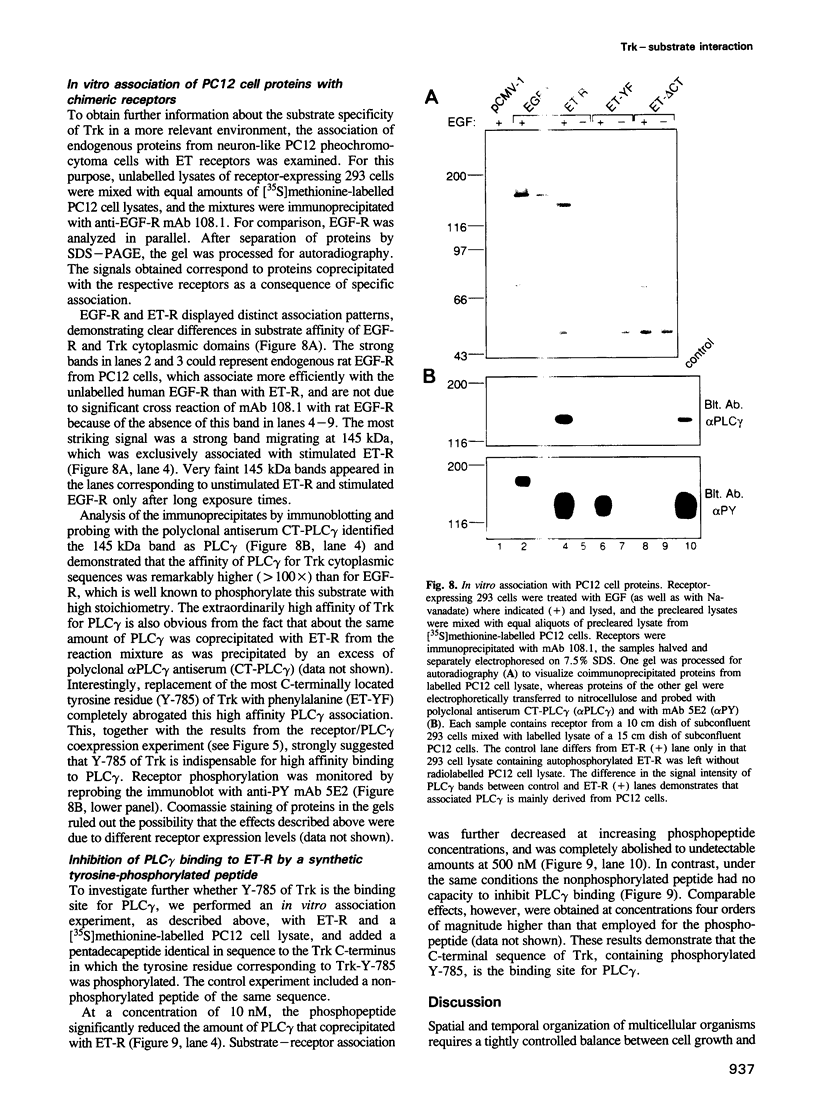
Interaction of the nerve growth factor (NGF) receptor/Trk with cellular substrates was investigated by transient co-overexpression in human 293 fibroblasts using ET-R, a chimeric receptor consisting of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGF-R) extracellular ligand binding domain and the Trk transmembrane and intracellular signal-generating sequences. The chimera was fully functional, and associated with and phosphorylated phospholipase C gamma (PLC gamma), ras GTPase-activating protein (GAP) and the non-catalytic subunit of phosphatidylinositol-3'-kinase, p85, in a ligand-dependent manner. Deletion of 15 C-terminal amino acids, including tyrosine 785 (Y-785) abrogated receptor and substrate phosphorylation activities. Mutation of Y-785 to phenylalanine somewhat impaired receptor phosphorylation activity, which was reflected in reduced GAP and p85 phosphorylation. In contrast, ET-YF phosphorylation of PLC gamma was significantly reduced, while the high affinity association potential with this substrate was abrogated by this point mutation in vitro and in intact cells. Furthermore, a tyrosine-phosphorylated synthetic C-terminal peptide competitively inhibited Trk cytoplasmic domain association with PLC gamma. Thus, the short C-terminal tail appears to be a crucial structural element of the Trk cytoplasmic domain, and phosphorylated Y-785 is a major and selective interaction site for PLC gamma.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballotti R., Lammers R., Scimeca J. C., Dull T., Schlessinger J., Ullrich A., Van Obberghen E. Intermolecular transphosphorylation between insulin receptors and EGF-insulin receptor chimerae. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3303–3309. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08491.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Sagi D., Feramisco J. R. Microinjection of the ras oncogene protein into PC12 cells induces morphological differentiation. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):841–848. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90280-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbacid M., Lamballe F., Pulido D., Klein R. The trk family of tyrosine protein kinase receptors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Dec 10;1072(2-3):115–127. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(91)90010-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess W. H., Dionne C. A., Kaplow J., Mudd R., Friesel R., Zilberstein A., Schlessinger J., Jaye M. Characterization and cDNA cloning of phospholipase C-gamma, a major substrate for heparin-binding growth factor 1 (acidic fibroblast growth factor)-activated tyrosine kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4770–4777. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Auger K. R., Carpenter C., Duckworth B., Graziani A., Kapeller R., Soltoff S. Oncogenes and signal transduction. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):281–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90639-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter A. N., Downes C. P. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase is activated by nerve growth factor and epidermal growth factor in PC12 cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 25;267(21):14563–14567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downing J. R., Margolis B. L., Zilberstein A., Ashmun R. A., Ullrich A., Sherr C. J., Schlessinger J. Phospholipase C-gamma, a substrate for PDGF receptor kinase, is not phosphorylated on tyrosine during the mitogenic response to CSF-1. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3345–3350. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08496.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton D. L., Wood W. I., Eaton D., Hass P. E., Hollingshead P., Wion K., Mather J., Lawn R. M., Vehar G. A., Gorman C. Construction and characterization of an active factor VIII variant lacking the central one-third of the molecule. Biochemistry. 1986 Dec 30;25(26):8343–8347. doi: 10.1021/bi00374a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantl W. J., Escobedo J. A., Martin G. A., Turck C. W., del Rosario M., McCormick F., Williams L. T. Distinct phosphotyrosines on a growth factor receptor bind to specific molecules that mediate different signaling pathways. Cell. 1992 May 1;69(3):413–423. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90444-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert C. D. Horizontal integration and cortical dynamics. Neuron. 1992 Jul;9(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90215-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr Tyrosine-phosphorylated proteins: mediators of signal transduction from the tyrosine kinases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Mar 16;1134(2):113–127. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(92)90034-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S. H., Rydel R. E., Connolly J. L., Greene L. A. PC12 cell mutants that possess low- but not high-affinity nerve growth factor receptors neither respond to nor internalize nerve growth factor. J Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;102(3):830–843. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.3.830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagag N., Halegoua S., Viola M. Inhibition of growth factor-induced differentiation of PC12 cells by microinjection of antibody to ras p21. Nature. 1986 Feb 20;319(6055):680–682. doi: 10.1038/319680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hempstead B. L., Martin-Zanca D., Kaplan D. R., Parada L. F., Chao M. V. High-affinity NGF binding requires coexpression of the trk proto-oncogene and the low-affinity NGF receptor. Nature. 1991 Apr 25;350(6320):678–683. doi: 10.1038/350678a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hempstead B. L., Patil N., Thiel B., Chao M. V. Deletion of cytoplasmic sequences of the nerve growth factor receptor leads to loss of high affinity ligand binding. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 15;265(17):9595–9598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbst R., Lammers R., Schlessinger J., Ullrich A. Substrate phosphorylation specificity of the human c-kit receptor tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):19908–19916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbst R., Shearman M. S., Obermeier A., Schlessinger J., Ullrich A. Differential effects of W mutations on p145c-kit tyrosine kinase activity and substrate interaction. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 5;267(19):13210–13216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honegger A. M., Dull T. J., Felder S., Van Obberghen E., Bellot F., Szapary D., Schmidt A., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Point mutation at the ATP binding site of EGF receptor abolishes protein-tyrosine kinase activity and alters cellular routing. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):199–209. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90147-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honegger A. M., Kris R. M., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Evidence that autophosphorylation of solubilized receptors for epidermal growth factor is mediated by intermolecular cross-phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):925–929. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibáez C. F., Ebendal T., Barbany G., Murray-Rust J., Blundell T. L., Persson H. Disruption of the low affinity receptor-binding site in NGF allows neuronal survival and differentiation by binding to the trk gene product. Cell. 1992 Apr 17;69(2):329–341. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90413-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan D. R., Hempstead B. L., Martin-Zanca D., Chao M. V., Parada L. F. The trk proto-oncogene product: a signal transducing receptor for nerve growth factor. Science. 1991 Apr 26;252(5005):554–558. doi: 10.1126/science.1850549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan D. R., Martin-Zanca D., Parada L. F. Tyrosine phosphorylation and tyrosine kinase activity of the trk proto-oncogene product induced by NGF. Nature. 1991 Mar 14;350(6314):158–160. doi: 10.1038/350158a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan D. R., Morrison D. K., Wong G., McCormick F., Williams L. T. PDGF beta-receptor stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of GAP and association of GAP with a signaling complex. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):125–133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90220-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashishian A., Kazlauskas A., Cooper J. A. Phosphorylation sites in the PDGF receptor with different specificities for binding GAP and PI3 kinase in vivo. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1373–1382. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05182.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazlauskas A., Ellis C., Pawson T., Cooper J. A. Binding of GAP to activated PDGF receptors. Science. 1990 Mar 30;247(4950):1578–1581. doi: 10.1126/science.2157284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim U. H., Fink D., Jr, Kim H. S., Park D. J., Contreras M. L., Guroff G., Rhee S. G. Nerve growth factor stimulates phosphorylation of phospholipase C-gamma in PC12 cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 25;266(3):1359–1362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R., Jing S. Q., Nanduri V., O'Rourke E., Barbacid M. The trk proto-oncogene encodes a receptor for nerve growth factor. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):189–197. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90419-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C. A., Anderson D., Moran M. F., Ellis C., Pawson T. SH2 and SH3 domains: elements that control interactions of cytoplasmic signaling proteins. Science. 1991 May 3;252(5006):668–674. doi: 10.1126/science.1708916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lammers R., Gray A., Schlessinger J., Ullrich A. Differential signalling potential of insulin- and IGF-1-receptor cytoplasmic domains. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1369–1375. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03517.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lammers R., Van Obberghen E., Ballotti R., Schlessinger J., Ullrich A. Transphosphorylation as a possible mechanism for insulin and epidermal growth factor receptor activation. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):16886–16890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lev S., Yarden Y., Givol D. Receptor functions and ligand-dependent transforming potential of a chimeric kit proto-oncogene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):6064–6068. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.6064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B., Rhee S. G., Felder S., Mervic M., Lyall R., Levitzki A., Ullrich A., Zilberstein A., Schlessinger J. EGF induces tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-II: a potential mechanism for EGF receptor signaling. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1101–1107. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90047-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B., Zilberstein A., Franks C., Felder S., Kremer S., Ullrich A., Rhee S. G., Skorecki K., Schlessinger J. Effect of phospholipase C-gamma overexpression on PDGF-induced second messengers and mitogenesis. Science. 1990 May 4;248(4955):607–610. doi: 10.1126/science.2333512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin-Zanca D., Hughes S. H., Barbacid M. A human oncogene formed by the fusion of truncated tropomyosin and protein tyrosine kinase sequences. 1986 Feb 27-Mar 5Nature. 319(6056):743–748. doi: 10.1038/319743a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin-Zanca D., Oskam R., Mitra G., Copeland T., Barbacid M. Molecular and biochemical characterization of the human trk proto-oncogene. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;9(1):24–33. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.1.24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meakin S. O., Shooter E. M. The nerve growth factor family of receptors. Trends Neurosci. 1992 Sep;15(9):323–331. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(92)90047-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meakin S. O., Suter U., Drinkwater C. C., Welcher A. A., Shooter E. M. The rat trk protooncogene product exhibits properties characteristic of the slow nerve growth factor receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2374–2378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisenhelder J., Suh P. G., Rhee S. G., Hunter T. Phospholipase C-gamma is a substrate for the PDGF and EGF receptor protein-tyrosine kinases in vivo and in vitro. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1109–1122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90048-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadi M., Dionne C. A., Li W., Li N., Spivak T., Honegger A. M., Jaye M., Schlessinger J. Point mutation in FGF receptor eliminates phosphatidylinositol hydrolysis without affecting mitogenesis. Nature. 1992 Aug 20;358(6388):681–684. doi: 10.1038/358681a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadi M., Honegger A. M., Rotin D., Fischer R., Bellot F., Li W., Dionne C. A., Jaye M., Rubinstein M., Schlessinger J. A tyrosine-phosphorylated carboxy-terminal peptide of the fibroblast growth factor receptor (Flg) is a binding site for the SH2 domain of phospholipase C-gamma 1. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):5068–5078. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.5068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molloy C. J., Bottaro D. P., Fleming T. P., Marshall M. S., Gibbs J. B., Aaronson S. A. PDGF induction of tyrosine phosphorylation of GTPase activating protein. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):711–714. doi: 10.1038/342711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran M. F., Koch C. A., Anderson D., Ellis C., England L., Martin G. S., Pawson T. Src homology region 2 domains direct protein-protein interactions in signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8622–8626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishibe S., Wahl M. I., Rhee S. G., Carpenter G. Tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-II in vitro by the epidermal growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10335–10338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishibe S., Wahl M. I., Wedegaertner P. B., Kim J. W., Rhee S. G., Carpenter G., Kim J. J. Selectivity of phospholipase C phosphorylation by the epidermal growth factor receptor, the insulin receptor, and their cytoplasmic domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):424–428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohmichi M., Decker S. J., Pang L., Saltiel A. R. Nerve growth factor binds to the 140 kd trk proto-oncogene product and stimulates its association with the src homology domain of phospholipase C gamma 1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Aug 30;179(1):217–223. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91357-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohmichi M., Decker S. J., Pang L., Saltiel A. R. Phospholipase C-gamma 1 directly associates with the p70 trk oncogene product through its src homology domains. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):14858–14861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandiella A., Lehvaslaiho H., Magni M., Alitalo K., Meldolesi J. Activation of an EGFR/neu chimeric receptor: early intracellular signals and cell proliferation responses. Oncogene. 1989 Nov;4(11):1299–1305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters K. G., Marie J., Wilson E., Ives H. E., Escobedo J., Del Rosario M., Mirda D., Williams L. T. Point mutation of an FGF receptor abolishes phosphatidylinositol turnover and Ca2+ flux but not mitogenesis. Nature. 1992 Aug 20;358(6388):678–681. doi: 10.1038/358678a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ragsdale C., Woodgett J. Neurobiology. trking neurotrophic receptors. Nature. 1991 Apr 25;350(6320):660–661. doi: 10.1038/350660a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riedel H., Dull T. J., Honegger A. M., Schlessinger J., Ullrich A. Cytoplasmic domains determine signal specificity, cellular routing characteristics and influence ligand binding of epidermal growth factor and insulin receptors. EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):2943–2954. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08444.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riedel H., Dull T. J., Schlessinger J., Ullrich A. A chimaeric receptor allows insulin to stimulate tyrosine kinase activity of epidermal growth factor receptor. Nature. 1986 Nov 6;324(6092):68–70. doi: 10.1038/324068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotin D., Margolis B., Mohammadi M., Daly R. J., Daum G., Li N., Fischer E. H., Burgess W. H., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. SH2 domains prevent tyrosine dephosphorylation of the EGF receptor: identification of Tyr992 as the high-affinity binding site for SH2 domains of phospholipase C gamma. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):559–567. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05087.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rönnstrand L., Mori S., Arridsson A. K., Eriksson A., Wernstedt C., Hellman U., Claesson-Welsh L., Heldin C. H. Identification of two C-terminal autophosphorylation sites in the PDGF beta-receptor: involvement in the interaction with phospholipase C-gamma. EMBO J. 1992 Nov;11(11):3911–3919. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05484.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlessinger J. Signal transduction by allosteric receptor oligomerization. Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Nov;13(11):443–447. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90219-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seedorf K., Felder S., Millauer B., Schlessinger J., Ullrich A. Analysis of platelet-derived growth factor receptor domain function using a novel chimeric receptor approach. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 5;266(19):12424–12431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seedorf K., Millauer B., Kostka G., Schlessinger J., Ullrich A. Differential effects of carboxy-terminal sequence deletions on platelet-derived growth factor receptor signaling activities and interactions with cellular substrates. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4347–4356. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soltoff S. P., Rabin S. L., Cantley L. C., Kaplan D. R. Nerve growth factor promotes the activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and its association with the trk tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 25;267(24):17472–17477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swarup G., Speeg K. V., Jr, Cohen S., Garbers D. L. Phosphotyrosyl-protein phosphatase of TCRC-2 cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7298–7301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. W., Ott J., Eckstein F. The rapid generation of oligonucleotide-directed mutations at high frequency using phosphorothioate-modified DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 20;13(24):8765–8785. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.24.8765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorpe G. H., Kricka L. J., Moseley S. B., Whitehead T. P. Phenols as enhancers of the chemiluminescent horseradish peroxidase-luminol-hydrogen peroxide reaction: application in luminescence-monitored enzyme immunoassays. Clin Chem. 1985 Aug;31(8):1335–1341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90801-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vetter M. L., Martin-Zanca D., Parada L. F., Bishop J. M., Kaplan D. R. Nerve growth factor rapidly stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-gamma 1 by a kinase activity associated with the product of the trk protooncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5650–5654. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl M. I., Olashaw N. E., Nishibe S., Rhee S. G., Pledger W. J., Carpenter G. Platelet-derived growth factor induces rapid and sustained tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-gamma in quiescent BALB/c 3T3 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):2934–2943. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.2934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weskamp G., Reichardt L. F. Evidence that biological activity of NGF is mediated through a novel subclass of high affinity receptors. Neuron. 1991 Apr;6(4):649–663. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90067-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Ullrich A. Growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:443–478. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.002303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]