Abstract
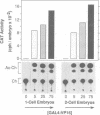
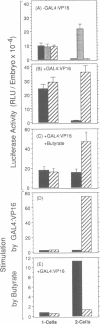
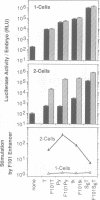
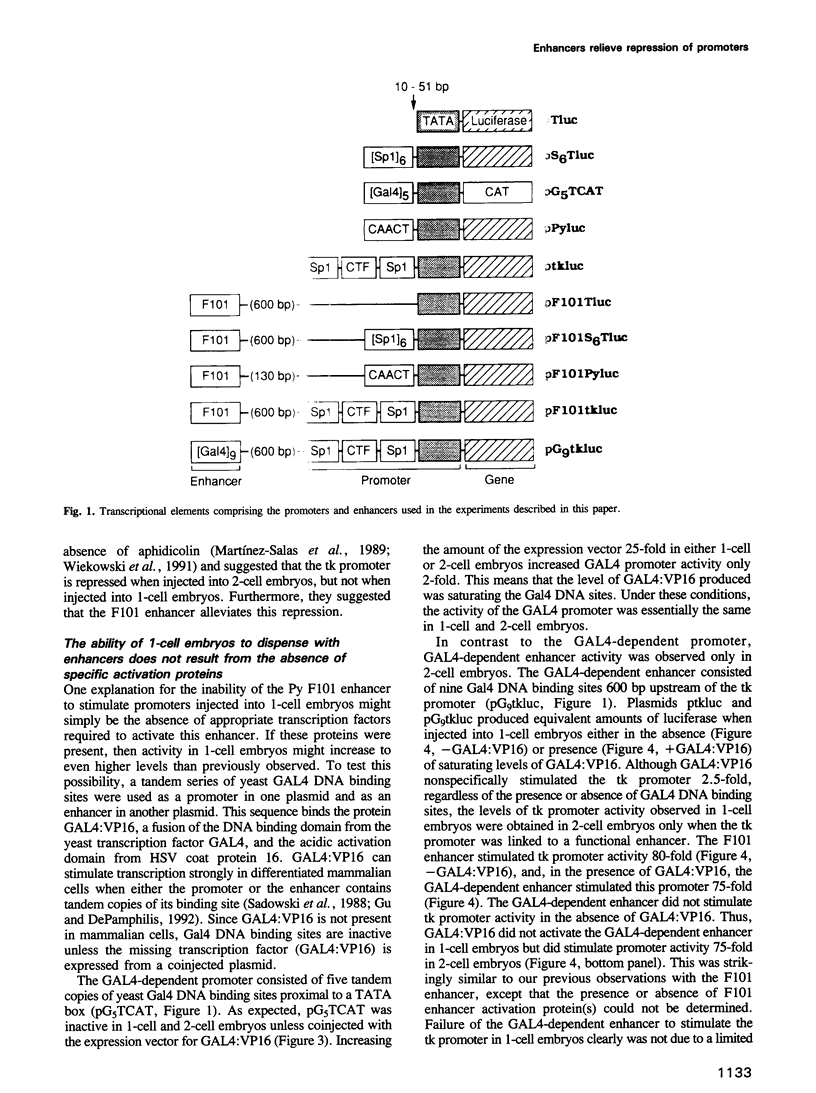
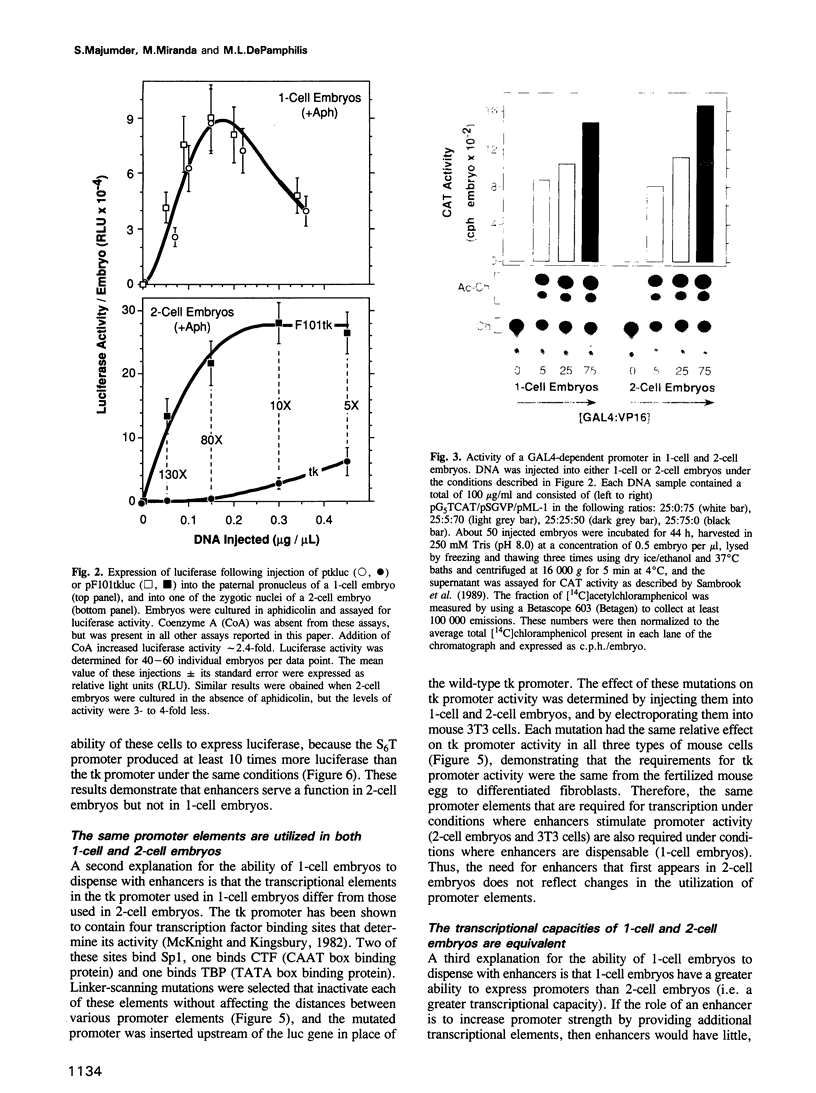
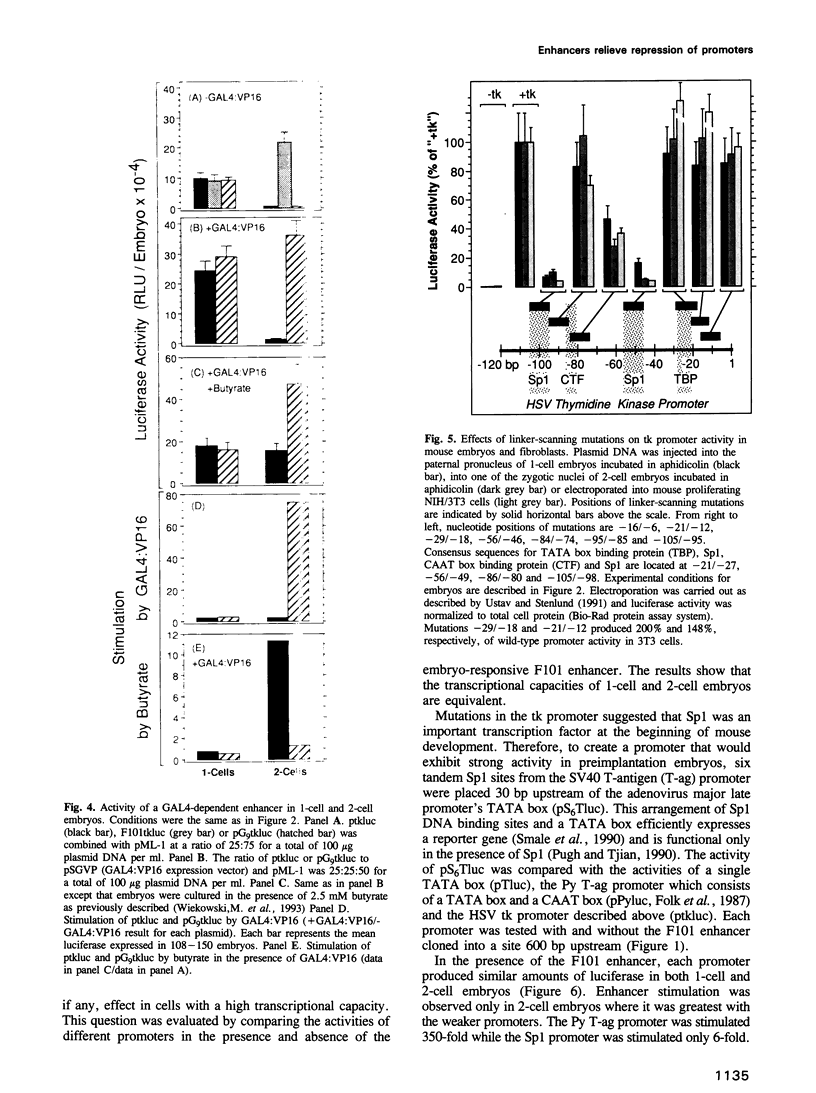
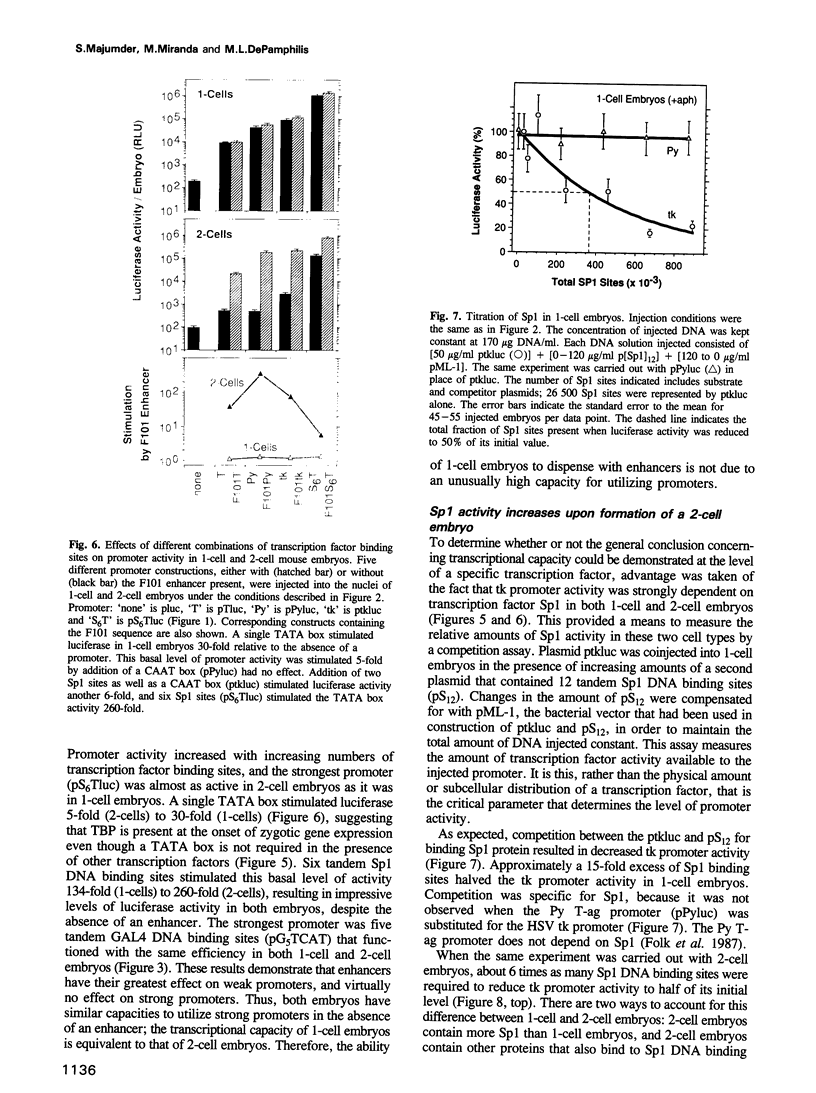
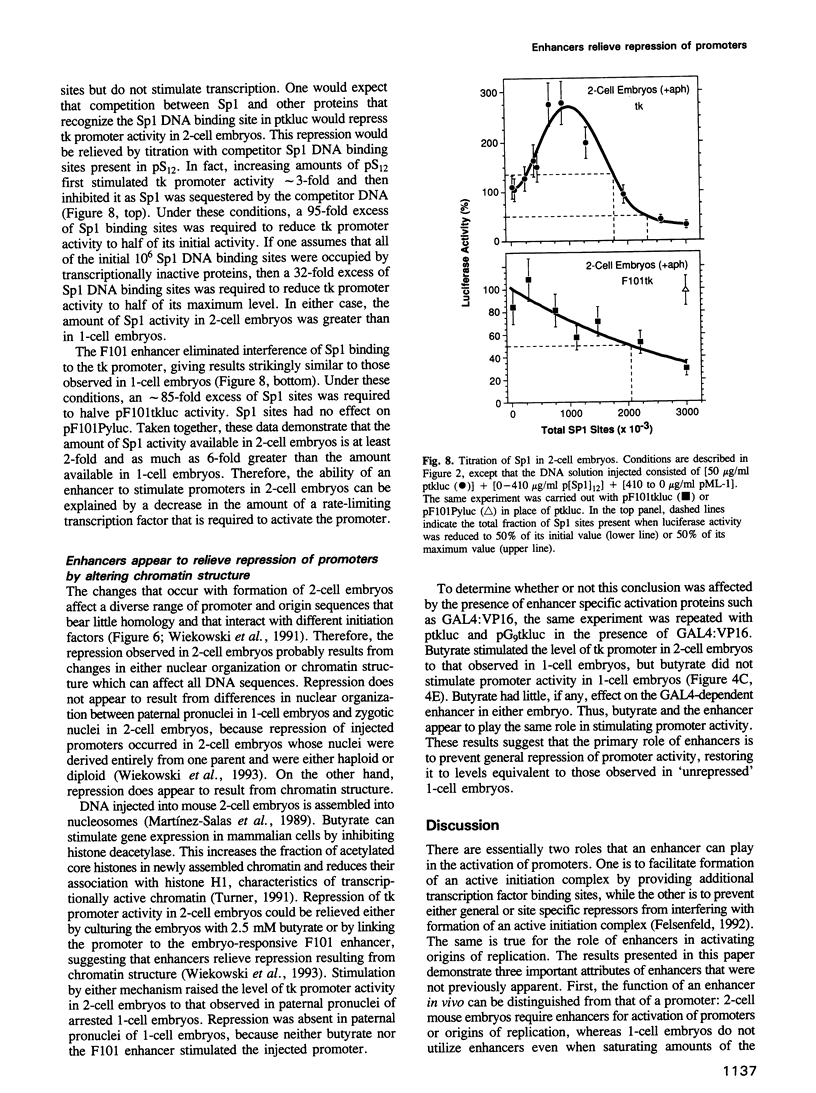
Enhancers are generally viewed simply as extensions of promoters, lacking a function of their own. However, previous studies of mouse preimplantation embryos revealed that 1-cell embryos can utilize enhancer-responsive promoters efficiently without an enhancer, whereas 2-cell embryos require an enhancer to achieve the same levels of expression. This suggested that enhancers relieved a repression in 2-cell embryos that is absent in 1-cell embryos. Results presented here demonstrate first that the ability of 1-cell embryos to dispense with enhancers does not result from the absence of specific activation proteins. Under conditions where GAL4-VP16 activated a GAL4-dependent promoter in both embryos, GAL4-VP16 activated a GAL4-dependent enhancer only in 2-cell embryos. Moreover, the role of an enhancer is not to compensate for either changes in promoter requirements, or for reduced levels of promoter-specific transcription factors. Linker-scanning mutations in a natural promoter revealed that both embryos utilized the same promoter elements, and comparison of different promoters revealed that these embryos have equivalent transcriptional capacities. In addition, titration experiments revealed less Sp1 activity in 1-cell embryos where enhancers are dispensable than in 2-cell embryos where enhancers are required. Therefore, we propose that the primary function of enhancers, first evident with formation of a mouse 2-cell embryo, is to prevent repression of weak promoters, probably by altering chromatin structure. Consistent with this hypothesis is the fact that butyrate, an agent that alters chromatin structure, stimulated promoters in 2-cell embryos, but not in 1-cell embryos.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carey M., Leatherwood J., Ptashne M. A potent GAL4 derivative activates transcription at a distance in vitro. Science. 1990 Feb 9;247(4943):710–712. doi: 10.1126/science.2405489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalifour L. E., Wirak D. O., Hansen U., Wassarman P. M., DePamphilis M. L. cis- and trans-acting sequences required for expression of simian virus 40 genes in mouse oocytes. Genes Dev. 1987 Dec;1(10):1096–1106. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.10.1096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalifour L. E., Wirak D. O., Wassarman P. M., DePamphilis M. L. Expression of simian virus 40 early and late genes in mouse oocytes and embryos. J Virol. 1986 Sep;59(3):619–627. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.3.619-627.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conover J. C., Temeles G. L., Zimmermann J. W., Burke B., Schultz R. M. Stage-specific expression of a family of proteins that are major products of zygotic gene activation in the mouse embryo. Dev Biol. 1991 Apr;144(2):392–404. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(91)90431-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courey A. J., Holtzman D. A., Jackson S. P., Tjian R. Synergistic activation by the glutamine-rich domains of human transcription factor Sp1. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):827–836. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90606-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePamphilis M. L., Herman S. A., Martínez-Salas E., Chalifour L. E., Wirak D. O., Cupo D. Y., Miranda M. Microinjecting DNA into mouse ova to study DNA replication and gene expression and to produce transgenic animals. Biotechniques. 1988 Jul-Aug;6(7):662–680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePamphilis M. L. Transcriptional elements as components of eukaryotic origins of DNA replication. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):635–638. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90398-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dooley T. P., Miranda M., Jones N. C., DePamphilis M. L. Transactivation of the adenovirus EIIa promoter in the absence of adenovirus E1A protein is restricted to mouse oocytes and preimplantation embryos. Development. 1989 Dec;107(4):945–956. doi: 10.1242/dev.107.4.945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S. P., Coen D. M., McKnight S. L. Promoter domains required for expression of plasmid-borne copies of the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene in virus-infected mouse fibroblasts and microinjected frog oocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1940–1947. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felsenfeld G. Chromatin as an essential part of the transcriptional mechanism. Nature. 1992 Jan 16;355(6357):219–224. doi: 10.1038/355219a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruss C., Gutierrez C., Burhans W. C., DePamphilis M. L., Koller T., Sogo J. M. Nucleosome assembly in mammalian cell extracts before and after DNA replication. EMBO J. 1990 Sep;9(9):2911–2922. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07482.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo Z. S., DePamphilis M. L. Specific transcription factors stimulate simian virus 40 and polyomavirus origins of DNA replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;12(6):2514–2524. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.6.2514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Yamamoto K. R., Tjian R. Two distinct transcription factors bind to the HSV thymidine kinase promoter in vitro. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):559–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90113-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami K., Scheidereit C., Roeder R. G. Identification and purification of a human immunoglobulin-enhancer-binding protein (NF-kappa B) that activates transcription from a human immunodeficiency virus type 1 promoter in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4700–4704. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latham K. E., Solter D., Schultz R. M. Acquisition of a transcriptionally permissive state during the 1-cell stage of mouse embryogenesis. Dev Biol. 1992 Feb;149(2):457–462. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(92)90300-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laybourn P. J., Kadonaga J. T. Role of nucleosomal cores and histone H1 in regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Science. 1991 Oct 11;254(5029):238–245. doi: 10.1126/science.254.5029.238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laybourn P. J., Kadonaga J. T. Threshold phenomena and long-distance activation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Science. 1992 Sep 18;257(5077):1682–1685. doi: 10.1126/science.1388287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lira S. A., Kinloch R. A., Mortillo S., Wassarman P. M. An upstream region of the mouse ZP3 gene directs expression of firefly luciferase specifically to growing oocytes in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):7215–7219. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.7215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manejwala F. M., Logan C. Y., Schultz R. M. Regulation of hsp70 mRNA levels during oocyte maturation and zygotic gene activation in the mouse. Dev Biol. 1991 Apr;144(2):301–308. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(91)90423-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Salas E., Cupo D. Y., DePamphilis M. L. The need for enhancers is acquired upon formation of a diploid nucleus during early mouse development. Genes Dev. 1988 Sep;2(9):1115–1126. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.9.1115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Salas E., Linney E., Hassell J., DePamphilis M. L. The need for enhancers in gene expression first appears during mouse development with formation of the zygotic nucleus. Genes Dev. 1989 Oct;3(10):1493–1506. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.10.1493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Kingsbury R. Transcriptional control signals of a eukaryotic protein-coding gene. Science. 1982 Jul 23;217(4557):316–324. doi: 10.1126/science.6283634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millar S. E., Lader E., Liang L. F., Dean J. Oocyte-specific factors bind a conserved upstream sequence required for mouse zona pellucida promoter activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;11(12):6197–6204. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.12.6197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müeller-Storm H. P., Sogo J. M., Schaffner W. An enhancer stimulates transcription in trans when attached to the promoter via a protein bridge. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):767–777. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90110-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonchev S., Tsanev R. Protamine-histone replacement and DNA replication in the male mouse pronucleus. Mol Reprod Dev. 1990 Jan;25(1):72–76. doi: 10.1002/mrd.1080250113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prives C., Murakami Y., Kern F. G., Folk W., Basilico C., Hurwitz J. DNA sequence requirements for replication of polyomavirus DNA in vivo and in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3694–3704. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh B. F., Tjian R. Mechanism of transcriptional activation by Sp1: evidence for coactivators. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1187–1197. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90683-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queen C., Stafford J. Fine mapping of an immunoglobulin gene activator. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;4(6):1042–1049. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.6.1042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski I., Ma J., Triezenberg S., Ptashne M. GAL4-VP16 is an unusually potent transcriptional activator. Nature. 1988 Oct 6;335(6190):563–564. doi: 10.1038/335563a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassone-Corsi P., Dougherty J. P., Wasylyk B., Chambon P. Stimulation of in vitro transcription from heterologous promoters by the simian virus 40 enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):308–312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatt M. D., Rusconi S., Schaffner W. A single DNA-binding transcription factor is sufficient for activation from a distant enhancer and/or from a promoter position. EMBO J. 1990 Feb;9(2):481–487. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08134.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schickler M., Lira S. A., Kinloch R. A., Wassarman P. M. A mouse oocyte-specific protein that binds to a region of mZP3 promoter responsible for oocyte-specific mZP3 gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):120–127. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seipel K., Georgiev O., Schaffner W. Different activation domains stimulate transcription from remote ('enhancer') and proximal ('promoter') positions. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):4961–4968. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05603.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. In vitro transcription of immunoglobulin genes in a B-cell extract: effects of enhancer and promoter sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1989–1994. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sergeant A., Bohmann D., Zentgraf H., Weiher H., Keller W. A transcription enhancer acts in vitro over distances of hundreds of base-pairs on both circular and linear templates but not on chromatin-reconstituted DNA. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 15;180(3):577–600. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smale S. T., Baltimore D. The "initiator" as a transcription control element. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90176-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smale S. T., Schmidt M. C., Berk A. J., Baltimore D. Transcriptional activation by Sp1 as directed through TATA or initiator: specific requirement for mammalian transcription factor IID. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4509–4513. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor I. C., Workman J. L., Schuetz T. J., Kingston R. E. Facilitated binding of GAL4 and heat shock factor to nucleosomal templates: differential function of DNA-binding domains. Genes Dev. 1991 Jul;5(7):1285–1298. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.7.1285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Telford N. A., Watson A. J., Schultz G. A. Transition from maternal to embryonic control in early mammalian development: a comparison of several species. Mol Reprod Dev. 1990 May;26(1):90–100. doi: 10.1002/mrd.1080260113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thali M., Rusconi S., Schaffner W. Immediate early protein of pseudorabies virus is a general transactivator but stimulates only suboptimally utilized promoters. A clue to specificity? J Mol Biol. 1990 Sep 20;215(2):301–311. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80348-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner B. M. Histone acetylation and control of gene expression. J Cell Sci. 1991 May;99(Pt 1):13–20. doi: 10.1242/jcs.99.1.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ustav M., Stenlund A. Transient replication of BPV-1 requires two viral polypeptides encoded by the E1 and E2 open reading frames. EMBO J. 1991 Feb;10(2):449–457. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07967.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B. Enhancers and transcription factors in the control of gene expression. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Nov 10;951(1):17–35. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(88)90021-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiekowski M., Miranda M., DePamphilis M. L. Regulation of gene expression in preimplantation mouse embryos: effects of the zygotic clock and the first mitosis on promoter and enhancer activities. Dev Biol. 1991 Oct;147(2):403–414. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(91)90298-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirak D. O., Chalifour L. E., Wassarman P. M., Muller W. J., Hassell J. A., DePamphilis M. L. Sequence-dependent DNA replication in preimplantation mouse embryos. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):2924–2935. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.2924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]