Abstract
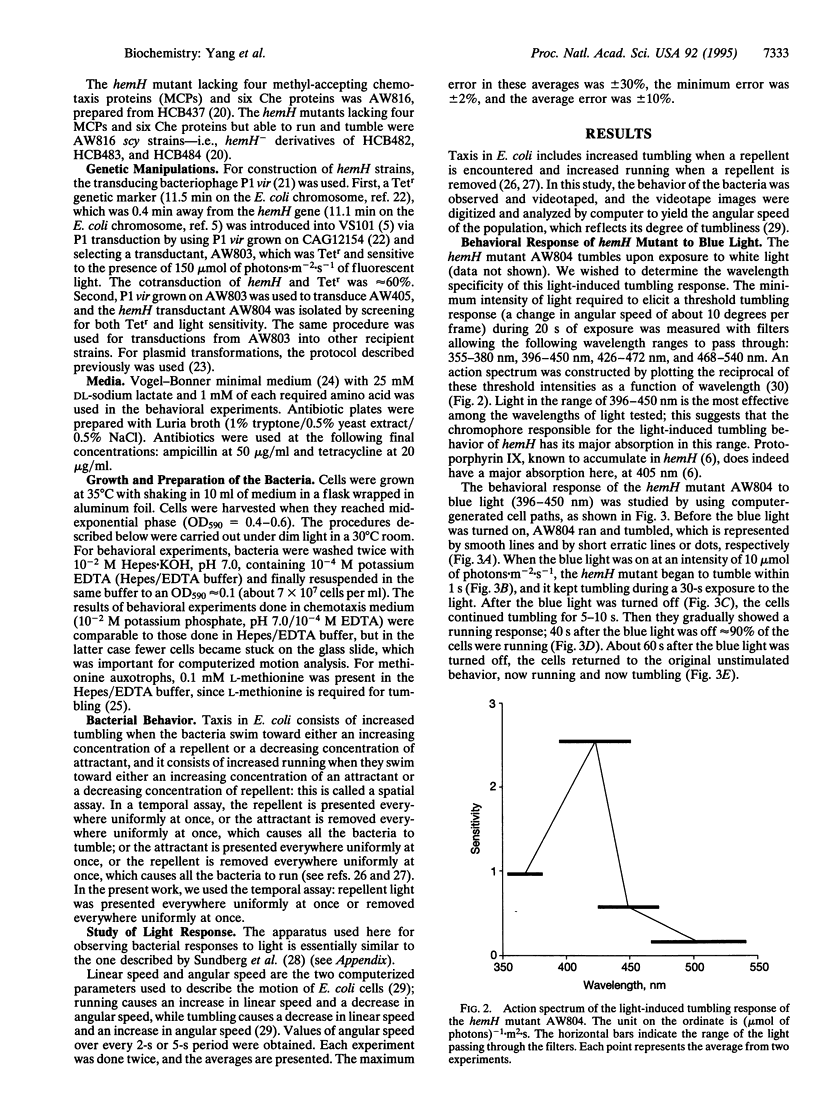
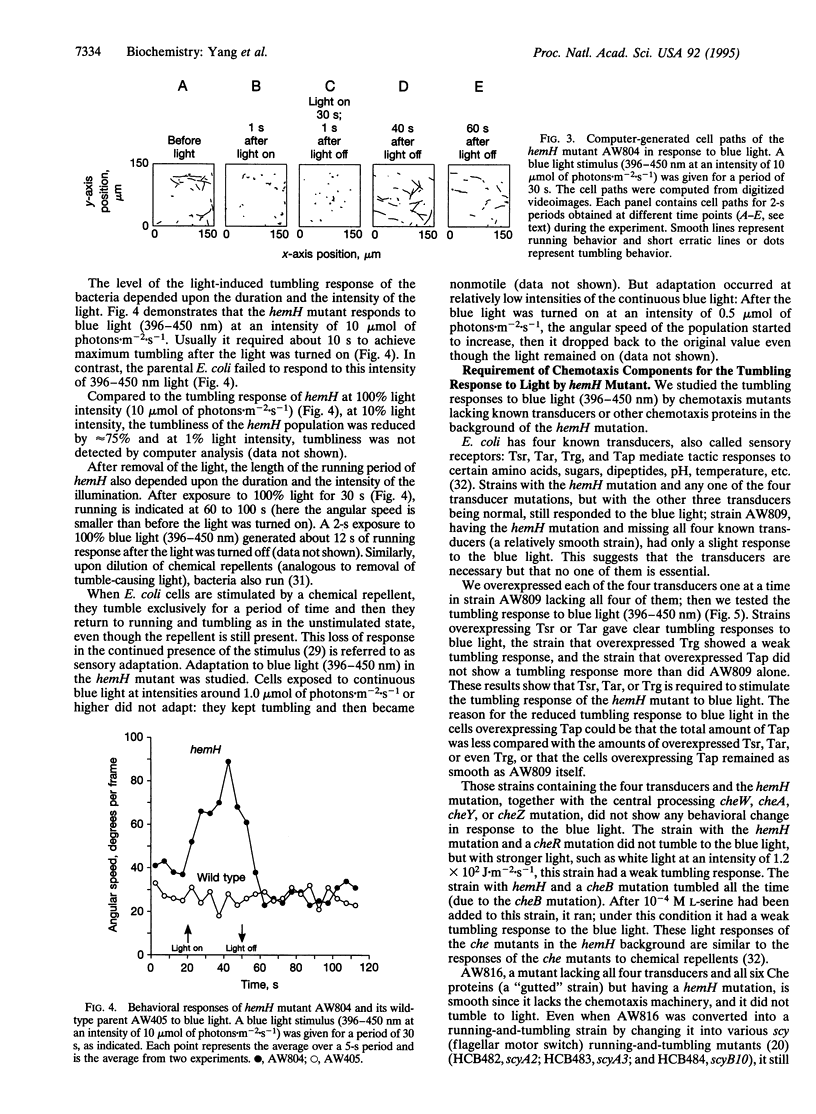
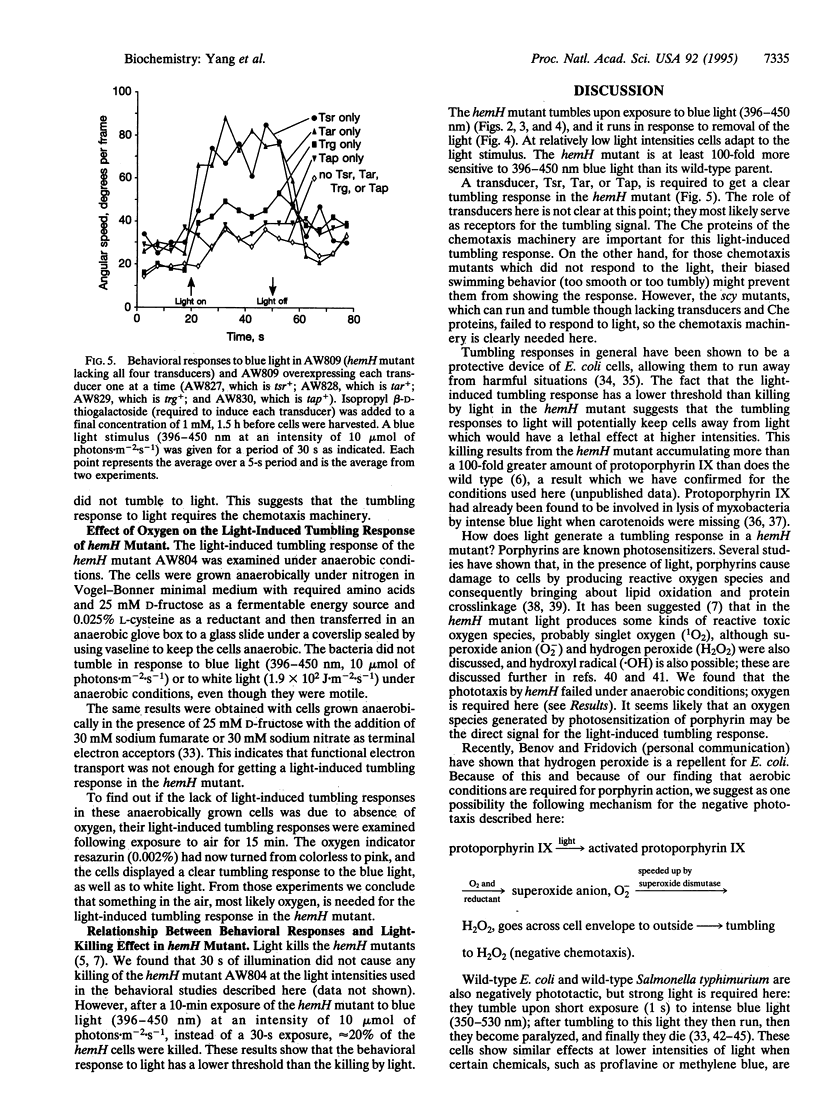
The hemH gene of Escherichia coli encodes ferrochelatase (EC 4.99.1.1), the enzyme that catalyzes the last step in the production of heme, namely the synthesis of heme from protoporphyrin IX plus Fe2+. The behavioral responses to light were studied in E. coli carrying a hemH mutation. It was shown that the hemH mutant displayed a tumbling response upon illumination and a running response upon removal of the light. The most effect light to induce a tumbling response in the hemH mutant was blue light (396-450 nm). The chemotaxis machinery was needed for the light-induced tumbling response in the hemH mutant. The bacterial defect is an analog of the human inherited disease erythropoietic protoporphyria.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armitage J. P. Behavioral responses in bacteria. Annu Rev Physiol. 1992;54:683–714. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.54.030192.003343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong J. B., Adler J., Dahl M. M. Nonchemotactic mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jan;93(1):390–398. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.1.390-398.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg H. C., Brown D. A. Chemotaxis in Escherichia coli analysed by three-dimensional tracking. Nature. 1972 Oct 27;239(5374):500–504. doi: 10.1038/239500a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borkovich K. A., Kaplan N., Hess J. F., Simon M. I. Transmembrane signal transduction in bacterial chemotaxis involves ligand-dependent activation of phosphate group transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1208–1212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burchard R. P., Dworkin M. Light-induced lysis and carotenogenesis in Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):535–545. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.535-545.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burchard R. P., Gordon S. A., Dworkin M. Action spectrum for the photolysis of Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):896–897. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.896-897.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrows G. G., Newcomer M. E., Hazelbauer G. L. Purification of receptor protein Trg by exploiting a property common to chemotactic transducers of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):17309–17315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R., Charles H. P. Porphyrin-accumulating mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jan;113(1):122–132. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.1.122-132.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frustaci J. M., O'Brian M. R. The Escherichia coli visA gene encodes ferrochelatase, the final enzyme of the heme biosynthetic pathway. J Bacteriol. 1993 Apr;175(7):2154–2156. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.7.2154-2156.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazelbauer G. L., Mesibov R. E., Adler J. Escherichia coli mutants defective in chemotaxis toward specific chemicals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Dec;64(4):1300–1307. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.4.1300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häder D. P. Photosensory behavior in procaryotes. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Mar;51(1):1–21. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.1.1-21.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondoh H., Ball C. B., Adler J. Identification of a methyl-accepting chemotaxis protein for the ribose and galactose chemoreceptors of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):260–264. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen S. H., Reader R. W., Kort E. N., Tso W. W., Adler J. Change in direction of flagellar rotation is the basis of the chemotactic response in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1974 May 3;249(452):74–77. doi: 10.1038/249074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu J. D., Parkinson J. S. Role of CheW protein in coupling membrane receptors to the intracellular signaling system of bacterial chemotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8703–8707. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnab R. M., Koshland D. E., Jr The gradient-sensing mechanism in bacterial chemotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2509–2512. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnab R., Koshland D. E., Jr Bacterial motility and chemotaxis: light-induced tumbling response and visualization of individual flagella. J Mol Biol. 1974 Apr 15;84(3):399–406. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90448-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mesibov R., Adler J. Chemotaxis toward amino acids in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1972 Oct;112(1):315–326. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.1.315-326.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. B., Koshland D. E., Jr Effects of cyanine dye membrane probes on cellular properties. Nature. 1978 Mar 2;272(5648):83–84. doi: 10.1038/272083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto K., Nakahigashi K., Nishimura K., Inokuchi H. Isolation and characterization of visible light-sensitive mutants of Escherichia coli K12. J Mol Biol. 1991 Jun 5;219(3):393–398. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90180-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto K., Nishimura K., Masuda T., Tsuji H., Inokuchi H. Accumulation of protoporphyrin IX in light-sensitive mutants of Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1992 Oct 5;310(3):246–248. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81341-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moan J., Berg K. Photochemotherapy of cancer: experimental research. Photochem Photobiol. 1992 Jun;55(6):931–948. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1992.tb08541.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakahigashi K., Nishimura K., Miyamoto K., Inokuchi H. Photosensitivity of a protoporphyrin-accumulating, light-sensitive mutant (visA) of Escherichia coli K-12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10520–10524. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nara T., Lee L., Imae Y. Thermosensing ability of Trg and Tap chemoreceptors in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1991 Feb;173(3):1120–1124. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.3.1120-1124.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park C., Hazelbauer G. L. Mutations specifically affecting ligand interaction of the Trg chemosensory transducer. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jul;167(1):101–109. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.1.101-109.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sager B. M., Sekelsky J. J., Matsumura P., Adler J. Use of a computer to assay motility in bacteria. Anal Biochem. 1988 Sep;173(2):271–277. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90189-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer M., Baker T. A., Schnitzler G., Deischel S. M., Goel M., Dove W., Jaacks K. J., Grossman A. D., Erickson J. W., Gross C. A. A collection of strains containing genetically linked alternating antibiotic resistance elements for genetic mapping of Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Mar;53(1):1–24. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.1.1-24.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slocum M. K., Parkinson J. S. Genetics of methyl-accepting chemotaxis proteins in Escherichia coli: null phenotypes of the tar and tap genes. J Bacteriol. 1985 Aug;163(2):586–594. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.2.586-594.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer M. S., Kort E. N., Larsen S. H., Ordal G. W., Reader R. W., Adler J. Role of methionine in bacterial chemotaxis: requirement for tumbling and involvement in information processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4640–4644. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundberg S. A., Alam M., Spudich J. L. Excitation signal processing times in Halobacterium halobium phototaxis. Biophys J. 1986 Nov;50(5):895–900. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83530-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szupica C. J., Adler J. Cell envelopes of chemotaxis mutants of Escherichia coli rotate their flagella counterclockwise. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):451–453. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.451-453.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor B. L., Koshland D. E., Jr Intrinsic and extrinsic light responses of Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1975 Aug;123(2):557–569. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.2.557-569.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor B. L., Koshland D. E., Jr Perturbation of the chemotactic tumbling of bacteria. J Supramol Struct. 1976;4(3):343–353. doi: 10.1002/jss.400040305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor B. L., Miller J. B., Warrick H. M., Koshland D. E., Jr Electron acceptor taxis and blue light effect on bacterial chemotaxis. J Bacteriol. 1979 Nov;140(2):567–573. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.2.567-573.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang N., Macnab R., Koshland D. E., Jr Common mechanism for repellents and attractants in bacterial chemotaxis. Science. 1973 Jul 6;181(4094):60–63. doi: 10.1126/science.181.4094.60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tso W. W., Adler J. Negative chemotaxis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1974 May;118(2):560–576. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.2.560-576.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGEL H. J., BONNER D. M. Acetylornithinase of Escherichia coli: partial purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe A. J., Conley M. P., Kramer T. J., Berg H. C. Reconstitution of signaling in bacterial chemotaxis. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):1878–1885. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.1878-1885.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



