Abstract
The conserved, abundant chromosomal protein HMG1 consists of two highly homologous, folded, basic DNA-binding domains, each of approximately 80 amino acid residues, and an acidic C-terminal tail. Each folded domain represents an 'HMG box', a sequence motif recently recognized in certain sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins and which also occurs in abundant HMG1-like proteins that bind to DNA without sequence specificity. The HMG box is defined by a set of highly conserved residues (most distinctively aromatic and basic) and appears to define a novel DNA-binding structural motif. We have expressed the HMG box region of the B-domain of rat HMG1 (residues 88-164 of the intact protein) in Escherichia coli and we describe here the determination of its structure by 2D 1H-NMR spectroscopy. There are three alpha-helices (residues 13-29, 34-48 and 50-74), which together account for approximately 75% of the total residues and contain many of the conserved basic and aromatic residues. Strikingly, the molecule is L-shaped, the angle of approximately 80 degrees between the two arms being defined by a cluster of conserved, predominantly aromatic, residues. The distinctive shape of the HMG box motif, which is distinct from hitherto characterized DNA-binding motifs, may be significant in relation to its recognition of four-way DNA junctions.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdul-Razzak K. K., Denton M. L., Cox D. J., Reeck G. R. Isolation and characterization of folded fragments released by Staphylococcal aureus proteinase from the non-histone chromosomal protein HMG-1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jun 13;996(1-2):125–131. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(89)90104-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arseniev A., Schultze P., Wörgötter E., Braun W., Wagner G., Vasák M., Kägi J. H., Wüthrich K. Three-dimensional structure of rabbit liver [Cd7]metallothionein-2a in aqueous solution determined by nuclear magnetic resonance. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jun 5;201(3):637–657. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90644-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
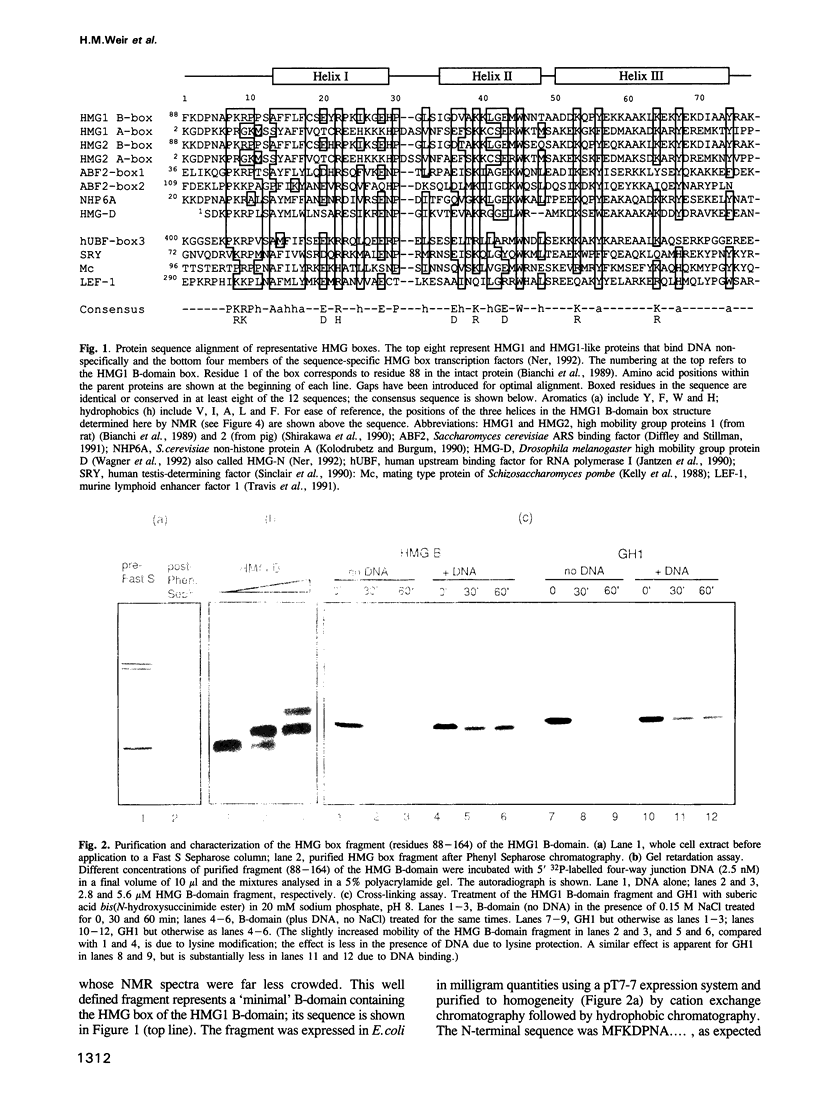
- Bianchi M. E., Beltrame M., Paonessa G. Specific recognition of cruciform DNA by nuclear protein HMG1. Science. 1989 Feb 24;243(4894 Pt 1):1056–1059. doi: 10.1126/science.2922595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi M. E., Falciola L., Ferrari S., Lilley D. M. The DNA binding site of HMG1 protein is composed of two similar segments (HMG boxes), both of which have counterparts in other eukaryotic regulatory proteins. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):1055–1063. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05144.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billeter M., Braun W., Wüthrich K. Sequential resonance assignments in protein 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectra. Computation of sterically allowed proton-proton distances and statistical analysis of proton-proton distances in single crystal protein conformations. J Mol Biol. 1982 Mar 5;155(3):321–346. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90008-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley E. K., Thomason J. F., Cohen F. E., Kosen P. A., Kuntz I. D. Studies of synthetic helical peptides using circular dichroism and nuclear magnetic resonance. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 20;215(4):607–622. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80172-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bustin M., Lehn D. A., Landsman D. Structural features of the HMG chromosomal proteins and their genes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jul 30;1049(3):231–243. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90092-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler A. P., Mardian J. K., Olins D. E. Nonhistone chromosomal protein HMG 1 interactions with DNA. Fluorescence and thermal denaturation studies. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 5;260(19):10613–10620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carballo M., Puigdomènech P., Palau J. DNA and histone H1 interact with different domains of HMG 1 and 2 proteins. EMBO J. 1983;2(10):1759–1764. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01654.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cary P. D., Turner C. H., Mayes E., Crane-Robinson C. Conformation and domain structure of the non-histone chromosomal proteins, HMG 1 and 2. Isolation of two folded fragments from HMG 1 and 2. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Mar 15;131(2):367–374. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07272.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diffley J. F., Stillman B. A close relative of the nuclear, chromosomal high-mobility group protein HMG1 in yeast mitochondria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7864–7868. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elborough K. M., West S. C. Specific binding of cruciform DNA structures by a protein from human extracts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 May 11;16(9):3603–3616. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.9.3603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari S., Harley V. R., Pontiggia A., Goodfellow P. N., Lovell-Badge R., Bianchi M. E. SRY, like HMG1, recognizes sharp angles in DNA. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(12):4497–4506. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05551.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giese K., Amsterdam A., Grosschedl R. DNA-binding properties of the HMG domain of the lymphoid-specific transcriptional regulator LEF-1. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12B):2567–2578. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12b.2567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giese K., Cox J., Grosschedl R. The HMG domain of lymphoid enhancer factor 1 bends DNA and facilitates assembly of functional nucleoprotein structures. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):185–195. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90129-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley V. R., Jackson D. I., Hextall P. J., Hawkins J. R., Berkovitz G. D., Sockanathan S., Lovell-Badge R., Goodfellow P. N. DNA binding activity of recombinant SRY from normal males and XY females. Science. 1992 Jan 24;255(5043):453–456. doi: 10.1126/science.1734522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison S. C. A structural taxonomy of DNA-binding domains. Nature. 1991 Oct 24;353(6346):715–719. doi: 10.1038/353715a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jantzen H. M., Admon A., Bell S. P., Tjian R. Nucleolar transcription factor hUBF contains a DNA-binding motif with homology to HMG proteins. Nature. 1990 Apr 26;344(6269):830–836. doi: 10.1038/344830a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly M., Burke J., Smith M., Klar A., Beach D. Four mating-type genes control sexual differentiation in the fission yeast. EMBO J. 1988 May;7(5):1537–1547. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02973.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kissinger C. R., Liu B. S., Martin-Blanco E., Kornberg T. B., Pabo C. O. Crystal structure of an engrailed homeodomain-DNA complex at 2.8 A resolution: a framework for understanding homeodomain-DNA interactions. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):579–590. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90453-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolodrubetz D., Burgum A. Duplicated NHP6 genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae encode proteins homologous to bovine high mobility group protein 1. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3234–3239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
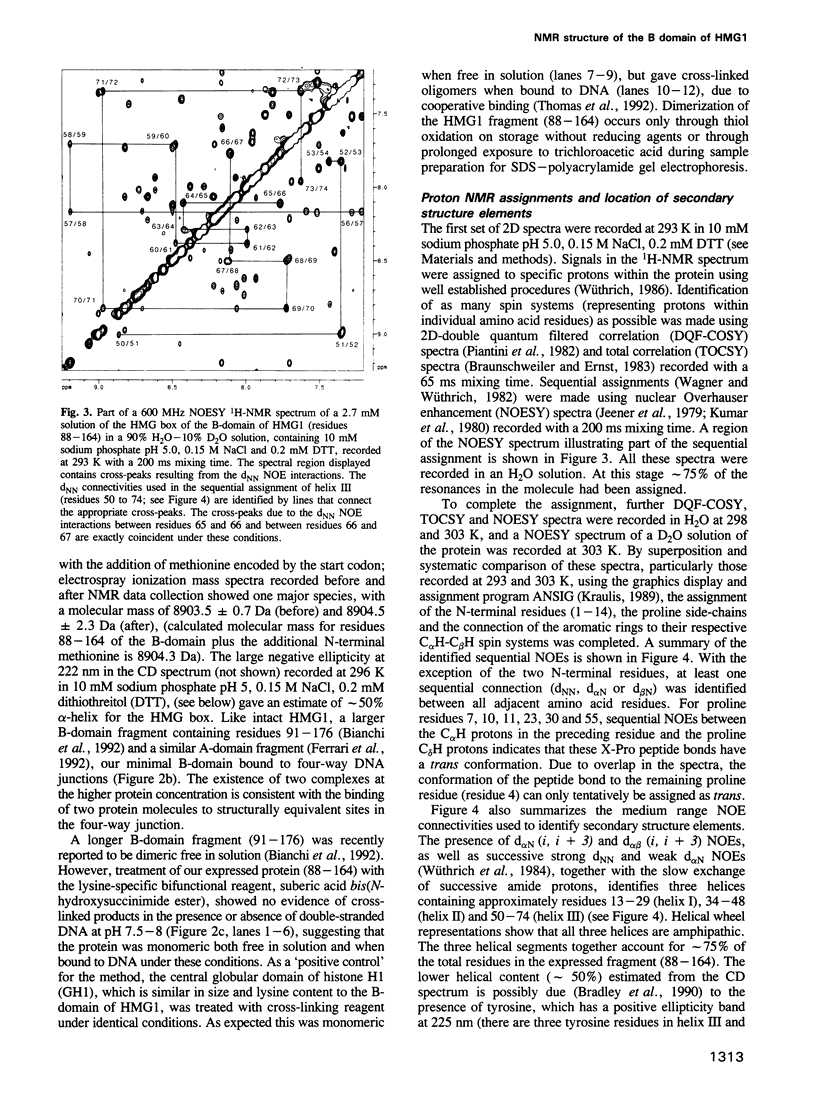
- Kumar A., Ernst R. R., Wüthrich K. A two-dimensional nuclear Overhauser enhancement (2D NOE) experiment for the elucidation of complete proton-proton cross-relaxation networks in biological macromolecules. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jul 16;95(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90695-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley D. M. DNA--protein interactions. HMG has DNA wrapped up. Nature. 1992 May 28;357(6376):282–283. doi: 10.1038/357282a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marion D., Wüthrich K. Application of phase sensitive two-dimensional correlated spectroscopy (COSY) for measurements of 1H-1H spin-spin coupling constants in proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jun 29;113(3):967–974. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91093-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
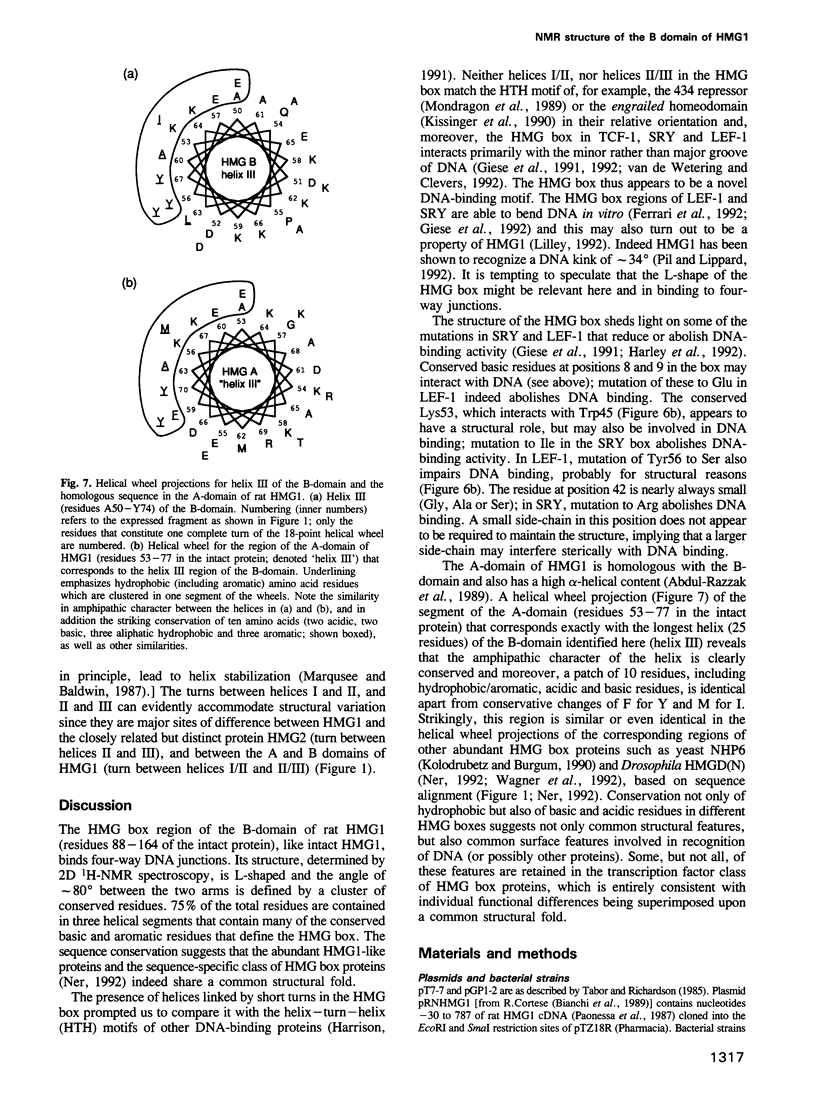
- Marqusee S., Baldwin R. L. Helix stabilization by Glu-...Lys+ salt bridges in short peptides of de novo design. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8898–8902. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mondragón A., Subbiah S., Almo S. C., Drottar M., Harrison S. C. Structure of the amino-terminal domain of phage 434 repressor at 2.0 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jan 5;205(1):189–200. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90375-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ner S. S. HMGs everywhere. Curr Biol. 1992 Apr;2(4):208–210. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(92)90541-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paonessa G., Frank R., Cortese R. Nucleotide sequence of rat liver HMG1 cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 11;15(21):9077–9077. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.21.9077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardi A., Billeter M., Wüthrich K. Calibration of the angular dependence of the amide proton-C alpha proton coupling constants, 3JHN alpha, in a globular protein. Use of 3JHN alpha for identification of helical secondary structure. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 15;180(3):741–751. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90035-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pil P. M., Lippard S. J. Specific binding of chromosomal protein HMG1 to DNA damaged by the anticancer drug cisplatin. Science. 1992 Apr 10;256(5054):234–237. doi: 10.1126/science.1566071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postnikov Y. V., Shick V. V., Belyavsky A. V., Khrapko K. R., Brodolin K. L., Nikolskaya T. A., Mirzabekov A. D. Distribution of high mobility group proteins 1/2, E and 14/17 and linker histones H1 and H5 on transcribed and non-transcribed regions of chicken erythrocyte chromatin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Feb 25;19(4):717–725. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.4.717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeck G. R., Isackson P. J., Teller D. C. Domain structure in high molecular weight high mobility group nonhistone chromatin proteins. Nature. 1982 Nov 4;300(5887):76–78. doi: 10.1038/300076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russel M., Model P. Replacement of the fip gene of Escherichia coli by an inactive gene cloned on a plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1984 Sep;159(3):1034–1039. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.3.1034-1039.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirakawa H., Tsuda K., Yoshida M. Primary structure of non-histone chromosomal protein HMG2 revealed by the nucleotide sequence. Biochemistry. 1990 May 8;29(18):4419–4423. doi: 10.1021/bi00470a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair A. H., Berta P., Palmer M. S., Hawkins J. R., Griffiths B. L., Smith M. J., Foster J. W., Frischauf A. M., Lovell-Badge R., Goodfellow P. N. A gene from the human sex-determining region encodes a protein with homology to a conserved DNA-binding motif. Nature. 1990 Jul 19;346(6281):240–244. doi: 10.1038/346240a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. A bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system for controlled exclusive expression of specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1074–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. O. Chemical cross-linking of histones. Methods Enzymol. 1989;170:549–571. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)70064-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. O., Kornberg R. D. The study of histone--histone associations by chemical cross-linking. Methods Cell Biol. 1978;18:429–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. O., Rees C., Finch J. T. Cooperative binding of the globular domains of histones H1 and H5 to DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jan 25;20(2):187–194. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.2.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis A., Amsterdam A., Belanger C., Grosschedl R. LEF-1, a gene encoding a lymphoid-specific protein with an HMG domain, regulates T-cell receptor alpha enhancer function [corrected]. Genes Dev. 1991 May;5(5):880–894. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.5.880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner C. R., Hamana K., Elgin S. C. A high-mobility-group protein and its cDNAs from Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 May;12(5):1915–1923. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.5.1915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner G., Wüthrich K. Sequential resonance assignments in protein 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectra. Basic pancreatic trypsin inhibitor. J Mol Biol. 1982 Mar 5;155(3):347–366. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wüthrich K., Billeter M., Braun W. Polypeptide secondary structure determination by nuclear magnetic resonance observation of short proton-proton distances. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 15;180(3):715–740. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90034-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Wetering M., Clevers H. Sequence-specific interaction of the HMG box proteins TCF-1 and SRY occurs within the minor groove of a Watson-Crick double helix. EMBO J. 1992 Aug;11(8):3039–3044. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05374.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]