Abstract
Although it is likely that a highly complex network of transcription factors acts in concert during mammalian brain development, relatively few such genes have been characterized to date. We describe here a novel murine homeobox gene, denoted Gtx, which in adult animals is specifically expressed within glial cells of the central nervous system, including the forebrain, and in germ cells of the testis. Gtx resides on chromosome 7 and does not cosegregate with any previously mapped homeobox gene. The amino acid sequence of the predicted protein encoded by Gtx is highly divergent from that of any other known homeobox genes. The Gtx homeodomain contains unique residues at positions predicted to contact DNA bases. It did not bind to known target sites for other homeobox genes in vitro but bound with high affinity to the MEF-2 motif, a binding site for the serum response factor-related proteins. GTX efficiently competed with RSRF to bind the MEF-2 element in vitro. Co-transfection of Gtx prevented the serum-induced activation of the MEF-2-containing reporter genes. Although the true biological role of Gtx is not known, these results suggest that Gtx is a novel cell-type specific homeobox gene that has the potential to act as a transcriptional repressor for a subset of serum-inducible genes.
Full text
PDF



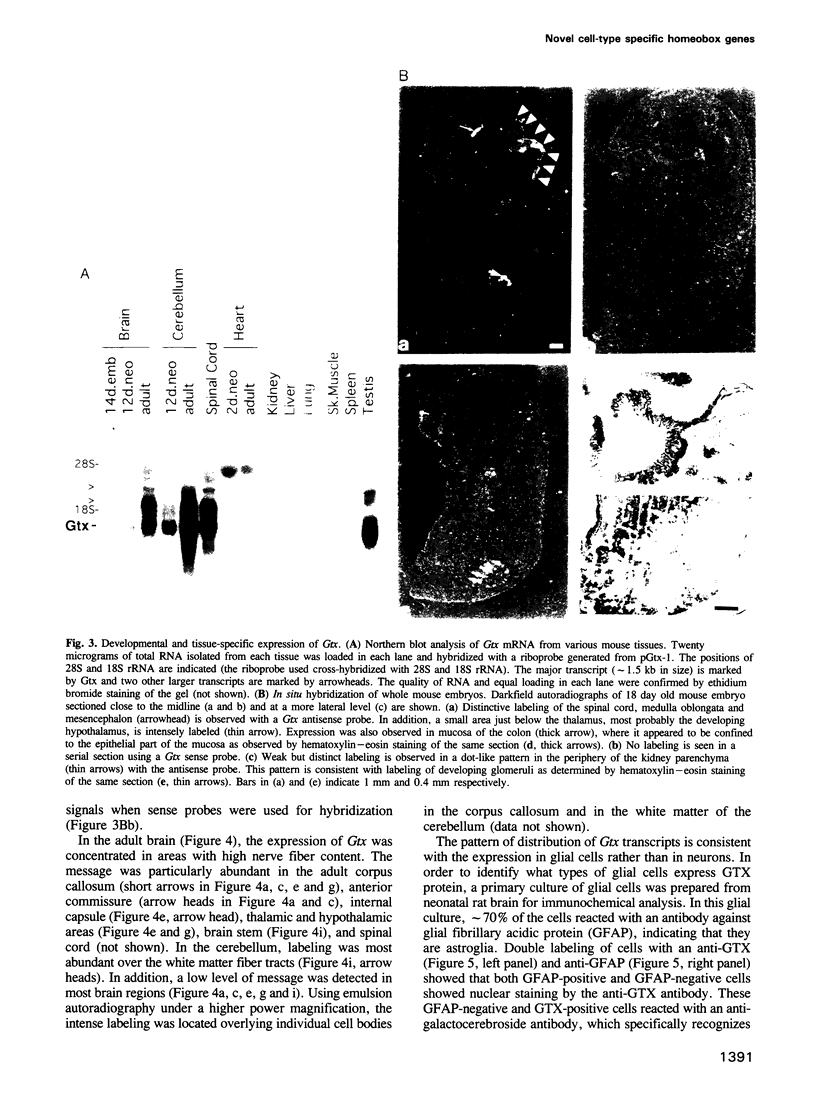
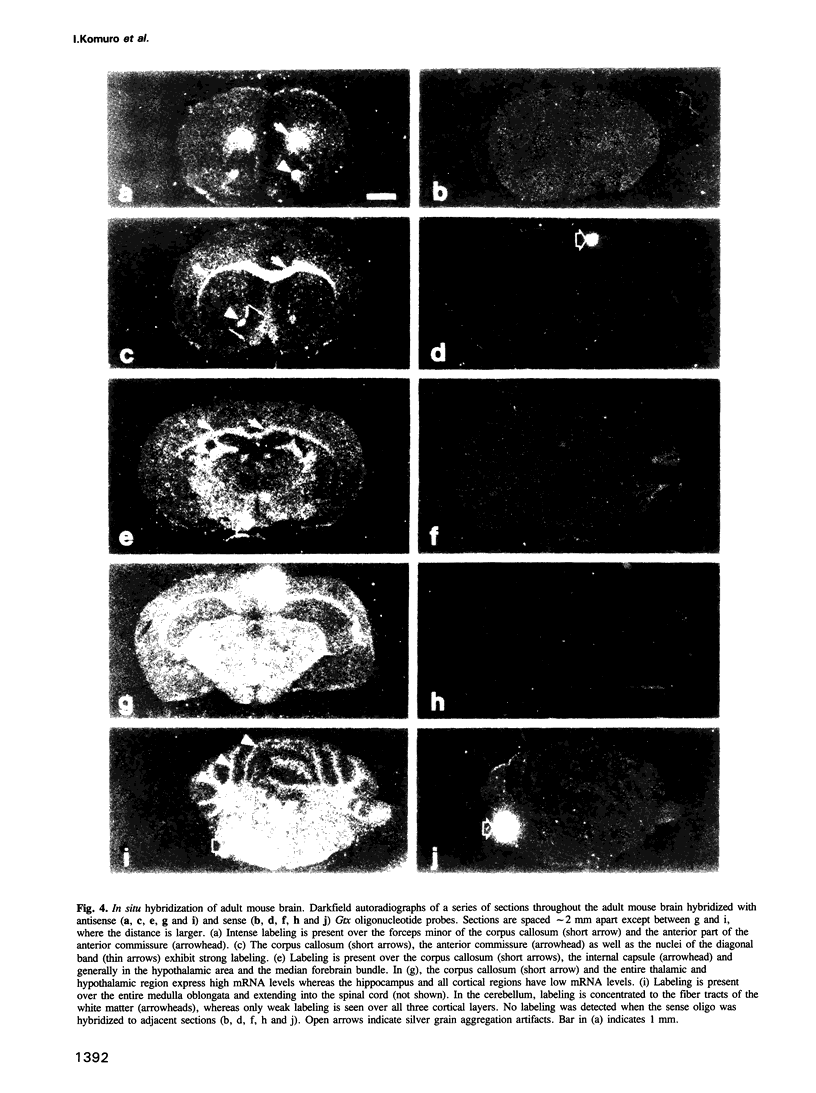

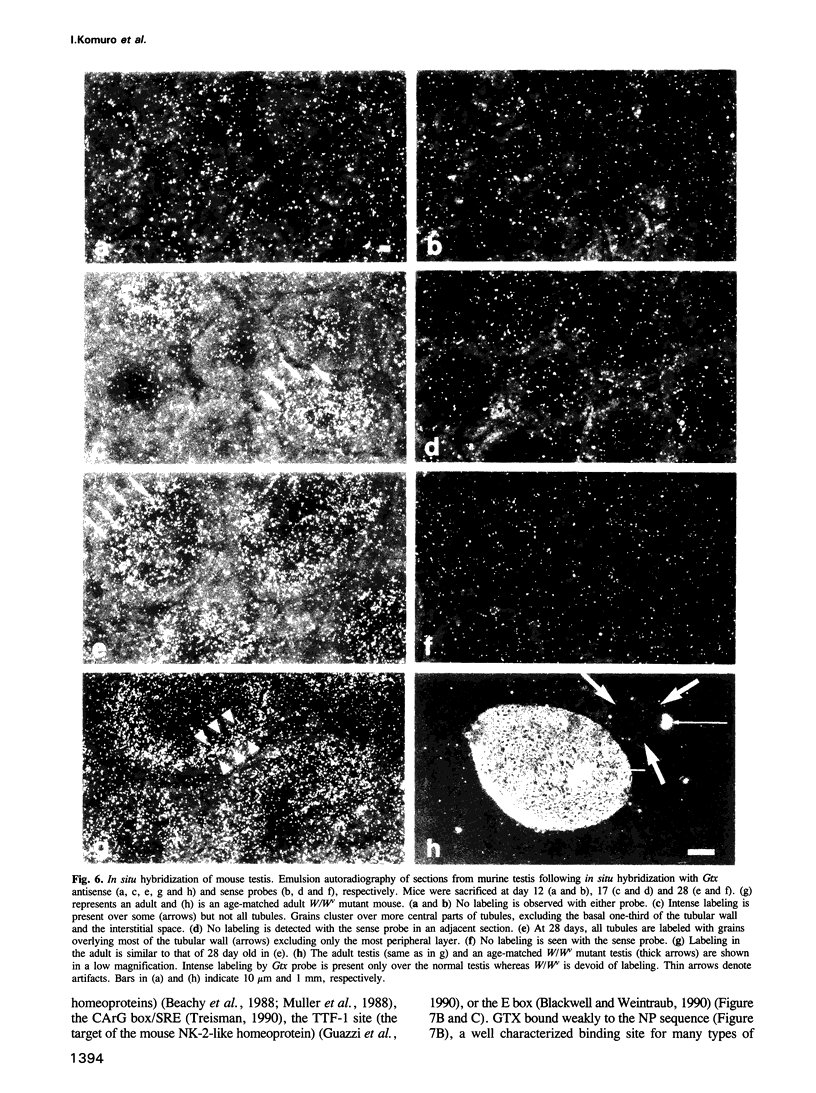


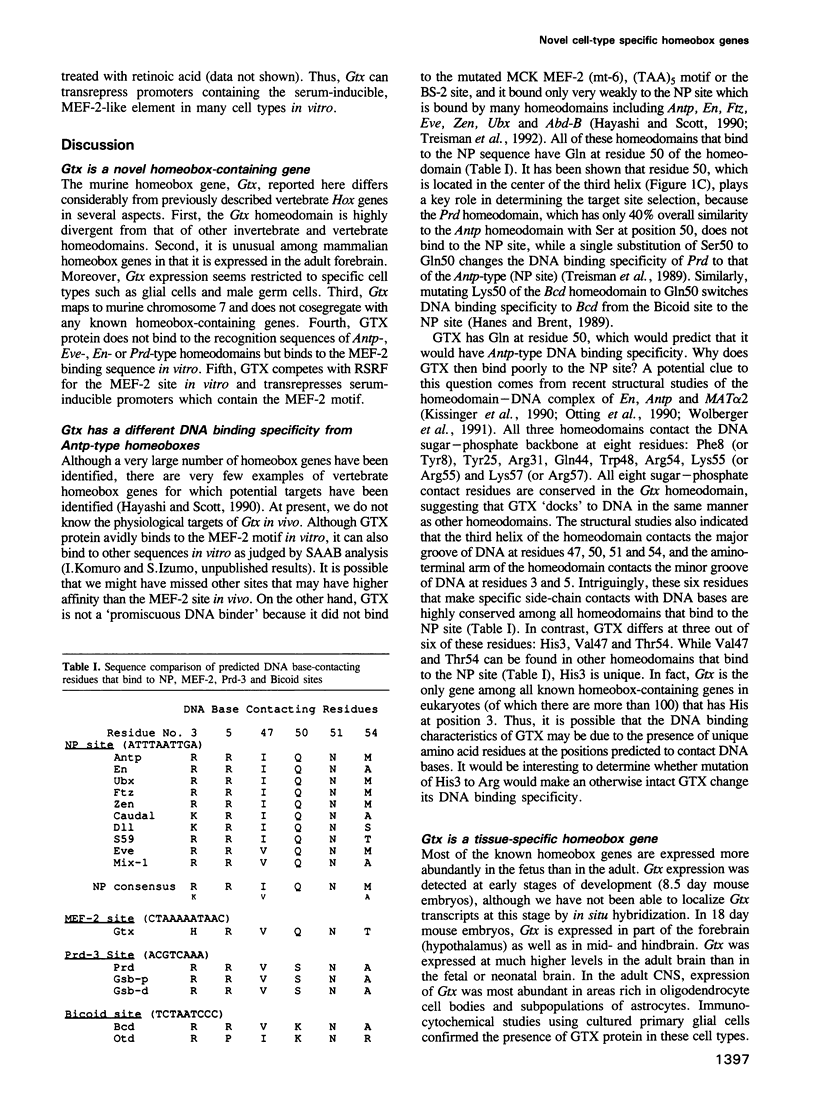




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Affolter M., Schier A., Gehring W. J. Homeodomain proteins and the regulation of gene expression. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;2(3):485–495. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(90)90132-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akam M. The molecular basis for metameric pattern in the Drosophila embryo. Development. 1987 Sep;101(1):1–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auffray C., Rougeon F. Purification of mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain messenger RNAs from total myeloma tumor RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartolomei M. S., Zemel S., Tilghman S. M. Parental imprinting of the mouse H19 gene. Nature. 1991 May 9;351(6322):153–155. doi: 10.1038/351153a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachy P. A., Krasnow M. A., Gavis E. R., Hogness D. S. An Ultrabithorax protein binds sequences near its own and the Antennapedia P1 promoters. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):1069–1081. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90251-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellvé A. R., Cavicchia J. C., Millette C. F., O'Brien D. A., Bhatnagar Y. M., Dym M. Spermatogenic cells of the prepuberal mouse. Isolation and morphological characterization. J Cell Biol. 1977 Jul;74(1):68–85. doi: 10.1083/jcb.74.1.68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell T. K., Weintraub H. Differences and similarities in DNA-binding preferences of MyoD and E2A protein complexes revealed by binding site selection. Science. 1990 Nov 23;250(4984):1104–1110. doi: 10.1126/science.2174572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodmer R., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N. A new homeobox-containing gene, msh-2, is transiently expressed early during mesoderm formation of Drosophila. Development. 1990 Nov;110(3):661–669. doi: 10.1242/dev.110.3.661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun T., Tannich E., Buschhausen-Denker G., Arnold H. H. Promoter upstream elements of the chicken cardiac myosin light-chain 2-A gene interact with trans-acting regulatory factors for muscle-specific transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2513–2525. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castrillo J. L., Theill L. E., Karin M. Function of the homeodomain protein GHF1 in pituitary cell proliferation. Science. 1991 Jul 12;253(5016):197–199. doi: 10.1126/science.1677216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisaka O., Capecchi M. R. Regionally restricted developmental defects resulting from targeted disruption of the mouse homeobox gene hox-1.5. Nature. 1991 Apr 11;350(6318):473–479. doi: 10.1038/350473a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A. Development and applications of a molecular genetic linkage map of the mouse genome. Trends Genet. 1991 Apr;7(4):113–118. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90455-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cserjesi P., Olson E. N. Myogenin induces the myocyte-specific enhancer binding factor MEF-2 independently of other muscle-specific gene products. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):4854–4862. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.4854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeChiara T. M., Robertson E. J., Efstratiadis A. Parental imprinting of the mouse insulin-like growth factor II gene. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):849–859. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90513-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohrmann C., Azpiazu N., Frasch M. A new Drosophila homeo box gene is expressed in mesodermal precursor cells of distinct muscles during embryogenesis. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12A):2098–2111. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12a.2098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donoghue M., Ernst H., Wentworth B., Nadal-Ginard B., Rosenthal N. A muscle-specific enhancer is located at the 3' end of the myosin light-chain 1/3 gene locus. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12B):1779–1790. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12b.1779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duboule D., Dollé P. The structural and functional organization of the murine HOX gene family resembles that of Drosophila homeotic genes. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1497–1505. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03534.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahrner K., Hogan B. L., Flavell R. A. Transcription of H-2 and Qa genes in embryonic and adult mice. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1265–1271. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02363.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gossett L. A., Kelvin D. J., Sternberg E. A., Olson E. N. A new myocyte-specific enhancer-binding factor that recognizes a conserved element associated with multiple muscle-specific genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5022–5033. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham A., Papalopulu N., Krumlauf R. The murine and Drosophila homeobox gene complexes have common features of organization and expression. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):367–378. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90912-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grueneberg D. A., Natesan S., Alexandre C., Gilman M. Z. Human and Drosophila homeodomain proteins that enhance the DNA-binding activity of serum response factor. Science. 1992 Aug 21;257(5073):1089–1095. doi: 10.1126/science.257.5073.1089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guazzi S., Price M., De Felice M., Damante G., Mattei M. G., Di Lauro R. Thyroid nuclear factor 1 (TTF-1) contains a homeodomain and displays a novel DNA binding specificity. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3631–3639. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07574.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanes S. D., Brent R. DNA specificity of the bicoid activator protein is determined by homeodomain recognition helix residue 9. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1275–1283. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90063-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison S. C., Aggarwal A. K. DNA recognition by proteins with the helix-turn-helix motif. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:933–969. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.004441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi S., Scott M. P. What determines the specificity of action of Drosophila homeodomain proteins? Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):883–894. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90492-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He X., Treacy M. N., Simmons D. M., Ingraham H. A., Swanson L. W., Rosenfeld M. G. Expression of a large family of POU-domain regulatory genes in mammalian brain development. Nature. 1989 Jul 6;340(6228):35–41. doi: 10.1038/340035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill R. E., Hall A. E., Sime C. M., Hastie N. D. A mouse homeo box-containing gene maps near a developmental mutation. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1987;44(2-3):171–174. doi: 10.1159/000132366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill R. E., Jones P. F., Rees A. R., Sime C. M., Justice M. J., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A., Graham E., Davidson D. R. A new family of mouse homeo box-containing genes: molecular structure, chromosomal location, and developmental expression of Hox-7.1. Genes Dev. 1989 Jan;3(1):26–37. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.1.26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobson G. M., Mitchell M. T., Molloy G. R., Pearson M. L., Benfield P. A. Identification of a novel TA-rich DNA binding protein that recognizes a TATA sequence within the brain creatine kinase promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Sep 26;16(18):8925–8944. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.18.8925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horlick R. A., Hobson G. M., Patterson J. H., Mitchell M. T., Benfield P. A. Brain and muscle creatine kinase genes contain common TA-rich recognition protein-binding regulatory elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4826–4836. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingraham H. A., Chen R. P., Mangalam H. J., Elsholtz H. P., Flynn S. E., Lin C. R., Simmons D. M., Swanson L., Rosenfeld M. G. A tissue-specific transcription factor containing a homeodomain specifies a pituitary phenotype. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):519–529. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90038-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones F. S., Chalepakis G., Gruss P., Edelman G. M. Activation of the cytotactin promoter by the homeobox-containing gene Evx-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2091–2095. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joyner A. L., Martin G. R. En-1 and En-2, two mouse genes with sequence homology to the Drosophila engrailed gene: expression during embryogenesis. Genes Dev. 1987 Mar;1(1):29–38. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.1.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessel M., Balling R., Gruss P. Variations of cervical vertebrae after expression of a Hox-1.1 transgene in mice. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):301–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90810-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessel M., Gruss P. Murine developmental control genes. Science. 1990 Jul 27;249(4967):374–379. doi: 10.1126/science.1974085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y., Nirenberg M. Drosophila NK-homeobox genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7716–7720. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kissinger C. R., Liu B. S., Martin-Blanco E., Kornberg T. B., Pabo C. O. Crystal structure of an engrailed homeodomain-DNA complex at 2.8 A resolution: a framework for understanding homeodomain-DNA interactions. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):579–590. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90453-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazzaro D., Price M., de Felice M., Di Lauro R. The transcription factor TTF-1 is expressed at the onset of thyroid and lung morphogenesis and in restricted regions of the foetal brain. Development. 1991 Dec;113(4):1093–1104. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.4.1093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lufkin T., Dierich A., LeMeur M., Mark M., Chambon P. Disruption of the Hox-1.6 homeobox gene results in defects in a region corresponding to its rostral domain of expression. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1105–1119. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90034-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MINTZ B., RUSSELL E. S. Gene-induced embryological modifications of primordial germ cells in the mouse. J Exp Zool. 1957 Mar;134(2):207–237. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401340202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malicki J., Schughart K., McGinnis W. Mouse Hox-2.2 specifies thoracic segmental identity in Drosophila embryos and larvae. Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):961–967. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90499-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy K. D., de Vellis J. Preparation of separate astroglial and oligodendroglial cell cultures from rat cerebral tissue. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jun;85(3):890–902. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.3.890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis N., Kuziora M. A., McGinnis W. Human Hox-4.2 and Drosophila deformed encode similar regulatory specificities in Drosophila embryos and larvae. Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):969–976. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90500-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis W., Krumlauf R. Homeobox genes and axial patterning. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):283–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90471-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mermod N., O'Neill E. A., Kelly T. J., Tjian R. The proline-rich transcriptional activator of CTF/NF-I is distinct from the replication and DNA binding domain. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):741–753. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90108-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizushima S., Nagata S. pEF-BOS, a powerful mammalian expression vector. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 11;18(17):5322–5322. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.17.5322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M., Affolter M., Leupin W., Otting G., Wüthrich K., Gehring W. J. Isolation and sequence-specific DNA binding of the Antennapedia homeodomain. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4299–4304. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03328.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordeen S. K. Luciferase reporter gene vectors for analysis of promoters and enhancers. Biotechniques. 1988 May;6(5):454–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkuma Y., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G., Desplan C. Engrailed, a homeodomain protein, can repress in vitro transcription by competition with the TATA box-binding protein transcription factor IID. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2289–2293. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otting G., Qian Y. Q., Billeter M., Müller M., Affolter M., Gehring W. J., Wüthrich K. Protein--DNA contacts in the structure of a homeodomain--DNA complex determined by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy in solution. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3085–3092. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07505.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier J., Schalling M., Buckler A. J., Rogers A., Haber D. A., Housman D. Expression of the Wilms' tumor gene WT1 in the murine urogenital system. Genes Dev. 1991 Aug;5(8):1345–1356. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.8.1345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock R., Treisman R. Human SRF-related proteins: DNA-binding properties and potential regulatory targets. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12A):2327–2341. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12a.2327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polson A., Coetzer T., Kruger J., von Maltzahn E., van der Merwe K. J. Improvements in the isolation of IgY from the yolks of eggs laid by immunized hens. Immunol Invest. 1985 Aug;14(4):323–327. doi: 10.3109/08820138509022667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price M., Lazzaro D., Pohl T., Mattei M. G., Rüther U., Olivo J. C., Duboule D., Di Lauro R. Regional expression of the homeobox gene Nkx-2.2 in the developing mammalian forebrain. Neuron. 1992 Feb;8(2):241–255. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90291-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price M., Lemaistre M., Pischetola M., Di Lauro R., Duboule D. A mouse gene related to Distal-less shows a restricted expression in the developing forebrain. Nature. 1991 Jun 27;351(6329):748–751. doi: 10.1038/351748a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard M. A., Baker E., Whitmore S. A., Sutherland G. R., Idzerda R. L., Park L. S., Cosman D., Jenkins N. A., Gilbert D. J., Copeland N. G. The interleukin-4 receptor gene (IL4R) maps to 16p11.2-16p12.1 in human and to the distal region of mouse chromosome 7. Genomics. 1991 Jul;10(3):801–806. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90466-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert B., Sassoon D., Jacq B., Gehring W., Buckingham M. Hox-7, a mouse homeobox gene with a novel pattern of expression during embryogenesis. EMBO J. 1989 Jan;8(1):91–100. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03352.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa F. M. Mix.1, a homeobox mRNA inducible by mesoderm inducers, is expressed mostly in the presumptive endodermal cells of Xenopus embryos. Cell. 1989 Jun 16;57(6):965–974. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90335-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin M. R., Toth L. E., Patel M. D., D'Eustachio P., Nguyen-Huu M. C. A mouse homeo box gene is expressed in spermatocytes and embryos. Science. 1986 Aug 8;233(4764):663–667. doi: 10.1126/science.3726554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz i Altaba A., Melton D. A. Interaction between peptide growth factors and homoeobox genes in the establishment of antero-posterior polarity in frog embryos. Nature. 1989 Sep 7;341(6237):33–38. doi: 10.1038/341033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalling M., Franco-Cereceda A., Hemsén A., Dagerlind A., Seroogy K., Persson H., Hökfelt T., Lundberg J. M. Neuropeptide Y and catecholamine synthesizing enzymes and their mRNAs in rat sympathetic neurons and adrenal glands: studies on expression, synthesis and axonal transport after pharmacological and experimental manipulations using hybridization techniques and radioimmunoassay. Neuroscience. 1991;41(2-3):753–766. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(91)90365-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz-Sommer Z., Huijser P., Nacken W., Saedler H., Sommer H. Genetic Control of Flower Development by Homeotic Genes in Antirrhinum majus. Science. 1990 Nov 16;250(4983):931–936. doi: 10.1126/science.250.4983.931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. P., Carroll S. B. The segmentation and homeotic gene network in early Drosophila development. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):689–698. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90092-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. P., Tamkun J. W., Hartzell G. W., 3rd The structure and function of the homeodomain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jul 28;989(1):25–48. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(89)90033-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simeone A., Acampora D., Gulisano M., Stornaiuolo A., Boncinelli E. Nested expression domains of four homeobox genes in developing rostral brain. Nature. 1992 Aug 20;358(6388):687–690. doi: 10.1038/358687a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Johnston D., Nüsslein-Volhard C. The origin of pattern and polarity in the Drosophila embryo. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):201–219. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90466-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman J., Gönczy P., Vashishtha M., Harris E., Desplan C. A single amino acid can determine the DNA binding specificity of homeodomain proteins. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):553–562. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90038-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman J., Harris E., Wilson D., Desplan C. The homeodomain: a new face for the helix-turn-helix? Bioessays. 1992 Mar;14(3):145–150. doi: 10.1002/bies.950140302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R., Ammerer G. The SRF and MCM1 transcription factors. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1992 Apr;2(2):221–226. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80277-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. The SRE: a growth factor responsive transcriptional regulator. Semin Cancer Biol. 1990 Feb;1(1):47–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolberger C., Vershon A. K., Liu B., Johnson A. D., Pabo C. O. Crystal structure of a MAT alpha 2 homeodomain-operator complex suggests a general model for homeodomain-DNA interactions. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):517–528. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90526-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu Y. T., Breitbart R. E., Smoot L. B., Lee Y., Mahdavi V., Nadal-Ginard B. Human myocyte-specific enhancer factor 2 comprises a group of tissue-restricted MADS box transcription factors. Genes Dev. 1992 Sep;6(9):1783–1798. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.9.1783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y., Tycko B. Monoallelic expression of the human H19 gene. Nat Genet. 1992 Apr;1(1):40–44. doi: 10.1038/ng0492-40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]